Analyse und Gebrauchsanweisung über die eingebaute Funktion
Schriftsteller:FMZ~Lydia, Erstellt: 2023-10-07 15:35:44, aktualisiert: 2024-01-02 21:17:16
Analyse und Gebrauchsanweisung über die eingebaute Funktion
Die _Cross-Funktion im Abschnitt Global Functions der API-Dokumentation wird zur Berechnung des Crossover-Zustands der beiden Indikatoren verwendet.
Die Funktionsumsetzung ist dem folgenden Code ähnlich:
Beachten Sie, dass wennarr1wird als eine Reihe von schnellen Indikatoren definiert undarr2als eine Reihe langsamer Indikatoren,
der Wert, der von der_Crossdie Funktion ist positiv, d. h. gemäß der Dokumentationa positive number is the period of upward penetration, a negative number indicates the period of downward penetration, and 0 means the same as the current price- Ich weiß.
Es kann gesehen werden, zu dieser Zeitarr1Aufwärts durchdrungen diearr2Es sind n Zyklen vergangen, zu diesem Zeitpunkt ist es die schnelle Linie, die aufwärts dringt, die langsame Linie, die eine Kreuzung darstellt.
Das gleiche._CrossDie Funktion gibt eine negative Zahl zurück, d.h. eine Crossdown.
Das Gegenteil ist der Fall, wennarr1wird als eine Reihe langsamer Indikatoren definiert undarr2als eine Reihe von schnellen Indikatoren.
Ein positiver Wert, der von der_CrossDie Funktion stellt eine Abkreuzung dar.
Ein negativer Wert wird von der_CrossDie Funktion stellt eine Kreuzung dar.
// Return to the number of periods of upward penetration, the positive number is the number of periods of upward penetration, the negative number indicates the number of periods of downward penetration, 0 means the same as the current price
$.Cross = function(arr1, arr2) { // The number of parameters is 2, it can be seen from the parameter name, these two parameters should be an array type, the array is like an array in the X-axis for the array index value, Y-axis for the index value of the line in the coordinate system, the function is to determine the intersection of the two lines
if (arr1.length !== arr2.length) { // The first step is to determine if the two arrays being compared are equal in length
throw "array length not equal"; // Throw an error if they are not equal, it is not possible to determine the intersection of unequal lines.
}
var n = 0; // Declare the variable n to record the intersection state, initially 0, unintersected
for (var i = arr1.length-1; i >= 0; i--) { // Iterate over the array arr1, from the last element forward.
if (typeof(arr1[i]) !== 'number' || typeof(arr2[i]) !== 'number') { // When any of the arrays arr1 or arr2 is of a non-numeric type (i.e., an invalid indicator), the traversal loop is broken.
break; // break out of a loop
}
if (arr1[i] < arr2[i]) { // If arr1 is smaller than arr2 then n--, will record the relative state of arr1, arr2 at the beginning, (i.e., at the beginning n will adjust itself according to the relative sizes of arr1[i], arr2[i], and once there is another relationship between the sizes of arr1[i], arr2[i] opposite to the state of n, i.e., a crossing of the two lines has occurred.)
if (n > 0) {
break;
}
n--;
} else if (arr1[i] > arr2[i]) { // If arr1 is greater than arr2 then n++
if (n < 0) {
break;
}
n++;
} else { // arr1[i] == arr2[i], then immediately break
break;
}
}
return n; // Returns the value of n, which represents the number of periods that have been crossed, and 0, which means that the indicator values are equal.
};
Lassen Sie uns eine Reihe von Daten simulieren, die in diesen Parameter übergeben werden, und sehen, wie es sich herausstellt
var arr1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,8,8,9] // fast line indicator
var arr2 = [2,3,4,5,6,7,7,7,7] // slow line indicator
function main(){
Log("_Cross(arr1, arr2) : ", _Cross(arr1, arr2))
Log("_Cross(arr2, arr1) : ", _Cross(arr2, arr1))
}

Wir können sehen, dass das Ergebnis 3, -3 ist.
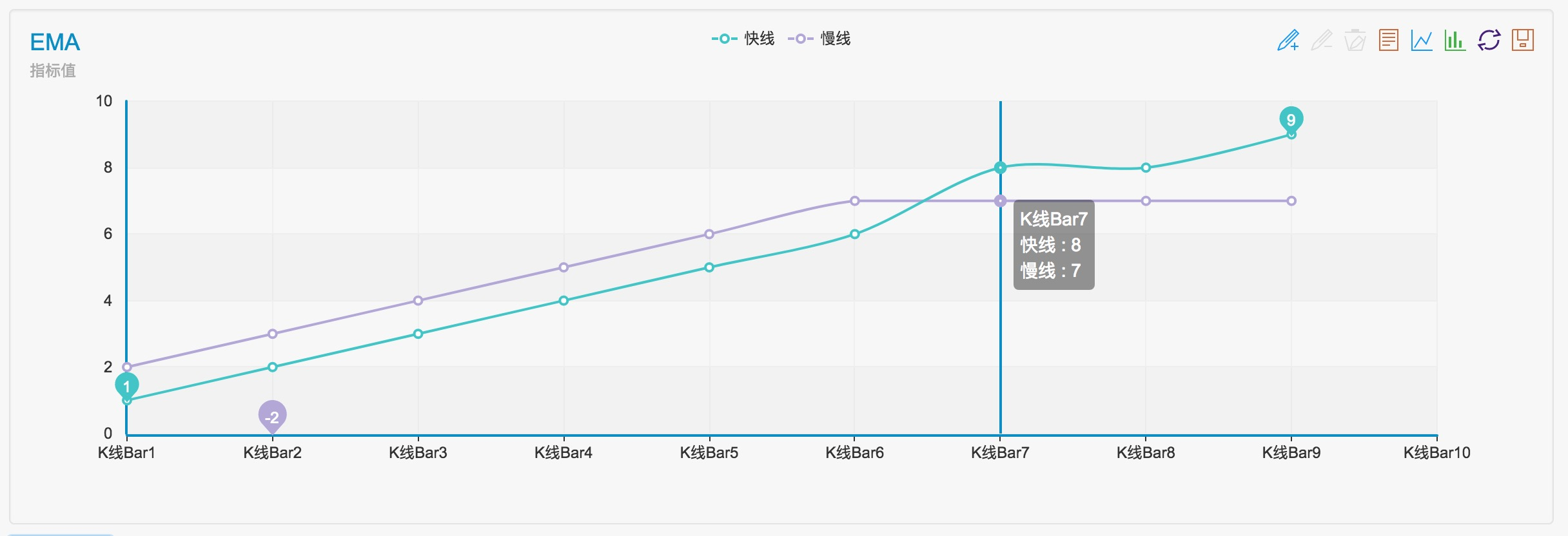
Wie wir in der Grafik sehen, tritt das Crossover vor drei K-Linienbalken auf.
- Analyse der Hochfrequenzhandelsstrategie - Penny Jump
- Alternative Handelsideen - Handelsstrategie im K-Linienbereich
- Konstruktion und Anwendung von Marktlärm
- PSY (psychologische Linie) Faktoren Upgrade und Umbau
- Analyse von Hochfrequenz-Handelsstrategien - Penny Jump
- Wie man Positionsrisiken misst - Einführung in die VaR-Methode
- Alternative Handelsideen - Handelsstrategien für die K-Fläche
- Einführung in die Methode VaR, um die Risikopositionen zu messen
- FMZ Mobile APP Trading Terminal, das Ihre quantitative Handelserfahrung erweitert
- FMZ Mobile APP Trading Terminal, das Ihnen eine qualifizierte Transaktionserfahrung gibt
- Delta-Hedging für Bitcoin-Optionen mit einer Lächeln-Kurve
- Überlegungen zu Hochfrequenzhandelsstrategien (5)
- Überlegungen zu Hochfrequenz-Handelsstrategien (4)
- Überlegungen zur Hochfrequenz-Handelstrategie (5)
- Denken Sie über die Strategie des Hochfrequenz-Handels nach (4)
- Überlegungen zu Hochfrequenzhandelsstrategien (3)
- Überlegungen zur Hochfrequenz-Handelsstrategie (3)
- Überlegungen zu Hochfrequenzhandelsstrategien (2)
- Denken Sie über die Strategie des Hochfrequenz-Handels nach.
- Überlegungen zu Hochfrequenzhandelsstrategien (1)