Elf gleitende Durchschnitte Kombination Crossover-Strategie
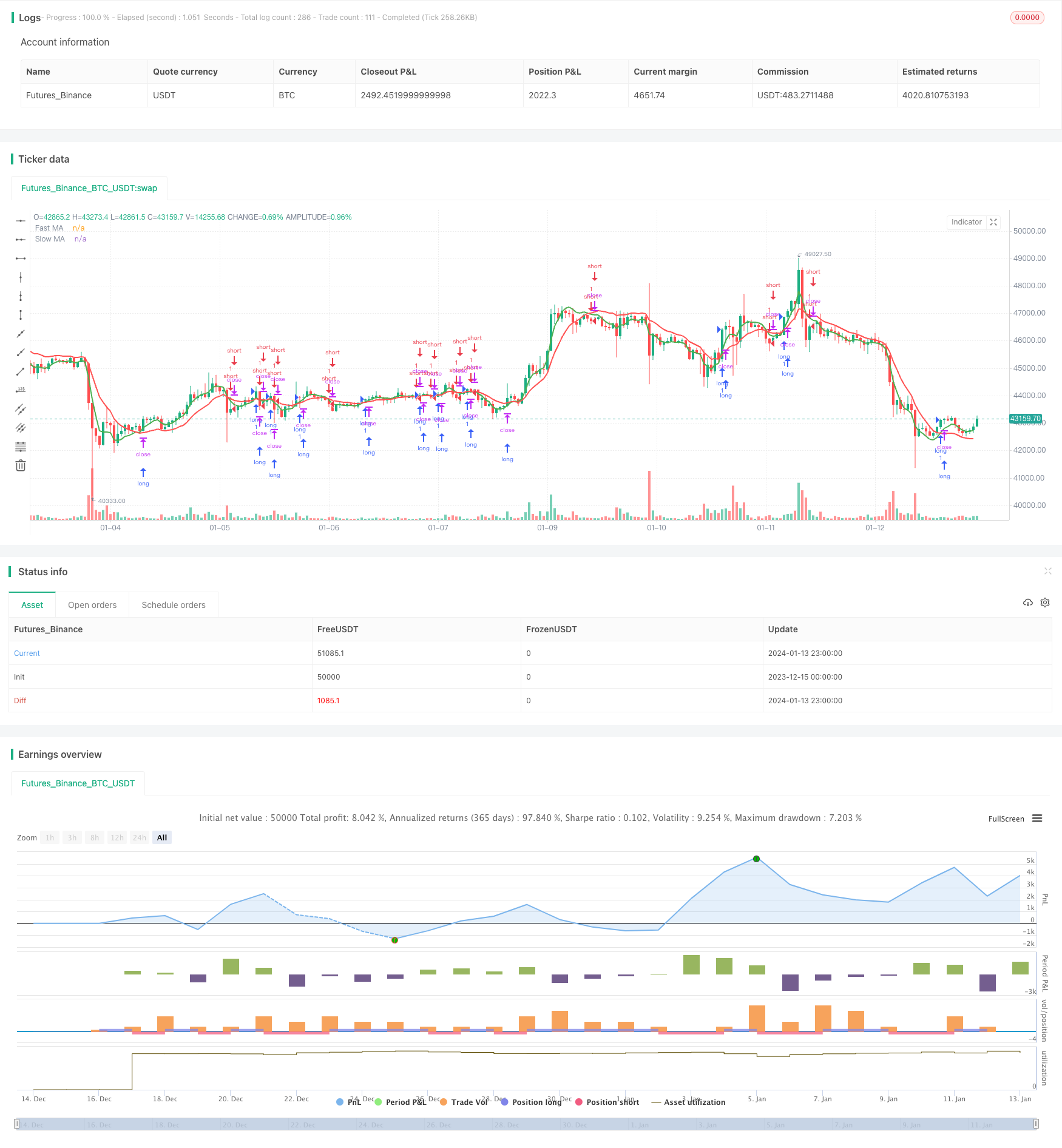
Überblick
Die Strategie kombiniert 11 verschiedene Arten von Moving Averages, um Über- und Unterziehung durchzuführen. Die 11 verwendeten Moving Averages sind: einfache Moving Averages (SMA), Index Moving Averages (EMA), Gewichtete Moving Averages (WMA), Gewichtete Moving Averages (VWMA), Gleitende Moving Averages (SMMA), Binäre Moving Averages (DEMA), Dreieckige Moving Averages (TEMA), Hull Moving Averages (HMA), Rückstandsleiste Moving Averages (ZEMA), Dreieckige Moving Averages (TMA) und Überflachschieber (SSMA).
Diese Strategie erlaubt es, zwei Moving Averages zu konfigurieren, einen schnelleren und einen langsameren, aus elf Optionen. Wenn ein schnellerer MA über dem langsameren MA überschreitet, wird ein Mehrwertsignal erzeugt. Wenn ein schnellerer MA unter dem langsameren MA liegt, wird ein Fehlwertsignal erzeugt.
Zusätzliche Funktionen umfassen die Einstellung der Treppe, die Bremsung und die Verluststufe.
Strategielogik
Die Kernstrategie-Logik beruht auf einer Kreuzung zwischen zwei Moving Averages, um Eintritt und Ausstieg zu bestimmen.
Die Eintrittsbedingungen sind:
Mehrmaliges Einsteigen: Schnell-MA > Langsam-MA
Eintritt in die Luft: schnelle MA < langsame MA
Der Austritt wird durch eines der folgenden drei Kriterien bestimmt:
- Stoppwert erreicht
- Stop-Loss-Level erreicht
- Erzeugt ein Gegensatzsignal ((Beweglicher Durchschnitt kreuzt in die entgegengesetzte Richtung))
Die Strategie erlaubt die Konfiguration wichtiger Parameter wie MA-Typ und -Länge, Steilreihen, Stopps und Stop-Loss-Prozentsätze. Dies bietet die Flexibilität, Strategien zu optimieren, die sich an unterschiedlichen Marktbedingungen und Risikopräferenzen orientieren.
Vorteile
- Kombination von 11 verschiedenen MA-Typen für ein starkes Signal
- Flexibilität bei der Konfiguration der Hauptparameter
- Stopp- und Verlustschutz, Gewinnschutz und Verlustbegrenzung
- Steigungen erlauben Positionen in einem starken Trend zu erhöhen
Die Gefahr
- Wie bei jedem technischen Indikator kann eine MA-Kreuzung ein falsches Signal erzeugen
- Überoptimierung der aktuellen Marktbedingungen könnte die zukünftige Performance beeinträchtigen
- Die Hard Stop-Tradition hat den wackligen, richtigen Handel zu früh beendet.
Risikomanagement kann durch die Bestätigung von Preisen für die Verwendung von Eingangssignalen, die Verwendung von Tracking-Stops anstelle von Hard-Stops und die Vermeidung von Überoptimierung gestärkt werden.
Optimierung des Raumes
Es gibt mehrere Möglichkeiten, diese Strategie zu verbessern:
- Zusätzliche Filter, z. B. Umsatz- und Preisprüfungen, vor der Einreise
- Systematische Tests der verschiedenen MA-Typen zur Auswahl der besten 1-2
- Optimierung der MA-Längen für bestimmte Handelsarten und Zeiträume
- Ersatz für Hard Stop mit Tracking Stop
- Mit zunehmender Tendenz wird eine Stufenstoppung hinzugefügt
Zusammenfassen
Die Moving-Average-Cross-Strategie bietet eine Methode zur systematischen Handelskreuzung. Durch die Kombination von Signalen über mehrere MA-Indikatoren und die Möglichkeit, die Schlüsselparameter zu konfigurieren, bietet sie einen starken und flexiblen Handelsrahmen.
/*backtest
start: 2023-12-15 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-14 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=3
strategy(title = "[STRATEGY] MA Cross Eleven", overlay = true)
// MA - type, source, length
// MA - type, source, length
// SMA --> Simple
// EMA --> Exponential
// WMA --> Weighted
// VWMA --> Volume Weighted
// SMMA --> Smoothed
// DEMA --> Double Exponential
// TEMA --> Triple Exponential
// HMA --> Hull
// TMA --> Triangular
// SSMA --> SuperSmoother filter
// ZEMA --> Zero Lag Exponential
type = input(defval="ZEMA", title="MA Type: ", options=["SMA", "EMA", "WMA", "VWMA", "SMMA", "DEMA", "TEMA", "HullMA", "ZEMA", "TMA", "SSMA"])
len1 = input(defval=8, title="Fast MA Length", minval=1)
srcclose1 = input(close, "Fast MA Source")
len2 = input(defval=21, title="Slow MA Length", minval=1)
srcclose2 = input(close, "Slow MA Source")
// Returns MA input selection variant, default to SMA if blank or typo.
variant(type, src, len) =>
v1 = sma(src, len) // Simple
v2 = ema(src, len) // Exponential
v3 = wma(src, len) // Weighted
v4 = vwma(src, len) // Volume Weighted
v5 = 0.0
v5 := na(v5[1]) ? sma(src, len) : (v5[1] * (len - 1) + src) / len // Smoothed
v6 = 2 * v2 - ema(v2, len) // Double Exponential
v7 = 3 * (v2 - ema(v2, len)) + ema(ema(v2, len), len) // Triple Exponential
v8 = wma(2 * wma(src, len / 2) - wma(src, len), round(sqrt(len))) // Hull
v11 = sma(sma(src,len),len) // Triangular
// SuperSmoother filter
// © 2013 John F. Ehlers
a1 = exp(-1.414*3.14159 / len)
b1 = 2*a1*cos(1.414*3.14159 / len)
c2 = b1
c3 = (-a1)*a1
c1 = 1 - c2 - c3
v9 = 0.0
v9 := c1*(src + nz(src[1])) / 2 + c2*nz(v9[1]) + c3*nz(v9[2])
// Zero Lag Exponential
e = ema(v2, len)
v10 = v2+(v2-e)
// return variant, defaults to SMA if input invalid.
type=="EMA"?v2 : type=="WMA"?v3 : type=="VWMA"?v4 : type=="SMMA"?v5 : type=="DEMA"?v6 : type=="TEMA"?v7 : type=="HullMA"?v8 : type=="SSMA"?v9 : type=="ZEMA"?v10 : type=="TMA"? v11: v1
ma_1 = variant(type, srcclose1, len1)
ma_2 = variant(type, srcclose2, len2)
plot(ma_1, title="Fast MA", color = green, linewidth=2, transp=0)
plot(ma_2, title="Slow MA", color = red, linewidth=2, transp=0)
longCond = na
shortCond = na
longCond := crossover(ma_1, ma_2)
shortCond := crossunder(ma_1, ma_2)
// Count your long short conditions for more control with Pyramiding
sectionLongs = 0
sectionLongs := nz(sectionLongs[1])
sectionShorts = 0
sectionShorts := nz(sectionShorts[1])
if longCond
sectionLongs := sectionLongs + 1
sectionShorts := 0
if shortCond
sectionLongs := 0
sectionShorts := sectionShorts + 1
// Pyramiding Inputs
pyrl = input(1, "Pyramiding")
// These check to see your signal and cross references it against the pyramiding settings above
longCondition = longCond and sectionLongs <= pyrl
shortCondition = shortCond and sectionShorts <= pyrl
// Get the price of the last opened long or short
last_open_longCondition = na
last_open_shortCondition = na
last_open_longCondition := longCondition ? high[1] : nz(last_open_longCondition[1])
last_open_shortCondition := shortCondition ? low[1] : nz(last_open_shortCondition[1])
// Check if your last postion was a long or a short
last_longCondition = na
last_shortCondition = na
last_longCondition := longCondition ? time : nz(last_longCondition[1])
last_shortCondition := shortCondition ? time : nz(last_shortCondition[1])
in_longCondition = last_longCondition > last_shortCondition
in_shortCondition = last_shortCondition > last_longCondition
// Take profit
isTPl = input(false, "Take Profit Long")
isTPs = input(false, "Take Profit Short")
tpl = input(3, "Take Profit Long %", type=float)
tps = input(30, "Take Profit Short %", type=float)
long_tp = isTPl and crossover(high, (1+(tpl/100))*last_open_longCondition) and in_longCondition == 1
short_tp = isTPs and crossunder(low, (1-(tps/100))*last_open_shortCondition) and in_shortCondition == 1
// Stop Loss
isSLl = input(false, "Stop Loss Long")
isSLs = input(false, "Stop Loss Short")
sl= 0.0
sl := input(3, "Stop Loss %", type=float)
long_sl = isSLl and crossunder(low, (1-(sl/100))*last_open_longCondition) and longCondition == 0 and in_longCondition == 1
short_sl = isSLs and crossover(high, (1+(sl/100))*last_open_shortCondition) and shortCondition == 0 and in_shortCondition == 1
// Create a single close for all the different closing conditions.
long_close = long_tp or long_sl ? 1 : 0
short_close = short_tp or short_sl ? 1 : 0
// Get the time of the last close
last_long_close = na
last_short_close = na
last_long_close := long_close ? time : nz(last_long_close[1])
last_short_close := short_close ? time : nz(last_short_close[1])
// Strategy entries
strategy.entry("long", strategy.long, when=longCondition == true, stop = open[1])
strategy.entry("short", strategy.short, when=shortCondition == true)
strategy.close("long", when = long_sl or long_tp)
strategy.close("short", when = short_sl or short_tp)