Built-in function_Cross analysis and instructions
Author: Inventors quantify - small dreams, Created: 2017-10-11 19:50:44, Updated: 2021-11-05 16:15:56Built-in function_Cross analysis and instructions
The _Cross function in the global function array in the API documentation is used to calculate the cross state of two pointer lines
- The ### function implements code similar to the following:
It's important to note thatarr1It is defined as a fast-track indicator array.arr2When defined as a slow-line indicator array,
可知,此时```arr1```上穿```arr2```已经n个周期,此时就是快线上穿慢线代表金叉。
同样```_Cross```函数如果返回负数,即为死叉。
如果定义```arr1```为慢线指标数组,```arr2```为快线指标数组,则相反。
```_Cross```函数返回的值为正数代表死叉。
```_Cross```函数返回的值为负数代表金叉。
// Returns the number of cycles of upward wear, the positive number is the number of weeks of upward wear, the negative number is the number of weeks of downward wear, 0 is the same as the current price
$.Cross = function ((arr1, arr2) { // The number of arguments is 2, as can be seen from the name of the arguments, these two arguments should be of the type of array, the array should be
// as if the line segment in the coordinate system where the X axis is the index value of the array and the Y axis is the indicator value, the function is to determine the intersection of the two lines
if (arr1.length!== arr2.length) { // First, we need to determine whether the two arrays are equal in length.
throw
- #### 我们模拟一组数据传入该参数看看结果如何
var arr1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 8,9] // the fast-line indicator
var arr2 = [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 7, 7] // the indicator of the slow line
function main (()) {
Log ((
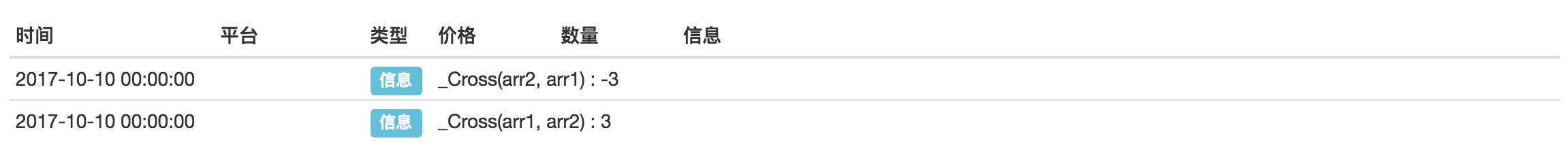
You can see that the result is 3, 3, 3.
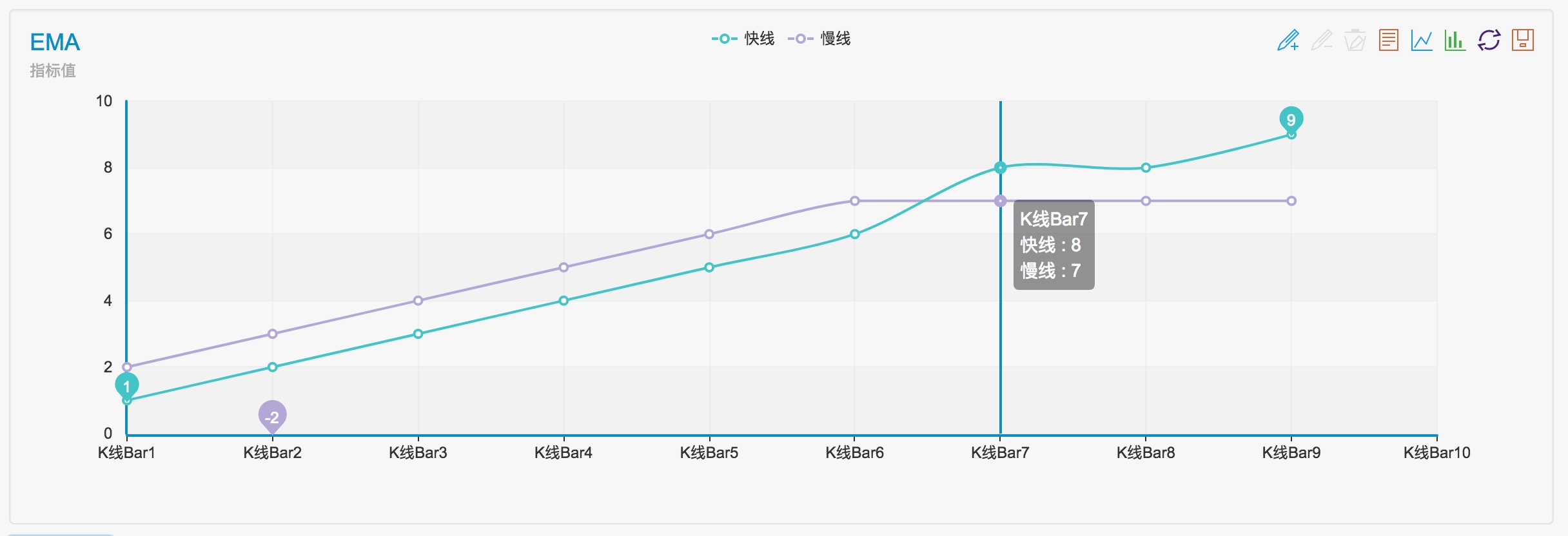
As can be seen in the diagram, the position of the intersection occurs before the three K-line columns.
- Submitted Bug: An interaction button without a default parameter value when creating a policy failed to save
- Can the retargeting system select other currencies?
- Please translate the buy plan page
- Bitfinex has three markets, how do you get the robot to choose?
- Options from a dynamic perspective are a win-win
- Bitfinex counter-measurement and counter-measurement currency units are inconsistent
- How do you view the effectiveness of the backsliding and gold forks?
- Bithumb received account information in error
- Feature request : please add support for JavaScript like console for ᴀᴘɪ access
- How do you make gold forks?
- “Plan expired” while I never bought a plan…
- How do we get data from decentralized exchanges?????
- Digital currency price monitoring analysis real-time analysis Bitcoin and Bitfinex failed to operate successfully
- Poloniex has reported an error?Error: (Exchange_Register): platformId: 27, currency: BTC_ETC, Msg: Peroid does not support Register FILE: 803 reg FILE:1264
- How to get the serial number of a specific exchange?
- But we have to look at it from a different perspective.
- In the review, did the yield curve not include the cost of the purchase?
- Catching insects, predicting the earnings, the commentary in the questionnaire is wrong
- Talk about how to optimize the parameters of several programmatic trading models.
- Please teach me how to quantify the inventor's drawing, where the horizontal coordinates are not the time axis, but rather a column graph or a folded graph of numbers.
alphaStrategy00XSo if you don't have a cross, you should return 0.
And the cabbage.What if we cross back and forth?
Inventors quantify - small dreamsWell, let's think about that.
alphaStrategy00XThank you for your reply! I mean, returning 0 is more reasonable, right?
Inventors quantify - small dreamsWhat's up? var arr1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 8,9] // the fast-line indicator var arr2 = [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 7, 7] // the indicator of the slow line function main (()) { Log (("_Cross ((arr1, arr2) ": ", _Cross ((arr1, arr2)) Log (("_Cross ((arr2, arr1) ": ", _Cross ((arr2, arr1)) I'm not sure. What's up? You can use this to run a set of non-crossing arrays. I'm not going to return 0.
Inventors quantify - small dreamsOnly the most recent cross-section is detected, and source code analysis can tell.