Análisis e instrucciones de uso sobre la función integrada _Cross
El autor:FMZ~Lydia, Creado: 2023-10-07 15:35:44, Actualizado: 2024-01-02 21:17:16
Análisis e instrucciones de uso sobre la función integrada _Cross
La función _Cross en la sección Funciones globales de la documentación de la API se utiliza para calcular el estado de cruce de los dos indicadores.
La implementación de la función es similar al siguiente código:
Observe que cuandoarr1se define como una serie de indicadores rápidos yarr2como una serie de indicadores lentos,
el valor devuelto por el_Crossla función es positiva, es decir, según la documentación,a positive number is the period of upward penetration, a negative number indicates the period of downward penetration, and 0 means the same as the current price¿ Qué pasa?
Se puede ver, en este momentoarr1hacia arriba penetrado en elarr2ha sido n ciclos, en este momento, es la línea rápida penetración hacia arriba la línea lenta, que representa un cruce.
Lo mismo._CrossLa función devuelve un número negativo, es decir, un crossdown.
Lo contrario es cierto siarr1se define como una serie de indicadores lentos yarr2como una serie de indicadores rápidos.
Un valor positivo devuelto por el_CrossLa función representa una cruz.
Un valor negativo devuelto por el_CrossLa función representa un cruce.
// Return to the number of periods of upward penetration, the positive number is the number of periods of upward penetration, the negative number indicates the number of periods of downward penetration, 0 means the same as the current price
$.Cross = function(arr1, arr2) { // The number of parameters is 2, it can be seen from the parameter name, these two parameters should be an array type, the array is like an array in the X-axis for the array index value, Y-axis for the index value of the line in the coordinate system, the function is to determine the intersection of the two lines
if (arr1.length !== arr2.length) { // The first step is to determine if the two arrays being compared are equal in length
throw "array length not equal"; // Throw an error if they are not equal, it is not possible to determine the intersection of unequal lines.
}
var n = 0; // Declare the variable n to record the intersection state, initially 0, unintersected
for (var i = arr1.length-1; i >= 0; i--) { // Iterate over the array arr1, from the last element forward.
if (typeof(arr1[i]) !== 'number' || typeof(arr2[i]) !== 'number') { // When any of the arrays arr1 or arr2 is of a non-numeric type (i.e., an invalid indicator), the traversal loop is broken.
break; // break out of a loop
}
if (arr1[i] < arr2[i]) { // If arr1 is smaller than arr2 then n--, will record the relative state of arr1, arr2 at the beginning, (i.e., at the beginning n will adjust itself according to the relative sizes of arr1[i], arr2[i], and once there is another relationship between the sizes of arr1[i], arr2[i] opposite to the state of n, i.e., a crossing of the two lines has occurred.)
if (n > 0) {
break;
}
n--;
} else if (arr1[i] > arr2[i]) { // If arr1 is greater than arr2 then n++
if (n < 0) {
break;
}
n++;
} else { // arr1[i] == arr2[i], then immediately break
break;
}
}
return n; // Returns the value of n, which represents the number of periods that have been crossed, and 0, which means that the indicator values are equal.
};
Vamos a simular un conjunto de datos pasados a este parámetro y ver cómo resulta
var arr1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,8,8,9] // fast line indicator
var arr2 = [2,3,4,5,6,7,7,7,7] // slow line indicator
function main(){
Log("_Cross(arr1, arr2) : ", _Cross(arr1, arr2))
Log("_Cross(arr2, arr1) : ", _Cross(arr2, arr1))
}

Podemos ver que los resultados son 3, -3.
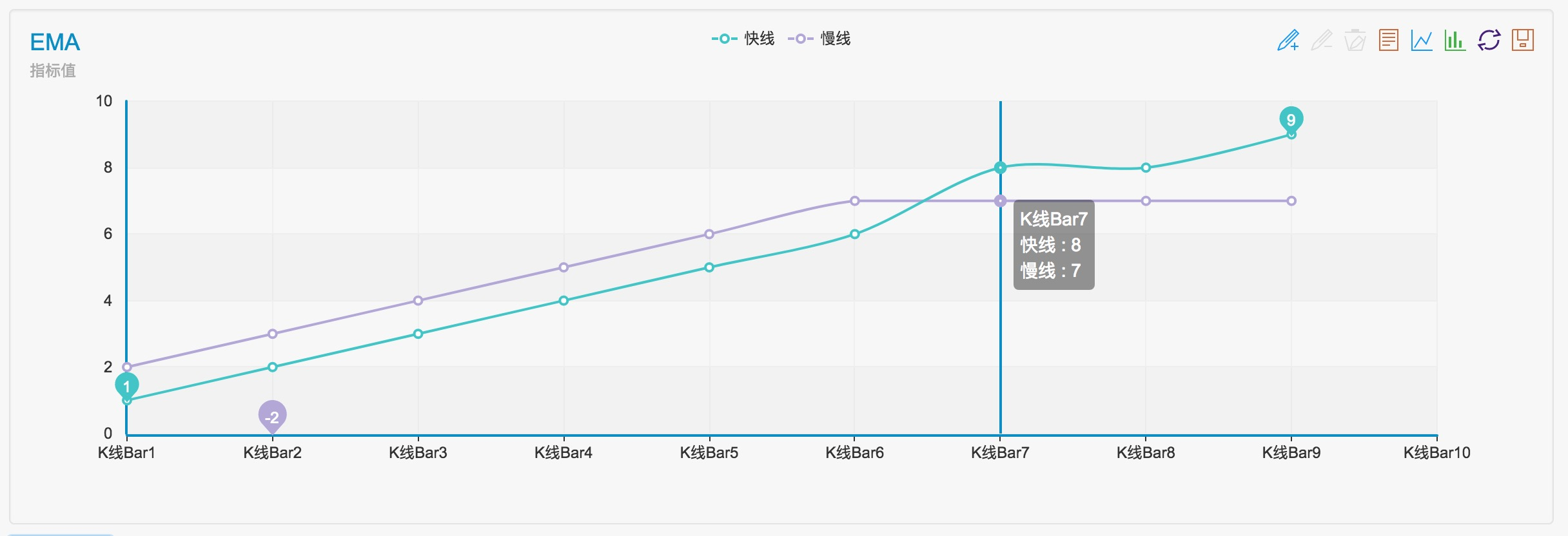
Como se ve en el gráfico, el cruce ocurre frente a tres barras de la línea K.
- Análisis de la estrategia de negociación de alta frecuencia - Penny Jump
- Ideas de negociación alternativas - Estrategia de negociación en el área de la línea K
- Construcción y aplicación del ruido del mercado
- Factor PSY (línea psicológica) de actualización y transformación
- Análisis de estrategias de operaciones de alta frecuencia - Penny Jump
- Cómo medir el riesgo de posición - Introducción al método VaR
- Ideas alternativas de negociación - estrategias de negociación de área de línea K
- Cómo medir el riesgo de la posesión de un valor añadido VaR
- FMZ Mobile APP Terminal de comercio, potenciando su experiencia comercial cuantitativa
- La aplicación móvil de FMZ es un terminal de operaciones que le permite una experiencia de transacción cuantificada.
- Hacer una cobertura delta con una curva de sonrisas para opciones de Bitcoin
- Opiniones sobre las estrategias de negociación de alta frecuencia (5)
- Opiniones sobre las estrategias de negociación de alta frecuencia (4)
- Pensamiento sobre estrategias de trading de alta frecuencia (5)
- Pensamiento sobre estrategias de trading de alta frecuencia (4)
- Opiniones sobre las estrategias de negociación de alta frecuencia (3)
- Pensamiento sobre estrategias de trading de alta frecuencia (3)
- Opiniones sobre las estrategias de negociación de alta frecuencia (2)
- Pensamiento sobre estrategias de trading de alta frecuencia (2)
- Opiniones sobre las estrategias de negociación de alta frecuencia (1)