Estrategia de cuadrícula simple en la versión de Python
El autor:FMZ~Lydia, Creado: 2022-12-23 21:00:45, Actualizado: 2025-01-11 18:19:24
Estrategia de cuadrícula simple en la versión de Python
No hay muchas estrategias de Python en el cuadrado de la estrategia. Aquí se escribe una versión de Python de la estrategia de red. El principio de la estrategia es muy simple. Una serie de nodos de red se generan por una distancia de precio fija dentro de un rango de precios. Cuando el mercado cambia y el precio alcanza una posición de precio de nodo de red, se coloca una orden de compra. Cuando se cierra la orden, es decir, de acuerdo con el precio de la orden pendiente más el margen de ganancia, se espera una orden de venta para cerrar la posición. Captura las fluctuaciones dentro del rango de precio establecido.
No hace falta decir que el riesgo de la estrategia de cuadrícula es que cualquier estrategia de tipo cuadrícula es una apuesta de que el precio fluctúa dentro de un cierto rango. Una vez que el precio sale del rango de la cuadrícula, puede causar serias pérdidas flotantes. Por lo tanto, el propósito de escribir esta estrategia es proporcionar referencia para las ideas de escritura de estrategias de Python o el diseño de programas.
La explicación de las ideas estratégicas está escrita directamente en los comentarios del código de estrategia.
Código de estrategia
'''backtest
start: 2019-07-01 00:00:00
end: 2020-01-03 00:00:00
period: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"OKEX","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
'''
import json
# Parameters
beginPrice = 5000 # Grid interval begin price
endPrice = 8000 # Grid interval end price
distance = 20 # Price distance of each grid node
pointProfit = 50 # Profit spread per grid node
amount = 0.01 # Number of pending orders per grid node
minBalance = 300 # Minimum fund balance of the account (at the time of purchase)
# Global variables
arrNet = []
arrMsg = []
acc = None
def findOrder (orderId, NumOfTimes, ordersList = []) :
for j in range(NumOfTimes) :
orders = None
if len(ordersList) == 0:
orders = _C(exchange.GetOrders)
else :
orders = ordersList
for i in range(len(orders)):
if orderId == orders[i]["Id"]:
return True
Sleep(1000)
return False
def cancelOrder (price, orderType) :
orders = _C(exchange.GetOrders)
for i in range(len(orders)) :
if price == orders[i]["Price"] and orderType == orders[i]["Type"]:
exchange.CancelOrder(orders[i]["Id"])
Sleep(500)
def checkOpenOrders (orders, ticker) :
global arrNet, arrMsg
for i in range(len(arrNet)) :
if not findOrder(arrNet[i]["id"], 1, orders) and arrNet[i]["state"] == "pending" :
orderId = exchange.Sell(arrNet[i]["coverPrice"], arrNet[i]["amount"], arrNet[i], ticker)
if orderId :
arrNet[i]["state"] = "cover"
arrNet[i]["id"] = orderId
else :
# Cancel
cancelOrder(arrNet[i]["coverPrice"], ORDER_TYPE_SELL)
arrMsg.append("Pending order failed!" + json.dumps(arrNet[i]) + ", time:" + _D())
def checkCoverOrders (orders, ticker) :
global arrNet, arrMsg
for i in range(len(arrNet)) :
if not findOrder(arrNet[i]["id"], 1, orders) and arrNet[i]["state"] == "cover" :
arrNet[i]["id"] = -1
arrNet[i]["state"] = "idle"
Log(arrNet[i], "The node closes the position and resets to the idle state.", "#FF0000")
def onTick () :
global arrNet, arrMsg, acc
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker) # Get the latest current ticker every time
for i in range(len(arrNet)): # Iterate through all grid nodes, find out the position where you need to pend a buy order according to the current market, and pend a buy order.
if i != len(arrNet) - 1 and arrNet[i]["state"] == "idle" and ticker.Sell > arrNet[i]["price"] and ticker.Sell < arrNet[i + 1]["price"]:
acc = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
if acc.Balance < minBalance : # If there is not enough money left, you can only jump out and do nothing.
arrMsg.append("Insufficient funds" + json.dumps(acc) + "!" + ", time:" + _D())
break
orderId = exchange.Buy(arrNet[i]["price"], arrNet[i]["amount"], arrNet[i], ticker) # Pending buy orders
if orderId :
arrNet[i]["state"] = "pending" # Update the grid node status and other information if the buy order is successfully pending
arrNet[i]["id"] = orderId
else :
# Cancel h/the order
cancelOrder(arrNet[i]["price"], ORDER_TYPE_BUY) # Cancel orders by using the cancel function
arrMsg.append("Pending order failed!" + json.dumps(arrNet[i]) + ", time:" + _D())
Sleep(1000)
orders = _C(exchange.GetOrders)
checkOpenOrders(orders, ticker) # Check the status of all buy orders and process them according to the changes.
Sleep(1000)
orders = _C(exchange.GetOrders)
checkCoverOrders(orders, ticker) # Check the status of all sell orders and process them according to the changes.
# The following information about the construction status bar can be found in the FMZ API documentation.
tbl = {
"type" : "table",
"title" : "grid status",
"cols" : ["node index", "details"],
"rows" : [],
}
for i in range(len(arrNet)) :
tbl["rows"].append([i, json.dumps(arrNet[i])])
errTbl = {
"type" : "table",
"title" : "record",
"cols" : ["node index", "details"],
"rows" : [],
}
orderTbl = {
"type" : "table",
"title" : "orders",
"cols" : ["node index", "details"],
"rows" : [],
}
while len(arrMsg) > 20 :
arrMsg.pop(0)
for i in range(len(arrMsg)) :
errTbl["rows"].append([i, json.dumps(arrMsg[i])])
for i in range(len(orders)) :
orderTbl["rows"].append([i, json.dumps(orders[i])])
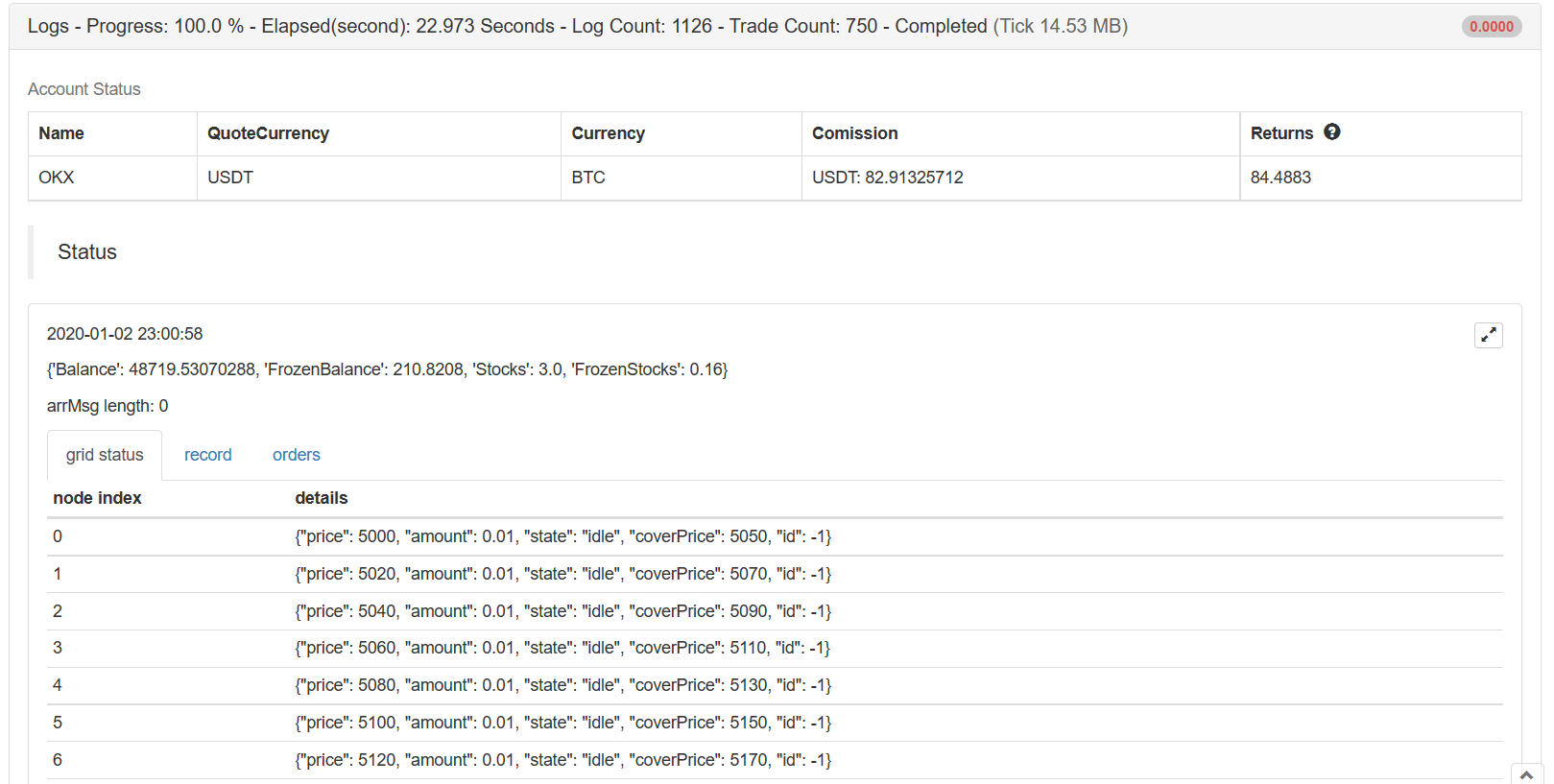
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", acc, "\n", "arrMsg length:", len(arrMsg), "\n", "`" + json.dumps([tbl, errTbl, orderTbl]) + "`")
def main (): # Strategy execution starts here
global arrNet
for i in range(int((endPrice - beginPrice) / distance)): # The for loop constructs a data structure for the grid based on the parameters, a list that stores each grid node, with the following information for each grid node:
arrNet.append({
"price" : beginPrice + i * distance, # Price of the node
"amount" : amount, # Number of orders
"state" : "idle", # pending / cover / idle # Node Status
"coverPrice" : beginPrice + i * distance + pointProfit, # Node closing price
"id" : -1, # ID of the current order related to the node
})
while True: # After the grid data structure is constructed, enter the main strategy loop
onTick() # Processing functions on the main loop, the main processing logic
Sleep(500) # Control polling frequency
La idea principal del diseño de la estrategia es comparar la lista actual de pedidos pendientes devueltos por elGetOrdersInterfaz de acuerdo con la estructura de datos de la cuadrícula mantenida por usted mismo. Analice los cambios de las órdenes pendientes (si están cerradas o no), actualice la estructura de datos de la cuadrícula y realice operaciones posteriores. Además, las órdenes pendientes no se cancelarán hasta que se complete la transacción, incluso si el precio se desvía, porque el mercado de divisas digitales a menudo tiene la situación de pines, estas órdenes pendientes también pueden recibir las órdenes de pines (si el número de órdenes pendientes está limitado en el intercambio, se ajustará).
La visualización de datos de estrategia utiliza elLogStatusfunción para mostrar datos en la barra de estado en tiempo real.
tbl = {
"type" : "table",
"title" : "grid status",
"cols" : ["node index", "details"],
"rows" : [],
}
for i in range(len(arrNet)) :
tbl["rows"].append([i, json.dumps(arrNet[i])])
errTbl = {
"type" : "table",
"title" : "record",
"cols" : ["node index", "details"],
"rows" : [],
}
orderTbl = {
"type" : "table",
"title" : "orders",
"cols" : ["node index", "details"],
"rows" : [],
}
Se construyen tres tablas. La primera muestra la información de cada nodo en la estructura de datos de la red actual, la segunda muestra información anormal, y la tercera muestra la información real del intercambio.
Prueba de retroceso
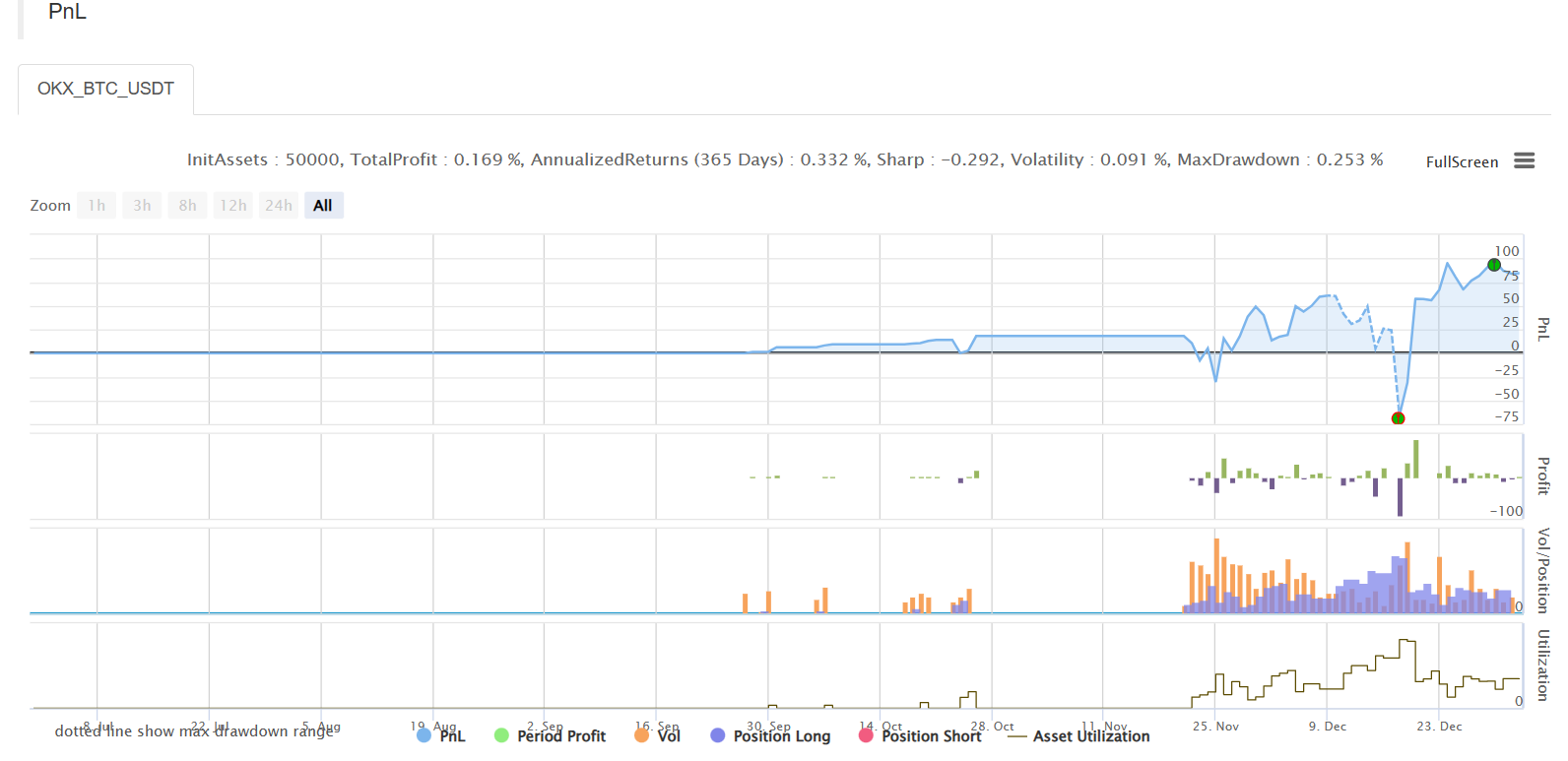

Dirección de la estrategia
La estrategia es para el aprendizaje y backtesting propósito sólo, y puede ser optimizado y actualizado si usted está interesado.
- Práctica cuantitativa de los intercambios DEX (2) -- Guía de usuario de hiperlíquidos
- Prácticas de cuantificación en el mercado DEX ((2) -- Guía de uso de Hyperliquid
- Práctica cuantitativa de los intercambios DEX (1) -- Guía de usuario de dYdX v4
- Introducción al arbitraje de lead-lag en criptomonedas (3)
- Prácticas de cuantificación de las bolsas DEX ((1) -- dYdX v4 Guía de uso
- Introducción al conjunto de Lead-Lag en las monedas digitales (3)
- Introducción al arbitraje de lead-lag en criptomonedas (2)
- Introducción al conjunto de Lead-Lag en las monedas digitales (2)
- Discusión sobre la recepción de señales externas de la plataforma FMZ: una solución completa para recibir señales con servicio HTTP incorporado en la estrategia
- Exploración de la recepción de señales externas de la plataforma FMZ: estrategias para una solución completa de recepción de señales de servicios HTTP integrados
- Introducción al arbitraje de lead-lag en criptomonedas (1)
- Mejores herramientas hacen un buen trabajo - aprender a utilizar el entorno de investigación para analizar los principios comerciales
- Estrategias de cobertura de divisas cruzadas en la negociación cuantitativa de activos de cadena de bloques
- Adquiere la guía de estrategia de moneda digital de FMex en FMZ Quant
- Enseñarle a escribir estrategias -- trasplantar una estrategia MyLanguage (Advanced)
- Enseñar a escribir estrategias -- trasplantar una estrategia MyLanguage
- Enseñarle a añadir soporte multi-gráfico a la estrategia
- Enseñar a escribir una función de síntesis de línea K en la versión de Python
- Análisis de la estrategia del canal de Donchian en el entorno de investigación
- Cuando FMZ se encuentra con ChatGPT, recuerde un intento de usar AI para ayudar a aprender transacciones cuantitativas
- En el caso de las opciones de divisas digitales, las opciones de divisas digitales son las opciones de divisas digitales disponibles para el mercado.
- Estrategia de flujo lineal de pedidos pendientes desarrollada sobre la base de la función de reproducción de datos
- Estrategia para comprar los ganadores de la versión de Python
- Viaje FMZ -- con estrategia de transición
- Enseñar a transformar una estrategia de Python de una sola especie en una estrategia de múltiples especies
- Implementar un robot de negociación cuantitativa de tiempo de inicio o parada gadget mediante el uso de Python
- Oak le enseña a usar JS para interfacer con FMZ API extendida
- Llame a la interfaz de Dingding para realizar el mensaje push del robot
- Estrategia de orden pendiente equilibrada (Estrategia de enseñanza)
- En el caso de las entidades de crédito, el valor de las pérdidas derivadas de las operaciones de cobertura de riesgo se calcula en función de las pérdidas derivadas de las operaciones de cobertura.
- Muchos años después, usted encontrará este artículo es el más valioso en su carrera de inversión - averiguar de dónde vienen los rendimientos y riesgos