Estrategia de flecha cruzada de media móvil doble
El autor:¿ Qué pasa?, Fecha: 2023-11-21 17:00:49Las etiquetas:
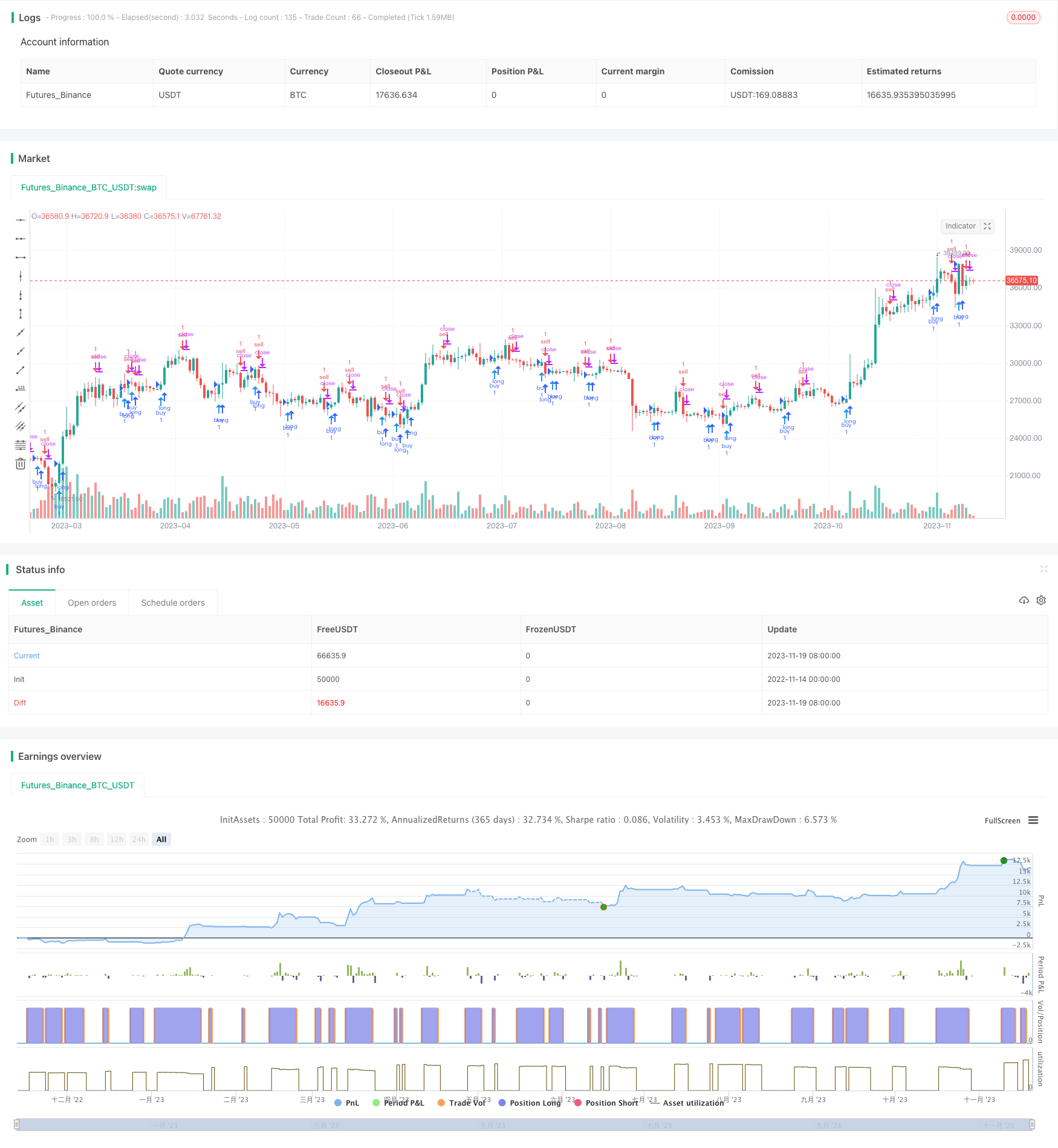
Resumen general
Esta estrategia identifica las señales de compra y venta calculando el cruce de las dos medias móviles del indicador MACD.
Principios
La estrategia primero calcula la línea rápida (EMA de 12 períodos), la línea lenta (EMA de 26 períodos) y la diferencia MACD. Luego determina señales largas y cortas basadas en el cruce de las líneas rápidas y lentas, así como el valor positivo / negativo de la diferencia MACD:
- Cuando la línea rápida cruza por encima de la línea lenta (cruz dorada) y la diferencia MACD cruza por encima de 0, es una señal de compra
- Cuando la línea rápida cruza por debajo de la línea lenta (cruz de muerte) y la diferencia MACD cruza por debajo de 0, es una señal de venta
Para filtrar las señales falsas, el código también comprueba la señal del candelabro anterior.
Además, se trazan en el gráfico formas de flechas para indicar señales de compra y venta.
Ventajas
Las ventajas de esta estrategia incluyen:
- El uso de un doble cruce de medias móviles ayuda a identificar tendencias y filtrar el ruido del mercado
- Incorporar la diferencia MACD evita operaciones perdidas y señales falsas
- Las flechas indican claramente las entradas y salidas
- Las reglas simples y fáciles de entender facilitan la replicación
Riesgos y soluciones
Algunos riesgos de esta estrategia:
- Los cruces pueden generar señales falsas y causar un exceso de operaciones.
- Incapaz de discernir los rangos en una tendencia, lo que podría conducir a pérdidas.
- Las reglas fijas no pueden adaptarse a los mercados cambiantes.
Oportunidades de mejora
Algunas maneras de mejorar la estrategia:
- Prueba diferentes combinaciones de parámetros para encontrar la configuración óptima para la línea rápida, la línea lenta y el MACD
- Añadir condiciones de entrada adicionales como las interrupciones de volumen a las señales de filtro
- Incorporar el stop loss para controlar las pérdidas de una sola operación
- Utilice indicadores de volatilidad como el VIX para medir el apetito por el riesgo
- Prueba modelos de aprendizaje automático en lugar de reglas fijas para crear optimización adaptativa
Resumen de las actividades
La estrategia de la flecha de cruce de la media móvil dual es bastante simple y práctica. Al utilizar el cruce de dos medias móviles y el filtrado de diferencias MACD, identifica entradas y salidas durante las tendencias a medio y largo plazo, evitando reversiones de precios perdidas. Las señales de flecha también proporcionan una guía de operación clara. Se pueden lograr mejoras adicionales en la estabilidad y la rentabilidad a través del ajuste de parámetros, filtros adicionales y optimización adaptativa.
/*backtest
start: 2022-11-14 00:00:00
end: 2023-11-20 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=3
//Daniels stolen code
strategy(shorttitle="Daniels Stolen Code", title="Daniels Stolen Code", overlay=true, calc_on_order_fills=true, pyramiding=0)
//Define MACD Variables
fast = 12, slow = 26
fastMACD = ema(hlc3, fast)
slowMACD = ema(hlc3, slow)
macd = fastMACD - slowMACD
signal = sma(macd, 9)
hist = macd - signal
currMacd = hist[0]
prevMacd = hist[1]
currPrice = hl2[0]
prevPrice = hl2[1]
buy = currPrice > prevPrice and currMacd > prevMacd
sell = currPrice < prevPrice and currMacd < prevMacd
neutral = (currPrice < prevPrice and currMacd > prevMacd) or (currPrice > prevPrice and currMacd < prevMacd)
//Plot Arrows
timetobuy = buy==1 and (sell[1]==1 or (neutral[1]==1 and sell[2]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and sell[3]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and sell[4]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and neutral[4]==1 and sell[5]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and neutral[4]==1 and neutral[5]==1 and sell[6]==1))
timetosell = sell==1 and (buy[1]==1 or (neutral[1]==1 and buy[2]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and buy[3]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and buy[4]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and neutral[4]==1 and buy[5]==1) or (neutral[1]==1 and neutral[2]==1 and neutral[3]==1 and neutral[4]==1 and neutral[5]==1 and buy[6]==1))
plotshape(timetobuy, color=blue, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.arrowup)
plotshape(timetosell, color=red, location=location.abovebar, style=shape.arrowdown)
//plotshape(neutral, color=black, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.circle)
//Test Strategy
// strategy.entry("long", true, 1, when = timetobuy and time > timestamp(2017, 01, 01, 01, 01)) // buy by market if current open great then previous high
// strategy.close("long", when = timetosell and time > timestamp(2017, 01, 01, 01, 01))
strategy.order("buy", true, 1, when=timetobuy==1 and time > timestamp(2019, 01, 01, 01, 01))
strategy.order("sell", false, 1, when=timetosell==1 and time > timestamp(2019, 01, 01, 01, 01))
// strategy.entry(id = "Short", long = false, when = enterShort())
// strategy.close(id = "Short", when = exitShort())
//strategy.entry("long", true, 1, when = open > high[1]) // enter long by market if current open great then previous high
// strategy.exit("exit", "long", profit = 10, loss = 5) // ge
- Estrategia de ruptura de la media móvil múltiple
- Estrategia estocástica de negociación OTT
- Estrategia de inversión de la media móvil doble
- Estrategia de inversión de doble clic de Quant Trading
- Estrategia de negociación de inversión de candlestick basada en el canal de Fibonacci
- Estrategia de cruce de tendencia de la media móvil dinámica
- Estrategia de ruptura de desviación estándar de bandas de Bollinger
- Las medidas de control se aplican a los datos de los Estados miembros y a los datos de los Estados miembros.
- Estrategia de pruebas de retroceso dinámicas de varios marcos de tiempo
- Estrategia de negociación de ruptura a corto plazo de inversión
- Estrategia de negociación de oscilación de impulso
- Las operaciones de las entidades de crédito se considerarán financiadas por el Banco Central Europeo.
- Estrategia de negociación cuantitativa de retroceso de Fibonacci
- Estrategia de oscilación de dos indicadores
- Estrategia de ruptura de precios de media móvil doble
- Estrategia dinámica de seguimiento de pérdidas
- Estrategia de combinación de promedio móvil alineado y índice alto bajo acumulado
- Estrategia de seguimiento de tendencias del indicador Williams de doble EMA
- Estrategia de seguimiento de tendencias de la EMA con doble cruz de oro
- Estrategia de TTM de impulso para el avance