Analyse et instructions d'utilisation concernant la fonction intégrée
Auteur:FMZ~Lydia, Créé: 2023-10-07 15:35:44, Mis à jour: 2024-01-02 21:17:16
Analyse et instructions d'utilisation concernant la fonction intégrée
La fonction _Cross dans la section Fonctions globales de la documentation API est utilisée pour calculer l'état de croisement des deux indicateurs.
La mise en œuvre de la fonction est similaire au code suivant:
Notez que lorsquearr1est défini comme un ensemble d'indicateurs rapides etarr2en tant qu'ensemble d'indicateurs lents,
la valeur renvoyée par le_Crossla fonction est positive, c'est-à-dire, selon la documentation,a positive number is the period of upward penetration, a negative number indicates the period of downward penetration, and 0 means the same as the current priceJe suis désolée.
On peut voir, à ce moment-làarr1vers le haut a pénétré learr2Il y a eu n cycles, à ce moment, c'est la ligne rapide qui pénètre vers le haut la ligne lente, représentant un croisement.
C' est la même chose._CrossLa fonction renvoie un nombre négatif, c'est-à-dire un croisement.
Le contraire est vrai siarr1est défini comme un ensemble d'indicateurs lents etarr2comme un ensemble d'indicateurs rapides.
Une valeur positive renvoyée par le_CrossLa fonction représente une traverse.
Une valeur négative renvoyée par le_Crossla fonction représente un croisement.
// Return to the number of periods of upward penetration, the positive number is the number of periods of upward penetration, the negative number indicates the number of periods of downward penetration, 0 means the same as the current price
$.Cross = function(arr1, arr2) { // The number of parameters is 2, it can be seen from the parameter name, these two parameters should be an array type, the array is like an array in the X-axis for the array index value, Y-axis for the index value of the line in the coordinate system, the function is to determine the intersection of the two lines
if (arr1.length !== arr2.length) { // The first step is to determine if the two arrays being compared are equal in length
throw "array length not equal"; // Throw an error if they are not equal, it is not possible to determine the intersection of unequal lines.
}
var n = 0; // Declare the variable n to record the intersection state, initially 0, unintersected
for (var i = arr1.length-1; i >= 0; i--) { // Iterate over the array arr1, from the last element forward.
if (typeof(arr1[i]) !== 'number' || typeof(arr2[i]) !== 'number') { // When any of the arrays arr1 or arr2 is of a non-numeric type (i.e., an invalid indicator), the traversal loop is broken.
break; // break out of a loop
}
if (arr1[i] < arr2[i]) { // If arr1 is smaller than arr2 then n--, will record the relative state of arr1, arr2 at the beginning, (i.e., at the beginning n will adjust itself according to the relative sizes of arr1[i], arr2[i], and once there is another relationship between the sizes of arr1[i], arr2[i] opposite to the state of n, i.e., a crossing of the two lines has occurred.)
if (n > 0) {
break;
}
n--;
} else if (arr1[i] > arr2[i]) { // If arr1 is greater than arr2 then n++
if (n < 0) {
break;
}
n++;
} else { // arr1[i] == arr2[i], then immediately break
break;
}
}
return n; // Returns the value of n, which represents the number of periods that have been crossed, and 0, which means that the indicator values are equal.
};
Simulons un ensemble de données transmises à ce paramètre et voyons comment ça se passe
var arr1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,8,8,9] // fast line indicator
var arr2 = [2,3,4,5,6,7,7,7,7] // slow line indicator
function main(){
Log("_Cross(arr1, arr2) : ", _Cross(arr1, arr2))
Log("_Cross(arr2, arr1) : ", _Cross(arr2, arr1))
}

On peut voir que les résultats sont 3, -3.
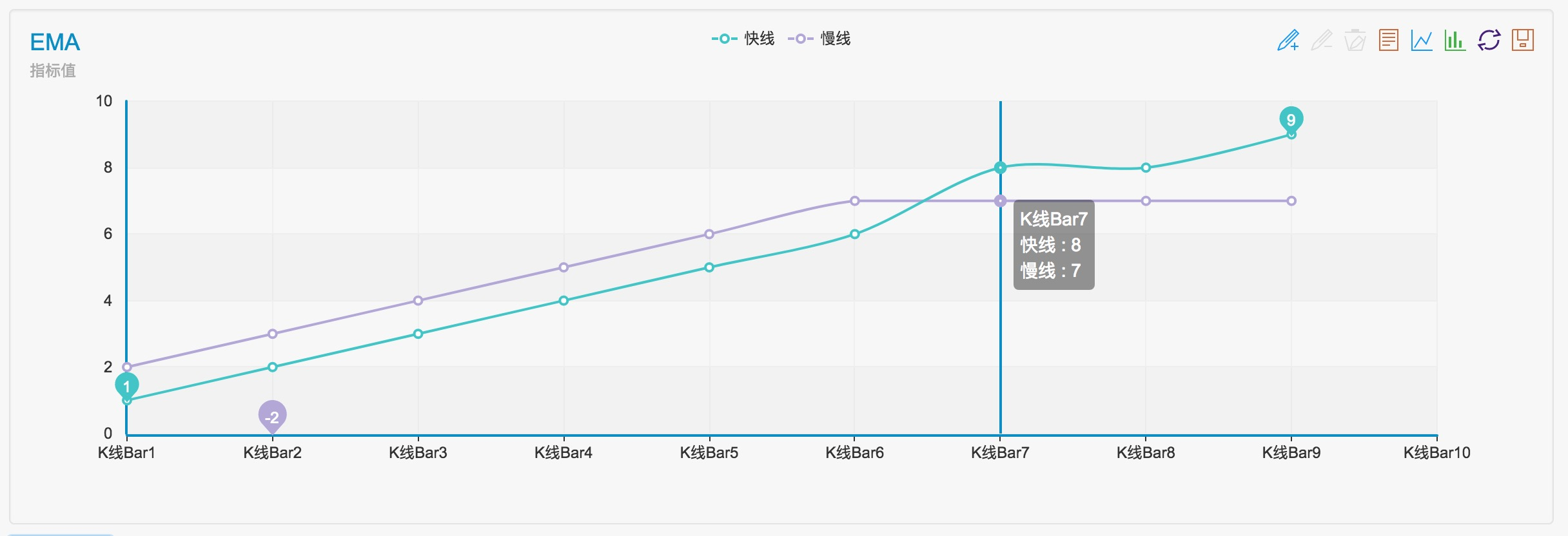
Comme vous le voyez sur le graphique, le croisement se produit devant trois barres de ligne K.
- Analyse de la stratégie de négociation à haute fréquence - Penny Jump
- Idées de négociation alternatives - Stratégie de négociation dans la zone de la ligne K
- Construction et application du bruit du marché
- L'amélioration et la transformation du facteur PSY
- Analyse des stratégies de trading à haute fréquence - Penny Jump
- Comment mesurer le risque de position - Introduction à la méthode VaR
- L'idée de négociation alternative - stratégie de négociation de l'espace K-Line
- Comment mesurer le risque de détention de VaR
- FMZ Mobile APP Terminal de trading, permettant votre expérience de trading quantitative
- L'application mobile FMZ est un terminal de négociation qui vous permet de quantifier votre expérience de négociation.
- Delta contre les options Bitcoin avec une courbe souriante
- Réflexions sur les stratégies de négociation à haute fréquence (5)
- Réflexions sur les stratégies de négociation à haute fréquence (4)
- Réflexion sur la stratégie de trading à haute fréquence (5)
- Réflexion sur les stratégies de trading à haute fréquence (4)
- Réflexions sur les stratégies de négociation à haute fréquence (3)
- Réflexion sur les stratégies de trading à haute fréquence (3)
- Réflexions sur les stratégies de négociation à haute fréquence (2)
- Réflexion sur la stratégie de trading à haute fréquence (2)
- Réflexions sur les stratégies de négociation à haute fréquence (1)