नौसिखिया, इसे देखें आपको क्रिप्टोकरेंसी मात्रात्मक व्यापार में ले जाएं (5)
लेखक:निनाबादास, बनाया गयाः 2022-04-18 17:20:53, अद्यतन किया गयाः 2022-04-18 17:30:27नौसिखिया, इसे देखें आपको क्रिप्टोकरेंसी मात्रात्मक व्यापार में ले जाएं (5)
पिछले लेख में, हमने एक सरल ग्रिड रणनीति के व्यापार तर्क विश्लेषण की व्याख्या की। इस लेख में, हम इस शिक्षण रणनीति के डिजाइन को पूरा करना जारी रखेंगे।
- व्यापारिक तर्क विश्लेषण जैसा कि हमने पिछले लेख में उल्लेख किया है, जब तक आप ग्रिड की प्रत्येक ग्रिड लाइन को पार करते हैं और यह तय करते हैं कि वर्तमान मूल्य ग्रिड लाइन को ऊपर या नीचे पार करता है, तब तक ट्रेडिंग क्रिया को ट्रिगर किया जा सकता है। लेकिन वास्तव में, अभी भी बहुत सारे तर्क विवरण हैं, और जो नौसिखिया रणनीति लेखन को नहीं समझते हैं वे अक्सर गलतफहमी पैदा करते हैं कि तर्क बहुत सरल है, कोड में केवल कुछ पंक्तियां होनी चाहिए, और वास्तविक लेखन में अभी भी बहुत सारे विवरण पाए जाते हैं।
पहला विवरण हम पर विचार करना है अनंत ग्रिड के डिजाइन है. पिछले लेख में याद है हम एक समारोह डिजाइन किया हैcreateNetएक साथ प्रारंभिक ग्रिड डेटा संरचना उत्पन्न करने के लिए? यह फ़ंक्शन ग्रिड डेटा संरचना को ग्रिड लाइनों की एक परिमित संख्या के साथ उत्पन्न करता है। तो क्या होगा यदि, जब रणनीति चल रही है, तो कीमत इस ग्रिड डेटा संरचना की सीमाओं से परे जाती है (ऊपरी ग्रिड लाइन से परे जहां कीमत सबसे अधिक है, और निचली ग्रिड लाइन जहां कीमत सबसे कम है)?
तो हमें पहले ग्रिड डेटा संरचना में एक विस्तार तंत्र जोड़ने की जरूरत है।
रणनीति मुख्य कार्य लिखने के लिए शुरू, और मुख्य कार्य कोड है जहां रणनीति निष्पादित करने के लिए शुरू होता है।
var diff = 50 // global variable, the grid interval, can be designed as parameter; for an easy explanation, we write it in an infinite loop
function main() {
// After the bot starts running, execute the strategy code from here
var ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker) // obtain the latest ticker data in the market; for the ticker data structure, you can refer to FMZ API documentation: https://www.fmz.com/api#ticker
var net = createNet(ticker.Last, diff) // the function to initially construct the grid data structure we designed in the previous article; here we construct a grid data structure net
while (true) { // then, the program logic enters the while infinite loop, and the strategy will repeatedly execute the code within the {} symbol from here
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker) // the first line of the infinite loop code gets the latest market quote data, and updates it to the variable ticker
// check the grid range
while (ticker.Last >= net[net.length - 1].price) {
net.push({
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : net[net.length - 1].price + diff,
})
}
while (ticker.Last <= net[0].price) {
var price = net[0].price - diff
if (price <= 0) {
break
}
net.unshift({
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : price,
})
}
// the code is not completed...
}
}
यह वह कोड है जो ग्रिड डेटा संरचना को विस्तार योग्य बनाता है (ऊपर दिए गए कोड से उद्धृत):
// check the grid range
while (ticker.Last >= net[net.length - 1].price) { // if the price exceeds the grid line with the highest price in the grid,
net.push({ // add a new grid line after the grid line with the highest price in the grid
buy : false, // initialize the sell mark
sell : false, // initialize the buy mark
price : net[net.length - 1].price + diff, // add a grid interval on the basis of the previous highest price
})
}
while (ticker.Last <= net[0].price) { // if the price is lower than the grid line with the lowest price in the grid,
var price = net[0].price - diff // distinguished from adding upwards, you should notice the price of the newly added grid line downwards cannot be less than or equal to 0, so you need to judge here
if (price <= 0) { // do not add when the price is less than or equal to 0, and break the loop
break
}
net.unshift({ // add a new grid line before the grid line with the lowest price in the grid
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : price,
})
}
इसके बाद, हमें विचार करने की आवश्यकता है कि ट्रेडिंग ट्रिगर को कैसे लागू किया जाए।
var diff = 50
var amount = 0.002 // add a global variable, which can also be designed as a parameter; for easy explanation, we can write it in an infinite loop
// the parameter controls the trading amount on the grid line each time the trading is triggered
function main() {
var ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
var net = createNet(ticker.Last, diff)
var preTicker = ticker // before the start of the main (infinite) loop, set a variable, to record the market quotes of last time
while (true) {
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
// check the grid range
while (ticker.Last >= net[net.length - 1].price) {
net.push({
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : net[net.length - 1].price + diff,
})
}
while (ticker.Last <= net[0].price) {
var price = net[0].price - diff
if (price <= 0) {
break
}
net.unshift({
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : price,
})
}
// index the grid
for (var i = 0 ; i < net.length ; i++) { // traverse all grid lines in the grid data structure
var p = net[i]
if (preTicker.Last < p.price && ticker.Last > p.price) { // upcross, and sell; when the current node has been traded, no matter SELL or BUY, no more trade
if (i != 0) {
var downP = net[i - 1]
if (downP.buy) {
exchange.Sell(-1, amount, ticker)
downP.buy = false
p.sell = false
continue
}
}
if (!p.sell && !p.buy) {
exchange.Sell(-1, amount, ticker)
p.sell = true
}
} else if (preTicker.Last > p.price && ticker.Last < p.price) { // downcross, and buy
if (i != net.length - 1) {
var upP = net[i + 1]
if (upP.sell) {
exchange.Buy(-1, amount * ticker.Last, ticker)
upP.sell = false
p.buy = false
continue
}
}
if (!p.buy && !p.sell) {
exchange.Buy(-1, amount * ticker.Last, ticker)
p.buy = true
}
}
}
preTicker = ticker // record the current market quotes in preTicker, which will be used as the "last" market quote data to compare with the new one in next loop, to judge upcross and downcross
Sleep(500)
}
}
आप देख सकते हैं:
- ग्रिड लाइन को पार करने की स्थिति:preTicker.Last < p.price && ticker.Last > p.price- ग्रिड लाइन के नीचे पार करने की स्थितिःpreTicker.Last > p.price && ticker.Last < p.price
पिछले लेख में इस बारे में बात की गई थी:
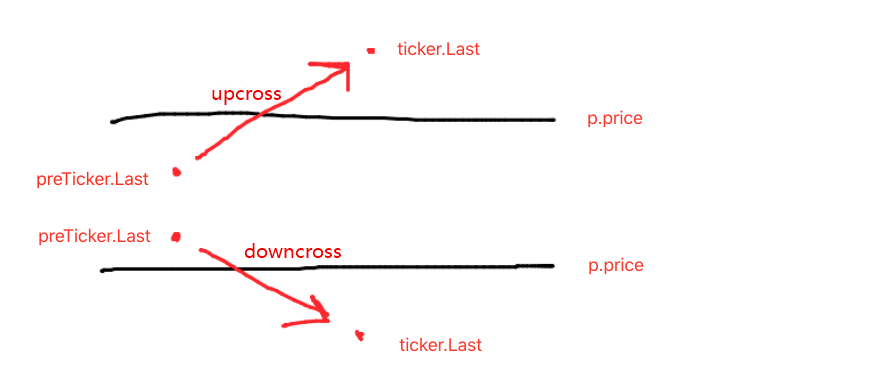
ऊपर की ओर या नीचे की ओर आकलन करना आदेश देने और व्यापार करने के लिए केवल पहला कदम है, और ग्रिड लाइन डेटा में चिह्न का भी आकलन करने की आवश्यकता है।
यदि यह अपक्रॉस है, तो निर्णय लें कि क्या कीमत वर्तमान ग्रिड लाइन से कम है, साथ ही नवीनतम ग्रिड लाइन पर खरीद चिह्न; यदि खरीद चिह्न का मूल्य सही है, तो इसका मतलब है कि अंतिम ग्रिड लाइन निष्पादित खरीद, और अंतिम ग्रिड लाइन के खरीद चिह्न को गलत के रूप में रीसेट करें, और वर्तमान ग्रिड लाइन के बिक्री चिह्न को गलत के रूप में रीसेट करें।
अभी उल्लिखित शर्तों का न्याय करने के बाद, यदि वे ट्रिगर नहीं होते हैं, तो न्याय करना जारी रखें। यदि वर्तमान ग्रिड लाइन का खरीद चिह्न और बिक्री चिह्न दोनों गलत हैं, तो इसका मतलब है कि वर्तमान ग्रिड लाइन व्यापार कर सकती है; क्योंकि यह ऊपर है, यहां हम बिक्री ऑपरेशन निष्पादित करते हैं, और निष्पादन के बाद ग्रिड लाइन के बिक्री चिह्न को सही के रूप में चिह्नित करते हैं।
नीचे क्रॉस के प्रसंस्करण का तर्क एक ही है. (नौसिखिया खुद के लिए इसके बारे में सोच सकते हैं.)
पूर्ण रणनीति बैकटेस्ट
बैकटेस्ट के दौरान कुछ डेटा देखने के लिए, एक समारोहshowTblडेटा प्रदर्शित करने के लिए लिखा जाता है।
function showTbl(arr) {
var tbl = {
type : "table",
title : "grid",
cols : ["grid information"],
rows : []
}
var arrReverse = arr.slice(0).reverse()
_.each(arrReverse, function(ele) {
var color = ""
if (ele.buy) {
color = "#FF0000"
} else if (ele.sell) {
color = "#00FF00"
}
tbl.rows.push([JSON.stringify(ele) + color])
})
LogStatus(_D(), "\n`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`", "\n account information:", exchange.GetAccount())
}
पूर्ण रणनीति कोडः
/*backtest
start: 2021-04-01 22:00:00
end: 2021-05-22 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"OKEX","currency":"ETH_USDT","balance":100000}]
*/
var diff = 50
var amount = 0.002
function createNet(begin, diff) {
var oneSideNums = 10
var up = []
var down = []
for (var i = 0 ; i < oneSideNums ; i++) {
var upObj = {
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : begin + diff / 2 + i * diff,
}
up.push(upObj)
var j = (oneSideNums - 1) - i
var downObj = {
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : begin - diff / 2 - j * diff,
}
if (downObj.price <= 0) { // the price cannot be less than or equal to 0
continue
}
down.push(downObj)
}
return down.concat(up)
}
function showTbl(arr) {
var tbl = {
type : "table",
title : "grid",
cols : ["grid information"],
rows : []
}
var arrReverse = arr.slice(0).reverse()
_.each(arrReverse, function(ele) {
var color = ""
if (ele.buy) {
color = "#FF0000"
} else if (ele.sell) {
color = "#00FF00"
}
tbl.rows.push([JSON.stringify(ele) + color])
})
LogStatus(_D(), "\n`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`", "\n account information:", exchange.GetAccount())
}
function main() {
var ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
var net = createNet(ticker.Last, diff)
var preTicker = ticker
while (true) {
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
// check the grid range
while (ticker.Last >= net[net.length - 1].price) {
net.push({
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : net[net.length - 1].price + diff,
})
}
while (ticker.Last <= net[0].price) {
var price = net[0].price - diff
if (price <= 0) {
break
}
net.unshift({
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : price,
})
}
// index grid
for (var i = 0 ; i < net.length ; i++) {
var p = net[i]
if (preTicker.Last < p.price && ticker.Last > p.price) { // upcross, and sell; when the current node has been traded, no matter SELL or BUY, no more trade
if (i != 0) {
var downP = net[i - 1]
if (downP.buy) {
exchange.Sell(-1, amount, ticker)
downP.buy = false
p.sell = false
continue
}
}
if (!p.sell && !p.buy) {
exchange.Sell(-1, amount, ticker)
p.sell = true
}
} else if (preTicker.Last > p.price && ticker.Last < p.price) { // downcross, and buy
if (i != net.length - 1) {
var upP = net[i + 1]
if (upP.sell) {
exchange.Buy(-1, amount * ticker.Last, ticker)
upP.sell = false
p.buy = false
continue
}
}
if (!p.buy && !p.sell) {
exchange.Buy(-1, amount * ticker.Last, ticker)
p.buy = true
}
}
}
showTbl(net)
preTicker = ticker
Sleep(500)
}
}
रणनीति बैकटेस्टः
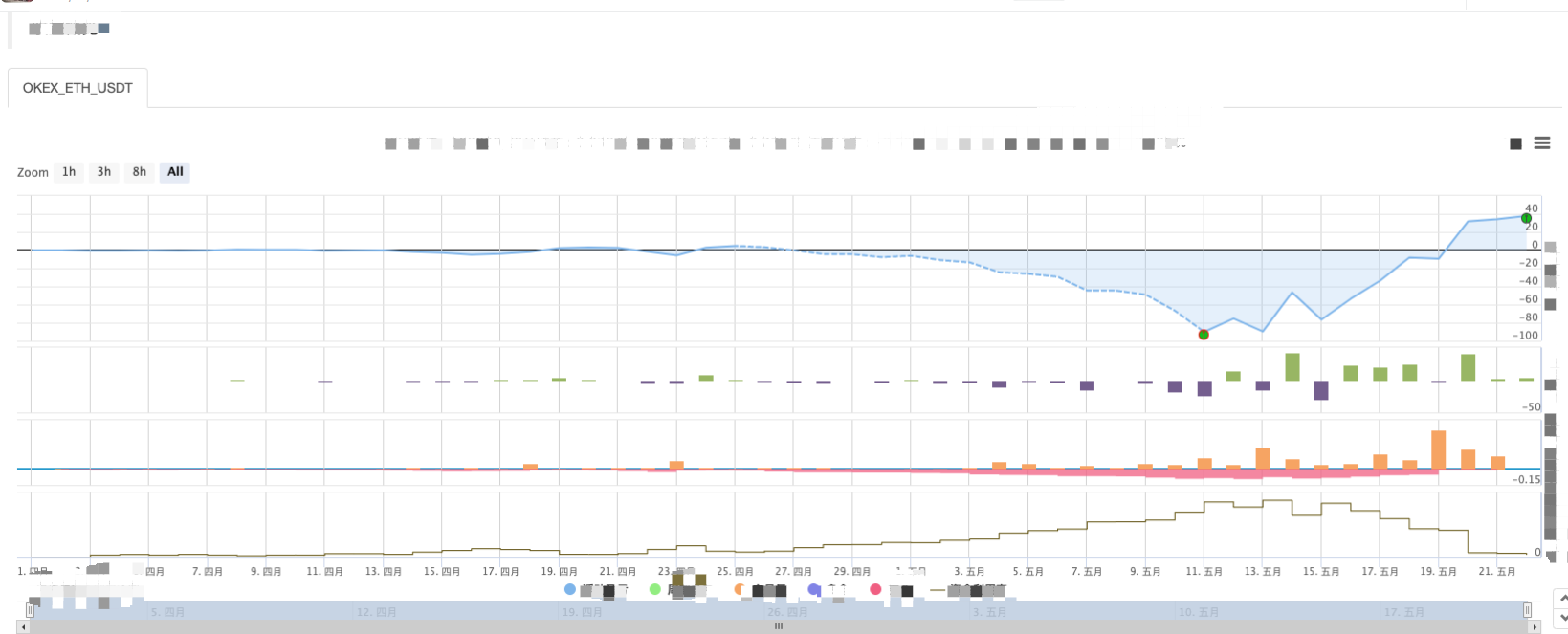
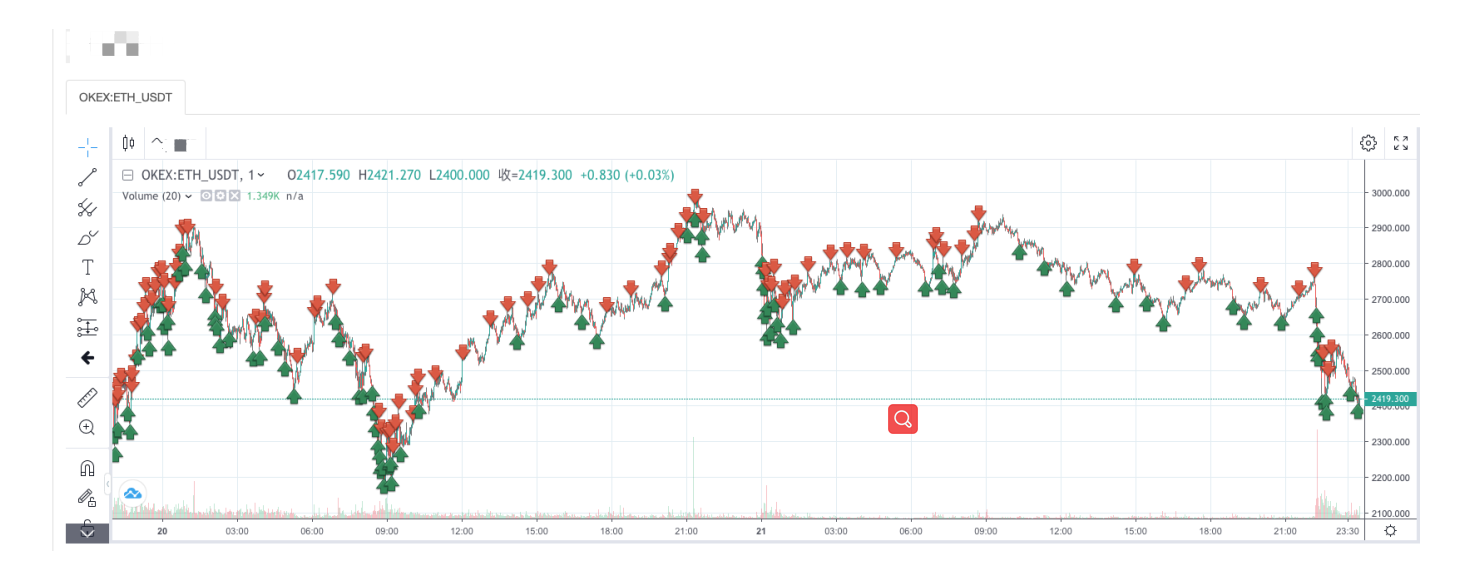
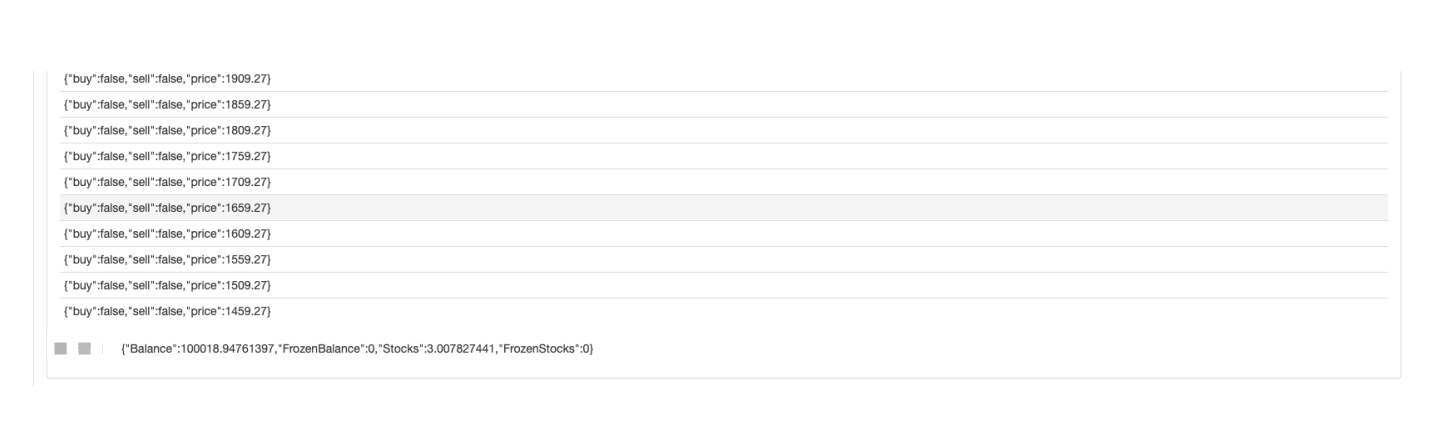
आप ग्रिड रणनीति की विशेषताओं को देख सकते हैं जब एक प्रवृत्ति बाजार है, वहाँ एक बड़ा तैरता नुकसान होगा, और रिटर्न एक अस्थिर बाजार में उछाल होगा। इसलिए, ग्रिड रणनीति जोखिम मुक्त नहीं है। स्पॉट रणनीति अभी भी इसे बनाए रखने के लिए रख सकती है, जबकि वायदा अनुबंधों की ग्रिड रणनीति अधिक जोखिमपूर्ण है और ग्रिड मापदंडों को संरक्षक रूप से सेट करने की आवश्यकता है।
- my भाषा में यहाँ कैसे लिखा जाता है ताकि संकेत हो सके एक बार प्रिंट आउटपुट करें
- डेरिबिट विकल्पों की गतिशील डेल्टा हेजिंग
- FMZ क्वांट डेटाबेस बनाने के लिए SQLite का उपयोग करें
- नौसिखिया, इसे देखें
आपको क्रिप्टोकरेंसी मात्रात्मक व्यापार में ले जाएं (8) - नौसिखिया, इसे देखें
आपको क्रिप्टोकरेंसी मात्रात्मक व्यापार में ले जाएं (7) - नौसिखिया, इसे देखें
आपको क्रिप्टोकरेंसी मात्रात्मक व्यापार में ले जाएं (6) - नौसिखिया, इसे देखें
आपको क्रिप्टोकरेंसी मात्रात्मक व्यापार में ले जाएं (3) - नौसिखिया, इसे देखें
आपको क्रिप्टोकरेंसी मात्रात्मक व्यापार में ले जाएं (2) - मेरे आविष्कारक का समय गलत है
- क्या आप एक महान प्रतिलेखन रणनीति के बारे में विचार दे सकते हैं?
- नौसिखिया, इसे देखें
आपको क्रिप्टोकरेंसी मात्रात्मक व्यापार में ले जाएं (4) - आदेश बनाने का समय और आदेश पूरा करने का समय
- मार्टिन के लिए खरीदारी की रणनीति
- मेरी भाषा समझने वाले भाइयों, कृपया मुझे इस कोड का अर्थ बताएं_TR:=MAX ((MAX ((((HIGH-LOW),ABS ((REF ((CLOSE,1)-HIGH)),ABS ((REF ((CLOSE,1)-LOW));
- वास्तविक डिस्क त्रुटि रिपोर्टिंग प्रश्न
- नौसिखिया, इसे देखें
आपको क्रिप्टोकरेंसी मात्रात्मक व्यापार में ले जाएं (1) - क्या टाइपस्क्रिप्ट का समर्थन बढ़ाया जा सकता है?
- क्रिप्टोकरेंसी स्पॉट हेज रणनीति (2)
- क्रिप्टोकरेंसी स्पॉट हेज रणनीति (1)
- Bitget API में, ADA, AVAX, AXS, BCH, DOT, EOS, ETC, FIL, LINK, LTC, LUNA, MATIC, SOL, XRP के लिए लेनदेन के साथ समस्याएं उत्पन्न होती हैं।