पायथन संस्करण में सरल ग्रिड रणनीति
लेखक:FMZ~Lydia, बनाया गयाः 2022-12-23 21:00:45, अद्यतनः 2025-01-11 18:19:24
पायथन संस्करण में सरल ग्रिड रणनीति
रणनीति वर्ग पर कई पायथन रणनीतियाँ नहीं हैं। यहाँ ग्रिड रणनीति का एक पायथन संस्करण लिखा गया है। रणनीति का सिद्धांत बहुत सरल है। ग्रिड नोड्स की एक श्रृंखला एक मूल्य सीमा के भीतर एक निश्चित मूल्य दूरी द्वारा उत्पन्न की जाती है। जब बाजार बदलता है और कीमत ग्रिड नोड मूल्य स्थिति तक पहुंच जाती है, तो एक खरीद आदेश रखा जाता है। जब आदेश बंद हो जाता है, यानी लंबित आदेश की कीमत प्लस लाभ स्प्रेड के अनुसार, स्थिति को बंद करने के लिए एक बिक्री आदेश लंबित करें। निर्धारित मूल्य सीमा के भीतर उतार-चढ़ाव को पकड़ें।
यह कहने की जरूरत नहीं है कि ग्रिड रणनीति का जोखिम यह है कि किसी भी ग्रिड-प्रकार की रणनीति एक शर्त है कि कीमत एक निश्चित सीमा में उतार-चढ़ाव करती है। एक बार कीमत ग्रिड सीमा से बाहर निकल जाती है, तो यह गंभीर फ्लोटिंग नुकसान का कारण बन सकती है। इसलिए, इस रणनीति को लिखने का उद्देश्य पायथन रणनीति लेखन विचारों या कार्यक्रम डिजाइन के लिए संदर्भ प्रदान करना है। यह रणनीति केवल सीखने के लिए उपयोग की जाती है, और यह वास्तविक बॉट में जोखिम भरा हो सकता है।
रणनीतिक विचारों की व्याख्या सीधे रणनीतिक कोड टिप्पणियों में लिखी गई है।
रणनीति कोड
'''backtest
start: 2019-07-01 00:00:00
end: 2020-01-03 00:00:00
period: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"OKEX","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
'''
import json
# Parameters
beginPrice = 5000 # Grid interval begin price
endPrice = 8000 # Grid interval end price
distance = 20 # Price distance of each grid node
pointProfit = 50 # Profit spread per grid node
amount = 0.01 # Number of pending orders per grid node
minBalance = 300 # Minimum fund balance of the account (at the time of purchase)
# Global variables
arrNet = []
arrMsg = []
acc = None
def findOrder (orderId, NumOfTimes, ordersList = []) :
for j in range(NumOfTimes) :
orders = None
if len(ordersList) == 0:
orders = _C(exchange.GetOrders)
else :
orders = ordersList
for i in range(len(orders)):
if orderId == orders[i]["Id"]:
return True
Sleep(1000)
return False
def cancelOrder (price, orderType) :
orders = _C(exchange.GetOrders)
for i in range(len(orders)) :
if price == orders[i]["Price"] and orderType == orders[i]["Type"]:
exchange.CancelOrder(orders[i]["Id"])
Sleep(500)
def checkOpenOrders (orders, ticker) :
global arrNet, arrMsg
for i in range(len(arrNet)) :
if not findOrder(arrNet[i]["id"], 1, orders) and arrNet[i]["state"] == "pending" :
orderId = exchange.Sell(arrNet[i]["coverPrice"], arrNet[i]["amount"], arrNet[i], ticker)
if orderId :
arrNet[i]["state"] = "cover"
arrNet[i]["id"] = orderId
else :
# Cancel
cancelOrder(arrNet[i]["coverPrice"], ORDER_TYPE_SELL)
arrMsg.append("Pending order failed!" + json.dumps(arrNet[i]) + ", time:" + _D())
def checkCoverOrders (orders, ticker) :
global arrNet, arrMsg
for i in range(len(arrNet)) :
if not findOrder(arrNet[i]["id"], 1, orders) and arrNet[i]["state"] == "cover" :
arrNet[i]["id"] = -1
arrNet[i]["state"] = "idle"
Log(arrNet[i], "The node closes the position and resets to the idle state.", "#FF0000")
def onTick () :
global arrNet, arrMsg, acc
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker) # Get the latest current ticker every time
for i in range(len(arrNet)): # Iterate through all grid nodes, find out the position where you need to pend a buy order according to the current market, and pend a buy order.
if i != len(arrNet) - 1 and arrNet[i]["state"] == "idle" and ticker.Sell > arrNet[i]["price"] and ticker.Sell < arrNet[i + 1]["price"]:
acc = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
if acc.Balance < minBalance : # If there is not enough money left, you can only jump out and do nothing.
arrMsg.append("Insufficient funds" + json.dumps(acc) + "!" + ", time:" + _D())
break
orderId = exchange.Buy(arrNet[i]["price"], arrNet[i]["amount"], arrNet[i], ticker) # Pending buy orders
if orderId :
arrNet[i]["state"] = "pending" # Update the grid node status and other information if the buy order is successfully pending
arrNet[i]["id"] = orderId
else :
# Cancel h/the order
cancelOrder(arrNet[i]["price"], ORDER_TYPE_BUY) # Cancel orders by using the cancel function
arrMsg.append("Pending order failed!" + json.dumps(arrNet[i]) + ", time:" + _D())
Sleep(1000)
orders = _C(exchange.GetOrders)
checkOpenOrders(orders, ticker) # Check the status of all buy orders and process them according to the changes.
Sleep(1000)
orders = _C(exchange.GetOrders)
checkCoverOrders(orders, ticker) # Check the status of all sell orders and process them according to the changes.
# The following information about the construction status bar can be found in the FMZ API documentation.
tbl = {
"type" : "table",
"title" : "grid status",
"cols" : ["node index", "details"],
"rows" : [],
}
for i in range(len(arrNet)) :
tbl["rows"].append([i, json.dumps(arrNet[i])])
errTbl = {
"type" : "table",
"title" : "record",
"cols" : ["node index", "details"],
"rows" : [],
}
orderTbl = {
"type" : "table",
"title" : "orders",
"cols" : ["node index", "details"],
"rows" : [],
}
while len(arrMsg) > 20 :
arrMsg.pop(0)
for i in range(len(arrMsg)) :
errTbl["rows"].append([i, json.dumps(arrMsg[i])])
for i in range(len(orders)) :
orderTbl["rows"].append([i, json.dumps(orders[i])])
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", acc, "\n", "arrMsg length:", len(arrMsg), "\n", "`" + json.dumps([tbl, errTbl, orderTbl]) + "`")
def main (): # Strategy execution starts here
global arrNet
for i in range(int((endPrice - beginPrice) / distance)): # The for loop constructs a data structure for the grid based on the parameters, a list that stores each grid node, with the following information for each grid node:
arrNet.append({
"price" : beginPrice + i * distance, # Price of the node
"amount" : amount, # Number of orders
"state" : "idle", # pending / cover / idle # Node Status
"coverPrice" : beginPrice + i * distance + pointProfit, # Node closing price
"id" : -1, # ID of the current order related to the node
})
while True: # After the grid data structure is constructed, enter the main strategy loop
onTick() # Processing functions on the main loop, the main processing logic
Sleep(500) # Control polling frequency
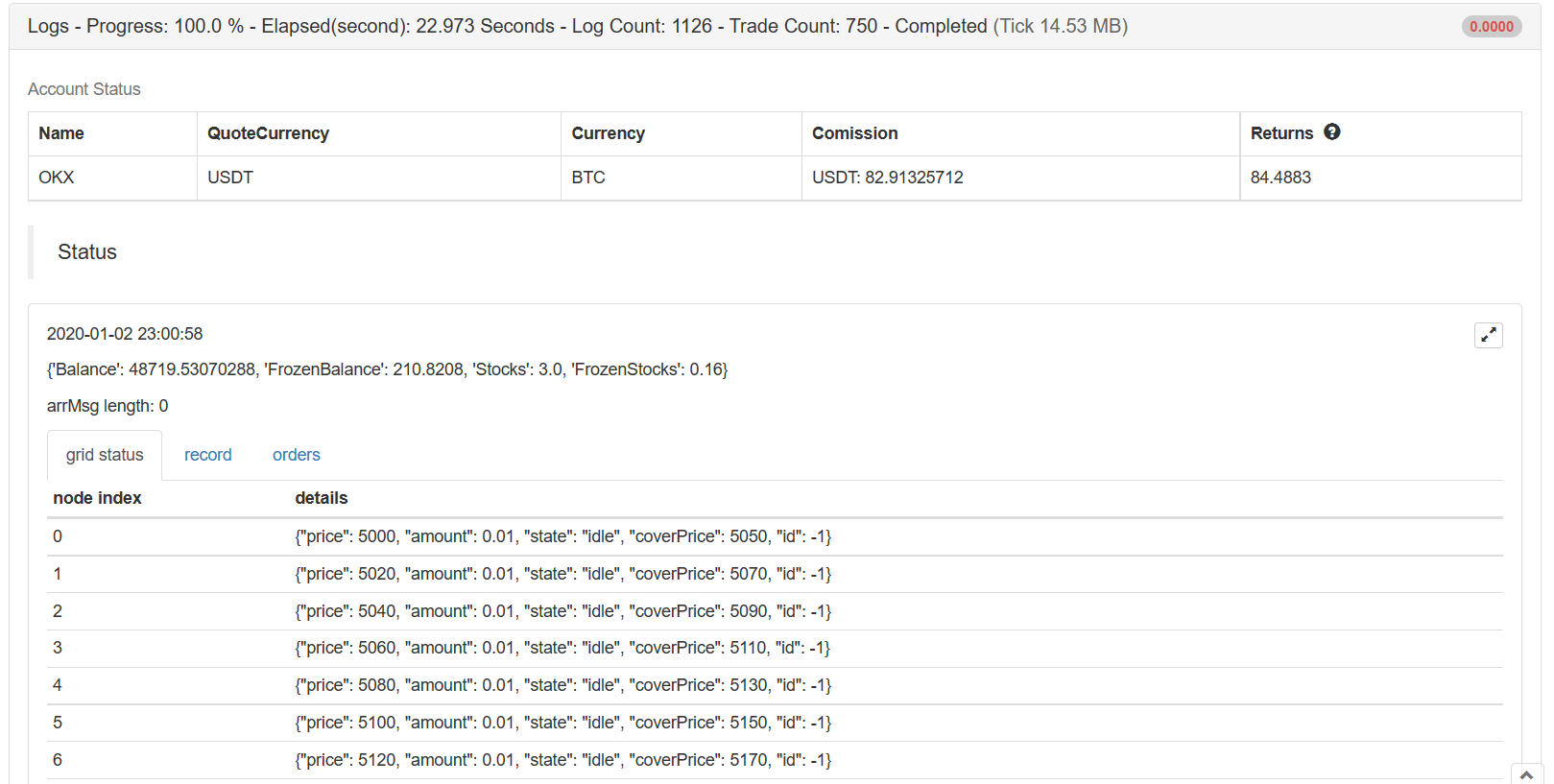
रणनीति का मुख्य डिजाइन विचार लंबित आदेशों की वर्तमान सूची की तुलना करना है।GetOrdersअपने द्वारा बनाए गए ग्रिड डेटा संरचना के अनुसार इंटरफ़ेस। लंबित आदेशों के परिवर्तनों का विश्लेषण करें (चाहे वे बंद हों या नहीं), ग्रिड डेटा संरचना को अपडेट करें, और बाद के संचालन करें। इसके अलावा, लेनदेन पूरा होने तक लंबित आदेश रद्द नहीं किए जाएंगे, भले ही कीमत विचलित हो, क्योंकि डिजिटल मुद्रा बाजार में अक्सर पिन की स्थिति होती है, ये लंबित आदेश पिन के आदेश भी प्राप्त कर सकते हैं (यदि एक्सचेंज में लंबित आदेशों की संख्या सीमित है, तो इसे समायोजित किया जाएगा) ।
रणनीति डेटा विज़ुअलाइज़ेशन का उपयोग करता हैLogStatusवास्तविक समय में स्थिति पट्टी पर डेटा प्रदर्शित करने के लिए कार्य।
tbl = {
"type" : "table",
"title" : "grid status",
"cols" : ["node index", "details"],
"rows" : [],
}
for i in range(len(arrNet)) :
tbl["rows"].append([i, json.dumps(arrNet[i])])
errTbl = {
"type" : "table",
"title" : "record",
"cols" : ["node index", "details"],
"rows" : [],
}
orderTbl = {
"type" : "table",
"title" : "orders",
"cols" : ["node index", "details"],
"rows" : [],
}
तीन तालिकाएं बनाई जाती हैं। पहली तालिका वर्तमान ग्रिड डेटा संरचना में प्रत्येक नोड की जानकारी प्रदर्शित करती है, दूसरी तालिका असामान्य जानकारी प्रदर्शित करती है, और तीसरी तालिका एक्सचेंज की वास्तविक लिस्टिंग जानकारी प्रदर्शित करती है।
बैकटेस्ट
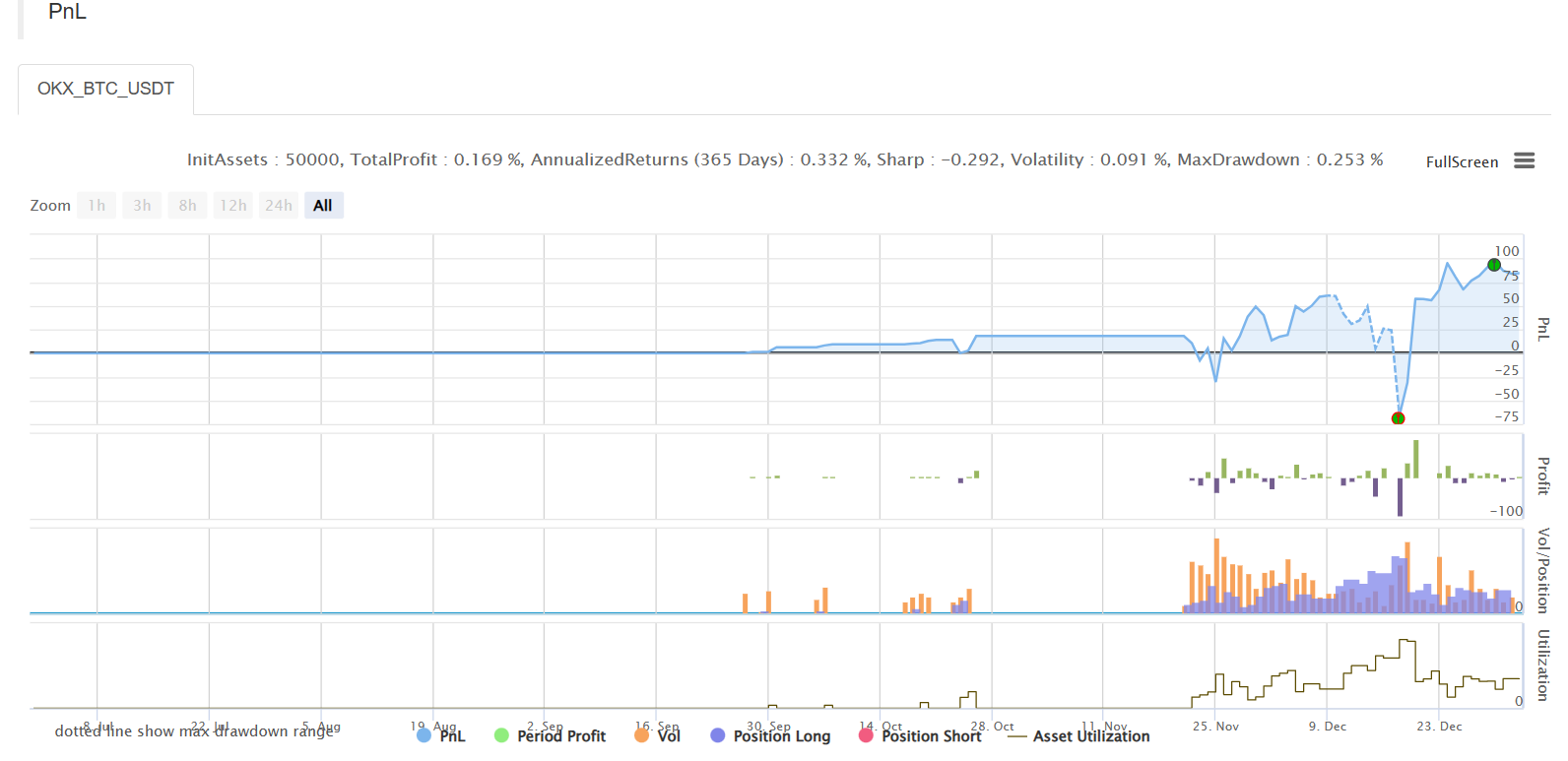

रणनीतिक पता
रणनीति केवल सीखने और बैकटेस्टिंग उद्देश्य के लिए है, और यह अनुकूलित किया जा सकता है और यदि आप रुचि रखते हैं उन्नयन.
- डीईएक्स एक्सचेंजों का मात्रात्मक अभ्यास (2) -- हाइपरलिक्विड यूजर गाइड
- DEX एक्सचेंज क्वांटिफाइंग प्रैक्टिस ((2) -- हाइपरलिक्विड उपयोग गाइड
- डीईएक्स एक्सचेंजों का मात्रात्मक अभ्यास (1) -- dYdX v4 उपयोगकर्ता गाइड
- क्रिप्टोकरेंसी में लीड-लैग आर्बिट्रेज का परिचय (3)
- DEX एक्सचेंज क्वांटिफाइड प्रैक्टिस ((1)-- dYdX v4 उपयोग गाइड
- डिजिटल मुद्रा में लीड-लैग सूट का परिचय (3)
- क्रिप्टोकरेंसी में लीड-लैग आर्बिट्रेज का परिचय (2)
- डिजिटल मुद्राओं में लीड-लैग सूट का परिचय (2)
- एफएमजेड प्लेटफॉर्म के बाहरी सिग्नल रिसेप्शन पर चर्चाः रणनीति में अंतर्निहित एचटीपी सेवा के साथ सिग्नल प्राप्त करने के लिए एक पूर्ण समाधान
- एफएमजेड प्लेटफॉर्म के लिए बाहरी सिग्नल प्राप्त करने का अन्वेषणः रणनीति अंतर्निहित एचटीटीपी सेवा के लिए सिग्नल प्राप्त करने के लिए पूर्ण समाधान
- क्रिप्टोकरेंसी में लीड-लैग आर्बिट्रेज का परिचय (1)
- बेहतर उपकरण अच्छा काम करते हैं -- व्यापार के सिद्धांतों का विश्लेषण करने के लिए अनुसंधान वातावरण का उपयोग करना सीखें
- ब्लॉकचेन परिसंपत्तियों के मात्रात्मक व्यापार में क्रॉस-वैल्यूएंस हेजिंग रणनीतियाँ
- एफएमजेड क्वांट पर एफएमएक्स की डिजिटल मुद्रा रणनीति गाइड प्राप्त करें
- आपको रणनीतियाँ लिखने के लिए सिखाएं -- MyLanguage रणनीति प्रत्यारोपित करें (उन्नत)
- आपको रणनीतियाँ लिखने के लिए सिखाएँ -- MyLanguage रणनीति प्रत्यारोपित करें
- आप रणनीति के लिए बहु चार्ट समर्थन जोड़ने के लिए सिखाएँ
- आप पायथन संस्करण में एक K-लाइन संश्लेषण समारोह लिखने के लिए सिखाओ
- अनुसंधान के माहौल में डोंचियन चैनल रणनीति का विश्लेषण
- जब FMZ ChatGPT का सामना करता है, तो एआई का उपयोग करके सीखने के लिए एक प्रयास याद रखें
- डिजिटल मुद्रा विकल्पों के लिए शेल्फ से बाहर मात्रात्मक व्यापार उपकरण
- डेटा प्लेबैक फ़ंक्शन के आधार पर विकसित रैखिक लंबित ऑर्डर प्रवाह रणनीति
- पायथन संस्करण के विजेताओं को खरीदने के लिए रणनीति
- एफएमजेड यात्रा -- संक्रमण रणनीति के साथ
- आपको सिखाता है कि पाइथन की एक प्रजाति की रणनीति को बहु-प्रजाति की रणनीति में कैसे बदलना है
- पायथन का उपयोग करके एक मात्रात्मक ट्रेडिंग रोबोट टाइम्ड स्टार्ट या स्टॉप गैजेट लागू करें
- ओक आपको FMZ विस्तारित एपीआई के साथ इंटरफेस करने के लिए जेएस का उपयोग करना सिखाता है
- रोबोट पुश संदेश का एहसास करने के लिए कॉल Dingding इंटरफ़ेस
- संतुलित लंबित आदेश रणनीति (शिक्षण रणनीति)
- कॉन्ट्रैक्ट हेजिंग रणनीति के माध्यम से परिसंपत्तियों की आवाजाही पर विचार
- कई साल बाद, आपको पता चलेगा कि यह लेख आपके निवेश करियर में सबसे मूल्यवान है - पता करें कि रिटर्न और जोखिम कहां से आते हैं