Dokumen MyLanguage
Penulis:Kebaikan, Dibuat: 2018-12-14 17:33:09, Diperbarui: 2019-04-10 09:11:27[TOC] - # Deskripsi Dasar
-
Kontrak
Kontrak berjangka komoditas, kontrak cryptocurrency
Kontrak berjangka komoditas/cryptocurrency
this_week OKEX futures contract for current week next_week OKEX futures contract for next week quarter OKEX futures contract for quarter XBTUSD BITMEX Perpetual Contract rb888 Rebar main contract MA000 Methanol Index Contract rb1901 Rebar contract …and so on.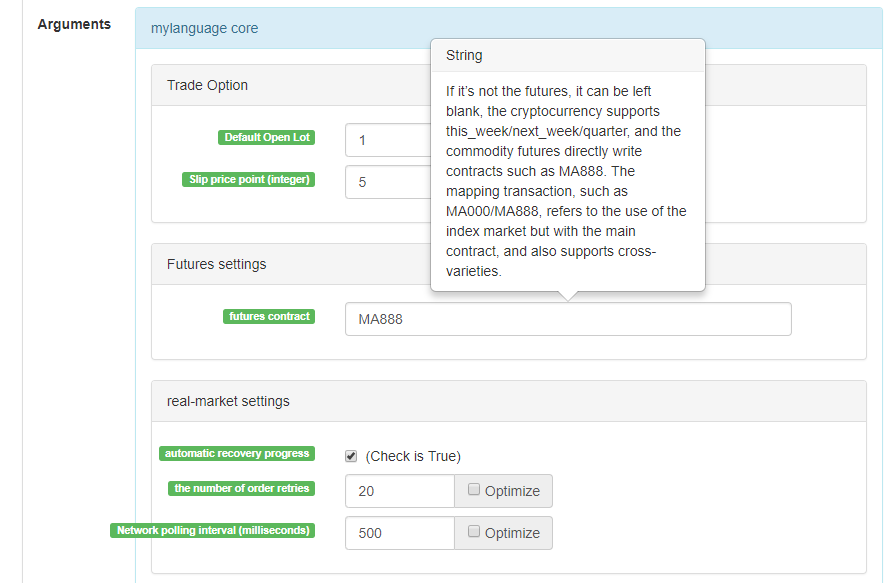
Saat mengatur kontrak, Anda dapat memilih rb1901/rb1905 Data pasar adalah rb1901, kontrak perdagangan order adalah rb1905
-
Variabel
Variabel adalah ruang yang terbuka di memori komputer untuk menyimpan data.
Mengumumkan variabel pertama
// Assign 1 to the variable a a:=1;Dalam
M Language , perbedaan sederhana dibuat dari data volume : - Data dengan nilai tunggal: hanya satu nilai, seperti 0, 1,
abc - Data deret: Deret data yang terdiri dari satu set data dengan nilai tunggal, seperti Close (harga penutupan), di mana Close berisi harga penutupan n siklus [ 10.1, 10.2, 10.3, 10.4, 10. 5... ]
Membedakan dari
tipe variabel - Jenis string: harus menggunakan
parcel, jenis string tidak diizinkan untuk digunakan secara langsung, Anda perlu mencocokkan output fungsi ke tampilan
INFO(CLSOE>OPEN,'OK!');- Tipe nilai: termasuk bilangan bulat, angka tanda mengapung (desimal)
// integer int:=2; // decimal float:=3.1;- Tipe Boolean, menggunakan 1 (untuk benar) atau 0 (untuk salah): 1, 0, benar atau salah, misalnya: A:=1>0; setelah pelaksanaan kode ini, nilai A adalah 1
// The current period closing price is greater than -999, you will find that the return value of each cycle is 1, representing true, because the closing price is almost impossible to be negative Is_true:=Close>-999;- Variabel global
VARIABLE:VALUE1:10; // Declare a global variable with a value of 10 and execute only once.- ### Aturan penamaan
Dalam sebagian besar sistem, penamaan variabel tidak memungkinkan penggunaan sistem
kata-kata yang disediakan (nama variabel bawaan, nama fungsi), seperti Close yang terkenal, C. Selain itu, bilangan murni tidak diizinkan, atau angka dimulai dengan, dan tidak bisa terlalu panjang, sistem yang berbeda, dan batas panjang yang berbeda berbeda. Pada kenyataannya, Anda tidak perlu membingungkan efisiensi sistem arus utama untuk analisis bahasa Inggris. Saya percaya bahwa M Language sangat ramah bagi penutur bahasa Inggris. Saya sarankan Anda menggunakan konvensi penamaan berikut: Bahasa Inggris + digariskan
// output Move_avg_5:=MA(C,5);Jika Anda lebih suka bahasa Inggris, tolong biarkan orang memahami arti variabel Anda sebanyak mungkin. Jangan menggunakan metode penamaan seperti: A1, AAA, BBB... Percayalah, setelah beberapa hari, ketika Anda meninjau kode indikator Anda lagi, Anda akan sangat sakit karena kurangnya memori. Demikian pula, ketika Anda mengekspor kode ke orang lain, pola pikir pembaca pasti telah runtuh.
Kemudian, mulai sekarang, gunakan
M Language sebanyak yang Anda bisa! Saya berharap itu akan menjadi alat yang ampuh untuk analisis dan pengambilan keputusan Anda. - Data dengan nilai tunggal: hanya satu nilai, seperti 0, 1,
-
Jenis data
Jenis data adalah konsep dasar. dalam pemrograman, ketika kita menetapkan data eksplisit untuk variabel, variabel menjadi jenis data itu sendiri.
- 1. jenis nilai:
1、2、3、1.1234、2.23456 ……- Jenis string (str):
'1' 、'2' 、'3' ,string type must be wrapped with ''- Data urutan:
a collection of data consisting of a series of single-valued data- 4. Tipe Boolean (Boolean):
Gunakan 1 untuk benar dan 0 untuk salah
Contoh
// Declare a variable of a numeric type var_int := 1; // Declare a variable of sequence data var_arr := Close; // String type can not be declared separately, you need to combine functions INFO(C>O, 'rising line'); -
Operator
Operasi dan perhitungan yang digunakan untuk mengeksekusi kode indikator, yang merupakan simbol dari operasi partisipasi.
- Operator penugasan
Digunakan untuk menugaskan nilai ke variabel
- 1. `:` a colon, representing the assignment and outputting to the diagram (deputy diagram) ``` Close1:Close; // Assign Close to the variable Close1 and output it to the diagram ``` - 2. `:=` The “colon equal”, representing the assignment, but is not output to the diagram (main diagram, subgraph...) and is not displayed in the status bar table. ``` Close2:=Close; // Assign Close to the variable Close2 ``` - 3. `^^` ^^ ,two ^ symbols represent assignments, assign values to variables and output them to the diagram (main diagram). ``` lastPrice^^C; ``` - 4. `..` .. ,two dot, The symbol represents the assignment, assigns a value to the variable and displays it in the status bar table, but does not output it to the diagram (main diagram, sub- diagram...). ``` openPrice..O ```- ### Relasional operator
Operator relasional adalah operator binokular yang digunakan dalam ekspresi bersyarat.
Mengembalikan nilai: Jenis Boolean, tidak benar (1), harus salah (0)
- 1. Greater than > ``` // Assign the result of 2 > 1 to the rv1 variable, at this time rv1=1 Rv1:=2>1; ``` - 2. Less than < ``` // returns false, which is 0, because 2 is greater than 1. :-) rv3:=2<1; ``` - 3. Greater than or equal to >= ``` x:=Close; // Assign the result of the operation with a closing price greater than or equal to ¥ 10 to the variable rv2 // Note that since “close” is a sequence of data, when the close>=10 operation is performed, the essence is that each cycle is performed, so each cycle will have a return value of 1, 0. rv2:=Close>=10; ``` - 4. Less than or equal to <= ``` Omitted here ``` - 5. Equal to = ``` A:=O=C; // Determine if the opening price is equal to the closing price. ``` - 6. Not equal to <> ``` 1<>2 // Judgment weather 1 is equal to 2 or not, the return value is 1 (true) ```- ### Operator Logis
Return value: Boolean type, not true (1), must be false (0)1. Logic and &&, can use “and” instead, and the left and right sides of the connection must be true at the same time.// determine whether cond_a, cond_b, cond_c is true at the same time, cond_a:=2>1; cond_b:=4>3; cond_c:=6>5; cond_a && cond_b and cond_c; // return value 1, true2. Logic or ||, can use “or” instead, “or” link the left and right sides, as long as the one side is true, the whole is true (return true)cond_a:=1>2; cond_b:=4>3; cond_c:=5>6; cond_a || cond_b or cond_c; // return value 1, true- ### Operator aritmatika
Return value: numeric typeIni adalah penyelesaian simbol operator aritmatika dasar, yang merupakan simbol yang digunakan untuk memproses empat operasi aritmatika.
- **Plus +** ``` A:=1+1; // return 2 ``` - **Subtract -** ``` A:=2-1; // return 1 ``` - **Multiply \*** ``` A:=2*2; // return 4 ``` - **Divide by /** ``` A:=4/2; // return 2 ``` -
Fungsi
- ### Fungsi
Dalam dunia pemrograman,
function sebenarnya adalah sepotong kode yang mengimplementasikan fungsi tertentu dan dapat dipanggil oleh kode lain. function(param1,param2,……)- Composition: The function name (parameter 1, parameter 2, ...), there may be no parameters, there may be multiple parameters, such as MA(x, n); represents a simple moving average of the inner x returning n cycles, where MA() is a The function, x and n are the parameters of the function. When using a function, we need to understand the basic definition of the function, that is, what data can be obtained by calling the function. In general, functions have parameters. When we pass in parameters, we need to ensure that the data type passed in is compliant. At current stage, the code hinting function of most IDEs is very imperfect. They are not showing the certain data types for the parameters given, which gives us some troubles. The interpretation of MA(x,n) is: ``` Return a simple moving average usage: AVG:=MA(X,N): N's simple moving average of X, algorithm (X1+X2+X3+...+Xn)/N,N supports variables ``` This is very unfriendly explanation for beginners. Next, we thoroughly analyze the function and try to find a way to quickly learn and use the function.- ### Mengembalikan nilai
Untuk mempelajari fungsi dengan cepat, kita harus memahami konsep yang disebut
return value . Return, seperti namanya, adalah return , nilainya mewakili nilai konkret , data yang dapat diperoleh. // Because it will be used in the following code, use the variable return_value to receive and save the return value of function() // retrun_value := function(param1,param2); // for example: AVG:=MA(C,10); // AVG is retrun_value , “function” function is: MA function, param1 parameter: C is the closing price sequence data, param2 parameter: 10.- ### Parameter
Kedua, konsep penting kedua dari fungsi adalah parameter, melewati dalam parameter yang berbeda, Anda bisa mendapatkan nilai yang berbeda kembali.
// variable ma5 receives 5 day closing price moving average ma5:=MA(C,5); // variable ma10 receives 10 day closing price moving average ma10:=MA(C,10);Parameter pertama X dari variabel di atas ma5, ma10 adalah C (harga penutupan), pada kenyataannya C juga merupakan fungsi (mengembalikan urutan harga penutupan sejak pembukaan), tetapi tidak memiliki parameter. parameter kedua 5, 10,Ini digunakan untuk memberitahu fungsi MA (), kita ingin mendapatkan moving average dari harga penutupan selama berapa hari, melalui parameter, fungsi menjadi lebih fleksibel.
-
Cara belajar
- Pertama, Anda perlu memahami fungsi
fungsi , yang merupakan data yang dapat diberikan fungsi ini. - 2. Memahami jenis nilai balik, setelah semua, kita menggunakan fungsi untuk mendapatkan nilai balik.
- 3. Kita perlu memahami jenis data parameter, MA (x, n), jika Anda tidak tahu jenis data parameter x, n, Anda tidak bisa mendapatkan nilai kembali dengan benar.
- Pertama, Anda perlu memahami fungsi
Dalam pengantar fungsi berikut, gunakan, ikuti tiga prinsip di atas.
-
Peningkatan bahasa
- Programming campuran antara bahasa M dan bahasa JavaScript
%% // here you can call any API function of FMZ Quant. scope.TEST = function(obj) { return obj.val * 100; } %% Closing price: C; The closing price is magnified 100 times: TEST(C); The previous closing price is magnified 100 times: TEST(REF(C, 1)); // The mouse moves to the backtest K line and the variable value is displayed.- scope object scope object, you can add attributes and assign anonymous functions to attributes. An anonymous function referenced by this attributes can be called in the M language code section. - scope.getRefs(obj) function In the JavaScript code block, call the scope.getRefs(obj) function, which returns the data of the incoming obj object.%%%% berikut dari kode JavaScript paket simbolis akan mendapatkan harga penutupan C masuk ketika fungsi TEST© dipanggil dalam kode bahasa M. Fungsi scope.getRefs mengembalikan semua harga penutupan untuk data K-line ini. Karena throw
stop interrupt routine digunakan, variabel arr hanya berisi harga penutupan Bar pertama dari k-line. Anda dapat mencoba menghapus throw stop dan itu akan mengeksekusi pengembalian terakhir kode JavaScript, mengembalikan semua data harga penutupan. %% scope.TEST = function(obj){ var arr = scope.getRefs(obj) Log("arr:", arr) throw "stop" return } %% TEST(C);- scope.bars In the JavaScript code block, access all K line bars. The TEST function returns a value, 1 is the falling k-line and 0 is the rising line. ``` %% scope.TEST = function(){ var bars = scope.bars return bars[bars.length - 1].Open > bars[bars.length - 1].Close ? 1 : 0 // can only return values } %% arr:TEST; ``` ``` # Note: # TEST Received anonymous function, the return value must be a numeric value # If the anonymous function has no parameters, write VAR:=TEST directly when calling TEST; write VAR:=TEST(); will report an error. # TEST in #scope.TEST must be uppercase. ``` - scope.bar In the JavaScript code block, access the current bar. Calculate the average of “opening high but closing low” of k-line’s prices. ``` %% scope.TEST = function(){ var bar = scope.bar var ret = (bar.Open + bar.Close + bar.High + bar.Low) / 4 return ret } %% avg^^TEST; ``` - scope.depth Access the market depth data (order book) ``` %% scope.TEST = function(){ Log(scope.depth) throw "stop" // Throw an exception after printing the depth data, pause. } %% TEST; ``` - scope.symbol Get the current trading pair name string ``` %% scope.TEST = function(){ Log(scope.symbol) throw "stop" } %% TEST; ``` - scope.barPos Get the K line Bar location. ``` %% scope.TEST = function(){ Log(scope.barPos) throw "stop" } %% TEST; ``` - scope.get\_locals('name') This function is used to get the variables in the M language code part ``` V:10; %% scope.TEST = function(obj){ return scope.get_locals('V') } %% GET_V:TEST(C); ``` ``` # Note: # If a variable does not calculate data when the period is insufficient, this time the scope.get_locals function is called in the JavaScript code. # When get this variable, it will give an error: line:XX - undefined locals a variable name undefined ``` -
Referensi multi-siklus
- Gunakan: #EXPORT Formula Nama... #END untuk membuat rumus. Jika Anda hanya ingin mendapatkan data untuk periode yang berbeda, Anda juga dapat menulis rumus kosong tanpa perhitungan rumus.
Rumus kosong adalah:
#EXPORT TEST NOP; #END // End- Penggunaan: #IMPORT [MIN, periode, nama rumus] AS variabel nilai, rumus referensi, mendapatkan data periode yang ditetapkan (harga penutupan, harga pembukaan, dll., diperoleh dengan nilai variabel).
Contoh kode:
// this code demonstrates how to reference formulas of different cycles in the same code // #EXPORT extends the syntax, ending with #END as a formula, you can declare multiple #EXPORT TEST Mean 1:EMA(C, 20); Mean 2:EMA(C, 10); #END // End #IMPORT [MIN,15,TEST] AS VAR15 // Reference formula, K line cycle is 15 minutes #IMPORT [MIN,30,TEST] AS VAR30 // Reference formula, K line cycle is 30 minutes CROSSUP(VAR15.Mean1, VAR30.Mean1),BPK; CROSSDOWN(VAR15.Mean2, VAR30.Mean2),SPK; The highest price of 15 mins:VAR15.HIGH; The highest price of 30 mins:VAR30.HIGH; AUTOFILTER; -
Deskripsi Mode
- ### 1、Satu posisi pembukaan dan satu posisi penutupan model penyaringan sinyal
Dalam model, dengan menulis fungsi AUTOFILTER untuk mengontrol dan mewujudkan penyaringan sinyal dari satu pembukaan dan satu penutupan.
Memfilter model mendukung perintah: BK, BP, BPK, SK, SP, SPK, CLOSEOUT, tidak mendukung BK (5) dan instruksi lain dengan banyak
E.g:
MA1:MA(CLOSE,5); MA2:MA(CLOSE,10); CROSSUP(C,MA1),BK; CROSSUP(MA1,MA2),BK; C>BKPRICE+10||C<BKPRICE-5,SP; AUTOFILTER;- ### 2、penjumlahan atau pengurangan model posisi
Fungsi AUTOFILTER tidak ditulis dalam model, memungkinkan sinyal posisi pembukaan terus menerus atau sinyal posisi penutupan terus menerus, yang dapat digunakan untuk meningkatkan atau mengurangi posisi.
Komando yang didukung: BK(N), BP(N), SK(N), SP(N), CLOSEOUT, BPK(N), SPK(N, tidak mendukung posisi terbuka dan dekat tanpa lot. (1) Pengelompokan instruksi pendukung. (2) Ketika beberapa kondisi instruksi terpenuhi pada saat yang sama, sinyal dieksekusi dalam urutan di mana pernyataan bersyarat ditulis. Misalnya:
MA1:MA(CLOSE,5); MA2:MA(CLOSE,10); CROSSUP(C,MA1),BK(1); CROSSUP(MA1,MA2),BK(1); C>BKPRICE+10||C<BKPRICE-5,SP(BKVOL);- ### 3、satu K-line dengan satu model sinyal
Satu K-line dengan satu model sinyal dapat dibagi menjadi model harga penutupan dan model harga instruksi.
1)Model harga akhir
Garis K melewati sinyal perhitungan untuk menempatkan pesanan (perhitungan juga dilakukan selama pembentukan garis K. Pada saat ini, sinyal akan tidak pasti, dan sinyal yang muncul ketika garis k tidak selesai akan diabaikan, dan tidak akan ditempatkan pesanan)
Arah sinyal konsisten dengan arah posisi tunggu, dan tidak ada kondisi hilangnya sinyal.
E.g: MA1:MA(CLOSE,5); MA2:MA(CLOSE,10); CROSSUP(MA1,MA2),BPK;//5 cycle moving average line up cross 10 cycle moving average line to buy long. CROSSDOWN(MA1,MA2),SPK;//5 cycle moving average line down cross 10 cycle moving average line to sell short. AUTOFILTER;2)Model harga instruksi
Terlepas dari apakah garis k selesai atau tidak, sinyal dihitung dan pesanan ditempatkan secara real time, yaitu pesanan ditempatkan sebelum garis K selesai;
Jika arah posisi tidak cocok dengan arah sinyal di akhir garis k, posisi akan disinkronkan secara otomatis.
E.g:
MA1:MA(CLOSE,5); MA2:MA(CLOSE,10); CROSSUP(MA1,MA2),BPK;//5 cycle moving average line up cross 10 cycle moving average line to buy long. CROSSDOWN(MA1,MA2),SPK;//5 cycle moving average line down cross 10 cycle moving average line to sell short. AUTOFILTER;- ### 4、Satu K-line dengan model sinyal ganda
Model ini menggunakan multsig atau multsig_min untuk mengontrol dan mengimplementasikan beberapa sinyal dari satu K-line.
Terlepas dari apakah garis k selesai, menghitung sinyal dan menempatkan pesanan real-time.
Sinyal tidak akan ditinjau, tidak ada kondisi sinyal menghilang, dan arah sinyal konsisten dengan arah posisi.
Eksekusi berulang dalam garis K jika kondisi sinyal ganda terpenuhi
E.g: MA1:MA(CLOSE,5); MA2:MA(CLOSE,10); CROSSUP(MA1,MA2),BK; C>BKPRICE+10||C<BKPRICE-5,SP; AUTOFILTER; MULTSIG(0,0,2,0);tambahan: 1、Mode penjumlahan dan pengurangan posisi, dua metode satu sinyal k-line: perintah penempatan harga penutupan dan perintah penempatan harga instruksi semuanya didukung.
2、Model posisi penjumlahan dan pengurangan,juga mendukung sinyal k-line tunggal untuk menempatkan pesanan.
Menambahkan dan mengurangi model posisi, menulis fungsi multsig atau multsig_min, mewujudkan beberapa kali penjumlahan dan pengurangan posisi pada satu k baris, atau mengurangi posisi beberapa kali.
-
Tampilan Bagan
- ### Diagram utama indikator tambahan
Gunakan operator
^^ untuk mengatur indikator yang akan ditampilkan pada gambar utama saat menetapkan nilai untuk variabel. MA60^^MA(C, 60); // Calculate the moving average indicator with a parameter of 60
- ### Sub-diagram indikator tambahan
Gunakan operator
: untuk mengatur indikator yang akan ditampilkan pada diagram sekunder saat menetapkan nilai untuk variabel. ATR:MA(MAX(MAX((HIGH-LOW),ABS(REF(CLOSE,1)-HIGH)),ABS(REF(CLOSE,1)-LOW)),26); // Assign a value to the ATR variable, The ":" symbol is followed by the formula for calculating the ATRJika Anda tidak ingin menampilkan pada utama atau sub-diagram Gunakan operator
.. MA60..MA(C, 60); // Calculate the moving average indicator with a parameter of 60Anda dapat menggunakan DOT dan COLORRED untuk mengatur jenis baris, warna, dll sesuai dengan kebiasaan pengguna yang akrab dengan bahasa M.
-
Masalah Umum
Memperkenalkan
masalah yang sering ditemui dalam persiapan indikator, biasanya poin yang perlu diperhatikan saat menulis indikator. Perhatikan akhir
; . Perhatikan bahwa kata kunci sistem tidak dapat dinyatakan sebagai variabel.
Perhatikan bahwa string menggunakan tanda kutip tunggal, misalnya:
opening hanya satu tanda kutip. -
Komentar
Anotasi
- ``` // The content of the comment ``` (the input method can be typed in both English and Chinese), which means that the code is not compiled during the execution process, that is, it does not execute // the content behind it. Usually we use the meaning of the code to facilitate the code review. Understanding, recall - ``` { Comment content } ``` Block comment. ``` A:=MA(C,10); {The previous line of code is the calculation of the moving average.} ``` - ``` (* Comment content *) ``` Block comment. ``` A:=MA(C,10); (*The previous line of code is the calculation of the moving average.*) ```- ### Metode input
Ketika menulis kode, seringkali menyebabkan kesalahan simbol karena metode input beralih antara bahasa Cina dan bahasa Inggris. Jenis umum adalah sebagai berikut: titik koma:, terminator; koma, tanda kurung (), dll, karakter yang berbeda ini dalam bahasa Cina dan bahasa Inggris perlu diperhatikan.
-
Logika yang rentan terhadap kesalahan
- Setidaknya tidak kurang dari tidak kurang dari: Operator relasional yang sesuai
>= - Paling tidak Paling tidak Tidak lebih: Operator relasional yang sesuai
<=
- Setidaknya tidak kurang dari tidak kurang dari: Operator relasional yang sesuai
-
Referensi data baris K
- ## OPEN
Dapatkan harga pembukaan grafik K-line
Harga pembukaan
Fungsi: OPEN, singkatan dari O
Parameter: Tidak ada
Penjelasan: Kembalikan harga pembukaan siklus
Data urutan
OPEN obtained the opening price of the K-line chart. Note: 1、can be shorthand as O. example 1: OO:=O; //Define OO as the opening price; pay attention to the difference between O and 0. example 2: NN:=BARSLAST(DATE<>REF(DATE,1)); OO:=REF(O,NN); //Get the opening price of the day example 3: MA5:=MA(O,5); //Define the 5-period moving average of the opening price (O is OPEN shorthand).- ## Tinggi
Dapatkan harga tertinggi dari grafik K-line
Harga tertinggi
Fungsi:HIGH, singkatan dari H
Parameter: Tidak ada
Penjelasan: mengembalikan harga tertinggi dari siklus
Data urutan
HIGH Get the highest price of the K-line chart. Note: 1、can be shorthand as H. example 1: HH:=H; //Define HH as the highest price. example 2: HH:=HHV(H,5); //Take the maximum value of the highest price within 5 cycles. example 3: REF(H,1); //Take the highest price of the previous K line- ## rendah
Dapatkan harga terendah dari grafik K-line
Harga Terendah
Fungsi: LOW, singkatan dari L
Parameter: Tidak ada
Penjelasan: Mengembalikan harga terendah dari siklus.
Data urutan
LOW gets the lowest price of the K-line chart. Note: 1、can be shorthand as L. example 1: LL:=L; //Define LL as the lowest price. example 2: LL:=LLV(L,5); //Get the minimum value of the lowest price in 5 cycles. example 3: REF(L,1); //Get the lowest price of the previous K line- ## Dekat
Dapatkan harga penutupan grafik K-line
Harga Penutupan
Fungsi: CLOSE, singkatan dari C
Parameter: Tidak ada
Penjelasan: Kembalikan harga penutupan siklus
Data urutan
CLOSE Get the closing price of the K-line chart. Note: 1、When the k-line in the market is not finished, get the latest price. 2、Can be shorthand as C. example 1: A:=CLOSE; //Define the variable A as the closing price (A is the latest price when the k line is not finished). example 2: MA5:=MA(C,5); //Define the 5-period moving average of the closing price (C is short for CLOSE). example 3: A:=REF(C,1); //Get the closing price of the previous k line.- ## VOL
Dapatkan volume grafik garis K
Volume Perdagangan
Fungsi:VOL, singkatan dari V
Parameter: Tidak ada
Penjelasan: Kembalikan volume siklus ini.
Data urutan
VOL gets the volume of the K-line chart. Note: Can be shorthand as V. The return value of this function on the root TICK is the cumulative value of all TICK transactions for the day. example 1: VV:=V; //Define VV as volume example 2: REF(V,1); //indicates the volume of the previous cycle example 3: V>=REF(V,1); //The volume is greater than the volume of the previous cycle, indicating that the volume increases (V is short for VOL).- ## REF
Referensi ke depan
Reference the value of X before N cycles. Note: 1、When N is a valid value, but the current number of k lines is less than N, a null value is returned; 2、When N is 0, the current X value is returned; 3、When N is null, it returns a null value. 4、N can be a variable example 1: REF(CLOSE,5); indicates the closing price of the 5th cycle before the current cycle example 2: AA:=IFELSE(BARSBK>=1,REF(C,BARSBK),C);//Take the closing price of the K line of latest buying long of the open position signal //1) When the k-line BARSBK of the BK signal returns a null value, the k-line REF(C, BARSBK) of the BK signal is returned. Null value; //2)When the BK signal is sent, the k-line BARSBK returns a null value, and if the BARSBK>=1 is not satisfied, then send the closing price of the k-line. //3)The k-line BARSBK after the BK signal is sent returns the number of cycles of the K-line of the open position from the current K-line, REF(C, BARSBK) Returns the closing price of the opening k line. //4)Example: 1, 2, 3 three k lines, 1 K line is the opening position signal K line, then return the closing price of this k line, 2, 3 K line returns the closing price of the 1 K line.- ## UNIT
Ambil unit transaksi dari kontrak data
Take the trading unit of the data contract. usage: UNIT takes the trading unit of the data loading contract.Masa Depan Komoditas
Nilai UNIT terkait dengan kontrak
rb contract - 1 hand, 10 (tons)Cryptocurrency Spot
Nilai UNIT adalah 1
Futures Cryptocurrency Nilai UNIT terkait dengan mata uang kontrak
OKEX Futures: 1 BTC contract represents $100, and 1 contract in other currencies represents $10- ## MINPRICE
Perubahan harga minimum untuk kontrak data
Take the minimum price change of the data contract. usage: MINPRICE; Take the minimum price change for loading data contracts.- ## MINPRICE1
Perubahan minimal dalam kontrak perdagangan
Take the minimum price change of the trading contract. usage: MINPRICE1; Take the minimum price change of the trading contract. -
Fungsi Waktu
- ## BARPOS
Take the position of the K line BARPOS,returns the number of cycles from the first K line to the current cycle. Note: 1、BARPOS returns the number of existing K lines in the local area, starting from the data existing on the local machine. 2、The return value of the first K line already on the local machine is 1. example 1:LLV(L,BARPOS);//Find the minimum value of the local existing data. example 2:IFELSE(BARPOS=1,H,0);//The current K line is the highest value of the first K line already in the local machine, otherwise it is 0.- ## PERIOD
Nilai periode adalah jumlah menit.
1, 3, 5, 15, 30, 60, 1440- ## Tanggal
Tanggal
Fungsi: Tanggal
Parameter: Tidak ada
Penjelasan: Dapatkan tanggal siklus dari 1900
Data urutan
- ## Waktu
Ambil waktu dari garis K
TIME,take the K line time. Note: 1、The function returns in real time on the real-market, and returns the start time of the K line after the K line is finished. 2、The function returns the exchange data reception time, which is the exchange time. 3、The TIME function returns a six-digit form when used in the second period, ie: HHMMSS, which is displayed in four-digit form on other periods, namely: HHMM. 4、The TIME function can only be loaded in the period below the daily period. The return value of the function is always 1500 in the period above the daily period (Included the daily period). 5、use the TIME function to close the position of the tail operation needs attention (1) The time set by the end of the closing position is recommended to be set to the actual time that can be taken in the K line return value (eg, the RB index is 5 minutes, the last K line return time is 1455, and the tail closing position is set to TIME> =1458, CLOSEOUT; the signal that the tail is closed can not appear in the effect test) (2) Using the TIME function as the condition for closing the position at the end of the market, it is recommended to open position condition also to make the corresponding time limit (such as setting the closing condition of the tail to TIME>=1458, CLOSEOUT; then the corresponding opening conditions are required Add condition TIME<1458; avoid opening the position again after closing the position) example 1: C>O&&TIME<1450,BK; C<O&&TIME<1450,SK; TIME>=1450,SP; TIME>=1450,BP; AUTOFILTER; //Close the position after 14:50. example 2: ISLASTSK=0&&C>O&&TIME>=0915,SK;- ## Tahun
Tahun
YEAR,the year is obtained. Note: YEAR ranges from 1970—2033。 example 1: N:=BARSLAST(YEAR<>REF(YEAR,1))+1; HH:=REF(HHV(H,N),N); LL:=REF(LLV(L,N),N); OO:=REF(VALUEWHEN(N=1,O),N); CC:=REF(C,N);//take the highest price, the lowest price, the opening price, and the closing price of the previous year. example 2: NN:=IFELSE(YEAR>=2000 AND MONTH>=1,0,1);- ## Bulan
Mengembalikan bulan siklus
MONTH, returns the month of a cycle. Note: MONTH has a value range of 1-12. example 1: VALUEWHEN(MONTH=3&&DAY=1,C);//The closing price is taken when the K-line date is March 1. example 2: C>=VALUEWHEN(MONTH<REF(MONTH,1),O),SP;- ## HARI
Dapatkan jumlah hari dalam siklus
DAY, returns the number of days in a cycle. Note: The DAY value ranges from 1-31. example 1: DAY=3&&TIME=0915,BK;//From the date of 3 days, the time is 9:15, buy long. example 2: N:=BARSLAST(DATE<>REF(DATE,1))+1; CC:=IFELSE(DAY=1,VALUEWHEN(N=1,O),0);//When the date is 1, the opening price is taken, otherwise the value is 0.- ## jam
Jam
HOUR,Returns the number of hours in a cycle. Note: HOUR ranges from 0 to 23 example 1: NX:=BARSLAST(CROSS(HOUR=9,0.5)); DRAWLINE3(CROSSDOWN(HOUR=14,0.5),REF(H,NX),NX,CROSSDOWN(HOUR=14,0.5),REF(H,1),1,0),COLORGREEN; //Connect 9:00 to the latest k-line high point before the market close. example 2: HOUR=10;//The return value is 1 on the K line at 10:00, and the return value on the remaining K lines is 0.- ## MINUT
Menit
MINUTE, Returns the number of minutes in a cycle. Note: 1:MINUTE has a value range of 0-59 2:This function can only be loaded on the minute period, returning the number of minutes since the current K line. example 1: MINUTE=0;//The return value on the minute K line at the beginning of an hour is 1, and the remaining K lines return a value of 0. example 2: TIME>1400&&MINUTE=50,SP;//close position at 14:50.- ## HARI BEKAS
Dapatkan jumlah minggu
WEEKDAY, get the number of weeks. Note: 1:WEEKDAY has a value range of 0-6. 2:The value displayed by the function on the weekly cycle is always 5, and the number of weeks on the day of the end of the K line is returned on the monthly cycle. example 1: N:=BARSLAST(MONTH<>REF(MONTH,1))+1; COUNT(WEEKDAY=5,N)=3&&TIME>=1450,BP; COUNT(WEEKDAY=5,N)=3&&TIME>=1450,SP; AUTOFILTER;//each month delivery date is automatically closed all position at the end of that day. example 2: C>VALUEWHEN(WEEKDAY<REF(WEEKDAY,1),O)+10,BK; AUTOFILTER; -
Fungsi Penghakiman Logis
- ## BARSTATUS
Mengembalikan status posisi siklus saat ini
BARSTATUS returns the position status of the current cycle. Note: The function returns 1 to indicate that the current cycle is the first cycle, return 2 to indicate the last cycle, and return 0 to indicate that the current cycle is in the middle position. example: A:=IFELSE(BARSTATUS=1,H,0); //If the current K line is the first cycle, the variable A returns the highest value of the K line, otherwise it takes 0.- ## Diantara
Antara
BETWEEN(X,Y,Z) indicates whether X is between Y and Z, and returns 1 (Yes), otherwise returns 0 (No). Note: 1、If X=Y, X=Z, or X=Y and Y=Z, the function returns a value of 1 (Yse). example 1: BETWEEN(CLOSE,MA5,MA10); //indicates that the closing price is between the 5-day moving average and the 10-day moving average.- ## CROSS
Fungsi silang
CROSS(A,B) means that A passes B from the bottom to up, and returns 1 (Yes), otherwise it returns 0 (No). Note: 1、The conditions for crossing must satisfy A<=B of pervious k line, and it is confirmed as crossing when the current k-line satisfies A>B. example 1: CROSS(CLOSE,MA(CLOSE,5)); //means the crossing line from below through the 5-period moving average- ## CrossSDOWN
Menuju ke bawah
CROSSDOWN(A,B):indicates that when A down crossing B from above, it returns 1 (Yes), otherwise it returns 0 (No). Note: 1、CROSSDOWN (A, B) is equivalent to CROSS (B, A), CROSSDOWN (A, B) is written to better understand example 1: MA5:=MA(C,5); MA10:=MA(C,10); CROSSDOWN(MA5,MA10),SK; //MA5 down cross MA10, sell short //CROSSDOWN(MA5,MA10),SK; and CROSSDOWN(MA5,MA10)=1, SK; express the same meaning- ## CROSSUP
Melalui
CROSSUP(A,B) When A passes up from bottom to B, it returns 1 (Yes), otherwise it returns 0 (No) Note: 1、CROSSUP (A, B) is equivalent to CROSS (A, B), CROSSUP (A, B) is written to better understand. example 1: MA5:=MA(C,5); MA10:=MA(C,10); CROSSUP(MA5,MA10),BK;//MA5 cross up MA10, buy long. //CROSSUP(MA5,MA10),BK; and CROSSUP(MA5,MA10)=1, BK; express the same meaning- ## Semua
Tentukan apakah masih memenuhi persyaratan
EVERY(COND,N),judge whether the COND condition is always satisfied in the N period. If it is, the function returns a value of 1; if it is not, the function returns a value of 0; Note: 1、N contains the current k line. 2、If N is a valid value, but there are not many K lines in front of it, or N is a null value, the condition is not satisfied, and the function returns 0. 3、N can be a variable example 1: EVERY(CLOSE>OPEN,5);//indicates that it has been a positive line for 5 cycles. example 2: MA5:=MA(C,5);//Define a 5-cycle moving average MA10:=MA(C,10);//Define the 10-cycle moving average EVERY(MA5>MA10,4),BK;//MA5 is greater than MA10 in 4 cycles, then buy long. //EVERY(MA5>MA10,4),BK; and EVERY(MA5>MA10,4)=1, BK; express the same meaning- ## EXIST
Tentukan apakah ada kepuasan
EXIST(COND,N) determines whether there are conditions for satisfying COND in N cycles Note: 1、N contains the current k line. 2、N can be a variable. 3、If N is a valid value, but there are not many K lines in front of it, calculate according to the actual number of cycles. example 1: EXIST(CLOSE>REF(HIGH,1),10);indicates whether there is a maximum price in the 10 cycles that is greater than the previous period, if it exist, return 1, and if it does not exist, returns 0. example 2: N:=BARSLAST(DATE<>REF(DATE,1))+1; EXIST(C>MA(C,5),N);//Indicates whether there is a k line that meets the closing price greater than the 5-period moving average. If it exist, return 1, and if it does not exist, return 0.- ## Jika
Fungsi bersyarat
IF(COND,A,B) Returns A if the COND condition is true, otherwise returns B Note: 1、COND is a judgment condition; A and B can be conditions or numerical values. 2、the function supports the variable loop to reference the previous period of its own variable, that is, support the following writing method Y: IF (CON, X, REF (Y, 1)); example 1: IF(ISUP,H,L);// k line is the rising line, take the highest price, otherwise take the lowest price example 2: A:=IF(MA5>MA10,CROSS(DIFF,DEA),IF(CROSS(D,K),2,0));//When MA5>MA10, take whether DIFF is cross up the DEA, otherwise (MA5 Not greater than MA10), when K, D is down crossing, let A be assigned a value of 2. If the above conditions are not met, A is assigned a value of 0. A=1,BPK;//When MA5>MA10, use DIFF cross up DEA as the buying long condition A=2,SPK;//When MA5 is not greater than MA10, K D down crossing are used as selling short conditions- ## IFELSE
Fungsi bersyarat
IFELSE(COND,A,B) Returns A if the COND condition is true, otherwise returns B Note: 1、COND is a judgment condition; A and B can be conditions or numerical values. 2、the function supports the variable loop to refer to the previous period of its own variable, that is, supports the following writing method Y: IFELSE (CON, X, REF (Y, 1)); example 1: IFELSE(ISUP,H,L);//k line is the rising line, take the highest price, otherwise take the lowest price example 2: A:=IFELSE(MA5>MA10,CROSS(DIFF,DEA),IFELSE(CROSS(D,K),2,0)); //When MA5>MA10, whether DIFF up cross DEA, otherwise (MA5 Not greater than MA10), when K, D down cross, let A be assigned a value of 2. If the above conditions are not met, A is assigned a value of 0. A=1,BPK;//When MA5>MA10, use DIFF up cross DEA as the buying long condition A=2,SPK;//When MA5 is not greater than MA10, K, D down cross are used as selling short conditions- ## ISCONTRACT
cuaca kontrak saat ini kontrak yang ditunjuk
weather ISCONTRACT(CODE) is currently the specified contract. Usage:ISCONTRACT(CODE); is the current contract returns 1, not the current contract returns 0. Note: 1、When judging whether it is a specified contract, CODE can be the transaction code of the contract. example: ISCONTRACT('MA888'); ISCONTRACT('rb1901'); ISCONTRACT('this_week'); // cryptocurrency OKEX Futures Contract ISCONTRACT('XBTUSD'); // cryptocurrency BITMEX Futures ContractDukungan untuk ekspresi reguler
Menentukan kontrak
ISCONTRACT('this_week'); // Determine if the current contract is OKEX futures this_week (week) contractMenghakimi nama bursa
ISCONTRACT('@Futures_(CTP|BitMEX)'); // Determine whether the current exchange object is a commodity futures or a cryptocurrency BITMEX futures exchange ISCONTRACT('@(OKEX|Bitfinex|Futures_CTP)'); // To determine the exchange, you need to add @ character at the beginning- ## ISDOWN
Garis K yang jatuh
ISDOWN determines whether the cycle is falling Note: 1、ISDOWN is equivalent to C<O example: ISDOWN=1&&C<REF(C,1),SK;//When the current k line is finished and the closing price is lower than the closing price of the previous period, then selling short //ISDOWN=1&&C<REF(C,1),SK; is equivalent to ISDOWN&&C<REF(C,1),SK;- ## SAMA
Harga pembukaan sama dengan harga penutupan
ISEQUAL determines if the cycle is "The opening price equal to closing price" Note: 1、ISEQUAL is equivalent to C=O example 1: EVERY(ISEQUAL=1,2),CLOSEOUT; //continue for 2 k lines are “The opening price equal to closing price “, then close all position.- ## ISLASTBAR
Tentukan apakah siklus adalah garis K terakhir
ISLASTBAR determines if the cycle is the last k line example 1: VALUEWHEN(ISLASTBAR=1,REF(H,1));//The current k-line is the last k-line, taking the highest price of the previous cycle.- ## ISNULL
Tentukan nol
ISNULL determine whether it is null or not Usage:ISNULL(N);if N is null, the function returns 1; if N is non-null, the function returns 0. Example: MA5:=IFELSE(ISNULL(MA(C,5))=1, C,MA(C,5));//Define a five-period moving average. When the number of K-lines is less than five, return the current K-line closing price.- ## ISUP
Garis naik
ISUP determines whether the cycle is rising Note: 1、ISUP is equivalent to C>O example: ISUP=1&&C>REF(C,1),BK; //If the current k line is a rising k line and the closing price is greater than the closing price of the previous period, then buying long. //ISUP=1&&C>REF(C,1),BK; and ISUP&&C>REF(C,1),BK; //Express the same meaning- ## Terakhir
Tentukan Fungsi
LAST(COND,N1,N2) Determines whether the COND condition has been met for the past N1 to N2 cycles. Note: 1、If N1 and N2 differ by only one cycle (eg, N1=3, N2=2), the function judges whether the condition is satisfied on the cycle closest to the current K line (ie, whether the K line in the past N2 cycles is meeting the conditions) 2、When N1/N2 is a valid value, but the current k-line number is less than N1/N2, or N1/N2 null, means is not true, and the function returns 0. 3、N1 and N2 cannot be variables. example 1: LAST(CLOSE>OPEN,10,5); // indicates that it has been a rising line from the 10th cycle to the 5th cycle in the past. example 2: MA5:=MA(C,5); LAST(C>MA5,4,3);//determine whether the K line from the current k-line 3 cycles satisfies “C greater than MA5”.- ## LONGCROSS
Mempertahankan Fungsi silang
LONGCROSS(A,B,N) indicates that A is less than B in N cycles, and this cycle A up cross B from bottom to top. Note: 1、When N is a valid value, but the current k-line number is less than N, the LONGCROSS function returns a null value. 2、N does not support variables. example 1: LONGCROSS(CLOSE,MA(CLOSE,10),20); //indicates that the closing price continues below the 10-day moving average for 20 cycles and then up cross the 10-day moving average from bottom to top.- ## Tidak
Tidak...
NOT(X):Take a non. Returns 1 when X=0, otherwise returns 0. example 1: NOT(ISLASTBK); If the previous signal is not a BK signal, the NOT (ISLASTBK) returns a value of 1; the previous signal is a BK signal, and the NOT (ISLASTBK) returns a value of 0. example 2: NOT(BARSBK>=1)=1;//The BK signal is sent to the current K line to satisfy the condition. //NOT(BARSBK>=1)=1 is equivalent to NOT (BARSBK>=1).- ## NULL
Kembali null
Return null usage: MA5:=MA(C,5); MA10:=MA(C,10); A:=IFELSE(MA5>MA10,MA5,NULL),COLORRED;//When MA5>MA10, draw the five-day moving average MA5, when MA5>MA10 is not satisfied, return null value, no drawing line.- ## VALUEWHEN
Nilai
VALUEWHEN(COND,X) Takes the current value of X when the COND condition is true. If the COND condition is not true, take the value of X when the COND condition is established last time. Note: X can be either a numerical value or a condition. example 1 VALUEWHEN(HIGH>REF(HHV(HIGH,5),1),HIGH);indicates that the current highest price is greater than the maximum value of the highest price of the first five cycles and returns the current highest price. example 2: VALUEWHEN(DATE<>REF(DATE,1),O);indicates the opening price of the first k-line of the day example 3: VALUEWHEN(DATE<>REF(DATE,1),L>REF(H,1));//indicates whether the current lowest price on the first k line of the day is greater than the highest price of the last K line yesterday. Returns 1, indicating that there is a price gap on that day. Returns 0, indicating that there are no price gap on that day. -
Fungsi Eksekusi Loop
- ## LOOP2
Fungsi kondisi loop
LOOP2(COND,A,B); loop condition function Returns A if the COND condition is true, otherwise returns B Note: 1、COND is a judgment condition; A and B can be conditions or numerical values. 2、the function supports variable loop reference to the previous period of its own variable, that is, support the following writing method Y: = LOOP2 (CON, X, REF (Y, 1)); example 1: X:=LOOP2(ISUP,H,REF(X,1));//k line is the rising line, take the highest price of the current K line, otherwise take the highest price of the pervious K line that is a rising k line; if it has not appeared before, X returns null example 2: BB:=LOOP2(BARSBK=1,LOOP2(L>LV(L,4),L,LV(L,4)),LOOP2(L>REF(BB,1),L,REF(BB,1)));//When holding long position, the lowest price in the first 4 cycles of opening position k line is the starting stop loss point BB, if the lowest price of the subsequent K line is higher than the previous lowest price, taking the current lowest price as stop loss point, otherwise take the previous lowest point to be the stop loss point. SS:=LOOP2(BARSSK=1,LOOP2(H<HV(H,4),H,HV(H,4)),LOOP2(H<REF(SS,1),H,REF(SS,1)));// When holding short position, the highest price in the first 4 cycles of opening position k line is the starting stop loss point SS, if the highest price is lower than the previous highest price, taking the current highest price as stop loss point, Otherwise take the previous high point as stop lose points H>HV(H,20),BK; L<LV(L,20),SK; C<BB,SP; C>SS,BP; AUTOFILTER; -
Fungsi Statistik Keuangan
- ## BARSCOUNT
Jumlah siklus yang pertama periode yang berlaku untuk yang saat ini
BARSCOUNT(COND) The number of cycles that the first valid period to the current one Note: 1、The return value is the number of cycles from which the COND is calculated from the first valid period and up to now. 2、The return value of BARSCOUNT(COND) on the current k line on the condition that the condition is first established is 0. example: BARSCOUNT(MA(C,4));//The calculation MA(C,4) has the first return value to the current number of cycles.- ## BARSLAST
Kondisi terakhir yang terbukti benar
BARSLAST(COND):The last condition COND was established to the current number of cycles Note: 1、The return value of BARSLAST(COND) on the current k line is 0. example 1: BARSLAST(OPEN>CLOSE); //The number of cycles from the previous falling k line to the present Example 2: N:=BARSLAST(DATE<>REF(DATE,1))+1;//minute period, the number of k line on the current day. //Because the condition is established, the return value of BARSLAST(COND) on the current k line is 0, so "+1" is the k-line number of current day.- ## BARSSINCE
Kondisi pertama ditetapkan untuk jumlah siklus saat ini
BARSSINCE(COND) The first condition is established to the current number of cycles. Note: 1、the return value is the first time the COND is established to the current number of cycles 2、The return value of BARSSINCE (COND) on the current k-line of the condition established for the first time is 0. example : BARSSINCE(CLOSE>OPEN); //Statistics of the number of cycles from the K line that satisfies the condition of the first line to the present.- ## BARSSINCEN
Statistik Kondisi pertama dalam periode N adalah menetapkan
- Jika Anda tidak memiliki akun Facebook, Anda tidak akan dapat mengaksesnya.
- Saya ingin menyediakan plugin protokol umum untuk BBX, tapi saya tidak bisa melakukannya.
- Masalah parameter GetOrder
- Kami ingin meluncurkan plugin sinkronisasi untuk VScode
- Waktu baris k dalam konfigurasi parameter
- Apakah strategi visualisasi tidak dapat mengatur leverage multiplier?
- Bagaimana saya bisa mendapatkan kedalaman pasar saat backtesting?
- ERR_INSUFFICIENT_ASSET dari huobi
- Sumber kode dari < synthesis arbitrary cycle K string > pada strategi square Panjang agregasi tidak benar
- Setelah selesai, Bitmex juga melarang
- Bitmex 403 kesalahan
- MONEYTOT masih mengalami masalah di hardisk bahasa Melayu
- Jika Anda ingin tahu apakah ada rencana untuk membeli token, terima kasih!
- Bagaimana cara menyimpan data dalam kebijakan untuk digunakan di kemudian hari?
- okex kontrak permanen
- Silahkan tanyakan bagaimana cara mengatur awal okx futures apakah ada yang memberi tahu saya
- OKEX Futures error 20020
- OKEX Futures Retest, GetRecords, GetTicker, dan lain-lain memberikan kesalahan symbol not set
- Apakah Anda selalu bisa menambahkan plugin lever token yang mengumpulkan K-string jika tidak banyak strategi yang tidak berjalan?
- Tidak ada posisi, tidak ada operasi posisi, dan muncul ERR_INVALID_POSITION saat membuka.