研究環境におけるドンキアン・チャネル戦略の分析
作者: リン・ハーンFMZ~リディア作成日:2022-12-26 09:19:00 更新日:2023-09-20 10:43:17 更新日:2020-09-20 更新日:2020-09-20 更新日:2020-09-20 更新日:2021-09-20 更新日:2020-09-20 更新日:2020-09-20 更新日:2020-09-20 更新日:2020-09-20 更新日:2020-09-20 更新日:2020-09-20 更新日:2020-09-20 更新日:2020-09-20 更新日:2020-09-20 更新日:2020-09-20 更新日:2020-09-20
研究環境におけるドンキアン・チャネル戦略の分析
戦略の導入
多くの取引戦略の中で,ドンチアンチャネル戦略は最も古典的な突破戦略の1つであるべきです. 1970年頃から有名でした. 当時は,外国企業が主流のプログラム取引戦略に関するシミュレーションテストと研究を実施しました. 結果は,ドンチアンチャネル戦略がすべての戦略テストの中で最も成功したものであることを示しました.
後に,貿易史上最も有名な"亀"トレーダートレーニングが米国で行われ,大成功を収めた.当時",亀"の取引方法は機密であったが,10年以上経った後",亀"の取引規則が公開され,人々は"亀"がドンチアンチャンネル戦略の改良版を使用していることを発見した.
突破トレード戦略は,比較的スムーズなトレンドを持つトレード品種に適しています.最も一般的な突破トレード方法は,特定のトレードポイントを判断するために価格,サポート,レジスタンスとの相対的なポジション関係を使用することです.この記事のドンチアンチャネル戦略もこの原則に基づいています.
ドンチアン運河戦略規則
ドンチアンチャネルはトレンドインジケーターであり,その外観とシグナルはボリンジャーバンドインジケーターに似ています.しかし,ドンチアンチャネルの価格チャネルは,特定の期間中の最高価格と最低価格に基づいて構築されています.例えば,最新の50Kラインの最高価格の最大値は上部トラックを形成するために計算されます.最新の50Kラインの最低価格の最小値を計算して下部トラックを形成します.
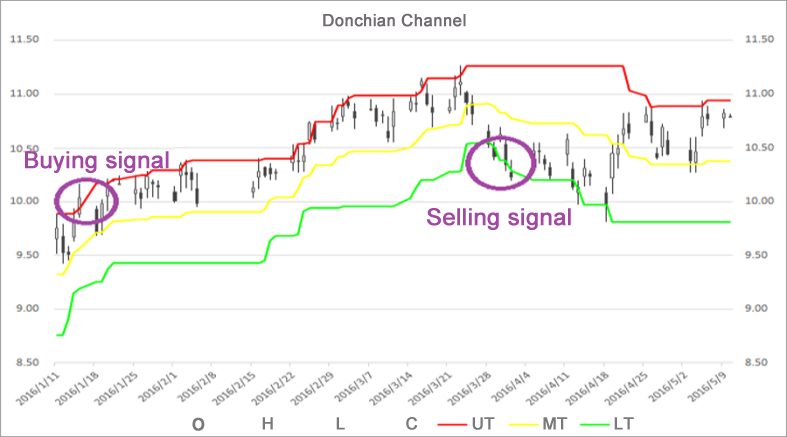
上記の図のように,この指標は3つの異なる色の曲線から構成されています. 20期間の最上位と最下位価格が市場価格の変動を示すためにデフォルトで使用されます.チャネルが狭い場合,市場の変動が小さいことを意味します.逆に,チャネルが広い場合,市場の変動が大きいことを意味します.
価格が上線線上線を超えると,それは購入信号である.逆に,価格が下線下線下線下線下線に下がると,それは販売信号である.上線と下線は最高値と最低値によって計算されるため,通常,価格は上線と下線を下線に同時に上昇し落ちることはめったにありません.ほとんどの場合,価格は上線または下線に沿って一方的に,または上線と下線の間に動きます.
戦略の論理
ドンキアンチャネルを使用する方法はいくつかあり,単独または他の指標と組み合わせて使用できます. 本レッスンでは,最も簡単な方法を使用します. つまり,価格が上から下へと上への上線を突破したとき,つまりプレッシャーラインの上から,多くの当事者の強さが増加していると信じています. 上昇市場の波が形成され,オープンポジションの購入信号が生成されています. 価格が上から下へと下へのトラックを下に落ちると,つまりサポートラインを下に落ちると,ショートポジション側が強化され,下向きのトレンドの波が形成され,セールオープニングポジションの信号が生成されています. 価格が上から下へと下がると,ショートポジションの側面が強化され,下向きのトレンドの波が形成され,セールオープニングポジションの信号が生成されています. 価格が上昇すると,市場が上昇し,市場が上昇し,市場が上昇し,市場が上昇し,市場が上昇し,市場が上昇し,市場が上昇し,市場が成長し,市場が成長し,市場が成長し,市場が成長し,市場が成長し,市場が成長し,
ポジションを開くために購入した後,価格がドンチアンチャネルの中央トラックに戻ると,マルチパーティフォースが弱体化している,またはショートポジションのパートフォースが強くなっていると考え,セールしてポジションを閉じるシグナルが生成されます. 販売ポジションを開いた後,価格がドンチアンチャネルの中央トラックに戻ると,ショートポジション側が弱体化している,またはマルチパーティフォースが強くなっていると考え,購入閉じるシグナルが生成されます.
購入・販売条件- ロング オープニング ポジション: ポジションがない場合,閉じる価格が上線値より高い場合 - ショート・オープニング・ポジション: ポジションがない場合,閉じる価格が下線値より低い場合 - ロング 閉店 ポジション: ロング ポジションを保有し,閉店 価格が 中間線より低い場合 ショートポジションを閉じます. ショートポジションを閉じると,閉じる価格が中間線よりも高くなります.
戦略コードの実施
次に,この戦略を FMZ Quant プラットフォームの研究環境で"つずつ理解します.
FMZ Quant プラットフォームの研究環境を入力します.
Python の Donchian Channel 戦略 バージョン.ipynb [1] において
from fmz import *
task = VCtx('''backtest
start: 2019-08-01 09:00:00
end: 2019-10-10 15:00:00
period: 5m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_CTP","currency":"FUTURES"}]
''')
# Create a Backtesting Environment
# The example format of the backtest information in red above can be obtained by clicking "Save settings" on the strategy edting page of the FMZ Quant platform.
[2] において
# First, we need to get the position information, and we define a mp() function to do this.
def mp():
positions = exchange.GetPosition() # Get position array
if len(positions) == 0: # If the length of the position array is 0
return 0 # Prove a short position, return 0
for i in range(len(positions)): # Iterate through the positions array
if (positions[i]['Type'] == PD_LONG) or (positions[i]['Type'] == PD_LONG_YD):
return 1 # If there are long position orders, return 1
elif (positions[i]['Type'] == PD_SHORT) or (positions[i]['Type'] == PD_SHORT_YD):
return -1 # If there are short position orders, return -1
print(positions)
mp() # Next, we execute this function to get the position information, and we can see that the result is 0, which means that the current position is short.
アウト[2]:0
[3] において
# Let's start testing this strategy using the current main rebar contract as an example.
exchange.SetContractType("rb888") # Set the variety code, the main contract is the contract code followed by the number 888.
アウト[3]:
{
次に,我々はK線配列を得ます.戦略的論理によると,市場が一定の期間実行され,その後論理的な判断を行う必要があるため,我々の戦略的論理が市場により良い適応できるようにします. ここで,我々は一時的に50K線をスタート要件として取るでしょう. FMZ QuantのK線情報は,最も高い価格,最も低い価格,オープニング価格,閉じる価格,取引量などの情報を含む配列の形で格納されます.この部分の内容については,FMZ Quantプラットフォームの公式API文書を参照してください:https://www.fmz.com/api
[4] において
# Next we define a variable to store the K-line array.
records = exchange.GetRecords() # Get the K-line array
[5] において
# According to the strategy logic description, we use the closing price as the price to open a position, so we need to calculate the closing price of the latest K-line.
close = records[len(records) - 1].Close # Get the latest K-line closing price
close
アウト[5]: 3846.0
標準として閉じる価格を使って,50K線内の最高価格の最大値と最低価格の最小値を計算する必要があります.
[6] において
upper = TA.Highest(records, 50, 'High') # Get the maximum value of the 50-period maximum price
upper
アウト[6]: 3903.0
[7]:
lower = TA.Lowest(records, 50, 'Low') # Get the minimum value of the 50-period minimum price
lower
アウト[7]: 3856.0
次に,このチャネルの上部と下部の線路の平均値を計算する必要があります.
[8] で:
middle = (upper + lower) / 2 # Calculate the average value of the upper and lower tracks.
middle
アウト[8]: 3879.5
上記では,この戦略に必要なすべての計算を完了しました.次に,開設条件を論理的に判断し,論理判断の結果に従って実際の開設ポジション操作を実行します. ここで,FMZ Quantプラットフォームの国内商品先物テンプレートを使用する必要があることに注意してください.現在の研究環境がこのテンプレートをサポートできないため,一時的に書き込みますが,操作はエラーを報告します.実際のコーディングのためにFMZ Quantプラットフォーム戦略書き出しページに,このテンプレートを問題なくインポートしてください.テンプレートのアドレス:https://www.fmz.com/strategy/24288このテンプレートを自分の戦略ライブラリにコピーし,バックテスト時にチェックアウトする必要があります.
[ ] で:
obj = ext.NewPositionManager() # When using the FMZ Quant trading class library, errors will be reported at runtime, which can be ignored. Now it is the research environment,
# This problem does not occur during the actual coding process, and the following is the same without further comment.
次のステップは戦略の論理を決定し その論理に従って ポジションを開閉することです
[ ] で:
if positions > 0 and close < middle: # If you hold a long position order and the closing price falls below the middle track
obj.CoverAll() # Close all positions
if positions < 0 and close > middle: # If you hold a short position order and the closing price rises above the middle track
obj.CoverAll() # Close all positions
if positions == 0: # If it's a short position
if close > upper: # If the closing price rises above the upper track
obj.OpenLong("rb888", 1) # Buy opening positions
elif close < lower: # If the closing price falls below the lower track
obj.OpenShort("rb888", 1) # Sell opening positions
[ ] で:
# Complete strategy code:
def mp():
positions = exchange.GetPosition() # Get the position array
if len(positions) == 0: # If the length of the position array is 0
return 0 # It proved a short position, return 0
for i in range(len(positions)): # Iterate through the positions array
if (positions[i]['Type'] == PD_LONG) or (positions[i]['Type'] == PD_LONG_YD):
return 1 # If there are long position orders, return 1
elif (positions[i]['Type'] == PD_SHORT) or (positions[i]['Type'] == PD_SHORT_YD):
return -1 # If there are short position orders, return -1
def main(): # Main function
exchange.SetContractType("rb888") # Set the variety code, the main contract is the contract code followed by the number 888
while True: # Enter the loop
records = exchange.GetRecords() # Get the K-line array
if len(records) < 50: continue # If there are less than 50 K-lines, skip the loop
close = records[len(records) - 1].Close # Get the latest K-line closing price
positions = mp() # Get position information function
upper = TA.Highest(records, 50, 'High') # Get the maximum value of the 50-period maximum price
lower = TA.Lowest(records, 50, 'Low') # Get the minimum value of the 50-period minimum price
middle = (upper + lower) / 2 # Calculate the average value of the upper and lower tracks
obj = ext.NewPositionManager() # Use the Trading Library
if positions > 0 and close < middle: # If you hold a long position order and the closing price falls below the middle track
obj.CoverAll() # Close all positions
if positions < 0 and close > middle: # If you hold a short position order and the closing price rises above the middle track
obj.CoverAll() # Close all positions
if positions == 0: # If it's a short position
if close > upper: # If the closing price rises above the upper track
obj.OpenLong("rb888", 1) # Buy opening positions
elif close < lower: # If the closing price falls below the lower track
obj.OpenShort("rb888", 1) # Sell opening positions
- DEX取引所の定量実践 (2) -- ハイパーリキッドユーザーガイド
- DEX取引所の量化実践 (2) -- Hyperliquidの使用ガイド
- DEX取引所の定量実践 (1) -- dYdX v4 ユーザーガイド
- 暗号通貨におけるリード・レイグ・アービトラージへの導入 (3)
- DEX取引所の量化実践 ((1)-- dYdX v4 ユーザーガイド
- デジタル通貨におけるリード-ラグ套路の紹介 (3)
- 暗号通貨におけるリード・ラグ・アービトラージへの導入 (2)
- デジタル通貨におけるリード-ラグ套路の紹介 (2)
- FMZプラットフォームの外部信号受信に関する議論: 戦略におけるHttpサービス内蔵の信号受信のための完全なソリューション
- FMZプラットフォームの外部信号受信に関する探求:戦略内蔵Httpサービス信号受信の完全な方案
- 暗号通貨におけるリード・ラグ・アービトラージへの導入 (1)
- 機械学習技術の取引への応用
- 研究環境を利用して,三角型ヘッジの詳細と,ヘッジ可能な価格差に対する処理手数料の影響を分析する.
- デリビットの先物取引APIを改革し,オプションの定量取引に適応する
- 取引の原則を分析するために研究環境を使用することを学びます
- ブロックチェーン資産の量的な取引におけるクロス通貨ヘッジ戦略
- FMexのデジタル通貨戦略ガイドを FMZ Quantで入手する
- MyLanguageの戦略を移植します (高度)
- MyLanguageの戦略を移植する
- 戦略にマルチチャートサポートを追加することを教える
- PythonのバージョンでK線合成関数を書くことを教える
- FMZがChatGPTに出くわしたとき,AIを使って量的な取引を学ぶのを助ける試みを記してください.
- デジタル通貨オプションの定量取引ツール
- Python バージョンのシンプルなグリッド戦略
- データ再生機能に基づいて開発された線形待機オーダーフロー戦略
- Python バージョンの勝者を購入する戦略
- 移行戦略とFMZの旅
- Pythonの単種戦略を 多種戦略に変える方法を教える
- Python を使って定量的な取引ロボットのタイムストップ・スタート・ガジェットを実装
- オークはJSを使って FMZ拡張APIとインタフェースすることを教えます
- ロボットプッシュメッセージを実現するためにDingdingインターフェースを呼んでください