Análise e instruções de utilização sobre a função integrada
Autora:FMZ~Lydia, Criado: 2023-10-07 15:35:44, Atualizado: 2024-01-02 21:17:16
Análise e instruções de utilização sobre a função integrada
A função _Cross na secção "Funções globais" da documentação da API é utilizada para calcular o estado de cruzamento dos dois indicadores.
A implementação da função é semelhante ao seguinte código:
Observe que quandoarr1é definido como uma matriz de indicadores rápidos earr2como um conjunto de indicadores lentos,
o valor devolvido pelo_Crossfunção é positiva, ou seja, de acordo com a documentação,a positive number is the period of upward penetration, a negative number indicates the period of downward penetration, and 0 means the same as the current price- Não.
Pode-se ver, neste momentoarr1para cima penetrou oarr2Tem sido n ciclos, neste momento, é a linha rápida penetração para cima a linha lenta, representando um cruzamento.
O mesmo._CrossA função retorna um número negativo, isto é, um crossdown.
O oposto é verdade searr1é definido como uma matriz de indicadores lentos earr2como um conjunto de indicadores rápidos.
Um valor positivo devolvido pelo_CrossFunção representa uma cruz.
Um valor negativo devolvido pelo_CrossFunção representa um cruzamento.
// Return to the number of periods of upward penetration, the positive number is the number of periods of upward penetration, the negative number indicates the number of periods of downward penetration, 0 means the same as the current price
$.Cross = function(arr1, arr2) { // The number of parameters is 2, it can be seen from the parameter name, these two parameters should be an array type, the array is like an array in the X-axis for the array index value, Y-axis for the index value of the line in the coordinate system, the function is to determine the intersection of the two lines
if (arr1.length !== arr2.length) { // The first step is to determine if the two arrays being compared are equal in length
throw "array length not equal"; // Throw an error if they are not equal, it is not possible to determine the intersection of unequal lines.
}
var n = 0; // Declare the variable n to record the intersection state, initially 0, unintersected
for (var i = arr1.length-1; i >= 0; i--) { // Iterate over the array arr1, from the last element forward.
if (typeof(arr1[i]) !== 'number' || typeof(arr2[i]) !== 'number') { // When any of the arrays arr1 or arr2 is of a non-numeric type (i.e., an invalid indicator), the traversal loop is broken.
break; // break out of a loop
}
if (arr1[i] < arr2[i]) { // If arr1 is smaller than arr2 then n--, will record the relative state of arr1, arr2 at the beginning, (i.e., at the beginning n will adjust itself according to the relative sizes of arr1[i], arr2[i], and once there is another relationship between the sizes of arr1[i], arr2[i] opposite to the state of n, i.e., a crossing of the two lines has occurred.)
if (n > 0) {
break;
}
n--;
} else if (arr1[i] > arr2[i]) { // If arr1 is greater than arr2 then n++
if (n < 0) {
break;
}
n++;
} else { // arr1[i] == arr2[i], then immediately break
break;
}
}
return n; // Returns the value of n, which represents the number of periods that have been crossed, and 0, which means that the indicator values are equal.
};
Vamos simular um conjunto de dados passados para este parâmetro e ver como resulta
var arr1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,8,8,9] // fast line indicator
var arr2 = [2,3,4,5,6,7,7,7,7] // slow line indicator
function main(){
Log("_Cross(arr1, arr2) : ", _Cross(arr1, arr2))
Log("_Cross(arr2, arr1) : ", _Cross(arr2, arr1))
}

Podemos ver que os resultados são 3, -3.
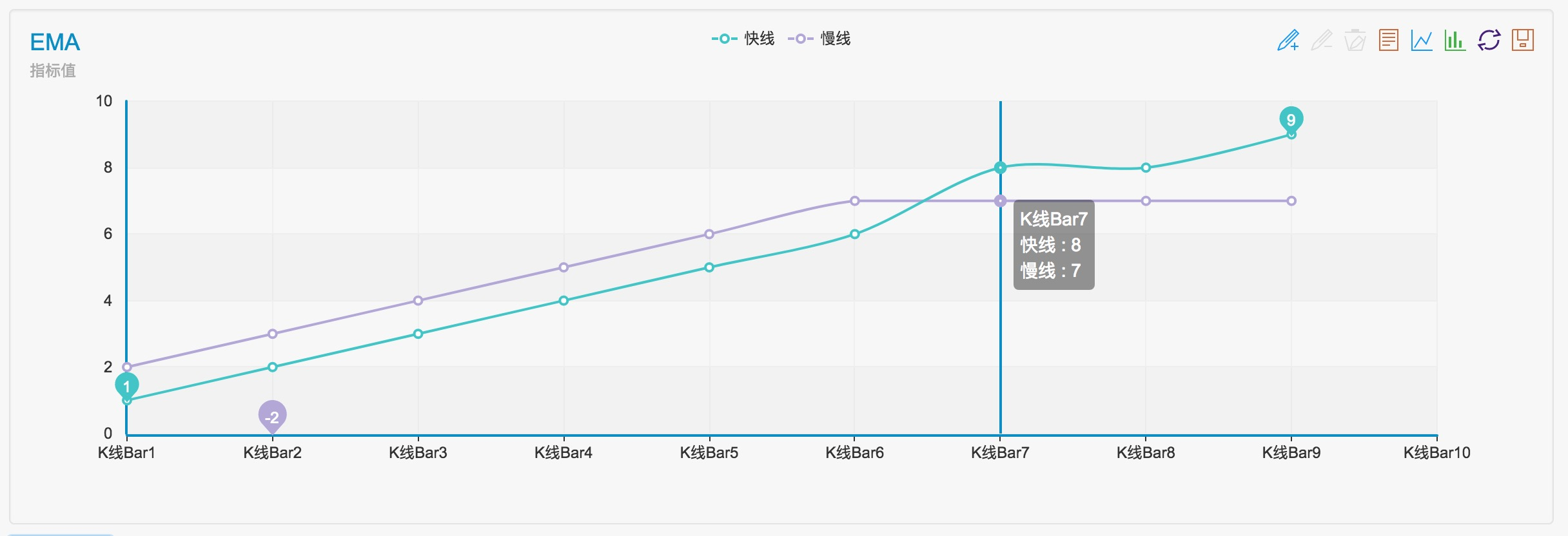
Como você vê no gráfico, o cruzamento ocorre na frente de três barras de linha K.
- Análise da estratégia de negociação de alta frequência - Penny Jump
- Ideias de negociação alternativas - Estratégia de negociação da área de linha K
- Construção e aplicação do ruído do mercado
- PSY (Psychological Line) Factor de atualização e transformação
- Análise de estratégias de negociação de alta frequência - Penny Jump
- Como medir o risco de posição - Introdução ao método VaR
- Ideias de negociação alternativas - estratégias de negociação da área da linha K
- Introdução ao método VaR para medir o risco de ações
- FMZ Mobile APP Trading Terminal, capacitando sua experiência quantitativa de negociação
- FMZ Mobile APP Terminal de negociação, que permite a sua experiência de negociação quantitativa
- Delta hedge com curva de sorrisos para opções de Bitcoin
- Reflexões sobre estratégias de negociação de alta frequência (5)
- Reflexões sobre estratégias de negociação de alta frequência (4)
- Pensamento sobre estratégias de negociação de alta frequência (5)
- Pensamento sobre estratégias de negociação de alta frequência (4)
- Reflexões sobre estratégias de negociação de alta frequência (3)
- Reflexões sobre estratégias de negociação de alta frequência (3)
- Reflexões sobre estratégias de negociação de alta frequência (2)
- Pensamento sobre estratégias de negociação de alta frequência (2)
- Reflexões sobre estratégias de negociação de alta frequência (1)