Доктор MyLanguage
Автор:Изобретатели количественного измерения - мечты, Создано: 2022-06-30 18:24:06, Обновлено: 2024-02-06 17:36:19[TOC]
MyLanguage - это программируемый язык торговли, совместимый и улучшенный с MyLanguage. MyLanguage FMZ Quant будет подвергаться строгой проверке синтаксиса. Например, при использовании улучшения языка для встраивания языкового кода JavaScript, дополнительный пробел после символа%%Оператор вызовет сообщение об ошибке.
-
Основные инструкции
- ## Контракт
Контракт на криптовалюту
Контракт на криптовалюту
this_week cryptocurrency futures contract this week next_week cryptocurrency futures contract next week month cryptocurrency futures contract month quarter cryptocurrency futures contract quarter next_quarter cryptocurrency futures contract next quarter third_quarter cryptocurrency futures contract third quarter last_quarter contract last quarter XBTUSD BITMEX perpetual contract swap cryptocurrency futures perpetual contracts other than BITMEX exchange For details, please refer to the exchange.SetContractType() function section of the JavaScript/Python/C++ documentation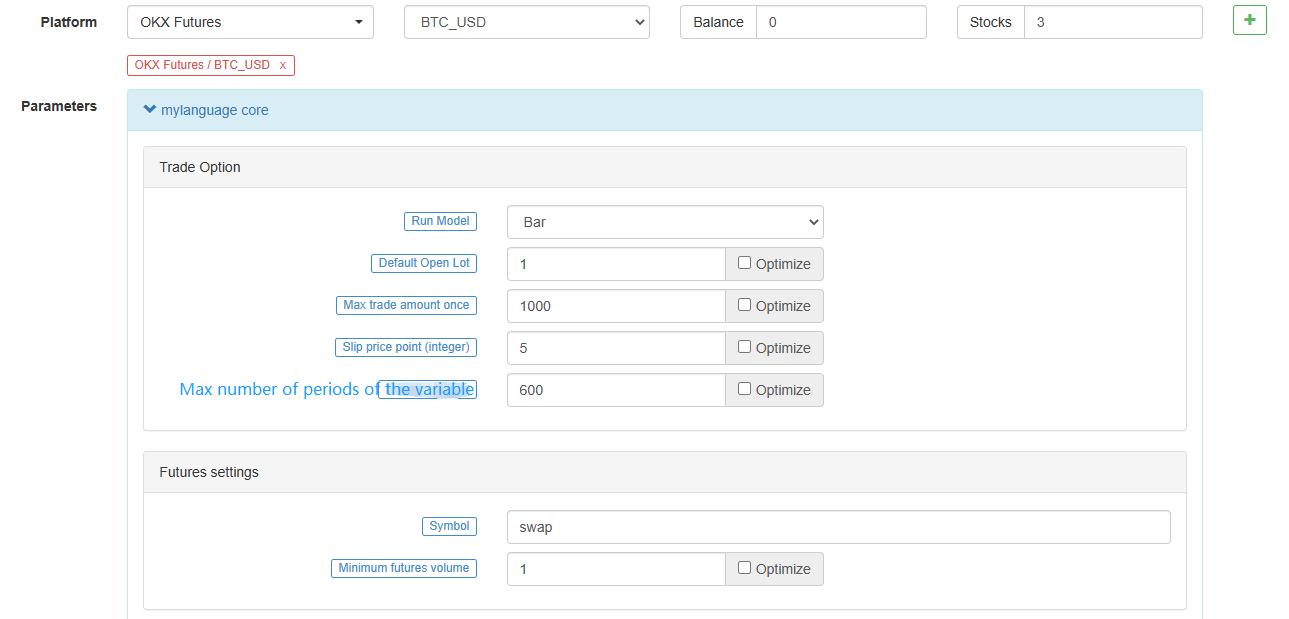
- ## Переменные
Переменная - это пространство, открытое в памяти компьютера для хранения данных.
Откройте первую переменную.
// assign 1 to variable a a:=1;Внутри.
MyLanguage, легко отличить отdata volume:- Однозначные данные: имеется только одно значение, например:
0,1,'abc'. - Данные последовательности: последовательность данных, состоящая из группы однозначных данных, таких как:
Close(цена закрытия), гдеCloseсодержит цену закрытияnperiods.[ 10.1 , 10.2 , 10.3 , 10.4 , 10.5 ...]
Отличить от
типа переменной - Тип строки: она должна быть обернута `
'', тип строки не разрешается использовать непосредственно, и он должен быть выведен в вид с функцией.
INFO(CLSOE>OPEN,'OK!');- Типы значений: включая целые числа, числа с плавающей запятой (десятники).
// integer int:=2; // decimal float:=3.1;- Булевой тип, использующий 1 (на истинный) или 0 (на ложный): 1, 0, истинный или ложный.
A:=1>0;После выполнения этого кода значениеAравен 1.
// The closing price of the current period is greater than -999, you will find that the return value of each period is 1, which means true, because the closing price is almost impossible to be negative. is_true:=Close>-999;- Глобальные переменные
VARIABLE:VALUE1:10; // Declare a global variable, assign the value 10, and execute it only once.Обратите внимание, что при обратном тестировании:
VARIABLE:NX:0; // The initial global variable NX is 0 NX..NX+1; // Accumulate 1 each time INFO(1,NX); // Print NX every timeПервоначально
INFOОтпечатки известий101Может быть, нет.0Сначала? Причина в том, что в обратном тесте есть 100 начальных K-линий, и 100 K-линий уже прошли, что было накоплено 100 раз. Фактическая цена зависит от количества первоначально полученных К-линий.- ### Правила названия
В большинстве систем, переменное наименование не позволяет использовать систему
резервированные слова (встроенные имена переменных, имена функций). Close,CКроме того, чистые числа или ведущие числа не допускаются. На самом деле, вам не нужно беспокоиться об эффективности анализа китайского языка в основной системе. Я считаю, чтоMyLanguage очень дружелюбен к китайскому языку. Для опытных программистов рекомендуется использовать следующие два правила именования: 1. Chinese name// elegant output 5-day moving average:=MA(C,5);2. English + underline// Output move_avg_5:=MA(C,5);Если вы предпочитаете английский, постарайтесь сделать значение ваших переменных как можно более понятным.
A1,AAA,BBBПоверьте мне, когда вы пересмотрите свой код индикатора снова через несколько дней, вы будете очень несчастны из-за потери памяти.Поэтому отныне используйте
MyLanguage в полной мере! Я надеюсь, что он станет мощным инструментом для вашего анализа и принятия решений. - ## Тип данных
Тип данных - это базовое понятие. Когда мы назначаем четкие данные переменной в письменном виде, переменная также становится типом самих данных.
- Вид стоимости:
1.2.3.1.1234.2.23456 ...- 2. Тип строки:
'1' .'2' .'3' ,String types must be wrapped with ''- Данные последовательности:
A collection of data consisting of a series of single-valued data- 4. Булевой тип (Булевой):
Использование
1представляетtrueи0дляfalse.Пример
// declare a variable of value type var_int := 1; // Declare a variable for sequence data var_arr := Close; // The string type cannot be declared alone, it needs to be combined with the function INFO(C>O, 'positive line');- ## Оператор
Операция и расчет, используемые для выполнения кода показателя, являются просто символами, участвующими в операции.
- ### Оператор назначения
присвоить значение переменной
- 1. `:` ```:```, represents assignment and output to the graph (subgraph). ``` Close1:Close; // Assign Close to the variable Close1 and output to the figure ``` - 2. `:=` ```:=```, represents assignment, but is not output to the graph (main graph, sub graph...), nor is it displayed in the status bar table. ``` Close2:=Close; // Assign Close to the variable Close2 ``` - 3. `^^` ```^^```, Two ```^``` symbols represent assignment, assign values to variables and output to the graph (main graph). ``` lastPrice^^C; ``` - 4. `..` ```..```, two ```.``` symbols represent assignment, assign values to variables and display variable names and values in the chart, but do not draw pictures to the chart (main picture, sub-picture...). ``` openPrice..O ```- ### Реляционные операторы
Относительные операторы - это двоичные операторы, которые используются в условных выражениях для определения отношения между двумя данными.
Возвращается значение: булевой тип, либо
true(1) илиfalse(0).- 1. more than```>``` ``` // Assign the operation result of 2>1 to the rv1 variable, at this time rv1=1 rv1:=2>1; ``` - 2. less than```<``` ``` // Returns false, which is 0, because 2 is greater than 1 rv3:=2<1; ``` - 3. more than or equal to```>=``` ``` x:=Close; // Assign the result of the operation that the closing price is more than or equal to 10 to the variable rv2 // Remark that since close is a sequence of data, when close>=10 is performed, the operation is performed in each period, so each period will have a return value of 1 and 0 rv2:=Close>=10; ``` - 4. less than or equal to```<=``` ``` omitted here ``` - 5. equal to```=``` ``` A:=O=C; // Determine whether the opening price is equal to the closing price. ``` - 6. Not equal to```<>``` ``` 1<>2 // To determine whether 1 is not equal to 2, the return value is 1 (true) ```- ### Логические операторы
Возвращается значение: булевой тип, либо
true(1) илиfalse(0).1. The logical and ```&&```, can be replaced by ```and```, and the left and right sides of the and connection must be established at the same time.// Determine whether cond_a, cond_b, cond_c are established at the same time cond_a:=2>1; cond_b:=4>3; cond_c:=6>5; cond_a && cond_b and cond_c; // The return value is 1, established2. Logical or ```||```, you can use ```or``` to replace the left and right sides of the or link, one side is true (true), the whole is true (return value true).cond_a:=1>2; cond_b:=4>3; cond_c:=5>6; cond_a || cond_b or cond_c; // The return value is 1, established3. ```()``` operator, the expression in parentheses will be evaluated first.1>2 AND (2>3 OR 3<5) // The result of the operation is false 1>2 AND 2>3 OR 3<5 // The result of the operation is true- Арифметические операторы
Return value: numeric typeАрифметические операторы - это символ для выполнения базовых арифметических операций (арифметических операторов), который является символом, используемым для обработки четырех арифметических операций.
- **plus +** ``` A:=1+1; // return 2 ``` - **minus -** ``` A:=2-1; // return 1 ``` - **multiply \** ``` A:=2*2; // return 4 ``` - **divide /** ``` A:=4/2; // return 2 ```-
Функции
- Функции
В мире программирования
function - это кусок кода, который реализует определенную функцию. function(param1,param2,...)- Composition: Function name (parameter1, parameter2, ...), may have no parameters or have multiple parameters. For example, ```MA(x,n);``` means to return to the simple moving average of ```x``` within ```n``` periods. Among them, ```MA()``` is a function, ```x``` and ```n``` are the parameters of the function. When using a function, we need to understand the basic definition of the function, that is, what data can be obtained by calling the function. Generally speaking, functions have parameters. When we pass in parameters, we need to ensure that the incoming data type is consistent. At this stage, the code hinting function of most IDEs is very imperfect. There is a data type of the parameter given, which brings some trouble to our use, and ```MA(x,n);``` is interpreted as: ``` Return to simple moving average Usage: AVG:=MA(X,N): N-day simple moving average of X, algorithm (X1+X2+X3+...+Xn)/N, N supports variables ``` This is very unfriendly to beginners, but next, we will dissect the function thoroughly, trying to find a quick way to learn and use the function.- ### Возвращение значения
Чтобы быстро выучить функции, нам нужно сначала понять понятие, оно называется
return value Возвращение, , как следует из названия, означает возврат обратно ; значение представляет специфическое значение , тогда значение возвращаемого значения: данные, которые могут быть получены. // Because it will be used in the following code, the variable return_value is used to receive and save the return value of function() // retrun_value := function(param1,param2); // For example: AVG:=MA(C,10); // AVG is retrun_value, function is MA function, param1 parameter: C is the closing price sequence data, param2 parameter: 10.- ### Параметры
Во-вторых, второе важное понятие функции - параметр, и различные значения возврата могут быть получены путем передачи различных параметров.
// The variable ma5 receives the 5-day moving average of closing prices ma5:=MA(C,5); // The variable ma10 receives the 10-day moving average of closing prices ma10:=MA(C,10);Первый параметр
Xиз переменных вышеma5,ma10этоC(цена закрытия), фактически,Cявляется также функцией (возвращает последовательность цен закрытия от открытия до настоящего), но он не имеет параметров.MA()Функция становится более гибкой для использования через параметры.-
Как учиться
- Во-первых, нам нужно понять, что делает функция, то есть, какие данные эта функция может вернуть нам.
- В конце концов, мы используем функции, чтобы получить возвращаемое значение.
- 3. Кроме того, мы должны знать тип данных параметра
MA(x,n), если вы не знаете тип данных параметраx,n, он не сможет получить обратное значение правильно.
При следующем введении и использовании функции следует следовать вышеуказанным трем принципам.
-
Улучшение языка
MyLanguageиJavaScriptсмешанное программирование языков
%% // This can call any API quantified of FMZ scope.TEST = function(obj) { return obj.val * 100; } %% Closing price: C; Closing price magnified 100 times: TEST(C); The last closing price is magnified by 100 times: TEST(REF(C, 1)); // When the mouse moves to the K-line of the backtest, the variable value will be prompted- ```scope```object The ```scope``` object can add attributes and assign anonymous functions to attributes, and the anonymous function referenced by this attribute can be called in the code part of MyLanguage. - ```scope.getRefs(obj)```function In ```JavaScript``` code block, call the ```scope.getRefs(obj)``` function to return the data of the passed in ```obj``` object. The ```JavaScript``` code wrapped with the following ```%% %%``` will get the ```C``` passed in when the ```TEST(C)``` function in MyLanguage code is called Close price. The ```scope.getRefs``` function will return all the closing prices of this K-line data. Because of the use of ```throw "stop"``` to interrupt the program, the variable ```arr``` contains the closing price of the first bar only. You can try to delete ```throw "stop"```, it will execute the ```return``` at the end of the ```JavaScript``` code, and return all closing price data. ``` %% scope.TEST = function(obj){ var arr = scope.getRefs(obj) Log("arr:", arr) throw "stop" return } %% TEST(C); ``` - scope.bars Access all K-line bars in the ``JavaScript`` code block. The ```TEST``` function returns a value. 1 is a negative line and 0 is a positive line. ``` %% scope.TEST = function(){ var bars = scope.bars return bars[bars.length - 1].Open > bars[bars.length - 1].Close ? 1 : 0 // Only numeric values can be returned } %% arr:TEST; ``` ``` # Attention: # An anonymous function received by TEST, the return value must be a numeric value. # If the anonymous function has no parameters, it will result in an error when calling TEST, writing VAR:=TEST; and writing VAR:=TEST(); directly. # TEST in scope.TEST must be uppercase. ``` - scope.bar In the ```JavaScript``` code block, access the current bar. Calculate the average of the high opening and low closing prices. ``` %% scope.TEST = function(){ var bar = scope.bar var ret = (bar.Open + bar.Close + bar.High + bar.Low) / 4 return ret } %% avg^^TEST; ``` - scope.depth Access to market depth data (order book). ``` %% scope.TEST = function(){ Log(scope.depth) throw "stop" // After printing the depth data once, throw an exception and pause } %% TEST; ``` - scope.symbol Get the name string of current trading pair. ``` %% scope.TEST = function(){ Log(scope.symbol) throw "stop" } %% TEST; ``` - scope.barPos Get the Bar position of the K-line. ``` %% scope.TEST = function(){ Log(scope.barPos) throw "stop" } %% TEST; ``` - scope.get\_locals('name') This function is used to get the variables in the code section of MyLanguage. ``` V:10; %% scope.TEST = function(obj){ return scope.get_locals('V') } %% GET_V:TEST(C); ``` ``` # Attention: # If a variable cannot calculate the data due to insufficient periods, call the scope.get_locals function in the JavaScript code at this time # When getting this variable, an error will be reported: line:XX - undefined locals A variable name is undefined ``` - scope.canTrade The ```canTrade``` attribute marks whether the current bar can be traded (whether the current Bar is the last one) For example, judging that the market data is printed when the strategy is in a state where the order can be traded ``` %% scope.LOGTICKER = function() { if(exchange.IO("status") && scope.canTrade){ var ticker = exchange.GetTicker(); if(ticker){ Log("ticker:", ticker); return ticker.Last; } } } %% LASTPRICE..LOGTICKER; ```Пример применения:
%% scope.TEST = function(a){ if (a.val) { throw "stop" } } %% O>C,BK; C>O,SP; TEST(ISLASTSP);Остановите стратегию после открытия и закрытия позиции один раз.
-
Ссылка на несколько периодов
Система автоматически выбирает подходящий базовый период K-линии и использует эти базовые данные периода K-линии для синтеза всех ссылающихся данных K-линии для обеспечения точности данных.
- Использование:
#EXPORT formula_name ... #ENDЕсли формула не рассчитывается только для получения данных различных периодов, вы также можете написать пустую формулу.
- Использование:
Пустая формула:
#EXPORT TEST NOP; #END // end- Использование:
#IMPORT [MIN,period,formula name] AS variable valueПолучить различные данные установленного периода (цена закрытия, цена открытия и т.д., полученные по переменному значению).
В
MINвIMPORTКоманда означаетминутное значение.MyLanguage платформы FMZ Quant, и толькоMINуровень поддерживается вIMPORTНестандартные периоды теперь поддерживаются.#IMPORT [MIN, 240, TEST] AS VAR240импортировать данные, такие как 240-минутный период (4 часа) K-линии.Пример кода:
// This code demonstrates how to reference formulas of different periods in the same code // #EXPORT extended grammar, ending with #END marked as a formula, you can declare multiple #EXPORT TEST Mean value 1: EMA(C, 20); Mean value 2: EMA(C, 10); #END // end #IMPORT [MIN,15,TEST] AS VAR15 // Quoting the formula, the K-line period takes 15 minutes #IMPORT [MIN,30,TEST] AS VAR30 // Quoting the formula, the K-line period takes 30 minutes CROSSUP(VAR15.Mean value is 1, VAR30.Mean value is 1),BPK; CROSSDOWN(VAR15.Mean value is 2, VAR30.Mean value is 2),SPK; The highest price in fifteen minutes:VAR15.HIGH; The highest price in thirty minutes:VAR30.HIGH; AUTOFILTER;- Необходимо обратить внимание при использовании
REF,LLV,HHVи другие инструкции по ссылке на данные при ссылке на данные в нескольких периодах.
(*backtest start: 2021-08-05 00:00:00 end: 2021-08-05 00:15:00 period: 1m basePeriod: 1m exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_OKCoin","currency":"ETH_USD"}] args: [["TradeAmount",100,126961],["ContractType","swap",126961]] *) %% scope.PRINTTIME = function() { var bars = scope.bars; return _D(bars[bars.length - 1].Time); } %% BARTIME:PRINTTIME; #EXPORT TEST REF1C:REF(C,1); REF1L:REF(L,1); #END // end #IMPORT [MIN,5,TEST] AS MIN5 INFO(1, 'C:', C, 'MIN5.REF1C:', MIN5.REF1C, 'REF(MIN5.C, 1):', REF(MIN5.C, 1), 'Trigger BAR time:', BARTIME, '#FF0000'); INFO(1, 'L:', L, 'MIN5.REF1L:', MIN5.REF1L, 'REF(MIN5.L, 1):', REF(MIN5.L, 1), 'Trigger BAR time:', BARTIME, '#32CD32'); AUTOFILTER;Сравнение различий между
MIN5.REF1CиREF(MIN5.C, 1), мы можем найти:```REF(MIN5.C, 1)``` is the K -line period of the current model (the above code backtest period is set to 1 minute, i.e. ```period: 1m``), the closing price of the 5-minute period where the penultimate BAR is located at the current moment. These two definitions are differentiated, and they can be used as needed. - ## Mode Description - ### Signal filtering model of one opening and one leveling In the model, the ```AUTOFILTER``` function is written to control and realize the signal filtering of one opening and one closing. When there are multiple opening signals that meet the conditions, the first signal is taken as the valid signal, and the same signal on the K-line will be filtered out. Instructions supported by filtering model: BK, BP, BPK, SK, SP, SPK, CLOSEOUT, etc. Instructions with lot numbers such as BK(5) are not supported. For exampleMA1:MA(CLOSE,5); MA2:MA ((CLOSE,10); CROSSUP ((C,MA1),BK; CROSSUP ((MA1,MA2),BK; C>BKPRICE+10 в течение нескольких месяцев
Понимание: Как и в приведенном выше примере, когда AUTOFILTER не настроен, третий ряд BK, четвертый ряд BK и пятый ряд SP запускаются последовательно, и каждая линия K запускает сигнал один раз. После открытия позиции и закрытия позиции состояние модели сбрасывается.
Если AUTOFILTER настроен, после запуска BK запускается только SP, другие сигналы BK игнорируются, и каждая линия K запускает сигнал один раз.- ### Increase and decrease position model The ```AUTOFILTER``` function is not written in the model, allowing continuous opening signals or continuous closing signals, which can increase and decrease positions. Supported instructions: BK(N), BP(N), SK(N), SP(N), CLOSEOUT, BPK(N), SPK(N), open and close orders without lot size are not supported. (1)Instruction grouping is supported. (2)When multiple instruction conditions are satisfied at the same time, the signals are executed in the order in which the conditional statements are written. For example:MA1:MA(CLOSE,5); MA2:MA ((CLOSE,10); CROSSUP ((C,MA1),BK ((1)); CROSSUP ((MA1,MA2),BK(1); C>BKPRICE+10 в течение нескольких месяцев
Use ```TRADE\_AGAIN``` It is possible to make the same command line, multiple signals in succession.Понимание: Приведенный выше пример выполняется один за другим, и сигнал после выполнения больше не запускается.
- ### Model with one K-line and one signal Regardless of whether the K-line is finished, the signal is calculated in real-time orders, that is, the K-line is placed before the order is completed; the K-line is reviewed at the end. If the position direction does not match the signal direction at the end of the K-line, the position will be automatically synchronized. For example:MA1:MA(CLOSE,5); MA2:MA ((CLOSE,10); CROSSUP(MA1,MA2),BPK; //Пятипериодная скользящая средняя пересекается вверх, а 10-периодная скользящая средняя длится долго. CROSSDOWN(MA1,MA2),SPK; //Пятипериодная скользящая средняя пересекается вниз, а 10-периодная скользящая средняя становится короткой. Автофильтр;
- ### A model of multiple signals on one K-line The model uses ```multsig``` to control and implement multiple signals from one K-line. Regardless of whether the K-line is finished, the signal is calculated in real-time. The signal is not reviewed, there is no signal disappearance, and the direction of the signal is always consistent with the direction of the position. If multiple signal conditions are met in one K-line, it can be executed repeatedly.Например: MA1:MA(CLOSE,5); MA2:MA ((CLOSE,10); CROSSUP ((MA1,MA2),BK; C>BKPRICE+10 в течение нескольких месяцев
```MULTSIG``` can execute multiple command lines within one K-line. A command line is only signaled once.O,BK; // Все эти условия могут быть выполнены в K-линейной строке, но только один сигнал на линию 10+O,BK; // Стратегия плюс TRADE_AGAIN(10); он может делать несколько сигналов на линию 20+O,BK; 40+O,BK; MULTSIG ((1,1,10);
Supplement: 1.The model of adding and reducing positions, two ways of one signal and one K-line: placing an order at the closing price and placing an order at the order price, are both supported. 2.The model of adding and reducing positions also supports ordering of multiple signals from one K-line. The model of adding and reducing positions, write the ```multsig``` function to realize multiple additions or multiple reductions on one K-line. - ## Execution mode 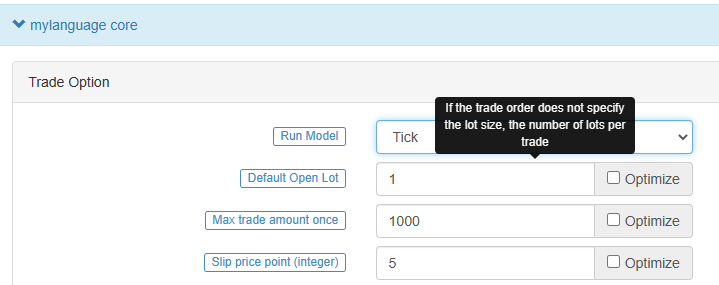 - ### Bar model The Bar model refers to the model that is executed after the current BAR is completed, and the trading is executed when the next BAR starts. - ### Tick model The Tick model means that the model is executed once for each price movement and trades immediately when there is a signal. The Tick model ignores the previous day's signal (the previous day's signal is executed immediately on the same day), and the Tick model focuses only on the current market data to determine whether the signal is triggered. - ## Chart display - ### Additional indicators for main chart > Use operator ```^^```, set indicators are displayed on the main chart while assigning values to variables.MA60^^MA(C, 60); // Расчет среднего показателя с параметром 60
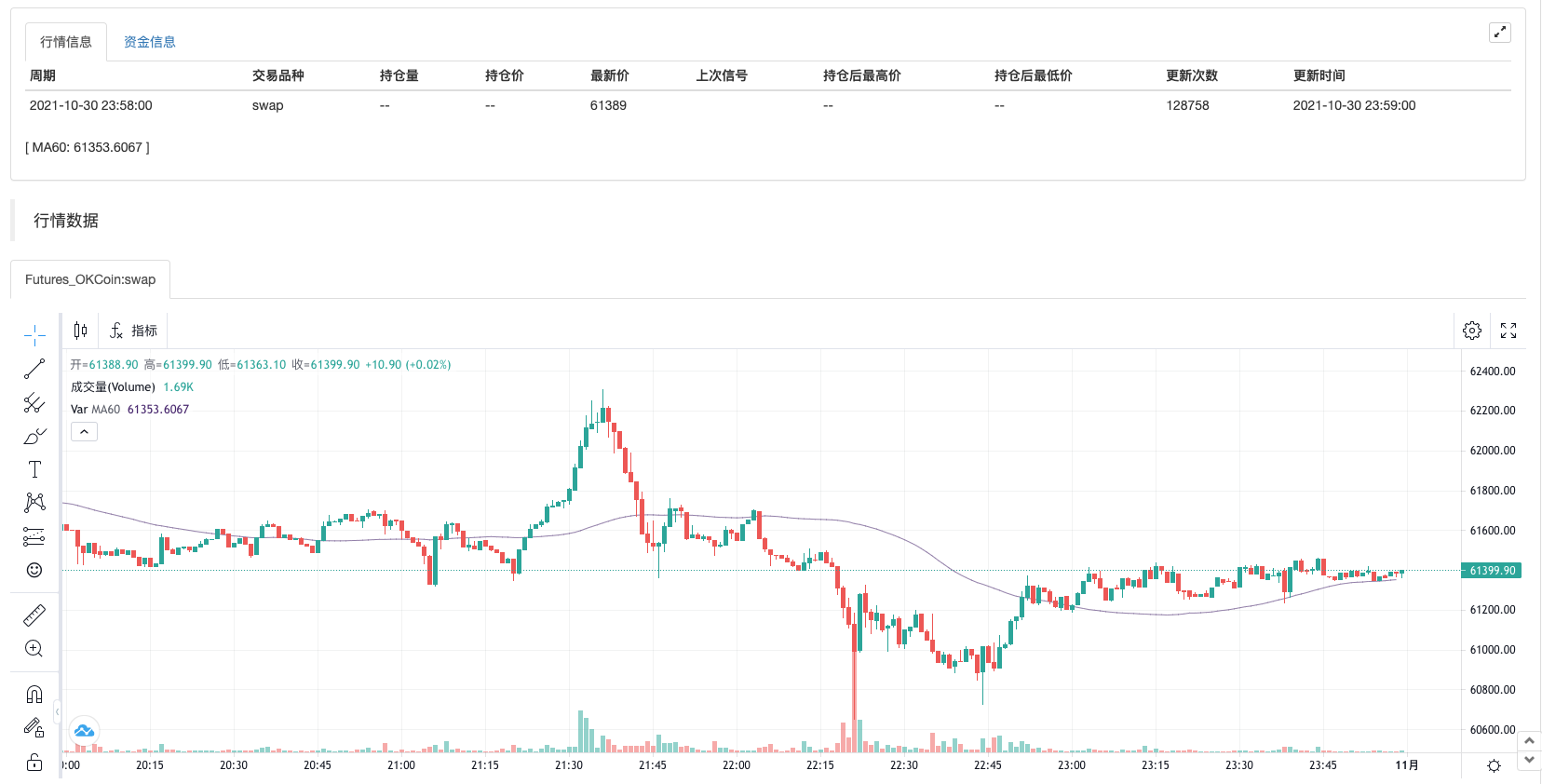 - ### Additional Indicators for sub-chart Use operator ```:```, set indicators are displayed on the sub-chart while assigning values to variables.ATR:MA(MAX(MAX((HIGH-LOW),ABS(REF(CLOSE,1)-HIGH)),ABS(REF(CLOSE,1)-LOW)),26); // Присвоите значение переменной ATR, после символа
: следует формула для расчета ATR 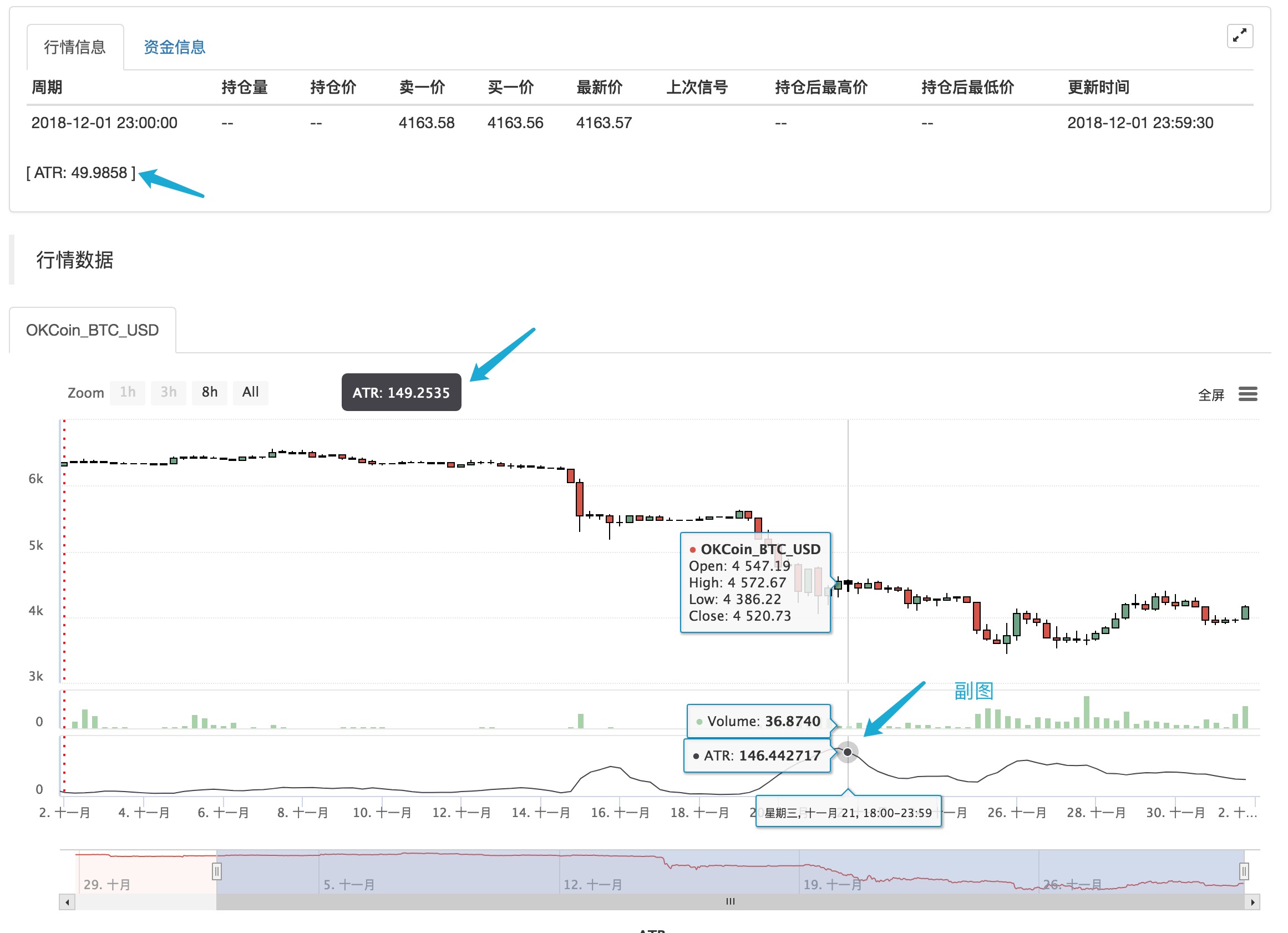 If you don't want it to be displayed on the main or subchart, use the "..." operator.MA60..MA(C, 60); // Расчет среднего показателя с параметром 60
You can use ```DOT``` and ```COLORRED``` to set the line type and color of the line, etc., in line with the habits of users familiar with the MyLanguage. - ## Common problems > Introduce the **problems** commonly encountered in the process of writing indicators, usually the points that need to be paid attention to when writing (continuously added). - Remark the semicolon ```;``` at the end. - Remark that system keywords cannot be declared as variables. - Remark that the string uses **single quotes**, for example: the string ```'Open position'```. - ### Remark Annotation - ```// The Remark content ``` (input method can be typed in both Chinese and English) means that the code is not compiled during the execution process, that is, the content after ```//``` is not executed. Usually we use it to mark the meaning of the code, when it is convenient for code review, it can be quickly understood and recalled. - ```{ Remark content }```Block Remark. ``` A:=MA(C,10); {The previous line of code is to calculate the moving average.} ``` - ```(* Remark content *)```Block Remark. ``` A:=MA(C,10); (*The previous line of code is to calculate the moving average.*) ``` - ### Input When writing code, because the input method is often switched between Chinese and English, resulting in symbol errors. The common errors are as follows: colon ```:```, terminator ```;```, comma ```, ```, brackets ```()```, etc. These characters in different states of Chinese and English need attention. > If you use Sogou, Baidu, or Bing input methods, you can quickly switch between Chinese and English by pressing the ```shift``` key once. - ### Error-prone logic 1. At least, not less than, not less than: the corresponding relational operator ```>=```. 2. Up to, at most, no more than: the corresponding relational operator ```<=```. - ### Strategy launch synchronization In the futures strategy, if there is a manually opened position before the strategy robot starts, when the robot starts, it will detect the position information and synchronize it to the actual position status. In the strategy, you can use the ```SP```, ```BP```, ```CLOSEOUT``` commands to close the position.% % если (!scope.init) { var ticker = exchange.GetTicker ((); обмен.покупка.продажа+10, 1); scope.init = верно; Я не знаю. % % C>0, CLOSEOUT;
` - ### Двусторонние позиции не поддерживаются
MyLanguage не поддерживает один и тот же контракт с длинными и короткими позициями.
-
Цитирование данных K-линии
- ## Открыто
Получите начальную цену на графике с линией K.
Открывающая цена
Функция: OPEN, сокращение от O
параметры: ни один
Объяснение: возвращает начальную цену
этого периода Данные последовательности
OPEN gets the opening price of the K-line chart. Remark: 1.It can be abbreviated as O. Example 1: OO:=O; //Define OO as the opening price; Remark that the difference between O and 0. Example 2: NN:=BARSLAST(DATE<>REF(DATE,1)); OO:=REF(O,NN); //Take the opening price of the day Example 3: MA5:=MA(O,5); //Define the 5-period moving average of the opening price (O is short for OPEN).- ## Высокий
Найди самую высокую цену на графике.
Самая высокая цена
Функция: HIGH, сокращение H
параметры: ни один
Объяснение: Вернуть самую высокую цену за
этот период Данные последовательности
HIGH achieved the highest price on the K-line chart. Remark: 1.It can be abbreviated as H. Example 1: HH:=H; // Define HH as the highest price Example 2: HH:=HHV(H,5); // Take the maximum value of the highest price in 5 periods Example 3: REF(H,1); // Take the highest price of the previous K-line- ## Низкий
Найди самую низкую цену на графике.
Самая низкая цена
Функция: Низкая, сокращенная L
параметры: ни один
Объяснение: Вернуть самую низкую цену за
этот период Данные последовательности
LOW gets the lowest price on the K-line chart. Remark: 1.It can be abbreviated as L. Example 1: LL:=L; // Define LL as the lowest price Example 2: LL:=LLV(L,5); // Get the minimum value of the lowest price in 5 periods Example 3: REF(L,1); // Get the lowest price of the previous K-line- ## Близко
Получите цену закрытия диаграммы.
Цена закрытия
Функция: CLOSE, сокращенная как C
параметры: ни один
Объяснение: возвращает цену закрытия
этого периода Данные последовательности
CLOSE Get the closing price of the K-line chart Remarks: 1.Obtain the latest price when the intraday K-line has not finished. 2.It can be abbreviated as C. Example 1: A:=CLOSE; //Define the variable A as the closing price (A is the latest price when the intraday K-line has not finished) Example 2: MA5:=MA(C,5); //Define the 5-period moving average of the closing price (C is short for CLOSE) Example 3: A:=REF(C,1); //Get the closing price of the previous K-line- ## ВОЛ
Получить объем торгов на K-линейном графике.
Объем торговли
Функция: VOL, сокращенно V
параметры: ни один
Объяснение: возвращает объем торгов за
этот период Данные последовательности
VOL obtains the trading volume of the K-line chart. Remarks: It can be abbreviated as V. The return value of this function on the current TICK is the cumulative value of all TICK trading volume on that day. Example 1: VV:=V; // Define VV as the trading volume Example 2: REF(V,1); // Indicates the trading volume of the previous period Example 3: V>=REF(V,1); // The trading volume is greater than the trading volume of the previous period, indicating that the trading volume has increased (V is the abbreviation of VOL)- ## ОПИ
Взять текущую общую позицию на рынке фьючерсов (контрактов).
OpenInterest:OPI;- ## REF
Ссылка на предложение.
Reference the value of X before N periods. Remarks: 1.When N is a valid value, but the current number of K-lines is less than N, returns null; 2.Return the current X value when N is 0; 3.Return a null value when N is null. 4.N can be a variable. Example 1: REF(CLOSE,5);Indicate the closing price of the 5th period before the current period is referenced Example 2: AA:=IFELSE(BARSBK>=1,REF(C,BARSBK),C);//Take the closing price of the K-line of the latest position opening signal // 1)When the BK signal is sent, the bar BARSBK returns null, then the current K-line REF(C, BARSBK) that sends out the BK signal returns null; // 2)When the BK signal is sent out, the K-line BARSBK returns null, and if BARSBK>=1 is not satisfied, it is the closing price of the K-line. // 3)The K-line BARSBK after the BK signal is sent, returns the number of periods from the current K-line between the K-line for purchasing and opening a position, REF(C,BARSBK) Return the closing price of the opening K-line. // 4)Example: three K-lines: 1, 2, and 3, 1 K-line is the current K-line of the position opening signal, then returns the closing price of the current K-line, 2, 3 The K-line returns the closing price of the 1 K-line.- ## UNIT
Получите торговую единицу контракта данных.
Get the trading unit of the data contract. Usage: UNIT takes the trading unit of the loaded data contract.Криптовалютный спот
Значение UNIT равняется 1.
Фьючерсы на криптовалюты
Значение в единицах относится к валюте контракта.
OKEX futures currency standard contracts: 1 contract for BTC represents $100, 1 contract for other currencies represents $10- ## MINPRICE
Минимальная вариационная цена контракта на данные.
Take the minimum variation price of the data contract. Usage: MINPRICE; Take the minimum variation price of the loaded data contract.- ## MINPRICE1
Минимальная вариационная цена торгового контракта.
Take the minimum variation price of a trading contract. Usage: MINPRICE1; Take the minimum variation price of a trading contract. -
Функция времени
- ## BARPOS
Возьмите позицию К-линии.
BARPOS, Returns the number of periods from the first K-line to the current one. Remarks: 1.BARPOS returns the number of locally available K-line, counting from the data that exists on the local machine. 2.The return value of the first K-line existing in this machine is 1. Example 1:LLV(L,BARPOS); // Find the minimum value of locally available data. Example 2:IFELSE(BARPOS=1,H,0); // The current K-line is the first K-line that already exists in this machine, and it takes the highest value, otherwise it takes 0.- ## DAYBARPOS
DAYBARPOS текущий K-линейный BAR является K-линейным BAR дня.
- ## Период
Значение периода - это количество минут.
1, 3, 5, 15, 30, 60, 1440- ## Дата
ДатаФункция DATE, получает год, месяц и день периода с 1900 года.
Example 1: AA..DATE; // The value of AA at the time of testing is 220218, which means February 18, 2022- Время
Пора делать К-линию.
TIME, the time of taking the K-line. Remarks: 1.The function returns in real time in the intraday, and returns the starting time of the K-line after the K-line is completed. 2.This function returns the exchange data reception time, which is the exchange time. 3.The TIME function returns a six-digit form when used on a second period, namely: HHMMSS, and displays a four-digit form on other periods, namely: HHMM. 4.The TIME function can only be loaded in periods less than the daily period, and the return value of the function is always 1500 in the daily period and periods above the daily period. 5. It requires attention when use the TIME function to close a position at the end of the day (1).It is recommended to set the time for closing positions at the end of the market to the time that can actually be obtained from the return value of the K-line (for example: the return time of the last K-line in the 5-minute period of the thread index is 1455, and the closing time at the end of the market is set to TIME>=1458, CLOSEOUT; the signal of closing the position at the end of the market cannot appear in the effect test) (2).If the TIME function is used as the condition for closing the position at the end of the day, it is recommended that the opening conditions should also have a corresponding time limit (for example, if the condition for closing the position at the end of the day is set to TIME>=1458, CLOSEOUT; then the condition TIME needs to be added to the corresponding opening conditions. <1458; avoid re-opening after closing) Example 1: C>O&&TIME<1450,BK; C<O&&TIME<1450,SK; TIME>=1450,SP; TIME>=1450,BP; AUTOFILTER; // Close the position after 14:50. Example 2: ISLASTSK=0&&C>O&&TIME>=0915,SK;- ## Год
Year.
YEAR, year of acquisition. Remark: The value range of YEAR is 1970-2033. Example 1: N:=BARSLAST(YEAR<>REF(YEAR,1))+1; HH:=REF(HHV(H,N),N); LL:=REF(LLV(L,N),N); OO:=REF(VALUEWHEN(N=1,O),N); CC:=REF(C,N); // Take the highest price, lowest price, opening price, and closing price of the previous year Example 2: NN:=IFELSE(YEAR>=2000 AND MONTH>=1,0,1);- ## Месяц
Возьми месяц.
MONTH, returns the month of a period. Remark: The value range of MONTH is 1-12. Example 1: VALUEWHEN(MONTH=3&&DAY=1,C); // Take its closing price when the K-line date is March 1 Example 2: C>=VALUEWHEN(MONTH<REF(MONTH,1),O),SP;- ## ДЕНЬ
Получить число дней в периоде
DAY, returns the number of days in a period. Remark: The value range of DAY is 1-31. Example 1: DAY=3&&TIME=0915,BK; // 3 days from the same day, at 9:15, buy it Example 2: N:=BARSLAST(DATE<>REF(DATE,1))+1; CC:=IFELSE(DAY=1,VALUEWHEN(N=1,O),0); // When the date is 1, the opening price is taken, otherwise the value is 0- ## Час
Hour.
HOUR, returns the number of hours in a period. Remark: The value range of HOUR is 0-23 Example 1: HOUR=10; // The return value is 1 on the K-line at 10:00, and the return value on the remaining K-lines is 0- ## МИНУТА
Minute.
MINUTE, returns the number of minutes in a period. Remarks: 1: The value range of MINUTE is 0-59 2: This function can only be loaded in the minute period, and returns the number of minutes when the K-line starts. Example 1: MINUTE=0; // The return value of the minute K-line at the hour is 1, and the return value of the other K-lines is 0 Example 2: TIME>1400&&MINUTE=50,SP; // Sell and close the position at 14:50- ## ДЕНЬ недели
Найди номер недели.
WEEKDAY, get the number of the week. Remark: 1: The value range of WEEKDAY is 0-6. (Sunday ~ Saturday) Example 1: N:=BARSLAST(MONTH<>REF(MONTH,1))+1; COUNT(WEEKDAY=5,N)=3&&TIME>=1450,BP; COUNT(WEEKDAY=5,N)=3&&TIME>=1450,SP; AUTOFILTER; // Automatically close positions at the end of the monthly delivery day Example 2: C>VALUEWHEN(WEEKDAY<REF(WEEKDAY,1),O)+10,BK; AUTOFILTER; -
Функция логического суждения
- ## Барстатус
Возвращение состояния позиции за текущий период.
BARSTATUS returns the position status for the current period. Remark: The function returns 1 to indicate that the current period is the first period, returns 2 to indicate that it is the last period, and returns 0 to indicate that the current period is in the middle. Example: A:=IFELSE(BARSTATUS=1,H,0); // If the current K-line is the first period, variable A returns the highest value of the K-line, otherwise it takes 0- ## Между тем
Between.
BETWEEN(X,Y,Z) indicates whether X is between Y and Z, returns 1 (Yes) if established, otherwise returns 0 (No). Remark: 1.The function returns 1(Yse) if X=Y, X=Z, or X=Y and Y=Z. Example 1: BETWEEN(CLOSE,MA5,MA10); // It indicates that the closing price is between the 5-day moving average and the 10-day moving average- ## BARSLASTCOUNT
BARSLASTCOUNT(COND) подсчитывает количество последовательных периодов, которые удовлетворяют условию, начиная от текущего периода.
Remark: 1. The return value is the number of consecutive non zero periods calculated from the current period 2. the first time the condition is established when the return value of the current K-line BARSLASTCOUNT(COND) is 1 Example: BARSLASTCOUNT(CLOSE>OPEN); //Calculate the number of consecutive positive periods within the current K-line- ## КРОСС
Крос-функция.
CROSS(A,B) means that A crosses B from bottom to top, and returns 1 (Yes) if established, otherwise returns 0 (No) Remark: 1.To meet the conditions for crossing, the previous k-line must satisfy A<=B, and when the current K-line satisfies A>B, it is considered to be crossing. Example 1: CROSS(CLOSE,MA(CLOSE,5)); // Indicates that the closing line crosses the 5-period moving average from below- ## КРАССДОУН
Пересечение
CROSSDOWN(A,B): indicates that when A passes through B from top to bottom, it returns 1 (Yes) if it is established, otherwise it returns 0 (No) Remark: 1.CROSSDOWN(A,B) is equivalent to CROSS(B,A), and CROSSDOWN(A,B) is easier to understand Example 1: MA5:=MA(C,5); MA10:=MA(C,10); CROSSDOWN(MA5,MA10),SK; // MA5 crosses down MA10 to sell and open a position // CROSSDOWN(MA5,MA10),SK; Same meaning as CROSSDOWN(MA5,MA10)=1,SK;- ## КРОССУП
Crossup.
CROSSUP(A,B) means that when A crosses B from the bottom up, it returns 1 (Yes) if it is established, otherwise it returns 0 (No) Remark: 1.CROSSUP(A,B) is equivalent to CROSS(A,B), and CROSSUP(A,B) is easier to understand. Example 1: MA5:=MA(C,5); MA10:=MA(C,10); CROSSUP(MA5,MA10),BK; // MA5 crosses MA10, buy open positions // CROSSUP(MA5,MA10),BK;与CROSSUP(MA5,MA10)=1,BK; express the same meaning- ## ВСЕ
Определите, удовлетворяется ли она постоянно.
EVERY(COND,N), Determine whether the COND condition is always satisfied within N periods. The return value of the function is 1 if it is satisfied, and 0 if it is not satisfied. Remarks: 1.N contains the current K-line. 2.If N is a valid value, but there are not so many K-lines in front, or N is a null value, it means that the condition is not satisfied, and the function returns a value of 0. 3.N can be a variable. Example 1: EVERY(CLOSE>OPEN,5); // Indicates that it has been a positive line for 5 periods Example 2: MA5:=MA(C,5); // Define a 5-period moving average MA10:=MA(C,10); // Define a 10-period moving average EVERY(MA5>MA10,4),BK; // If MA5 is greater than MA10 within 4 periods, then buy the open position // EVERY(MA5>MA10,4),BK; has the same meaning as EVERY(MA5>MA10,4)=1,BK;- ## Существуют
Определите, есть ли удовлетворение.
EXIST(COND, N) judges whether there is a condition that satisfies COND within N periods. Remarks: 1.N contains the current K-line. 2.N can be a variable. 3.If N is a valid value, but there are not so many K-lines in front, it is calculated according to the actual number of periods. Example 1: EXIST(CLOSE>REF(HIGH,1),10); // Indicates whether there is a closing price greater than the highest price of the previous period in 10 periods, returns 1 if it exists, and returns 0 if it does not exist Example 2: N:=BARSLAST(DATE<>REF(DATE,1))+1; EXIST(C>MA(C,5),N); // Indicates whether there is a K-line that satisfies the closing price greater than the 5-period moving average on the day, returns 1 if it exists, returns 0 if it does not exist- ## Если
Функция состояния.
IF(COND,A,B)Returns A if the COND condition is true, otherwise returns B. Remarks: 1.COND is a judgment condition; A and B can be conditions or values. 2.This function supports the variable circular reference to the previous period's own variable, that is, supports the following writing Y: IF(CON,X,REF(Y,1)). Example 1: IF(ISUP,H,L); // The K-line is the positive line, the highest price is taken, otherwise the lowest price is taken Example 2: A:=IF(MA5>MA10,CROSS(DIFF,DEA),IF(CROSS(D,K),2,0)); // When MA5>MA10, check whether it satisfies the DIFF and pass through DEA, otherwise (MA5 is not greater than MA10), when K and D are dead fork, let A be assigned a value of 2, if none of the above conditions are met, A is assigned a value of 0 A=1,BPK; // When MA5>MA10, the condition for opening a long position is to cross DEA above the DIFF A=2,SPK; // When MA5 is not greater than MA10, use K and D dead forks as the conditions for opening short positions- ## IFELSE
Функция состояния.
` IFELSE(COND,A,B) возвращает A, если условие COND верно, иначе возвращает B. Примечания: 1.COND - это условие суждения; A и B могут быть условиями или значениями. 2.Эта функция поддерживает циркулярную ссылку переменной на собственную переменную предыдущего периода, т.е. поддерживает следующее написание Y: IFELSE(CON,X,REF(Y,1)); Пример 1: IFELSE ((ISUP,H,L); // К-линия является положительной линией, принимается самая высокая цена, в противном случае принимается самая низкая цена Пример 2: A:=IFELSE(MA5>MA10,CROSS(DIFF,DEA),IFELSE(CROSS(D,K,2,0)); // Когда MA5>MA10, проверьте, удовлетворяет ли он DIFF и проходит через DEA, в противном случае (MA5 не превышает MA10), когда K и D являются мертвыми форками, давайте присвоим A значение 2, если ни одно из вышеперечисленных условий не выполнено, A присваивается значение 0 A=1,BPK; // Когда MA5>MA10, условием для открытия длинной позиции является пересечение DEA над DIFF A=2,SPK; // Когда MA5 не больше MA10, используйте K и D мертвые вилки как conditio
- расчет наклонности ema
- Проблема высокочастотного обмена
- Новое открытие: цепочка данных + данные о сделках в поле = основные точки входа и выхода
- Попросите помощи в вопросах процедурной структуры и комбинации многостратегий
- Может ли pine script напрямую переключать данные с рынка?
- Сайт Вопросы по загрузке
- Если вы не знаете, что это такое, вы не знаете, что это такое, но вы не знаете, что это такое.
- Макад, король индикаторов, владеет одним из крупнейших индикаторов.
- Телевизионные стратегии предупреждают о том, как FMZ реализует заказ.
- Новая версия иконы "ТВ-рецензия" не очень удобна.
- Самый передовой способ торговли: владеть стеной заказов!
- Спросите, в какой единице измеряется объем.
- Какой из них в последнее время имеет более высокую годовую амортизацию - прямой или обратный?
- Вопрос о tradeview Сигнал всегда задерживается от 1 до 2 секунд между FMZ
- Как управлять несколькими аккаунтами на одном диске
- Мы не можем получить уведомления о политике.
- Диаграмма распределения цены на кукурузные изделия
- Проблема с сообщениями об ошибках на диске
- Почему микрокредиты не могут быть пересчитаны?
- Стратегия сетки