ابتدائی، اسے چیک کریں آپ کو کریپٹوکرنسی کی کوانٹیٹیٹیو ٹریڈنگ میں لے جائیں (5)
مصنف:نینا باداس, تخلیق: 2022-04-18 17:20:53, تازہ کاری: 2022-04-18 17:30:27ابتدائی، اسے چیک کریں آپ کو کریپٹوکرنسی کی کوانٹیٹیٹیو ٹریڈنگ میں لے جائیں (5)
پچھلے مضمون میں ، ہم نے ایک سادہ گرڈ حکمت عملی کے تجارتی منطق تجزیہ کی وضاحت کی۔ اس مضمون میں ، ہم اس تدریسی حکمت عملی کے ڈیزائن کو مکمل کرتے رہیں گے۔
- تجارتی منطق کا تجزیہ
جیسا کہ ہم نے پچھلے مضمون میں ذکر کیا ہے ، جب تک کہ آپ گرڈ کی ہر گرڈ لائن کو عبور کرتے ہیں اور فیصلہ کرتے ہیں کہ موجودہ قیمت گرڈ لائن کو اوپر یا نیچے عبور کرتی ہے ، تب ہی تجارتی عمل شروع ہوسکتا ہے۔ لیکن حقیقت میں ، ابھی بھی بہت ساری منطقی تفصیلات موجود ہیں ، اور ابتدائی لوگ جو حکمت عملی کی تحریر کو نہیں سمجھتے ہیں وہ اکثر غلط فہمی کا شکار ہوتے ہیں کہ
منطق بہت آسان ہے ، کوڈ میں صرف چند لائنیں ہونی چاہئیں ، اور اصل تحریر میں ابھی بھی بہت ساری تفصیلات ملتی ہیں۔
پہلی تفصیل جس پر ہمیں غور کرنا ہے وہ ہے لامحدود گرڈ کا ڈیزائن۔ یاد رکھیں پچھلے مضمون میں ہم نے ایک فنکشن ڈیزائن کیا تھاcreateNetایک ساتھ مل کر ابتدائی گرڈ ڈیٹا ڈھانچہ تیار کرنے کے لئے؟ یہ فنکشن گرڈ ڈیٹا ڈھانچہ تیار کرتا ہے جس میں گرڈ لائنوں کی ایک محدود تعداد ہوتی ہے۔ تو کیا ہوگا اگر ، جب حکمت عملی چل رہی ہے تو ، قیمت اس گرڈ ڈیٹا ڈھانچے کی حدود سے باہر جاتی ہے (اوپر گرڈ لائن سے آگے جہاں قیمت سب سے زیادہ ہے ، اور نیچے گرڈ لائن جہاں قیمت سب سے کم ہے) ۔
تو سب سے پہلے ہمیں گرڈ ڈیٹا ڈھانچے میں ایک توسیع میکانزم شامل کرنے کی ضرورت ہے۔
حکمت عملی کا بنیادی فنکشن لکھنا شروع کریں، اور بنیادی فنکشن وہ کوڈ ہے جہاں حکمت عملی کا نفاذ شروع ہوتا ہے۔
var diff = 50 // global variable, the grid interval, can be designed as parameter; for an easy explanation, we write it in an infinite loop
function main() {
// After the bot starts running, execute the strategy code from here
var ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker) // obtain the latest ticker data in the market; for the ticker data structure, you can refer to FMZ API documentation: https://www.fmz.com/api#ticker
var net = createNet(ticker.Last, diff) // the function to initially construct the grid data structure we designed in the previous article; here we construct a grid data structure net
while (true) { // then, the program logic enters the while infinite loop, and the strategy will repeatedly execute the code within the {} symbol from here
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker) // the first line of the infinite loop code gets the latest market quote data, and updates it to the variable ticker
// check the grid range
while (ticker.Last >= net[net.length - 1].price) {
net.push({
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : net[net.length - 1].price + diff,
})
}
while (ticker.Last <= net[0].price) {
var price = net[0].price - diff
if (price <= 0) {
break
}
net.unshift({
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : price,
})
}
// the code is not completed...
}
}
یہ وہ کوڈ ہے جو گرڈ ڈیٹا ڈھانچے کو توسیع پذیر بناتا ہے (اوپر والے کوڈ سے اخذ کیا گیا ہے):
// check the grid range
while (ticker.Last >= net[net.length - 1].price) { // if the price exceeds the grid line with the highest price in the grid,
net.push({ // add a new grid line after the grid line with the highest price in the grid
buy : false, // initialize the sell mark
sell : false, // initialize the buy mark
price : net[net.length - 1].price + diff, // add a grid interval on the basis of the previous highest price
})
}
while (ticker.Last <= net[0].price) { // if the price is lower than the grid line with the lowest price in the grid,
var price = net[0].price - diff // distinguished from adding upwards, you should notice the price of the newly added grid line downwards cannot be less than or equal to 0, so you need to judge here
if (price <= 0) { // do not add when the price is less than or equal to 0, and break the loop
break
}
net.unshift({ // add a new grid line before the grid line with the lowest price in the grid
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : price,
})
}
اگلا، ہمیں غور کرنے کی ضرورت ہے کہ کس طرح ٹریڈنگ ٹرگر کو لاگو کرنا ہے.
var diff = 50
var amount = 0.002 // add a global variable, which can also be designed as a parameter; for easy explanation, we can write it in an infinite loop
// the parameter controls the trading amount on the grid line each time the trading is triggered
function main() {
var ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
var net = createNet(ticker.Last, diff)
var preTicker = ticker // before the start of the main (infinite) loop, set a variable, to record the market quotes of last time
while (true) {
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
// check the grid range
while (ticker.Last >= net[net.length - 1].price) {
net.push({
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : net[net.length - 1].price + diff,
})
}
while (ticker.Last <= net[0].price) {
var price = net[0].price - diff
if (price <= 0) {
break
}
net.unshift({
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : price,
})
}
// index the grid
for (var i = 0 ; i < net.length ; i++) { // traverse all grid lines in the grid data structure
var p = net[i]
if (preTicker.Last < p.price && ticker.Last > p.price) { // upcross, and sell; when the current node has been traded, no matter SELL or BUY, no more trade
if (i != 0) {
var downP = net[i - 1]
if (downP.buy) {
exchange.Sell(-1, amount, ticker)
downP.buy = false
p.sell = false
continue
}
}
if (!p.sell && !p.buy) {
exchange.Sell(-1, amount, ticker)
p.sell = true
}
} else if (preTicker.Last > p.price && ticker.Last < p.price) { // downcross, and buy
if (i != net.length - 1) {
var upP = net[i + 1]
if (upP.sell) {
exchange.Buy(-1, amount * ticker.Last, ticker)
upP.sell = false
p.buy = false
continue
}
}
if (!p.buy && !p.sell) {
exchange.Buy(-1, amount * ticker.Last, ticker)
p.buy = true
}
}
}
preTicker = ticker // record the current market quotes in preTicker, which will be used as the "last" market quote data to compare with the new one in next loop, to judge upcross and downcross
Sleep(500)
}
}
آپ دیکھ سکتے ہیں:
- گرڈ لائن کو عبور کرنے کی حالت:preTicker.Last < p.price && ticker.Last > p.price- گرڈ لائن کو عبور کرنے کی شرط:preTicker.Last > p.price && ticker.Last < p.price
پچھلے مضمون میں اس کے بارے میں بات کی گئی تھی:
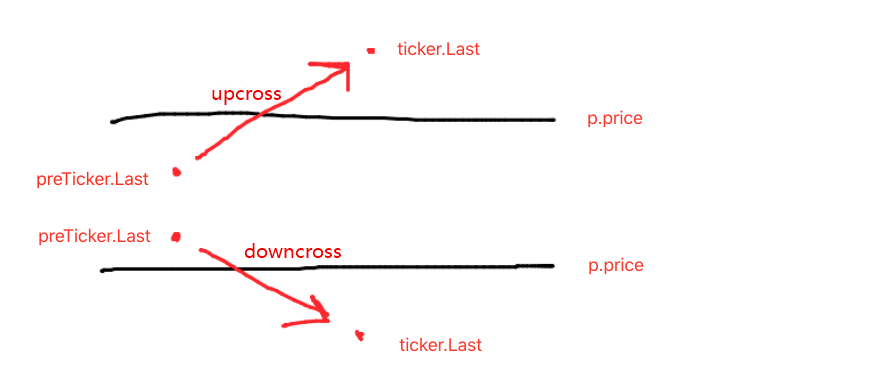
اپ کراس یا ڈاون کراس کا فیصلہ کرنا صرف پہلا قدم ہے کہ آیا آرڈر اور تجارت کرنا ہے ، اور گرڈ لائن کے اعداد و شمار میں نشان کا بھی فیصلہ کرنے کی ضرورت ہے۔
اگر یہ اوپر کی طرف ہے تو ، فیصلہ کریں کہ کیا قیمت موجودہ گرڈ لائن سے کم ہے ، نیز تازہ ترین گرڈ لائن پر خرید مارک۔ اگر خرید مارک کی قدر درست ہے تو ، اس کا مطلب ہے کہ آخری گرڈ لائن نے خریدا ، اور آخری گرڈ لائن کے خرید مارک کو غلط کے طور پر ری سیٹ کریں ، اور موجودہ گرڈ لائن کے فروخت مارک کو غلط کے طور پر ری سیٹ کریں۔
ابھی ذکر کردہ شرائط کا فیصلہ کرنے کے بعد ، اگر وہ متحرک نہیں ہوتے ہیں تو ، فیصلہ کرنا جاری رکھیں۔ اگر موجودہ گرڈ لائن کا خرید مارک اور فروخت مارک دونوں غلط ہیں تو ، اس کا مطلب یہ ہے کہ موجودہ گرڈ لائن تجارت کرسکتی ہے۔ کیونکہ یہ اوپر کی طرف ہے ، یہاں ہم فروخت آپریشن کو انجام دیتے ہیں ، اور عمل درآمد کے بعد گرڈ لائن کے فروخت مارک کو درست کے طور پر نشان زد کرتے ہیں۔
ڈاون کراس پروسیسنگ کا منطق ایک ہی ہے. (نوائے کاروں کو اپنے آپ کو اس کے بارے میں سوچ سکتے ہیں.)
مکمل حکمت عملی بیک ٹیسٹ
backtest کے دوران کچھ اعداد و شمار کو دیکھنے کے لئے، ایک تقریبshowTblاعداد و شمار کو ظاہر کرنے کے لئے لکھا جاتا ہے.
function showTbl(arr) {
var tbl = {
type : "table",
title : "grid",
cols : ["grid information"],
rows : []
}
var arrReverse = arr.slice(0).reverse()
_.each(arrReverse, function(ele) {
var color = ""
if (ele.buy) {
color = "#FF0000"
} else if (ele.sell) {
color = "#00FF00"
}
tbl.rows.push([JSON.stringify(ele) + color])
})
LogStatus(_D(), "\n`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`", "\n account information:", exchange.GetAccount())
}
مکمل حکمت عملی کا کوڈ:
/*backtest
start: 2021-04-01 22:00:00
end: 2021-05-22 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"OKEX","currency":"ETH_USDT","balance":100000}]
*/
var diff = 50
var amount = 0.002
function createNet(begin, diff) {
var oneSideNums = 10
var up = []
var down = []
for (var i = 0 ; i < oneSideNums ; i++) {
var upObj = {
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : begin + diff / 2 + i * diff,
}
up.push(upObj)
var j = (oneSideNums - 1) - i
var downObj = {
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : begin - diff / 2 - j * diff,
}
if (downObj.price <= 0) { // the price cannot be less than or equal to 0
continue
}
down.push(downObj)
}
return down.concat(up)
}
function showTbl(arr) {
var tbl = {
type : "table",
title : "grid",
cols : ["grid information"],
rows : []
}
var arrReverse = arr.slice(0).reverse()
_.each(arrReverse, function(ele) {
var color = ""
if (ele.buy) {
color = "#FF0000"
} else if (ele.sell) {
color = "#00FF00"
}
tbl.rows.push([JSON.stringify(ele) + color])
})
LogStatus(_D(), "\n`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`", "\n account information:", exchange.GetAccount())
}
function main() {
var ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
var net = createNet(ticker.Last, diff)
var preTicker = ticker
while (true) {
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
// check the grid range
while (ticker.Last >= net[net.length - 1].price) {
net.push({
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : net[net.length - 1].price + diff,
})
}
while (ticker.Last <= net[0].price) {
var price = net[0].price - diff
if (price <= 0) {
break
}
net.unshift({
buy : false,
sell : false,
price : price,
})
}
// index grid
for (var i = 0 ; i < net.length ; i++) {
var p = net[i]
if (preTicker.Last < p.price && ticker.Last > p.price) { // upcross, and sell; when the current node has been traded, no matter SELL or BUY, no more trade
if (i != 0) {
var downP = net[i - 1]
if (downP.buy) {
exchange.Sell(-1, amount, ticker)
downP.buy = false
p.sell = false
continue
}
}
if (!p.sell && !p.buy) {
exchange.Sell(-1, amount, ticker)
p.sell = true
}
} else if (preTicker.Last > p.price && ticker.Last < p.price) { // downcross, and buy
if (i != net.length - 1) {
var upP = net[i + 1]
if (upP.sell) {
exchange.Buy(-1, amount * ticker.Last, ticker)
upP.sell = false
p.buy = false
continue
}
}
if (!p.buy && !p.sell) {
exchange.Buy(-1, amount * ticker.Last, ticker)
p.buy = true
}
}
}
showTbl(net)
preTicker = ticker
Sleep(500)
}
}
حکمت عملی بیک ٹیسٹ:
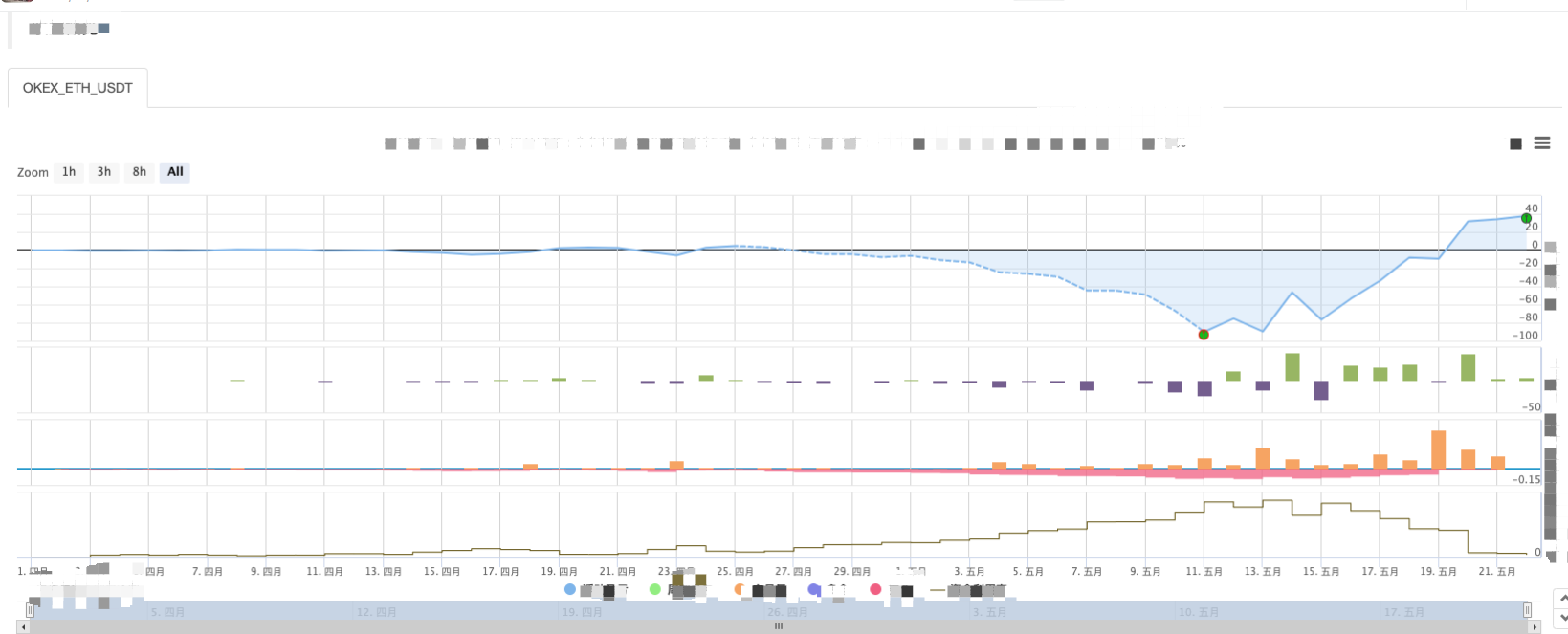
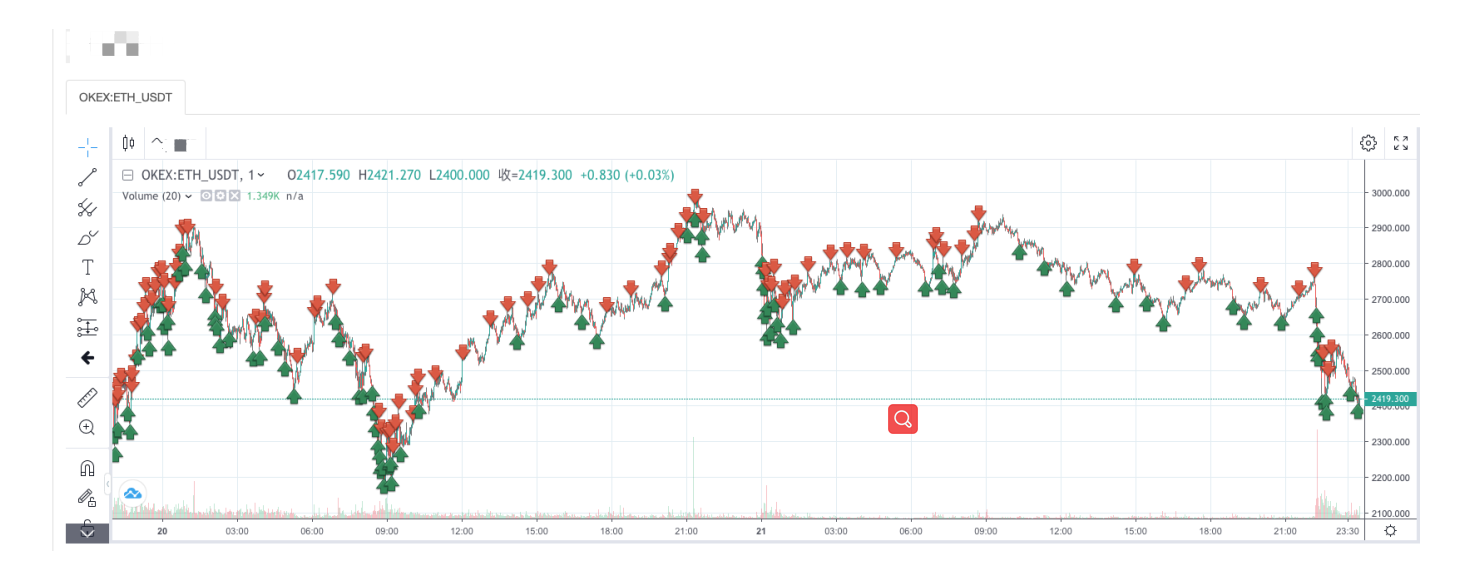
آپ گرڈ کی حکمت عملی کی خصوصیات دیکھ سکتے ہیں۔ جب مارکیٹ میں رجحان ہوتا ہے تو ، ایک بڑا تیرتا نقصان ہوگا ، اور واپسی ایک غیر مستحکم مارکیٹ میں بحال ہوگی۔ لہذا ، گرڈ حکمت عملی خطرے سے پاک نہیں ہے۔ اسپاٹ حکمت عملی اب بھی اسے برابر کرنے کے لئے برقرار رکھ سکتی ہے ، جبکہ مستقبل کے معاہدوں کی گرڈ حکمت عملی زیادہ خطرناک ہے اور اسے گرڈ پیرامیٹرز کو محتاط طریقے سے ترتیب دینے کی ضرورت ہے۔
- my زبان میں یہاں کیسے لکھا جائے تاکہ سگنل ہو سکے صرف ایک بار پرنٹ کریں اور آؤٹ پٹ کریں
- ڈیریبیٹ آپشنز کی متحرک ڈیلٹا ہیجنگ
- FMZ کوانٹ ڈیٹا بیس کی تعمیر کے لئے SQLite کا استعمال کریں
- ابتدائی، اسے چیک کریں
آپ کو کریپٹوکرنسی کی کوانٹیٹیٹیو ٹریڈنگ میں لے جائیں (8) - نوکریاں، اسے چیک کریں
آپ کو کریپٹوکرنسی کی مقدار کی تجارت میں لے جائیں (7) - ابتدائی، اسے چیک کریں
آپ کو کریپٹوکرنسی کی مقدار کی تجارت میں لے جائیں (6) - ابتدائی، اسے چیک کریں
آپ کو کریپٹوکرنسی مقداری تجارت میں لے جائیں (3) - ابتدائی، اسے چیک کریں
آپ کو کریپٹوکرنسی مقداری تجارت میں لے جائیں (2) - میرے موجد کی ٹائمنگ غلط ہے
- کیا آپ کو لگتا ہے کہ آپ کو اس کے بارے میں مزید جاننے کی ضرورت ہے؟
- ابتدائی، اسے چیک کریں
آپ کو کریپٹوکرنسی کی مقدار کی تجارت میں لے جائیں (4) - آرڈر بنانے کا وقت اور آرڈر مکمل کرنے کا وقت
- مارٹن کی خریداری کے لئے فوری نیٹ کی حکمت عملی
- میری زبان کو سمجھنے والے بھائیو ، مجھے اس کوڈ کا مطلب سمجھنے میں مدد کریں _TR:=MAX ((MAX (((HIGH-LOW ،ABS ((REF ((CLOSE ،1) -HIGH) ،ABS ((REF ((CLOSE ،1) -LOW));
- غلطی کی اطلاع دینے کے لئے سوالات
- نوکریاں، اسے چیک کریں
آپ کو کریپٹوکرنسی مقداری تجارت میں لے جائیں (1) - کیا آپ ٹائپسکرپٹ کی حمایت میں اضافہ کر سکتے ہیں؟
- کریپٹوکرنسی اسپاٹ ہیجنگ حکمت عملی (2)
- کریپٹوکرنسی اسپاٹ ہیجنگ حکمت عملی (1)
- Bitget API میں ، ADA ، AVAX ، AXS ، BCH ، DOT ، EOS ، ETC ، FIL ، LINK ، LTC ، LUNA ، MATIC ، SOL ، XRP کے ساتھ لین دین کے ساتھ مسائل پیدا ہوتے ہیں۔