Automated Trading Systems: The Pros and Cons
 0
0
 1430
1430
Traders and investors can turn precise entry, exit and money management rules into automated trading systems that allow computers to execute and monitor the trades. One of the biggest attractions of strategy automation is that it can take some of the emotion out of trading since trades are automatically placed once certain criteria are met.
This article introduces readers to and explains some of the advantages and disadvantages, as well as the realities, of automated trading systems.
What Is an Automated Trading System?
Automated trading systems — also referred to as mechanical trading systems, algorithmic trading, automated trading or system trading — allow traders to establish specific rules for both trade entries and exits that, once programmed, can be automatically executed via a computer. In fact, roughly 75% of shares traded on U.S. stock exchanges come from automatic trading systems.
The trade entry and exit rules can be based on simple conditions such as a moving average crossover or they can be complicated strategies that require a comprehensive understanding of the programming language specific to the user’s trading platform. They can also be based on the expertise of a qualified programmer.
Automated trading systems typically require the use of software linked to a direct access broker, and any specific rules must be written in that platform’s proprietary language. The TradeStation platform, for example, uses the EasyLanguage programming language. On the other hand, the NinjaTrader platform utilizes NinjaScript. The figure below shows an example of an automated strategy that triggered three trades during a trading session.
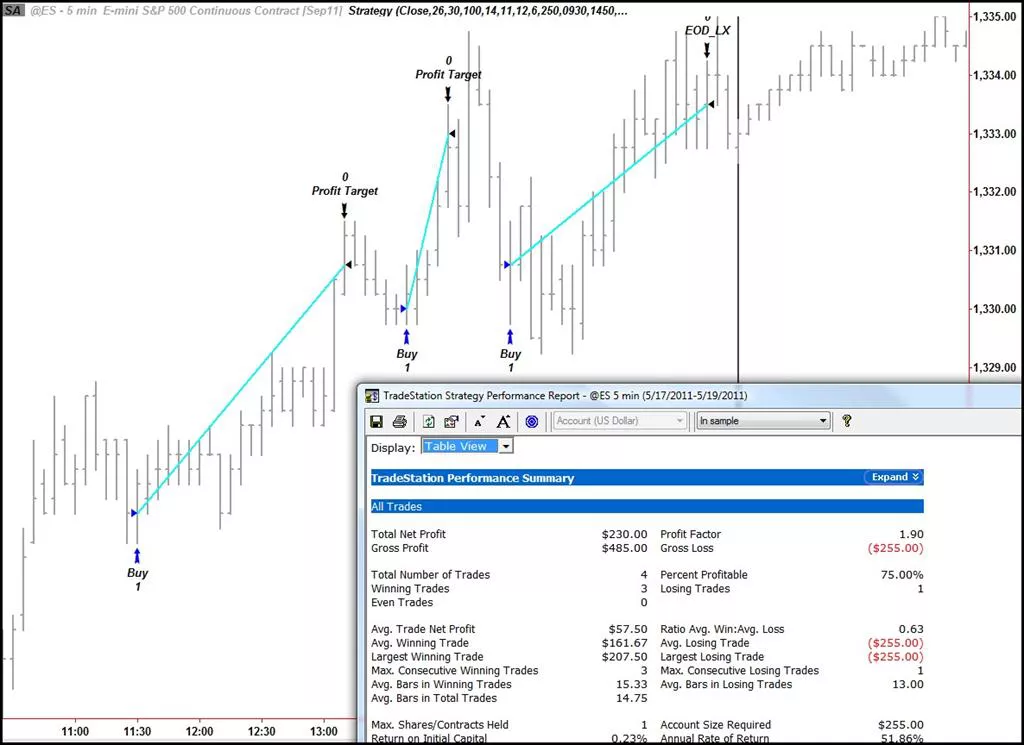
A five-minute chart of the ES contract with an automated strategy applied.
Establishing the “Rules” of Trading
Some trading platforms have strategy-building “wizards” that allow users to make selections from a list of commonly available technical indicators to build a set of rules that can then be automatically traded. The user could establish, for example, that a long trade will be entered once the 50-day moving average crosses above the 200-day moving average on a five-minute chart of a particular trading instrument. Users can also input the type of order (market or limit, for instance) and when the trade will be triggered (for example, at the close of the bar or open of the next bar), or use the platform’s default inputs.
Many traders, however, choose to program their own custom indicators and strategies or work closely with a programmer to develop the system. While this typically requires more effort than using the platform’s wizard, it allows a much greater degree of flexibility, and the results can be more rewarding. Just like anything else in the trading world, there is, unfortunately, no perfect investment strategy that will guarantee success.
Once the rules have been established, the computer can monitor the markets to find buy or sell opportunities based on the trading strategy’s specifications. Depending on the specific rules, as soon as a trade is entered, any orders for protective stop losses, trailing stops and profit targets will be automatically generated. In fast-moving markets, this instantaneous order entry can mean the difference between a small loss and a catastrophic loss in the event the trade moves against the trader.
Advantages of Automated Trading Systems
There is a long list of advantages to having a computer monitor the markets for trading opportunities and execute the trades, including:
Minimizing emotions. Automated trading systems minimize emotions throughout the trading process. By keeping emotions in check, traders typically have an easier time sticking to the plan. Since trade orders are executed automatically once the trade rules have been met, traders will not be able to hesitate or question the trade. In addition to helping traders who are afraid to “pull the trigger,” automated trading can curb those who are apt to overtrade — buying and selling at every perceived opportunity.
Backtesting. Backtesting applies trading rules to historical market data to determine the viability of the idea. When designing a system for automated trading, all rules need to be absolute, with no room for interpretation. The computer cannot make guesses and it has to be told exactly what to do. Traders can take these precise sets of rules and test them on historical data before risking money in live trading. Careful backtesting allows traders to evaluate and fine-tune a trading idea, and to determine the system’s expectancy – i.e., the average amount a trader can expect to win (or lose) per unit of risk.
Preserving discipline. Because trade rules are established and trade execution is performed automatically, discipline is preserved even in volatile markets. Discipline is often lost due to emotional factors such as fear of taking a loss, or the desire to eke out a little more profit from a trade. Automated trading helps ensure discipline is maintained because the trading plan will be followed exactly. In addition, “pilot error” is minimized. For instance, an order to buy 100 shares will not be incorrectly entered as an order to sell 1,000 shares.
Achieving consistency. One of the biggest challenges in trading is to plan the trade and trade the plan. Even if a trading plan has the potential to be profitable, traders who ignore the rules are altering any expectancy the system would have had. There is no such thing as a trading plan that wins 100% of the time. After all, losses are a part of the game. But losses can be psychologically traumatizing, so a trader who has two or three losing trades in a row might decide to skip the next trade. If this next trade would have been a winner, the trader has already destroyed any expectancy the system had. Automated trading systems allow traders to achieve consistency by trading the plan.
Improving Order Entry Speed. Since computers respond immediately to changing market conditions, automated systems are able to generate orders as soon as trade criteria are met. Getting in or out of a trade a few seconds earlier can make a big difference in the trade’s outcome. As soon as a position is entered, all other orders are automatically generated, including protective stop losses and profit targets. Markets can move quickly, and it is demoralizing to have a trade reach the profit target or blow past a stop-loss level – before the orders can even be entered. An automated trading system prevents this from happening.
Diversifying Trading. Automated trading systems permit the user to trade multiple accounts or various strategies at one time. This has the potential to spread risk over various instruments while creating a hedge against losing positions. What would be incredibly challenging for a human to accomplish is efficiently executed by a computer in milliseconds. The computer is able to scan for trading opportunities across a range of markets, generate orders and monitor trades.
Cons and Realities of Automated Trading Systems
Automated trading systems boast many advantages, but there are some downfalls and realities traders should be aware of.
Mechanical failures. The theory behind automated trading makes it seem simple: Set up the software, program the rules and watch it trade. In reality, automated trading is a sophisticated method of trading, yet not infallible. Depending on the trading platform, a trade order could reside on a computer, not a server. What that means is that if an internet connection is lost, an order might not be sent to the market. There could also be a discrepancy between the “theoretical trades” generated by the strategy and the order entry platform component that turns them into real trades. Most traders should expect a learning curve when using automated trading systems, and it is generally a good idea to start with small trade sizes while the process is refined.
Monitoring. Although it would be great to turn on the computer and leave for the day, automated trading systems do require monitoring. This is because of the potential for technology failures, such as connectivity issues, power losses or computer crashes, and to system quirks. It is possible for an automated trading system to experience anomalies that could result in errant orders, missing orders or duplicate orders. If the system is monitored, these events can be identified and resolved quickly.
Over-optimization. Though not specific to automated trading systems, traders who employ backtesting techniques can create systems that look great on paper and perform terribly in a live market. Over-optimization refers to excessive curve-fitting that produces a trading plan unreliable in live trading. It is possible, for example, to tweak a strategy to achieve exceptional results on the historical data on which it was tested. Traders sometimes incorrectly assume a trading plan should have close to 100% profitable trades or should never experience a drawdown to be a viable plan. As such, parameters can be adjusted to create a “near perfect” plan — that completely fails as soon as it is applied to a live market.
Avoid the Scams
While you search for your preferred system, remember: If it sounds too good to be true, it probably is. There are a lot of scams going around. Some systems promise high profits all for a low price. So how do you tell whether a system is legitimate or fake? Here are a few basic tips:
Scrutinize anything you’d have to pay for before you pay or lay down any money for a trading account and always ask questions. If you don’t, you may lose money in the end.
Do your research and make sure you know everything about the system in question. And be sure to read the terms and conditions before you commit.
Are there any testimonials you can read? Check third-party sites or even financial regulatory sites for reviews.
Does the system come with a trial period? A lot of scam sites won’t offer you a trial.
Server-Based Automation
Traders do have the option to run their automated trading systems through a server-based trading platform. These platforms frequently offer commercial strategies for sale so traders can design their own systems or the ability to host existing systems on the server-based platform. For a fee, the automated trading system can scan for, execute and monitor trades, with all orders residing on the server. This often results in potentially faster, more reliable order entries.
What to Know Before you Automate
The word “automation” may seem like it makes the task simpler, but there are definitely a few things you will need to keep in mind before you start using these systems.
Ask yourself if you should use an automated trading system. There are definitely promises of making money, but it can take longer than you may think. Will you be better off to trade manually? After all, these trading systems can be complex and if you don’t have the experience, you may lose out.
Know what you’re getting into and make sure you understand the ins and outs of the system. That means keeping your goals and your strategies simple before you turn to more complicated trading strategies.
And remember, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. You will need to figure out your preferred strategy, where you want to apply it and just how much you want to customize to your own personal situation. All of that, of course, goes along with your end goals
The Bottom Line
Although appealing for a variety of reasons, automated trading systems should not be considered a substitute for carefully executed trading. Technology failures can happen, and as such, these systems do require monitoring. Server-based platforms may provide a solution for traders wishing to minimize the risks of mechanical failures. Remember, you should have some trading experience and knowledge before you decide to use automated trading systems.
- How to make your own trading bot
- Top 5 Essential Beginner Books for Algorithmic Trading
- Can Algorithmic Traders Still Succeed at the Retail Level?
- 网格
- Steps to Becoming a Quant Trader
- 增加期货定单类型
- 扩展API里有添加交易所的API接口么
- 求助,部署的托管着不好使
- 请问如何做一个监控地址的程序
- Everything You Need To Know About Automated Trading
- Learn Algorithmic Trading: A Step By Step Guide
- High-Frequency Trading: A Primer
- Intro To Algo Trading
- Basics of Algorithmic Trading: Concepts and Examples
- The explanation of "Fundamental Analysis"
- bitmex
- Linux托管者安装和升级最佳方法
- 12.Chart Analyzing Tutorials: Conclusion
- There are 3 major categories for purchase or rent strategies on our platform
- 11.Chart Analyzing Tutorials: Round Bottoms