Lehren Sie, eine K-Linie Synthese-Funktion in der Python-Version zu schreiben
Schriftsteller:FMZ~Lydia, Erstellt: 2022-12-26 09:28:58, Aktualisiert: 2024-12-15 16:36:45
Lehren Sie, eine K-Linie Synthese-Funktion in der Python-Version zu schreiben
Bei der Erstellung und Verwendung von Strategien verwenden wir oft einige selten verwendete K-Linien-Periodendaten. Allerdings liefern Austausch und Datenquellen keine Daten zu diesen Perioden. Es kann nur durch die Verwendung von Daten mit einer vorhandenen Periode synthetisiert werden. Der synthetisierte Algorithmus hat bereits eine JavaScript-Version (VerbindungEs ist einfach, ein Stück JavaScript-Code in Python zu transplantieren. Als nächstes schreiben wir eine Python-Version des K-Line-Synthese-Algorithmus.
JavaScript-Version
function GetNewCycleRecords (sourceRecords, targetCycle) { // K-line synthesis function
var ret = []
// Obtain the period of the source K-line data first
if (!sourceRecords || sourceRecords.length < 2) {
return null
}
var sourceLen = sourceRecords.length
var sourceCycle = sourceRecords[sourceLen - 1].Time - sourceRecords[sourceLen - 2].Time
if (targetCycle % sourceCycle != 0) {
Log("targetCycle:", targetCycle)
Log("sourceCycle:", sourceCycle)
throw "targetCycle is not an integral multiple of sourceCycle."
}
if ((1000 * 60 * 60) % targetCycle != 0 && (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24) % targetCycle != 0) {
Log("targetCycle:", targetCycle)
Log("sourceCycle:", sourceCycle)
Log((1000 * 60 * 60) % targetCycle, (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24) % targetCycle)
throw "targetCycle cannot complete the cycle."
}
var multiple = targetCycle / sourceCycle
var isBegin = false
var count = 0
var high = 0
var low = 0
var open = 0
var close = 0
var time = 0
var vol = 0
for (var i = 0 ; i < sourceLen ; i++) {
// Get the time zone offset value
var d = new Date()
var n = d.getTimezoneOffset()
if (((1000 * 60 * 60 * 24) - sourceRecords[i].Time % (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24) + (n * 1000 * 60)) % targetCycle == 0) {
isBegin = true
}
if (isBegin) {
if (count == 0) {
high = sourceRecords[i].High
low = sourceRecords[i].Low
open = sourceRecords[i].Open
close = sourceRecords[i].Close
time = sourceRecords[i].Time
vol = sourceRecords[i].Volume
count++
} else if (count < multiple) {
high = Math.max(high, sourceRecords[i].High)
low = Math.min(low, sourceRecords[i].Low)
close = sourceRecords[i].Close
vol += sourceRecords[i].Volume
count++
}
if (count == multiple || i == sourceLen - 1) {
ret.push({
High : high,
Low : low,
Open : open,
Close : close,
Time : time,
Volume : vol,
})
count = 0
}
}
}
return ret
}
Es gibt JavaScript-Algorithmen. Python kann Zeile für Zeile übersetzt und transplantiert werden. Wenn Sie auf JavaScript-Eingebettete Funktionen oder inhärente Methoden stoßen, können Sie zu Python gehen, um die entsprechenden Methoden zu finden. Daher ist die Migration einfach.
Die Algorithmuslogik ist genau die gleiche, außer dass JavaScript Funktion Anrufevar n=d.getTimezoneOffset(). Wenn Sie auf Python migrieren,n=time.altzonein Python
Migrationscode für Python:
import time
def GetNewCycleRecords(sourceRecords, targetCycle):
ret = []
# Obtain the period of the source K-line data first
if not sourceRecords or len(sourceRecords) < 2 :
return None
sourceLen = len(sourceRecords)
sourceCycle = sourceRecords[-1]["Time"] - sourceRecords[-2]["Time"]
if targetCycle % sourceCycle != 0 :
Log("targetCycle:", targetCycle)
Log("sourceCycle:", sourceCycle)
raise "targetCycle is not an integral multiple of sourceCycle."
if (1000 * 60 * 60) % targetCycle != 0 and (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24) % targetCycle != 0 :
Log("targetCycle:", targetCycle)
Log("sourceCycle:", sourceCycle)
Log((1000 * 60 * 60) % targetCycle, (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24) % targetCycle)
raise "targetCycle cannot complete the cycle."
multiple = targetCycle / sourceCycle
isBegin = False
count = 0
barHigh = 0
barLow = 0
barOpen = 0
barClose = 0
barTime = 0
barVol = 0
for i in range(sourceLen) :
# Get the time zone offset value
n = time.altzone
if ((1000 * 60 * 60 * 24) - (sourceRecords[i]["Time"] * 1000) % (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24) + (n * 1000)) % targetCycle == 0 :
isBegin = True
if isBegin :
if count == 0 :
barHigh = sourceRecords[i]["High"]
barLow = sourceRecords[i]["Low"]
barOpen = sourceRecords[i]["Open"]
barClose = sourceRecords[i]["Close"]
barTime = sourceRecords[i]["Time"]
barVol = sourceRecords[i]["Volume"]
count += 1
elif count < multiple :
barHigh = max(barHigh, sourceRecords[i]["High"])
barLow = min(barLow, sourceRecords[i]["Low"])
barClose = sourceRecords[i]["Close"]
barVol += sourceRecords[i]["Volume"]
count += 1
if count == multiple or i == sourceLen - 1 :
ret.append({
"High" : barHigh,
"Low" : barLow,
"Open" : barOpen,
"Close" : barClose,
"Time" : barTime,
"Volume" : barVol,
})
count = 0
return ret
# Test
def main():
while True:
r = exchange.GetRecords()
r2 = GetNewCycleRecords(r, 1000 * 60 * 60 * 4)
ext.PlotRecords(r2, "r2")
Sleep(1000)
Prüfung
Marktdiagramm von Huobi
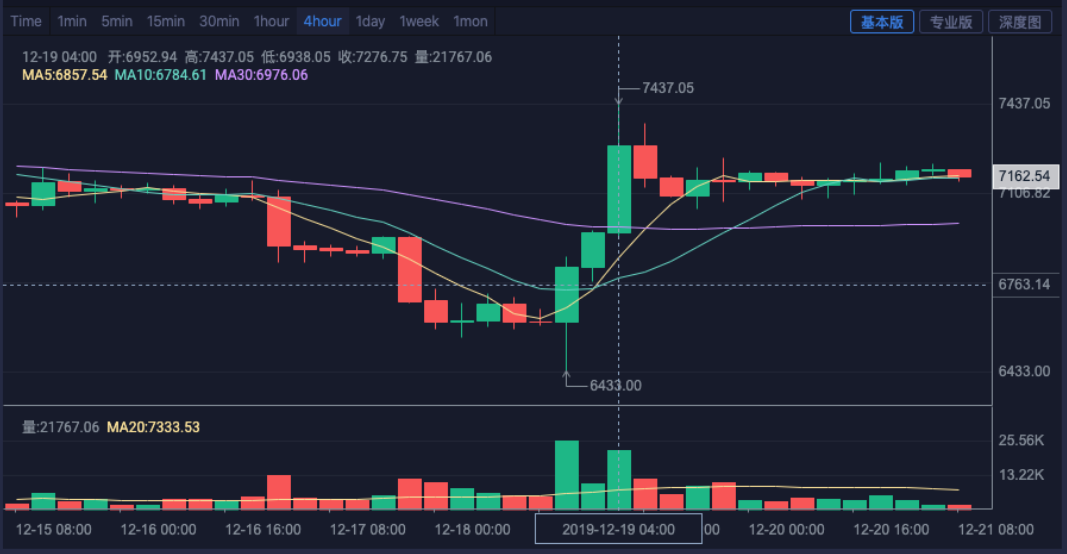
4-Stunden-Diagramm der Backtest-Synthese
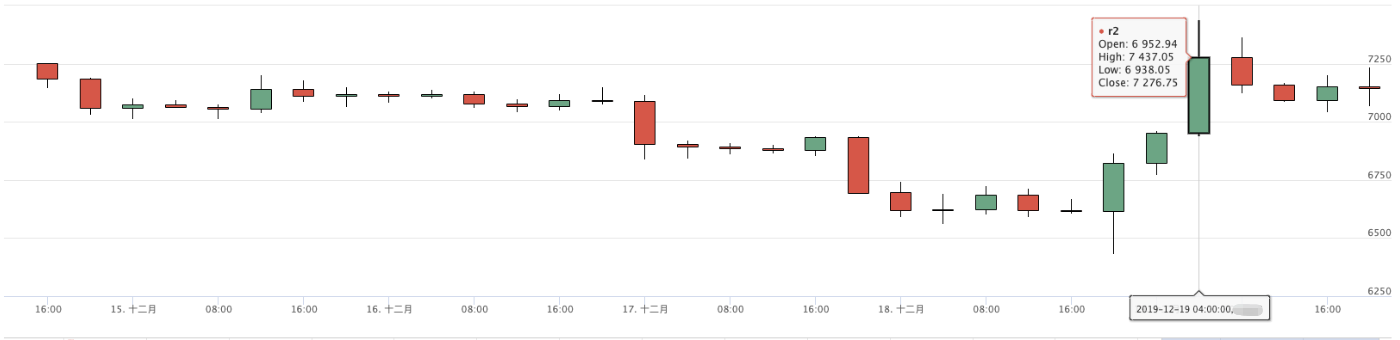
Der oben genannte Code dient nur als Referenz; wenn er in spezifischen Strategien verwendet wird, wird er entsprechend den spezifischen Anforderungen geändert und getestet. Wenn es einen Fehler oder Verbesserungsvorschlag gibt, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht. Vielen Dank. o^_^ o
- Einführung in Lead-Lag-Arbitrage in Kryptowährungen (2)
- Einführung der Lead-Lag-Suite in der digitalen Währung (2)
- Diskussion über den externen Signalempfang der FMZ-Plattform: Eine Komplettlösung für den Empfang von Signalen mit integriertem Http-Service in der Strategie
- FMZ-Plattform: Erforschung von Signalempfangsstrategien für externe Netzwerke
- Einführung in Lead-Lag-Arbitrage in Kryptowährungen (1)
- Einführung der Lead-Lag-Suite in der Kryptowährung (1)
- Diskussion über den externen Signalempfang der FMZ-Plattform: Erweiterte API VS Strategie eingebauter HTTP-Service
- FMZ-Plattform-External Signal Reception: Erweiterung der API vs. Strategien für den eingebauten HTTP-Dienst
- Diskussion über die Strategie-Testmethode auf Basis eines Zufalls-Ticker-Generators
- Strategie-Testmethoden basierend auf Random-Market-Generatoren untersucht
- Neue Funktion von FMZ Quant: _Serve-Funktion zum einfachen Erstellen von HTTP-Diensten
- Paarhandel auf Basis datengetriebener Technologie
- Anwendung der Maschinellen Lerntechnologie im Handel
- Nutzung des Forschungsumfelds zur Analyse der Einzelheiten der dreieckigen Absicherung und der Auswirkungen der Abwicklungsgebühren auf die abgesicherten Preisdifferenzen
- Reform der Deribit-Futures-API zur Anpassung an den quantitativen Handel mit Optionen
- Bessere Werkzeuge machen gute Arbeit - lernen Sie, die Forschungsumgebung zu verwenden, um Handelsprinzipien zu analysieren
- Währungsübergreifende Absicherungsstrategien beim quantitativen Handel mit Blockchain-Assets
- Erwerben Sie den Leitfaden zur Digitalwährungsstrategie von FMex auf FMZ Quant
- Ich lehre Sie Strategien zu schreiben - eine MyLanguage-Strategie transplantieren (Advanced)
- Sie lernen, Strategien zu schreiben -- transplantieren Sie eine MyLanguage-Strategie
- Sie lernen, Multi-Chart-Unterstützung der Strategie hinzuzufügen
- Analyse der Donchian Channel Strategie im Forschungsumfeld
- Wenn FMZ ChatGPT trifft, erinnern Sie sich an einen Versuch, mit AI quantitative Transaktionen zu lernen.
- Nicht mehr verfügbares quantitatives Handelsinstrument für digitale Währungsoptionen
- Einfache Rasterstrategie in Python Version
- Lineare Strategie für den Auftragsfluss, die auf der Grundlage der Datenwiedergabefunktion entwickelt wurde
- Strategie für den Kauf der Gewinner der Python-Version
- FMZ-Reise - mit Übergangsstrategie
- Sie lernen, eine Python-Strategie für eine einzige Art in eine Multi-Species-Strategie umzuwandeln.
- Implementieren Sie ein quantitatives Trading-Roboter-Zeitbeginn oder Stopp-Gadget mit Python
- Oak lehrt Sie, JS zu verwenden, um mit FMZ erweiterte API zu interagieren