Goldener Schnitt - Bandoszillationsstrategie
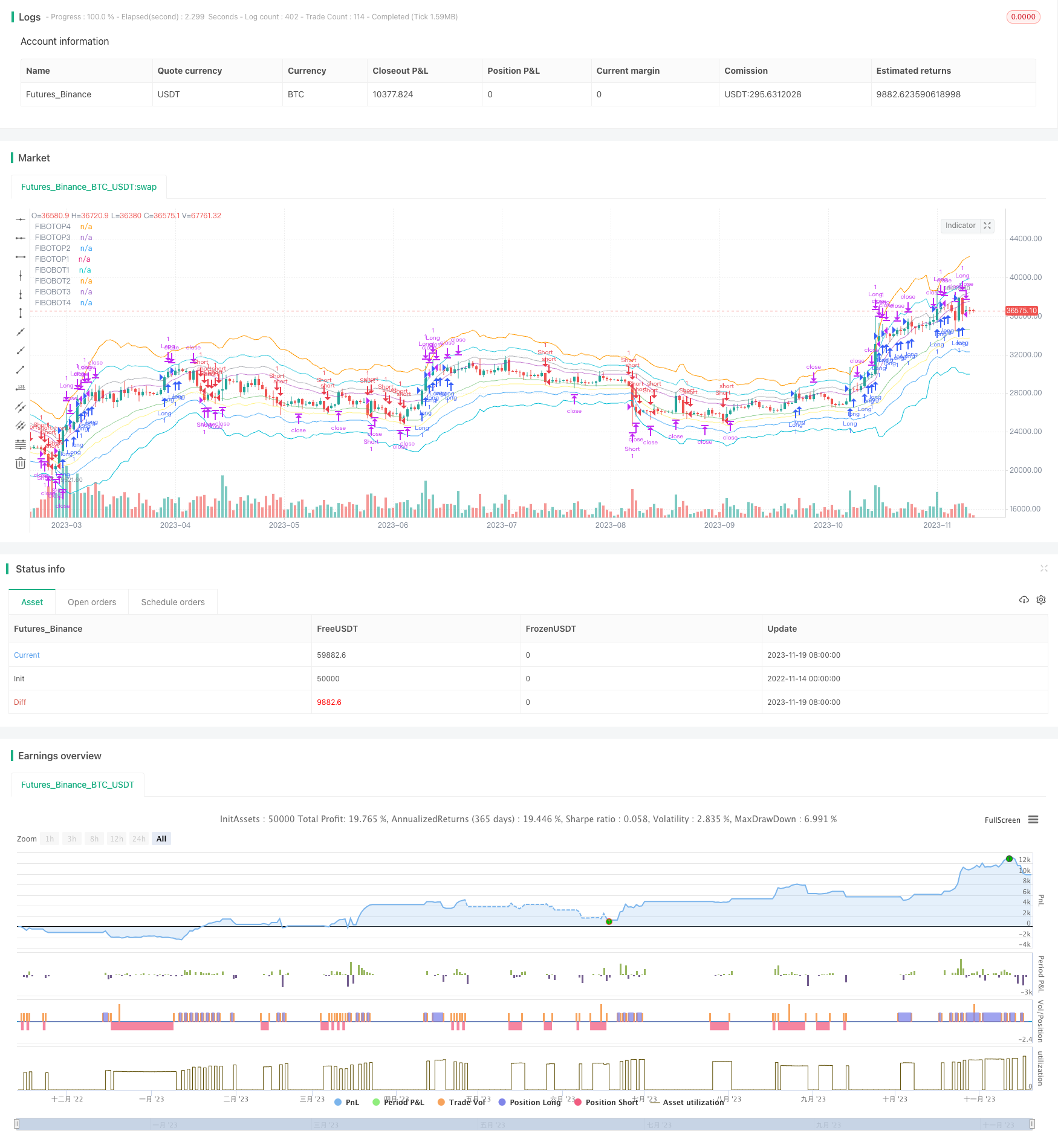
Überblick
Die Goldspaltungsbandschwankungen-Strategie ist eine quantitative Strategie, die auf der Goldspaltungstheorie basiert. Die Strategie verwendet hauptsächlich die Goldspaltungsregel, um mehrere Preisbänder zu berechnen, um die oberen und unteren Bands zu bilden. Die Handelssignale werden erzeugt, wenn der Preis die Bandbrechungen durchbricht, um durch die Erfassung der Eigenschaften der Preisschwankungen zwischen den Bandbrechungen Gewinne zu erzielen.
Strategieprinzip
Die zentrale Logik des Codes besteht darin, den Gold-Splitting-Bereich des Preises als Schlüsselpunkt zu berechnen. Die Hauptschritte sind:
- Berechnen Sie die EMA-Mittellinie für 14 Perioden als mittlere Achse
- Die folgenden 4 Bandbreiten basieren auf der ATR und dem Gold-Split-Ratio.
- Handelsignale werden erzeugt, wenn der Preis eine fallende Bandbreite nach oben oder eine steigende Bandbreite nach unten durchbricht
- Setzen Sie eine Stop-Loss-Stopp-Liste, um Preisschwankungen zu verfolgen
Durch diese Methode, basierend auf einem KPI-Breakthrough, können kurzfristige Marktschwankungen effektiv erfasst und zwischen den Phasen profitabel gehandelt werden.
Strategische Vorteile
Der größte Vorteil dieser Strategie besteht darin, dass die Goldspaltung, ein wichtiger theoretischer Indikator, zur Bestimmung der Schlüsselpreise verwendet wird, um die Gewinnwahrscheinlichkeit zu erhöhen. Die konkreten Vorteile bestehen hauptsächlich aus:
- Die Goldspaltung ist klar und lässt einen Durchbruch erkennen.
- Die richtige Bandbreite, nicht zu klein und nicht zu groß
- Mehrfache Bandbreite zur Auswahl, sowohl aggressiv als auch konservativ
- Die Wellenbänder schwanken deutlich, die Kurzstrecken-Manipulation wirkt.
Strategisches Risiko
Da diese Strategie auf kurzfristige Gewinne ausgerichtet ist, gibt es einige Risiken, die beachtet werden müssen:
- Der Großzyklus ist nicht rentabel
- Das Stop-Loss-Risiko bei starken Preisschwankungen ist höher.
- Mehr Durchbruchsignale, Vorsicht geboten
- Wirkungslos, wenn die Bandschwingungsmerkmale verschwunden sind
Diese Risiken können durch geeignete Parameteranpassungen, die Auswahl geeigneter Bandbreiten und die Vermögensverwaltung gemanagt werden.
Strategieoptimierung
Die Strategie kann noch weiter optimiert werden:
- In Kombination mit einem Trendfilter wird ein Trendsignal erzeugt.
- Strategie abschalten, wenn ein bestimmter Zeitraum oder ein wichtiger Ereignisort vorhanden ist
- Dynamische Anpassung der Stop-Loss-Marge an die Häufigkeit von Marktbewegungen
- Optimierungsparameter für die Auswahl unterschiedlicher Perioden-EMA als Mittelwert
Zusammenfassen
Die Goldsplit-Strategie ist eine sehr praktische Short-Line-Strategie insgesamt. Sie nutzt die Goldsplit-Theorie, um Preis-Kritikpunkte zu setzen, von denen ein großer Gewinn erzielt werden kann, wenn die Preise in der Nähe dieser Punkte schwanken. Diese Bandbrech-basierte Methode eignet sich für Märkte mit einer bestimmten Volatilität und Merkmalen und kann einzeln oder in Kombination mit anderen Strategien verwendet werden.
/*backtest
start: 2022-11-14 00:00:00
end: 2023-11-20 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © drhakankilic
//@version=5
strategy("FIBONACCI BANDS Strategy", shorttitle="FBANDS Strategy", overlay=true)
// === Date === {
//Backtest dates
fromDay = input.int(defval=1, title='From Day',minval=1,maxval=31)
fromMonth = input.int(defval=2, title='From Month',minval=1,maxval=12)
fromYear = input.int(defval=2022, title='From Year')
thruDay = input.int(defval=1, title='Thru Day',minval=1,maxval=31)
thruMonth = input.int(defval=1, title='Thru Month',minval=1,maxval=12)
thruYear = input.int(defval=2112, title='Thru Year')
showDate = true // input(defval=true, title="Show Date Range")
start = timestamp(fromYear, fromMonth, fromDay, 00, 00) // backtest start window
finish = timestamp(thruYear, thruMonth, thruDay, 23, 59) // backtest finish window
window() => // create function "within window of time"
time >= start and time <= finish ? true : false
// }
// === Long or Short ===
tradeDirection = input.string(title="Long veya Short", options=["Long", "Short", "Both"], defval="Both", group="Bot")
// Translate input into trading conditions
longOK = (tradeDirection == "Long") or (tradeDirection == "Both")
shortOK = (tradeDirection == "Short") or (tradeDirection == "Both")
copypaste = input('{{strategy.order.alert_message}}', title='alert message to copy/paste', group="Bot")
// }
// === FIBONACCI BANDS === {
EMAperiod = input.int(14, title='EMAperiod', minval=1, maxval=500, group="Fibonacci")
ATRperiod = input.int(14, title='ATRperiod', minval=1, maxval=500, group="Fibonacci")
EMA = ta.ema(close, EMAperiod)
TR1 = math.max(high - low, math.abs(high - close[1]))
TR = math.max(TR1, math.abs(low - close[1]))
ATR = ta.sma(TR, ATRperiod)
F2 = input(defval=1.618, title='Fibonacci Ratio 2', group="Fibonacci")
F3 = input(defval=2.618, title='Fibonacci Ratio 3', group="Fibonacci")
F4 = input(defval=4.236, title='Fibonacci Ratio 4', group="Fibonacci")
R1 = ATR
R2 = ATR * F2
R3 = ATR * F3
R4 = ATR * F4
FIBOTOP4 = EMA + R4
FIBOTOP3 = EMA + R3
FIBOTOP2 = EMA + R2
FIBOTOP1 = EMA + R1
FIBOBOT1 = EMA - R1
FIBOBOT2 = EMA - R2
FIBOBOT3 = EMA - R3
FIBOBOT4 = EMA - R4
plot(FIBOTOP4[1], title='FIBOTOP4', linewidth=1, color=color.new(color.orange, 0))
plot(FIBOTOP3[1], title='FIBOTOP3', linewidth=1, color=color.new(color.aqua, 20))
plot(FIBOTOP2[1], title='FIBOTOP2', linewidth=1, color=color.new(color.gray, 40))
plot(FIBOTOP1[1], title='FIBOTOP1', linewidth=1, color=color.new(color.purple, 40))
plot(FIBOBOT1[1], title='FIBOBOT1', linewidth=1, color=color.new(color.green, 40))
plot(FIBOBOT2[1], title='FIBOBOT2', linewidth=1, color=color.new(color.yellow, 40))
plot(FIBOBOT3[1], title='FIBOBOT3', linewidth=1, color=color.new(color.blue, 20))
plot(FIBOBOT4[1], title='FIBOBOT4', linewidth=1, color=color.new(color.aqua, 0))
// plot(EMA[1], style=plot.style_cross, title='EMA', color=color.new(color.red, 0))
prefm = input.string(title="Fibo", options=["close>FIBOTOP4(orange)", "close>FIBOTOP3(aqua)","close>FIBOTOP2(gray)","close>FIBOTOP1(purple)", "Disable"] , defval="close>FIBOTOP1(purple)", group="Long")
_prefm = false
if (prefm == "close>FIBOTOP4(orange)" )
_prefm := close>FIBOTOP4[1]
if (prefm == "close>FIBOTOP3(aqua)" )
_prefm := close>FIBOTOP3[1]
if (prefm == "close>FIBOTOP2(gray)" )
_prefm := close>FIBOTOP2[1]
if (prefm == "close>FIBOTOP1(purple)" )
_prefm := close>FIBOTOP2[1]
if (prefm == "Disable" )
_prefm := low<low[1] or low>low[1]
prefmS = input.string(title="Fibo", options=["close<FIBOBOT1(green)", "close<FIBOBOT2(yellow)", "close<FIBOBOT3(blue)", "close<FIBOBOT4(aqua)", "Disable"] , defval="close<FIBOBOT1(green)", group="Short")
_prefmS = false
if (prefmS == "close<FIBOBOT1(green)" )
_prefmS := close<FIBOBOT1[1]
if (prefmS == "close<FIBOBOT2(yellow)" )
_prefmS := close<FIBOBOT2[1]
if (prefmS == "close<FIBOBOT3(blue)" )
_prefmS := close<FIBOBOT3[1]
if (prefmS == "close<FIBOBOT4(aqua)" )
_prefmS := close<FIBOBOT4[1]
if (prefmS == "Disable" )
_prefmS := low<low[1] or low>low[1]
// }
long2= _prefm
short2= _prefmS
//
// === Bot Codes === {
enterlong = input("Long Code", title='Long İlk Alım', group="Long Code")
entershort= input("Short Code", title='Short İlk Alım', group="Short Code")
exitlong = input("Long Exit Code", title='Long Exit', group="Long Code")
exitshort= input("Short Exit Code", title='Short Exit', group="Short Code")
// }
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////TPSL
// Inputs
sl_inp = input.float(4, title='Stop %', step=0.1, group="Long") / 100
tp_inp = input.float(1.5, title='TP %', step=0.1, group="Long") / 100
sl_inp2 = input.float(4, title='Stop %', step=0.1, group="Short") / 100
tp_inp2 = input.float(1.5, title='TP %', step=0.1, group="Short") / 100
longtp = strategy.position_avg_price * (1 + tp_inp)
longstop= strategy.position_avg_price * (1 - sl_inp)
shortstop= strategy.position_avg_price * (1 + sl_inp2)
shorttp = strategy.position_avg_price * (1 - tp_inp2)
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
if window() and strategy.position_size==0 and longOK
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long, when= long2, alert_message=enterlong, comment="Long")
if strategy.position_size>0
strategy.exit("Long", stop= longstop, limit=longtp, alert_message=exitlong, comment="TPSL")
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////SHORT
if window() and strategy.position_size==0 and shortOK
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short, when= short2, alert_message=entershort, comment="Short")
if strategy.position_size<0
strategy.exit("Short", stop= shortstop, limit= shorttp, alert_message=exitshort, comment="TPSL")