FMZ PINE Script documentation is provided.
Author: Inventors quantify - small dreams, Created: 2022-05-06 14:27:06, Updated: 2024-10-12 15:27:04[TOC]
Keywords, grammar, setting up a profile
Code structure
The general structure of the code in Pine is:
<version>
<declaration_statement>
<code>
Notes
FMZ's Pine language supported annotation symbols: single line annotation//This is the first time I've seen it./* */For example, the following examples of commentary spelling:
[macdLine, signalLine, histLine] = ta.macd(close, 12, 26, 9) // 计算MACD指标
/*
plot函数在图表上画出指标线
*/
plot(macdLine, color = color.blue, title='macdLine')
plot(signalLine, color = color.orange, title='signalLine')
plot(histLine, color = color.red, title='histLine')
The version
A compiler instruction in the following form tells the compiler which version of Pine the script is written in:
//@version=5
The default version is v5, which can be omitted from the code.//@version=5。
Statement of purpose
indicator()strategy()
Statements define the type of script, which in turn determines what content is allowed in it, and how it is used and executed. Sets the key attributes of the script, such as its name, where it will appear when it is added to the chart, the precision and format of the values it displays, and controls certain values of its behavior at runtime, such as the maximum number of drawing objects it will display in the chart. For a policy, the attributes include parameters that control retrieval, such as initial capital, commissions, slippage points, etc. FMZ's Pine does not require a policy code to includeindicator()Orstrategy()The statement is as follows:
The Code
A line in a script that is not a comment or a compiler instruction is a statement that implements the script's algorithm. A statement can be one of these.
- Variable declaration
- Reassignment of variables
- The function declaration
- Built-in function calls, user defined function calls
if,for,whileorswitchand so on.
Sentences can be arranged in many ways.
- Some statements can be expressed in a single line, such as most variable declarations, which contain only one function call line, or single-line function declarations; others, like structures, always require multiple lines because they require a local block.
- The global statements of the script (i.e. the parts that do not belong to the sub-block) cannot be used to describe the entire script.
空格or制表符(tab key) start. Their first character must also be the first character of the line. A line that starts at the first position in the line is, by definition, part of the global scope of the script. - A structure or multi-line function statement always requires a
local blockA local block must be compressed into a semicolon or four spaces (otherwise, it will be parsed as the serial code of the previous line, i.e. determined to be the continuous content of the previous line of code), and each local block defines a different local range. - Multiple single-line statements can be connected in a single line by using the comma ((,) as a separator.
- A line can contain a commentary or just a commentary.
- A line can also be wrapped (continue on multiple lines).
For example, include three local blocks, one in a custom function declaration, two in a variable declaration using an if structure, code as follows:
indicator("", "", true) // 声明语句(全局范围),可以省略不写
barIsUp() => // 函数声明(全局范围)
close > open // 本地块(本地范围)
plotColor = if barIsUp() // 变量声明 (全局范围)
color.green // 本地块 (本地范围)
else
color.red // 本地块 (本地范围)
runtime.log("color", color = plotColor) // 调用一个内置函数输出日志 (全局范围)
Change the code
Long rows can be divided into multiple rows, or they can be wrapped up. Wrapped rows must compress any number of spaces, as long as it is not a multiple of 4 (these boundaries are used to compress sub-roots).
a = open + high + low + close
It can be packaged as (note that the number of spaces that are compressed per line is not a multiple of 4):
a = open +
high +
low +
close
A long plot ((()) call can be wrapped up in a.
close1 = request.security(syminfo.tickerid, "D", close) // syminfo.tickerid 当前交易对的日线级别收盘价数据系列
close2 = request.security(syminfo.tickerid, "240", close) // syminfo.tickerid 当前交易对的240分钟级别收盘价数据系列
plot(ta.correlation(close, open, 100), // 一行长的plot()调用可以被包装
color = color.new(color.purple, 40),
style = plot.style_area,
trackprice = true)
Statements in user-defined function declarations can also be wrapped. However, since the local block must syntactically start with a contraction (four spaces or one check mark), when dividing it into the next line, the continuation of the statement must start with more than one contraction (not equal to a multiple of four spaces). For example:
test(c, o) =>
ret = c > o ?
(c > o+5000 ?
1 :
0):
(c < o-5000 ?
-1 :
0)
a = test(close, open)
plot(a, title="a")
Time series
Time series is not a data type or format, but a basic structure concept in the PINE language. It is used to store values that change continuously over time, each value corresponding to a point in time. The structure of this concept is well suited for processing and recording a series of data that changes over time.
with built-in variablesopenFor example,openThe built-in variable records the opening price of each K-line BAR, if thisopenSo this is the data for the five-minute K-line cycle.openWhat is recorded in the variable is the opening price of the K-line BAR (column) every 5 minutes.openThis refers to the opening price of the current location of the K-line BAR. To refer to the previous value in the time sequence (past value), we use[]The history operator, when a policy is executed on a certain K-line BAR, is used to display the policy.open[1]This means that the opening price of the previous K line BAR of the current K line BAR is referenced.
AlthoughTime seriesIt's easy to think of data structures as "array", although the PINE language also has array types.
The PINE language designed time sequences in this way to calculate the cumulative value of the closing price in the strategy code very easily, and without the need to use loop structures such as for, just using the built-in functions of the PINE language.ta.cum(close)To give another example, we need to calculate the average of the maximum price and minimum price difference of the last 14 K-string BAR (i.e. the 14 K-string BAR closest to the current moment of execution of the code) which can be written as:ta.sma(high - low, 14)
The result of calling a function on a time sequence also leaves a trace on the time sequence.[]The historical operator refers to the previous value. For example, we can write that the closing price of the current K-line BAR exceeds the maximum value of the highest price in the last 10 K-line BARs (excluding the current K-line BAR).breach = close > ta.highest(close, 10)[1]It can also be written asbreach = close > ta.highest(close[1], 10)So what?ta.highest(close, 10)[1]andta.highest(close[1], 10)It's not just a question of time.
The following code can be used to verify:
strategy("test pine", "test", true)
a = ta.highest(close, 10)[1]
b = ta.highest(close[1], 10)
plotchar(true, title="a", char=str.tostring(a), location=location.abovebar, color=color.red)
plotchar(true, title="b", char=str.tostring(b), location=location.belowbar, color=color.green)
The above test code outputs a and b on each BAR with their corresponding values in the time series, and it can be seen that a and b are always equal, so the two representation methods are equivalent.
Template parameters for the Pine language transaction library
The built-in template for the PINE policy, "Pine language transaction library", has parametric settings.
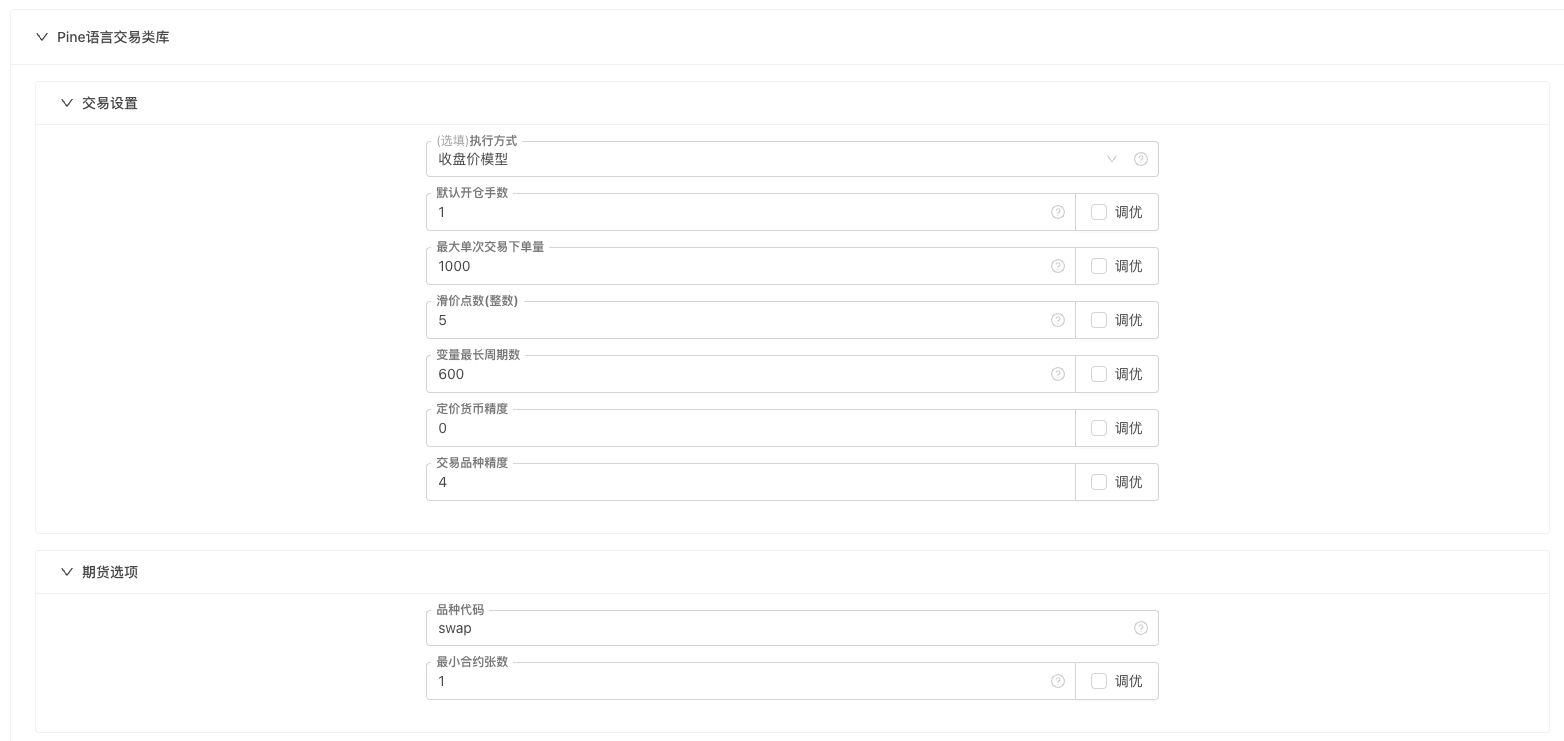
Settings for transactions
- How to execute Closing price model: The model is executed at the end of the current BAR and executes the transaction at the beginning of the lower root BAR. Real-time price model: The model is executed every time the price changes, with signals to execute the transaction immediately.
- Default number of open positions: If the trading instruction does not specify the number of trades, the number of trades executed according to this setting;
- Maximum number of orders per transaction: based on the actual discount, in combination with this parameter setting, determine the maximum number of orders per transaction to avoid impacting the discount.
- The number of price points:
定价货币精度Parameters and this parameter determine the slippage price when the order is placed. For example, if the pricing currency precision is set to 2, i.e. precise to the second decimal place, precise to 0.01 then the slippage point number represents 0.01 of each pricing unit. - The number of longest cycles of the variable: affects the number of K-line BARs in the graph, with
javascriptCalls in policySetMaxBarLenThe function works the same way.
Futures options
- Variety codes: Contract codes, which are only required when the exchange object is a non-cash exchange object.
- Minimum number of contracts: the minimum amount of contracts traded when the order is placed.
The real disk option
- Auto-reset progress: Auto-reset to the state before the last policy was stopped.
- Order retry number: The order is not executed and the order is cancelled and the order is retried. This parameter is used to limit the maximum number of retries.
- Network query interval ((milliseconds): valid only for the REST protocol, control the network request interval, avoid requests that are too frequent and exceed the limits of the exchange.
- Account synchronization time ((seconds): The time period for synchronizing account data.
- Post-opening position synchronization time (milliseconds): Only for repeated openings caused by data delays on some exchanges, setting the synchronization time to be larger can mitigate such problems.
- Leverage multiplier: Set the leverage multiplier.
Cash transactions, other settings
- One-handed transaction volume: The default one-handed transaction volume is only valid for spot transactions.
- Minimum trading volume: Minimum trading volume is the minimum amount of transactions.
- Price accuracy: Price accuracy, i.e. the small number of digits of the price.
- Transaction variety accuracy: the precision of the next unit, i.e. the small number of digits of the next unit.
- Fee: 0.002 is 2 parts per thousand for some data calculated according to this setting.
- Gain-loss statistics interval: only on the physical disk shows the use of gain-loss statistics.
- Failed retry (millisecond): Interval of retry when network request fails.
- Use of proxies: valid only for the REST protocol.
- Hide common network errors: Hide common error logs in the log area.
- Switch base addresses: valid only for the REST protocol.
- Push notifications: Push messages to the inbox etc.
Subscribe
Opening of the market
strategy(title = "open long example", pyramiding = 3) // pyramiding 允许的同方向下单的次数
strategy.entry("long1", strategy.long, 0.01) // 市价开多仓,指定分组标签为long1
strategy.entry("long2", strategy.long, 0.02, when = close > ta.ema(close, 10)) // 条件触发,执行下单,市价开多仓
strategy.entry("long3", strategy.long, 0.03, limit = 30000) // 指定(较低的)价格,计划下买单订单,等待成交开仓,限价开仓
Plainly
strategy(title = "close long example", pyramiding = 2) // pyramiding 允许的同方向下单的次数
strategy.entry("long1", strategy.long, 0.1) // 市价开多仓,指定分组标签为long1
strategy.entry("long2", strategy.long, 0.1) // 市价开多仓,指定分组标签为long2
strategy.close("long1", when = strategy.position_size > 0.1, qty_percent = 50, comment = "close buy entry for 50%") // 平仓,指定平掉分组标签为long1的仓位的50%持仓
strategy.close("long2", when = strategy.position_size > 0.1, qty_percent = 80, comment = "close buy entry for 80%") // 平仓,指定平掉分组标签为long2的仓位的80%持仓
Mechanism of trade
The PINE language holdings mechanism is similar to one-way holdings. For example, when holding a multi-headed position ("multi-headed holdings"), if there are sell orders, plan lists, etc. (in the reverse direction of the holdings), the order is triggered to execute. The multi-headed position is first flattened ("flatten all multi-headed holdings") and then executed (in the reverse direction of the holdings).
Schedule of events
When using the order ordering command, the default is market ordering if no price is specified. In addition to market ordering, you can also order from a plan order, which does not immediately operate the order. Plan ordering can be performed in the plan order queue of a program that exists when it is not triggered.Discs and re-testsThe time status information (i.e. the status bar when the policy is running) is seen in the "schedule orders" tab section. The system will only actually place orders when the real-time market price conditions are met to trigger these orders.strategy.entrySo we can specify that when we order a function, we can specifylimit、stopParameters are.
var isTrade = false
if not barstate.ishistory and not isTrade
isTrade := true
strategy.entry("test 1", strategy.long, 0.1, stop=close*1.3, comment="test 1 order") // stop
strategy.entry("test 2", strategy.long, 0.2, limit=close*0.7, comment="test 2 order") // limit
strategy.entry("test 3", strategy.short, 0.3, stop=close*0.6, limit=close*1.4, comment="test 3 order") // stop-limit
- Limit orders
Set a limit price for the order, i.e. when the order is for paymentdirectionThe parameter isstrategy.longThe order is triggered only when the current market price is below that price.
When the order is for sale (i.e.directionThe parameter isstrategy.shortThe order is triggered only when the current market price is higher than that price.
- Stop order
Set the stop-loss price of the order, when the order is a buy, and only trigger the order when the current market price is higher than that price. When the order is a sell order, the order is triggered only when the current market price is lower than that price.
- Stop-limit orders
Can be set simultaneouslylimit、stopParameters, orders are triggered at the first price that meets the conditions.
Percentage of rights and interests
//@version=5
strategy("Percent of Equity Order", overlay=true, default_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equity, default_qty_value=100)
// 简单的均线交叉策略
longCondition = ta.crossover(ta.sma(close, 14), ta.sma(close, 28))
shortCondition = ta.crossunder(ta.sma(close, 14), ta.sma(close, 28))
// 如果均线交叉条件满足,则买入或卖出
if (longCondition)
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
if (shortCondition)
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
Specifydefault_qty_type=strategy.percent_of_equityThen, setdefault_qty_valueFor a percentage number ((0-100), 1 is 1%;; calculate the unit quantity according to the number of billing currencies in the account;; for example: the current account has 10000 USDT, set the order quantity to 1%, i.e. use a 100 USDT scale order quantity ((calculated according to the current price at the time of sale)).
Statements, logical structure keywords and so on.
var
var is the keyword for assignment and one-time initialization of variables. Typically, variable assignment syntax that does not include the keyword var will result in variable values being overlaid each time the data is updated. Conversely, when variables are assigned with the keyword var, they can be kept in a state-like state even though the data is updated, changing it only when the conditions in the if-expressions are met.
说明:
- ```variable_name``` - Pine Script中允许的用户变量的任何名称(可以包含大写和小写的拉丁字符,数字和下划线(_),但不能以数字开头)。
- ```expression``` - 任何算术表达式,就像定义常规变量一样。 将计算表达式并将其分配给变量一次。
**例子**
```pine
// Var keyword example
var a = close
var b = 0.0
var c = 0.0
var green_bars_count = 0
if close > open
var x = close
b := x
green_bars_count := green_bars_count + 1
if green_bars_count >= 10
var y = close
c := y
plot(a, title = "a")
plot(b, title = "b")
plot(c, title = "c")
The variable
The FMZ is divided into real-time price models, closing price models, and price comparisons.var、varipWe test the declared variable using the following code.
strategy("test pine", "test 1", true)
// 测试 var varip
var i = 0
varip ii = 0
// 将策略逻辑每轮改变的i、ii打印在图上
plotchar(true, title="ii", char=str.tostring(ii), location=location.abovebar, color=color.red)
plotchar(true, title="i", char=str.tostring(i), location=location.belowbar, color=color.green)
// 每轮逻辑执行都给i、ii递增1
if true
i := i + 1
ii := ii + 1
Real-time pricing model The above test code is divided into two phases during execution: 1st, the historical K-line phase; 2nd, the real-time K-line phase.
var、varipThe declared variable i, ii will perform incremental operations every time the policy code is executed, becauseif trueSo it is certain to execute the corresponding conditional code block); so it can be seen that the numbers shown on the retrieval result K line BAR are each incremented by 1; when the historical K line phase ends, the real-time K line phase begins.var、varipThe declared variables start to change differently. Because it is a real-time price model, every price change in a K-line BAR is executed with a repeated strategy code.i := i + 1andii := ii + 1The difference is that ii is modified every time. Although i is also modified each time, the value of i is restored when the next round of execution of the policy logic is executed, until the current K-line BAR runs out and the update determines the value of i (i.e. the value is no longer restored when the next round of execution of the policy logic is executed).The closing model Since the closing price model executes one strategy logic at the end of each K-line BAR, the historical K-line phase and the real-time K-line phase are used in the closing price model.
var、varipThe declared variables are perfectly consistent in the incremental representation in the above example, with BAR incrementing by 1 for each K line.
varip
varip (var intrabar persist) is a keyword used to allocate and initialize variables once. It is similar to the var keyword, but a variable with a varip declaration retains its value between real-time K-line updates.
说明:
- ```variable_name``` - Pine脚本中允许的用户变量的任何名称(可以包含大写和小写拉丁字符、数字和下划线(_),但不能以数字开头)。
- ```expression``` - 任何算术表达式,就像定义常规变量时一样。在第一根K线上,表达式仅计算一次并将其分配给变量一次。
**例子**
```pine
// varip
varip int v = -1
v := v + 1
plot(v)
When var is used, the graph returns the value of bar_index. Using varip, the same behavior occurs on the historical K line, but on the real-time K line, the graph returns a value that increases by one for each tick.
NotesCan only be used with simple types such as float, int, boolean, string, and arrays of these types.
true
Indicates the value of a Boolean variable, or when an expression is usedComparisonorLogicThe value that can be calculated when the operator is used.
NotesSee alsoComparisonOperators andLogicDescription of the operator.
See you later
### false
表示一个布尔类型变量的值,以及比较操作、逻辑操作的结果。
**备注**
请参阅**比较**运算符和**逻辑**运算符的描述。
**另见**
```bool```
### if
If语句定义了在满足表达式条件时必须执行的语句块。第4版的Pine脚本语言允许您使用“else if”语法。
通用编码来自:
var_declarationX = if condition var_decl_then0 var_decl_then1 … var_decl_thenN return_expression_then else if [optional block] var_decl_else0 var_decl_else1 … var_decl_elseN return_expression_else else var_decl_else0 var_decl_else1 … var_decl_elseN return_expression_else
**备注**
```var_declarationX``` - 此变量获取if语句的值
```condition``` - 如果条件为true,则使用语句块```then```中的逻辑(```var_decl_then0```,```var_decl_then1```等)。如果条件为false,则使用语句块```else if```或者```else```中的逻辑(```var_decl_else0```,```var_decl_else1```等)。
```return_expression_then , return_expression_else``` - 模块中的最后一个表达式或者来自块else的表达式将返回语句的最终值。 如果变量的声明在最后,它的值将是结果值。
if语句的返回值的类型取决于```return_expression_then```和```return_expression_else```类型。TradingView上运行时,它们的类型必须匹配:当你在else块中有一个字符串值时,不可能从then语句块返回一个整数值。在FMZ上运行时,以下例子不会报错,当y值取值"open"时,plot画图时的数值为n/a。
**例子**
```pine
// This code compiles
x = if close > open
close
else
open
// This code doesn’t compile by trading view
// y = if close > open
// close
// else
// "open"
plot(x)
Can be omittedelseblocks. In this case, if the condition is false, the variable var_declarationX is assigned a??empty threshold ((na、false or??):
Examples
// if
x = if close > open
close
// If current close > current open, then x = close.
// Otherwise the x = na.
plot(x)
You can use multiple
Examples
// if
x = if open > close
5
else if high > low
close
else
open
plot(x)
Can be ignoredifThe result value of the statement ((
Examples
if (ta.crossover(high, low))
strategy.entry("BBandLE", strategy.long, stop=low)
else
strategy.cancel(id="BBandLE")
If statements can contain each other:
Examples
// if
float x = na
if close > open
if close > close[1]
x := close
else
x := close[1]
else
x := open
plot(x)
for
The for-construction allows multiple statements to be executed repeatedly:
[var_declaration =] for counter = from_num to to_num [by step_num]
statements | continue | break
return_expression
```counter``` - 保存回圈计数器值的变数,在回圈的每次迭代中递增/递减 1 或 step_num 值。
```from_num``` - 计数器的起始值。允许使用“series int/float”值/表达式。
```to_num``` - 计数器的最终值。当计数器大于to_num(或小于to_num在from_num > to_num的情况下)时,循环中断。允许使用“series int/float”值/表达式,但它们仅在循环的第一次迭代时进行评估。
```step_num``` - 计数器的递增/递减值。它是可选的。默认值为+1或-1,具体取决于from_num或to_num中最大的一个。使用值时,计数器也会根据from_num或to_num中最大的那个而递增/递减,因此step_num的+/-符号是可选的。
```statements | continue | break``` - 任意数量的语句,或'continue'或'break'关键字,缩进4个空格或一次 tab。
```return_expression``` - 循环的返回值,如果存在,则分配给var_declaration中的变量。 如果循环由于“continue”或“break”关键字而退出,则循环的返回值是在循环退出之前分配值的最后一个变量的返回值。
```continue``` - 只能在回圈中使用的关键字。它导致回圈的下一次迭代被执行。
```break``` - 退出回圈的关键字。
**例子**
```pine
// Here, we count the quantity of bars in a given 'lookback' length which closed above the current bar's close
qtyOfHigherCloses(lookback) =>
int result = 0
for i = 1 to lookback
if close[i] > close
result += 1
result
plot(qtyOfHigherCloses(14))
See you later
### for...in
`for...in` 结构允许为数组中的每个元素重复执行多个语句。它可以与任一参数一起使用:`array_element`,或与两个参数一起使用:`[index, array_element]`。 第二种形式不影响循环的功能。它在元组的第一个变量中跟踪当前迭代的索引。
[var_declaration =] for array_element in array_id statements | continue | break return_expression
[var_declaration =] for [index, array_element] in array_id statements | continue | break return_expression
```var_declaration``` - 一个可选的变量声明,将被赋予循环的 `return_expression` 的值。
```index``` - 跟踪当前迭代索引的可选变量。索引从 0 开始。变量在循环体中是不可变的。使用时,它必须包含在一个也包含 `array_element` 的元组中。
```array_element``` - 包含要在循环中处理的每个连续阵列元素的变量。该变量在循环体中是不可变的。
```array_id``` - 回圈迭代的阵列ID。
```statements | continue | break``` - 任意数量的语句,或'continue'或'break'关键字,缩进4个空格或一次 tab。
```return_expression``` - 循环的返回值分配给 `var_declaration` 中的变量,如果存在的话。 如果循环由于'continue'或'break'关键字而退出,则循环的返回值是循环退出前最后一个赋值的变量。
```continue``` - 只能在回圈中使用的关键字。它导致回圈的下一次迭代被执行。
```break``` - 退出回圈的关键字。
允许在循环内修改阵列的元素或其大小。
在这里,我们使用 `for...in` 的单参数形式来确定在每个K线上,有多少K线的OHLC值大于'close'值的SMA:
**例子**
```pine
// Here we determine on each bar how many of the bar's OHLC values are greater than the SMA of 'close' values
float[] ohlcValues = array.from(open, high, low, close)
qtyGreaterThan(value, array) =>
int result = 0
for currentElement in array
if currentElement > value
result += 1
result
plot(qtyGreaterThan(ta.sma(close, 20), ohlcValues))
Here, we use the two parameters form of for...in to get ourisPosThe value of the array is set totrueAnd when they're in ourvaluesArrayThe corresponding value in the array is:
Examples
// for...in
var valuesArray = array.from(4, -8, 11, 78, -16, 34, 7, 99, 0, 55)
var isPos = array.new_bool(10, false)
for [index, value] in valuesArray
if value > 0
array.set(isPos, index, true)
if barstate.islastconfirmedhistory
runtime.log(str.tostring(isPos))
See you later
### while
`while`语句允许本地代码块的条件迭代。
variable_declaration = while boolean_expression … continue … break … return_expression
说明:
```variable_declaration``` - 可选的变量声明。`return expression`可以为这个变量提供初始化值。
```boolean_expression``` - 如果为true,则执行`while`语句的本地块。如果为false,则在`while`语句之后继续执行脚本。
```continue``` - `continue` 关键字导致循环分支到下一次迭代。
```break``` - `break` 关键字导致循环终止。脚本的执行在 `while` 语句之后恢复。
```return_expression``` - 提供 `while` 语句返回值的可选行。
**例子**
```pine
// This is a simple example of calculating a factorial using a while loop.
int i_n = input.int(10, "Factorial Size", minval=0)
int counter = i_n
int factorial = 1
while counter > 0
factorial := factorial * counter
counter := counter - 1
plot(factorial)
NotesEarlywhileThe local code block after the line must be compressed into four spaces or a punctuation mark.whileThe circle.whileThe following Boolean expression must eventually become false, or it must be executed.break。
switch
The switch operator transfers control to one of several statements based on the value of the condition and expression.
[variable_declaration = ] switch expression
value1 => local_block
value2 => local_block
...
=> default_local_block
[variable_declaration = ] switch
boolean_expression1 => local_block
boolean_expression2 => local_block
...
=> default_local_block
It's the same with the switch with the expression:
Examples
// Switch using an expression
string i_maType = input.string("EMA", "MA type", options = ["EMA", "SMA", "RMA", "WMA"])
float ma = switch i_maType
"EMA" => ta.ema(close, 10)
"SMA" => ta.sma(close, 10)
"RMA" => ta.rma(close, 10)
// Default used when the three first cases do not match.
=> ta.wma(close, 10)
plot(ma)
It's not just the words that make up the name of the game.
Examples
strategy("Switch without an expression", overlay = true)
bool longCondition = ta.crossover( ta.sma(close, 14), ta.sma(close, 28))
bool shortCondition = ta.crossunder(ta.sma(close, 14), ta.sma(close, 28))
switch
longCondition => strategy.entry("Long ID", strategy.long)
shortCondition => strategy.entry("Short ID", strategy.short)
Returns the valueThe value of the last expression in the executed local statement block.
NotesCan only be executedlocal_blockExample ordefault_local_blockOne of them.default_local_blockOnly with=>Markers are introduced together, and are executed only when the previous block is not executed; ifswitchThe result of the statement is assigned to a variable and is not specifieddefault_local_blockIf not executedlocal_blockThe sentence is returned.naI will.switchWhen the result of the statement is assigned to a variable, alllocal_blockThe instance must return a value of the same type.
See you later
### series
series是一个关键字,表示数据系列类型。显式使用 `series` 关键字通常是不必要的。
## 运算符
### =
用于给变量赋值,但仅在声明变量时(第一次使用)。
### :=
赋值运算符,给左侧变量赋值。用于为先前声明的变量赋值。
### !=
不等于。适用于任何类型的表达式。
expr1 != expr2
**返回值**
布尔值,或一系列布尔值。
### %
模数(整数余数)。 适用于数值表达式。
expr1 % expr2
**返回值**
整数或浮点值,或一系列值。
**备注**
在Pine脚本中,当计算整数的余数时,商将被截断。 即,将其四舍五入到最小绝对值。 所得值将具有与股息相同的符号。
示例:-1 % 9 = -1 - 9 * truncate(-1/9) = -1 - 9 * truncate(-0.111) = -1 - 9 * 0 = -1。
### %=
模数指派。适用于数值表达式。
expr1 %= expr2
**例子**
```pine
// Equals to expr1 = expr1 % expr2.
a = 3
b = 3
a %= b
// Result: a = 0.
plot(a)
Returns the valueAn integer or floating-point value, or a series of values.
*
Multiplication. It is used for numerical expressions.
expr1 * expr2
Returns the valueAn integer or floating-point value, or a series of values.
*=
Multiplication assignment. It is used for numerical expressions.
expr1 *= expr2
Examples
// Equals to expr1 = expr1 * expr2.
a = 2
b = 3
a *= b
// Result: a = 6.
plot(a)
Returns the valueAn integer or floating-point value, or a series of values.
+
Adding or uniting digits. Use for numeric expressions or strings.
expr1 + expr2
+ expr
Returns the valueString binary+Returns the combinations of express1 and express2
A number returns an integer or floating point value, or a series of values:
The binomial helium + helium returns expr1 plus expr2.
One-value + one-value returns the expression ((add nothing to the one-value operator symmetry)).
NotesYou can use arithmetic operators with numbers as well as arrays of variables. In the case of arrays, the operator applies to elements.
+=
Additive notation. Useful for numerical expressions or strings.
expr1 += expr2
Examples
// Equals to expr1 = expr1 + expr2.
a = 2
b = 3
a += b
// Result: a = 5.
plot(a)
Returns the valueFor strings, returns a string of expres1 and expres2; for numbers, returns an integer or floating point value, or a series of values.
NotesYou can use arithmetic operators with numbers as well as arrays of variables. In the case of arrays, the operator applies to elements.
-
Subtraction law or unit negative number.
expr1 - expr2
- expr
Returns the valueReturns an integer or floating point value, or a series of values:
The binomial helium + helium returns express1 minus express2.
One dollar-Returns the negation of expr.
NotesYou can use arithmetic operators with numbers as well as arrays of variables. In the case of arrays, the operator applies to elements.
-=
Subtraction assignment ⇒ Useful for numerical expressions.
expr1 -= expr2
Examples
// Equals to expr1 = expr1 - expr2.
a = 2
b = 3
a -= b
// Result: a = -1.
plot(a)
Returns the valueAn integer or floating-point value, or a series of values.
/
Except for the fact that it applies to numerical expressions.
expr1 / expr2
Returns the valueAn integer or floating-point value, or a series of values.
/=
Except assignment. It is used for numerical expressions.
expr1 /= expr2
Examples
// Equals to expr1 = expr1 / expr2.
a = 3
b = 3
a /= b
// Result: a = 1.
plot(a)
Returns the valueAn integer or floating-point value, or a series of values.
<
Less than. Applies to numerical expressions.
expr1 < expr2
Returns the valueA Boolean value, or a set of Boolean values.
<=
Less than or equal to. Applies to numerical expressions.
expr1 <= expr2
Returns the valueA Boolean value, or a set of Boolean values.
==
Equivalent to ▽ applicable to any type of expression.
expr1 == expr2
Returns the valueA Boolean value, or a set of Boolean values.
=>
The switchI'm not sure what you mean by that.
The syntax of the function declaration is:
<identifier>([<parameter_name>[=<default_value>]], ...) =>
<local_block>
<function_result>
One<local_block>It's zero or more Pine sentences.
**例子**
```pine
// single-line function
f1(x, y) => x + y
// multi-line function
f2(x, y) =>
sum = x + y
sumChange = ta.change(sum, 10)
// Function automatically returns the last expression used in it
plot(f1(30, 8) + f2(1, 3))
NotesYou can learn more about user-defined functions on the declaration and script library pages of the user manual.
>
Greater than. Applies to numerical expressions.
expr1 > expr2
Returns the valueA Boolean value, or a set of Boolean values.
>=
greater than or equal to ≠ ≠ ≠ ≠ ≠ ≠
expr1 >= expr2
Returns the valueA Boolean value, or a set of Boolean values.
?:
The triangular conditional operator.
expr1 ? expr2 : expr3
Examples
// Draw circles at the bars where open crosses close
s2 = ta.cross(open, close) ? math.avg(open,close) : na
plot(s2, style=plot.style_circles, linewidth=2, color=color.red)
// Combination of ?: operators for 'switch'-like logic
c = timeframe.isintraday ? color.red : timeframe.isdaily ? color.green : timeframe.isweekly ? color.blue : color.gray
plot(hl2, color=c)
Returns the valueIf express1 is evaluated as true, then express2 is evaluated as true, otherwise it is considered to be express3。 The zero value ((0 and NaN+, Infinity,-Infinity) is considered false, all other values are true。
NotesIf you don't need it, use na as a branch of the
See you later
### []
系列下标。 提供对expr1系列的以前值的访问。 expr2是过去k线的数目,必须是数值。 浮动将被向下舍入。
expr1[expr2]
**例子**
```pine
// [] can be used to "save" variable value between bars
a = 0.0 // declare `a`
a := a[1] // immediately set current value to the same as previous. `na` in the beginning of history
if high == low // if some condition - change `a` value to another
a := low
plot(a)
Returns the valueA series of values.
See you later
### and
逻辑 AND。适用于布尔表达式。
expr1 and expr2
**返回值**
布尔值,或一系列布尔值。
### or
逻辑 OR。适用于布尔表达式。
expr1 or expr2
**返回值**
布尔值,或一系列布尔值。
### not
逻辑求反(NOT)。 适用于布尔表达式。
not expr1
**返回值**
布尔值,或一系列布尔值。
## 数据类型关键字
### bool
用于显式声明变量或参数的“bool”(布尔)类型的关键字。"Bool"变量的值可以是true、false或na。
**例子**
```pine
// bool
bool b = true // Same as `b = true`
b := na
plot(b ? open : close)
NotesIt is optional to explicitly mention a type in the variable declaration unless it is initialized with na. Learn more about the type type in the user manual page of the type system.
See you later
### int
用于显式声明变量或参数的“int”(整数)类型的关键字。
**例子**
```pine
// int
int i = 14 // Same as `i = 14`
i := na
plot(i)
NotesIt is optional to explicitly mention a type in the variable declaration unless it is initialized with na. Learn more about the type type in the user manual page of the type system.
See you later
### float
用于显式声明变量或参数的“float”(浮点)类型的关键字。
**例子**
```pine
// float
float f = 3.14 // Same as `f = 3.14`
f := na
plot(f)
NotesIt is optional to explicitly mention the type in the variable declaration, unless it is initialized with na.
See you later
### string
用于显式声明变量或参数的"string"类型的关键字。
**例子**
```pine
// string
string s = "Hello World!" // Same as `s = "Hello world!"`
// string s = na // same as ""
plot(na, title=s)
NotesIt is optional to explicitly mention a type in the variable declaration unless it is initialized with na. Learn more about the type type in the user manual page of the type system.
See you later
### color
用于显式声明变量或参数的"color"类型的关键字。
**例子**
```pine
// color
color textColor = color.green
if barstate.islastconfirmedhistory
runtime.log("test", textcolor = textColor)
NotesThe color character has the following format: #RRGGBB or #RRGGBBAA. The letter represents a sixteenth digit value from 00 to FF (0 to 255 in the decimal system), where RR, GG and BB are the values of the red, green and blue components of the color. AA is an optional value for color transparency (or alpha component), where 00 is invisible and FF is opaque. It is optional to explicitly mention a type in the variable declaration unless it is initialized with na. Learn more about the type type in the user manual page of the type system.
See you later
### array
用于显式声明变量或参数的“阵列”类型的关键字。可以使用```array.new<type>```,```array.from```函数创建阵列对象(或ID)。
**例子**
```pine
// array
array<float> a = na
a := array.new<float>(1, close)
plot(array.get(a, 0))
NotesArray objects are always in the form of arrays in a hierarchical array.
See you later
### Objects
PINE语言的Objects对象是用户定义类型(UDT)的实例,可以理解为无方法类,允许用户在策略中创建自定义类型在一个实体中组织不同的值。
**定义类型**
让我们定义一个order类型来保存订单信息:
```pine
type order
float price
float amount
string symbol
- Use
typeKeyword declaration type. - Type is followed by type name.
- After the first line type defines the type name, narrow down to four spaces to define the fields that the type contains.
- Each field needs to declare its data type, e.g. int, float, string.
Create objects
Use the declared type, callnew()The function creates objects:
order1 = order.new()
order1 = order.new(100, 0.1, "BTC_USDT")
order1 = order.new(amount = 0.1, symbol = "BTC_USDT", price = 100)
You can also create empty objects:
order order1 = na
Here is a real example:
type order
float price
float amount
string symbol
if strategy.position_size == 0 and open > close
strategy.entry("long", strategy.long, 1)
order1 = order.new(strategy.opentrades.entry_price(strategy.opentrades - 1), strategy.opentrades.size(strategy.opentrades - 1), syminfo.ticker)
// runtime.log(order1) // 输出 {"data":{"price":46002.8,"amount":1,"symbol":"swap"},"_meta":0,"_type":"order"}
In the example, this sentence:
order1 = order.new(strategy.opentrades.entry_price(strategy.opentrades - 1), strategy.opentrades.size(strategy.opentrades - 1), syminfo.ticker)
It can also be written in the following form:
order order1 = na
order1 := order.new(strategy.opentrades.entry_price(strategy.opentrades - 1), strategy.opentrades.size(strategy.opentrades - 1), syminfo.ticker)
Object type used for var keyword
//@version=5
indicator("Objects using `var` demo")
//@type A custom type to hold index, price, and volume information.
type BarInfo
int index = bar_index
float price = close
float vol = volume
//@variable A `BarInfo` instance whose fields persist through all iterations, starting from the first bar.
var BarInfo firstBar = BarInfo.new()
//@variable A `BarInfo` instance declared on every bar.
BarInfo currentBar = BarInfo.new()
// Plot the `index` fields of both instances to compare the difference.
plot(firstBar.index, "firstBar")
plot(currentBar.index, "currentBar")
When a variable is assigned to an object of a user-defined type using the var keyword declaration, the keyword is automatically applied to all fields of that object. This means that an object declared with the var keyword declaration will maintain its state between each iteration without having to re-initialize its field value in each iteration.
- The firstBar object is declared using the var keyword, so its fields (index, price, vol) will keep their values in each iteration, starting from the first entry until the end of the last entry.
- The currentBar object does not use the var keyword declaration, so its field will be re-initialized in each entry, and there will be a new object in each iteration.
By drawing the index fields of the two objects, you can compare the differences between them. firstBar.index will keep the previously set value in each iteration, while currentBar.index will re-initialize the bar_index value of the current entry in each iteration.
Object type used for varip keywords
//@version=5
indicator("Objects using `varip` fields demo")
//@type A custom type that counts the bars and ticks in the script's execution.
type Counter
int bars = 0
varip int ticks = 0
//@variable A `Counter` object whose reference persists throughout all bars.
var Counter counter = Counter.new()
// Add 1 to the `bars` and `ticks` fields. The `ticks` field is not subject to rollback on unconfirmed bars.
counter.bars += 1
counter.ticks += 1
// Plot both fields for comparison.
plot(counter.bars, "Bar counter", color.blue, 3)
plot(counter.ticks, "Tick counter", color.purple, 3)
In Pine, the use of the varip keyword indicates that the object's field persists throughout the execution of the script, without scrolling back in an unconfirmed column. In the Counter type declaration, the bars field does not use the varip keyword, so it scrolls in every unconfirmed column; whereas the ticks field uses the varip keyword, so it does not scroll in every unconfirmed column. The counter object is declared using the var keyword, so it will persist throughout the script execution. In each iteration, the bars and ticks fields are added together. The bars field scrolls in each unconfirmed column, while the ticks field does not scroll. Finally, by drawing the counter.bars and counter.ticks fields, the differences between them can be compared. The value of the counter.bars will roll back in each unconfirmed column, while the value of the counter.ticks will continue to increase until the script is finished.
Change the field value
type order
float price
float amount
string symbol
if strategy.position_size == 0 and open > close
strategy.entry("long", strategy.long, 1)
order1 = order.new(strategy.opentrades.entry_price(strategy.opentrades - 1), strategy.opentrades.size(strategy.opentrades - 1), syminfo.ticker)
if strategy.position_size != 0
runtime.log(order1)
order1.price := 999
order1.amount := 100
runtime.log(order1)
runtime.error("stop")
Can be used:=Reassignment operator changes the value of the object field.
The collection of objects
The example declares an empty array that will store objects of the user-defined order type:
type order
float price
float amount
string symbol
arrOrder = array.new<order>()
order1 = order.new(99, 1, "BTC_USDT")
order2 = order.new(100, 2, "ETH_USDT")
array.push(arrOrder, order1)
array.push(arrOrder, order2)
runtime.log(arrOrder)
runtime.error("stop")
Or
type order
float price
float amount
string symbol
var array<order> arrOrder = na
arrOrder := array.new<order>()
order1 = order.new(99, 1, "BTC_USDT")
order2 = order.new(100, 2, "ETH_USDT")
array.push(arrOrder, order1)
array.push(arrOrder, order2)
runtime.log(arrOrder)
runtime.error("stop")
Replicated objects
In Pine, objects are assigned by reference. When an existing object is assigned to a new variable, they both point to the same object.
//@version=5
indicator("")
type pivotPoint
int x
float y
pivot1 = pivotPoint.new()
pivot1.x := 1000
pivot2 = pivot1
pivot2.x := 2000
// Both plot the value 2000.
plot(pivot1.x)
plot(pivot2.x)
In the example below, we create a pivot1 object and set its x-field to 1000. Then we declare a pivot2 contains a variable that refers to that pivot1 object, so they both point to the same instance. So changing pivot2.x also changes pivot1.x, because they both refer to the x-field of the same object.
To create a copy independent of the original object, in this case we can use the built-in copy() method. In this example, we declare pivot2 to refer to a variable of the replica instance of pivot1 object. Now, changing pivot2.x does not change pivot1.x, because it refers to a field of x as a separate object:
//@version=5
indicator("")
type pivotPoint
int x
float y
pivot1 = pivotPoint.new()
pivot1.x := 1000
pivot2 = pivotPoint.copy(pivot1)
pivot2.x := 2000
// Plots 1000 and 2000.
plot(pivot1.x)
plot(pivot2.x)
It is important to note that the copy method in TradingView is shorthand. If an object has fields of a special type (array, etc.), the fields in the shorthand copy of that object will point to the same instance as that object. The FMZ platform implements deep copying directly without any additional processing, as can be seen in the following examples:
Deep copying
//@version=5
indicator("test deepCopy")
type orderInfo
float price
float amount
type labelInfo
orderInfo order
string labelMsg
labelInfo1 = labelInfo.new(orderInfo.new(100, 0.1), "test labelInfo1")
labelInfo2 = labelInfo.copy(labelInfo1)
labelInfo1.labelMsg := "labelInfo1->2" // 修改 labelInfo1 的基础类型字段,看是否影响 labelInfo2
labelInfo1.order.price := 999 // 修改 labelInfo1 的复合类型字段,看是否影响 labelInfo2
runtime.log(labelInfo1)
runtime.log(labelInfo2)
runtime.error("stop")
Test results, labelInfo.copy ((labelInfo1) is executed as a deep copy, modifying any field in labelInfo1 does not affect labelInfo2。
Methods
Methods in the Pine language are specialized functions associated with the built-in or user-defined type of a particular instance. In most respects, they are essentially the same as regular functions, but provide shorter, more convenient syntax. Users can directly access methods on variables using dot symbols, just as they would access fields on a Pine object.
Built-in methods
For example, a script code like this:
//@version=5
indicator("Custom Sample BB", overlay = true)
float sourceInput = input.source(close, "Source")
int samplesInput = input.int(20, "Samples")
int n = input.int(10, "Bars")
float multiplier = input.float(2.0, "StdDev")
var array<float> sourceArray = array.new<float>(samplesInput)
var float sampleMean = na
var float sampleDev = na
// Identify if `n` bars have passed.
if bar_index % n == 0
// Update the queue.
array.push(sourceArray, sourceInput)
array.shift(sourceArray)
// Update the mean and standard deviaiton values.
sampleMean := array.avg(sourceArray)
sampleDev := array.stdev(sourceArray) * multiplier
// Calculate bands.
float highBand = sampleMean + sampleDev
float lowBand = sampleMean - sampleDev
plot(sampleMean, "Basis", color.orange)
plot(highBand, "Upper", color.lime)
plot(lowBand, "Lower", color.red)
The equivalent can be written as:
//@version=5
indicator("Custom Sample BB", overlay = true)
float sourceInput = input.source(close, "Source")
int samplesInput = input.int(20, "Samples")
int n = input.int(10, "Bars")
float multiplier = input.float(2.0, "StdDev")
var array<float> sourceArray = array.new<float>(samplesInput)
var float sampleMean = na
var float sampleDev = na
// Identify if `n` bars have passed.
if bar_index % n == 0
// Update the queue.
sourceArray.push(sourceInput)
sourceArray.shift()
// Update the mean and standard deviaiton values.
sampleMean := sourceArray.avg()
sampleDev := sourceArray.stdev() * multiplier
// Calculate band values.
float highBand = sampleMean + sampleDev
float lowBand = sampleMean - sampleDev
plot(sampleMean, "Basis", color.orange)
plot(highBand, "Upper", color.lime)
plot(lowBand, "Lower", color.red)
You can see that PINE supportsMethodsAfter that, code.array.avg(sourceArray)The user can write the following in the form of methods:sourceArray.avg()I'm not sure.
Please note FMZ is currently not supported.array.avgI'm not going to say anything about it.
User-defined methods
Pine allows a user to define a custom method to be used with any built-in or user-defined type object. The definition method is essentially the same as the definition function, but with two key differences:
The method keyword must be included before the function name. 2, the parameter of the method, where the type of the first parameter must be explicitly declared, as it indicates the type of the object to which the method will be associated.
For example, using the following code to wrap the code for calculating the Brin indicator as a user-defined method:
//@version=5
indicator("Custom Sample BB", overlay = true)
float sourceInput = input.source(close, "Source")
int samplesInput = input.int(20, "Samples")
int n = input.int(10, "Bars")
float multiplier = input.float(2.0, "StdDev")
var array<float> sourceArray = array.new<float>(samplesInput)
var float sampleMean = na
var float sampleDev = na
// Identify if `n` bars have passed.
if bar_index % n == 0
// Update the queue.
sourceArray.push(sourceInput)
sourceArray.shift()
// Update the mean and standard deviaiton values.
sampleMean := sourceArray.avg()
sampleDev := sourceArray.stdev() * multiplier
// Calculate band values.
float highBand = sampleMean + sampleDev
float lowBand = sampleMean - sampleDev
plot(sampleMean, "Basis", color.orange)
plot(highBand, "Upper", color.lime)
plot(lowBand, "Lower", color.red)
Changed to:
”`pine //@version=5 indicator(“Custom Sample BB”, overlay = true)
float sourceInput = input.source(close, “Source”) int samplesInput = input.int(20, “Samples”) int n = input.int(10, “Bars”) float multiplier = input.float(2.0, “StdDev”)
var array sour
- This is the first time I have seen this video.
- Please tell me how to add a flat full store.
- Please guys, tradeview's alert_message changes how to pair FMZ.
- Questions about the retesting system
- I've been trying to figure out why this is happening all of a sudden today.
- The two days ago, because of these two mistakes, the show stopped, and I asked God to help me see.
- Help
- Exposure of an unprofessional QC
- The real-time records read and the actual data read are incompatible.
- exchange.Buy ((Price, Amount) did not return ID
- BTCUP and BTCDOWN hedging
- Guys, buy a tactic and run it wrong, trouble god help me to see what caused it.
- Interaction patterns
- Parameter adjustment of the retesting system
- Follow the system
- Problems with the ta library source code
- FMZ PINE Script Doc
- Notes & Explanation of Futures Reverse Doubling Algorithm Strategy
- Solutions to Obtaining Docker Http Request Message
- Extending Custom Template by Visual (Blockly ) Strategy Editing
wuhuoyanHow do you do it if you want to have multiple transactions running simultaneously?
Light cloudsPlease tell me, can pine do more transactions? Can it also go through transactions like JS? Thank you.
lisa20231Thank you for providing detailed documentation.
artistryWow! How does this pine script use the okex simulation on the platform?
artistryThis is equivalent to copying the tradingview platform's strategy directly to the inventor platform and using it!
Inventors quantify - small dreamsThe PINE language can only do single-variety strategies, multi-variety strategies are best written in python, javascript, c++.
Inventors quantify - small dreamsOh, yes, OKX is special, their analog environment and the real disk environment have the same address, only the difference is made elsewhere.
Light cloudsI can't use the okx analogue disc.
Inventors quantify - small dreamsThis multi-variety architecture problem cannot be solved, because each exchange has a different interface, and the frequency limitation of the interface is not the same, which causes many problems.
Inventors quantify - small dreamsWell, thank you for the suggestion, please report this request here.
Light cloudsIt feels better to be able to mix with JS and JS can be better adapted to different trading methods.
The trend hunterIn the future, will we consider more varieties?
Inventors quantify - small dreamsI'm not being polite.
Light cloudsGood, thank you very much.
Inventors quantify - small dreamsHello, the PINE language policy is currently only for single varieties.
Inventors quantify - small dreamsThank you for your support. The documentation will continue to be improved.
Inventors quantify - small dreamsYes, I did.
Inventors quantify - small dreamsPINE template library, where parameters can be set to switch exchange base addresses.