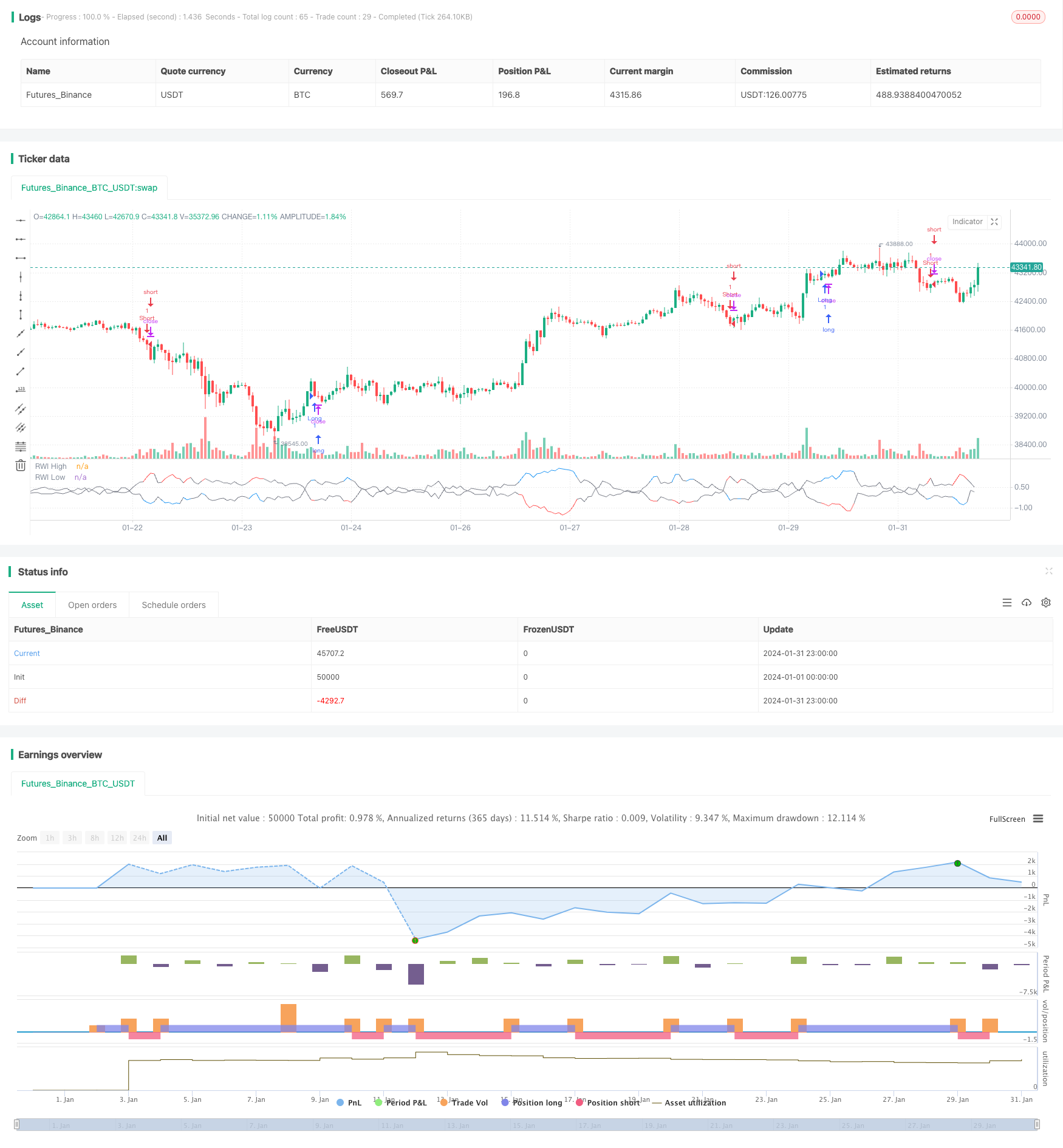
Overview
The RWI volatility contrarian strategy calculates the RWI highs and lows over a certain period to determine whether the market is in a reversal state in order to discover reversal opportunities. It adopts a contrarian strategy, going short at the highs and long at the lows, aiming for profit.
Strategy Principle
The strategy first calculates the RWI highs and lows over a certain length period (such as 14 candles). The calculation formulas are as follows:
RWI High = (High - Lowest of N Periods Ago) / (ATR of N Periods * sqrt(N))
RWI Low = (Highest of N Periods Ago - Low) / (ATR of N Periods * sqrt(N))
Then calculate the difference between the RWI highs/lows and the threshold to determine if it is below the threshold (such as 1). If both RWI highs and lows are below the threshold, the market is determined to be ranging. In this case, no action is taken.
If the RWI high is above the RWI low by more than the threshold, it is determined that the price is about to reverse, and one may consider going short. If the RWI low is above the RWI high by more than the threshold, it is determined that the price is about to reverse, and one may consider going long. This forms a contrarian trading strategy based on RWI to determine market reversal states.
Advantage Analysis
The RWI volatility contrarian strategy has the following advantages:
- Using the RWI indicator to determine reversal points is accurate with high winning rate
- Adopting contrarian strategies is suitable for ranging markets
- The strategy logic is clear and easy to understand, parameters are flexible
- Long and short cycles can be configured to improve signal quality
Risk Analysis
The RWI volatility contrarian strategy also has the following risks:
- Reversal signals may have false breakouts, resulting in losses
- More reversal signals occur during sustained trends, leading to losses
- Improper RWI parameter settings may reduce signal quality
- RWI indicator fails when volatility increases
To control risks, RWI parameters can be adjusted accordingly, filters can be added, reversal ranges can be limited, etc.
Optimization Directions
The strategy can be further optimized in the following ways:
- Add double time frame analysis using long and short RWI periods to improve signals
- Combine with other indicators like KD and MACD to avoid false breakouts
- Configure stop loss strategies to strictly control single loss
- Dynamically optimize RWI parameters to adapt to market changes
- Optimize position management, add or reduce positions based on market conditions
Summary
The RWI volatility contrarian strategy has clear logic using RWI to determine reversals. The trading logic is solid and works well in ranging markets. By optimizing parameters, controlling risks etc, the strategy can be applied more steadily and efficiently.
/*backtest
start: 2024-01-01 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-31 23:59:59
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=4
// Copyright (c) 2020-present, JMOZ (1337.ltd)
strategy("RWI Strategy", overlay=false)
length = input(title="Length", type=input.integer, defval=14, minval=1)
threshold = input(title="Threshold", type=input.float, defval=1.0, step=0.1)
rwi(length, threshold) =>
rwi_high = (high - nz(low[length])) / (atr(length) * sqrt(length))
rwi_low = (nz(high[length]) - low) / (atr(length) * sqrt(length))
is_rw = rwi_high < threshold and rwi_low < threshold
[is_rw, rwi_high, rwi_low]
[is_rw, rwi_high, rwi_low] = rwi(length, threshold)
long = not is_rw and rwi_high > rwi_low
short = not is_rw and rwi_low > rwi_high
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long, when=long)
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short, when=short)
plot(rwi_high, title="RWI High", linewidth=1, color=is_rw?color.gray:color.blue, transp=0)
plot(rwi_low, title="RWI Low", linewidth=1, color=is_rw?color.gray:color.red, transp=0)