FMZ Quant: Análisis de ejemplos de diseño de requisitos comunes en el mercado de criptomonedas (I)
El autor:FMZ~Lydia, Creado: 2023-12-19 16:02:58, Actualizado: 2024-11-06 21:19:16
En el espacio de comercio de activos de criptomonedas, la obtención y el análisis de datos de mercado, las tasas de consulta y el monitoreo de los movimientos de activos de la cuenta son operaciones críticas.
1. ¿Cómo escribo el código para obtener la moneda con el mayor aumento en 4 horas en Binance Spot?
Cuando se escribe un programa de estrategia comercial cuantitativa en la plataforma FMZ, lo primero que debe hacer cuando se encuentra con un requisito es analizarlo.
- ¿Qué lenguaje de programación usar? El plan es usar Javascript para implementarlo.
- Requiere cotizaciones al contado en tiempo real en todas las monedas
Lo primero que hicimos cuando vimos el requisito fue buscar el documento de la API de Binance para averiguar si había cotizaciones agregadas (es mejor tener cotizaciones agregadas, es mucho trabajo buscar una por una).
Encontramos la interfaz de citas agregadas:
GET https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price¿ Qué pasa? En la plataforma FMZ, utilice elHttpQueryFunción para acceder a la interfaz del ticker de intercambio (interfaz pública que no requiere una firma). - Necesidad de contar datos para un período de ventana de 4 horas Conceptualizar cómo diseñar la estructura del programa estadístico.
- Calcular las fluctuaciones de precios y clasificarlas
Pensando en el algoritmo de fluctuaciones de precios, es:
price fluctuations (%) = (current price - initial price) / initial price * 100en% .
Después de averiguar el problema, así como definir el programa, luego nos pusimos a trabajar en el diseño del programa.
Diseño de código
var dictSymbolsPrice = {}
function main() {
while (true) {
// GET https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price
try {
var arr = JSON.parse(HttpQuery("https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price"))
if (!Array.isArray(arr)) {
Sleep(5000)
continue
}
var ts = new Date().getTime()
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
var symbolPriceInfo = arr[i]
var symbol = symbolPriceInfo.symbol
var price = symbolPriceInfo.price
if (typeof(dictSymbolsPrice[symbol]) == "undefined") {
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol] = {name: symbol, data: []}
}
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data.push({ts: ts, price: price})
}
} catch(e) {
Log("e.name:", e.name, "e.stack:", e.stack, "e.message:", e.message)
}
// Calculate price fluctuations
var tbl = {
type : "table",
title : "Price fluctuations",
cols : ["trading pair", "current price", "price 4 hours ago", "price fluctuations", "data length", "earliest data time", "latest data time"],
rows : []
}
for (var symbol in dictSymbolsPrice) {
var data = dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data
if (data[data.length - 1].ts - data[0].ts > 1000 * 60 * 60 * 4) {
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data.shift()
}
data = dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].percentageChange = (data[data.length - 1].price - data[0].price) / data[0].price * 100
}
var entries = Object.entries(dictSymbolsPrice)
entries.sort((a, b) => b[1].percentageChange - a[1].percentageChange)
for (var i = 0; i < entries.length; i++) {
if (i > 9) {
break
}
var name = entries[i][1].name
var data = entries[i][1].data
var percentageChange = entries[i][1].percentageChange
var currPrice = data[data.length - 1].price
var currTs = _D(data[data.length - 1].ts)
var prePrice = data[0].price
var preTs = _D(data[0].ts)
var dataLen = data.length
tbl.rows.push([name, currPrice, prePrice, percentageChange + "%", dataLen, preTs, currTs])
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`")
Sleep(5000)
}
}
Análisis del código
- 1. Estructura de los datos
- 2. Main function main()
2.1. Infinite loop
mientras (verdadero) { - ¿Qué quieres decir? ¿ Por qué?
The program continuously monitors the Binance API trading pair prices through an infinite loop.
2.2. Get price information
var arr = JSON.parse ((HttpQuery))https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price”))
Get the current price information of the trading pair via Binance API. If the return is not an array, wait for 5 seconds and retry.
2.3. Update price data
para (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { - ¿Qué quieres decir? ¿ Por qué?
Iterate through the array of obtained price information and update the data in dictSymbolsPrice. For each trading pair, add the current timestamp and price to the corresponding data array.
2.4. Exception processing
¿ Por qué no lo haces?
Log ((
Catch exceptions and log the exception information to ensure that the program can continue to execute.
2.5. Calculate the price fluctuations
para (símbolo var en dictSymbolsPrice) { - ¿Qué quieres decir? ¿ Por qué?
Iterate through dictSymbolsPrice, calculate the price fluctuations of each trading pair, and remove the earliest data if it is longer than 4 hours.
2.6. Sort and generate tables
Las entradas var = Object.entries ((dictSymbolsPrice) las entradas.sort((a, b) => b[1].porcentajeCambiar - a[1].porcentajeCambiar)
para (var i = 0; i < entradas.longth; i++) { - ¿Qué quieres decir? ¿ Por qué?
Sort the trading pairs in descending order of their price fluctuations and generate a table containing information about the trading pairs.
2.7. Log output and delay
LogStatus ((_D(), " + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "
Output the table and the current time in the form of a log and wait for 5 seconds to continue the next round of the loop.
The program obtains the real-time price information of the trading pair through Binance API, then calculates the price fluctuations, and outputs it to the log in the form of a table. The program is executed in a continuous loop to realize the function of real-time monitoring of the prices of trading pairs. Note that the program includes exception processing to ensure that the execution is not interrupted by exceptions when obtaining price information.
### Live Trading Running Test
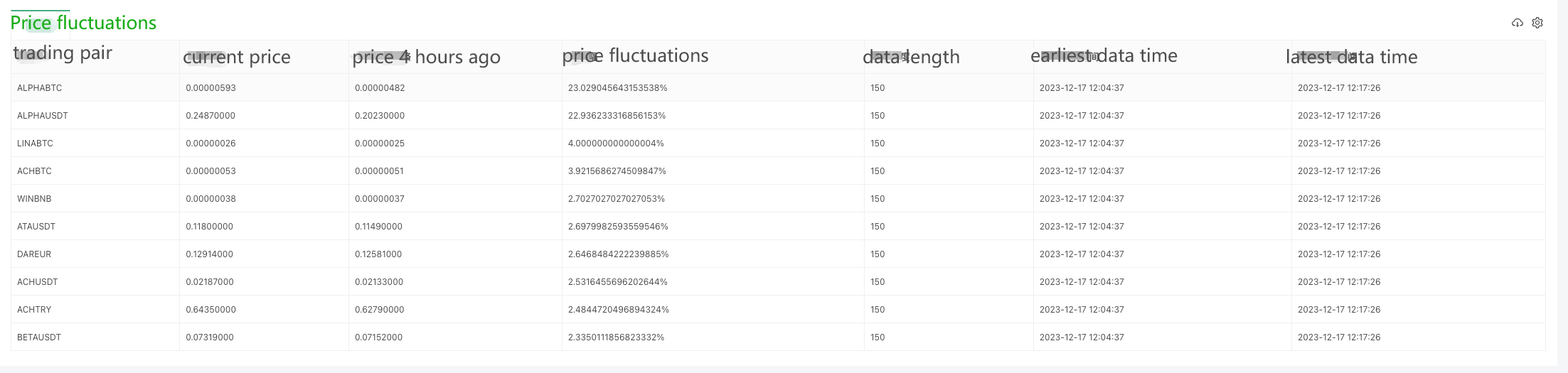
Since data can only be collected bit by bit at the beginning, it is not possible to calculate the price fluctuations on a rolling basis without collecting enough data for a 4-hour window. Therefore, the initial price is used as the base for calculation, and after collecting enough data for 4 hours, the oldest data will be eliminated in order to maintain the 4-hour window for calculating the price fluctuations.
## 2. Check the full variety of funding rates for Binance U-denominated contracts
Checking the funding rate is similar to the above code, first of all, we need to check the Binance API documentation to find the funding rate related interface. Binance has several interfaces that allow us to query the rate of funds, here we take the interface of the U-denominated contract as an example:
GEThttps://fapi.binance.com/fapi/v1/premiumIndex
### Code Implementation
Since there are so many contracts, we're exporting the top 10 largest funding rates here.
Función principal mientras (verdadero) { // GEThttps://fapi.binance.com/fapi/v1/premiumIndex¿ Por qué no lo haces? var arr = JSON.parse ((HttpQuery))https://fapi.binance.com/fapi/v1/premiumIndex”)) si (!Array.isArray(arr)) { El sueño (5.000) Sigue adelante. ¿ Por qué?
arr.sort((a, b) => parseFloat(b.lastFundingRate) - parseFloat(a.lastFundingRate))
var tbl = {
type: "table",
title: "Top 10 funding rates for U-denominated contracts",
cols: ["contracts", "funding rate", "marked price", "index price", "current rate time", "next rate time"],
rows: []
}
for (var i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
var obj = arr[i]
tbl.rows.push([obj.symbol, obj.lastFundingRate, obj.markPrice, obj.indexPrice, _D(obj.time), _D(obj.nextFundingTime)])
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`")
} catch(e) {
Log("e.name:", e.name, "e.stack:", e.stack, "e.message:", e.message)
}
Sleep(1000 * 10)
}
}
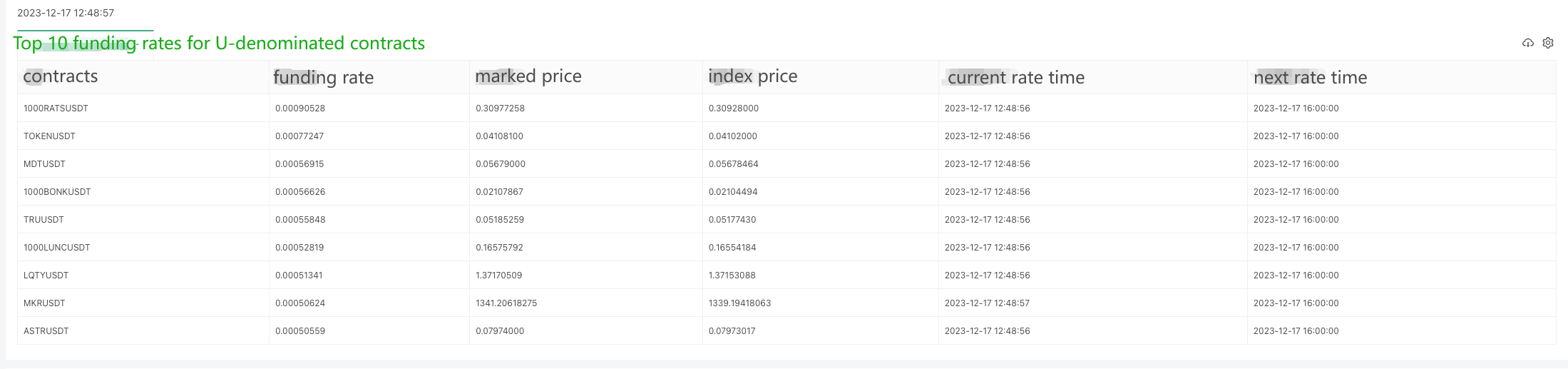
The returned data structure is as follows, and check the Binance documentation, it shows that lastFundingRate is the funding rate we want.
¿ Qué pasa?
Live trading running test:
### Getting OKX exchange contract funding rates of Python version
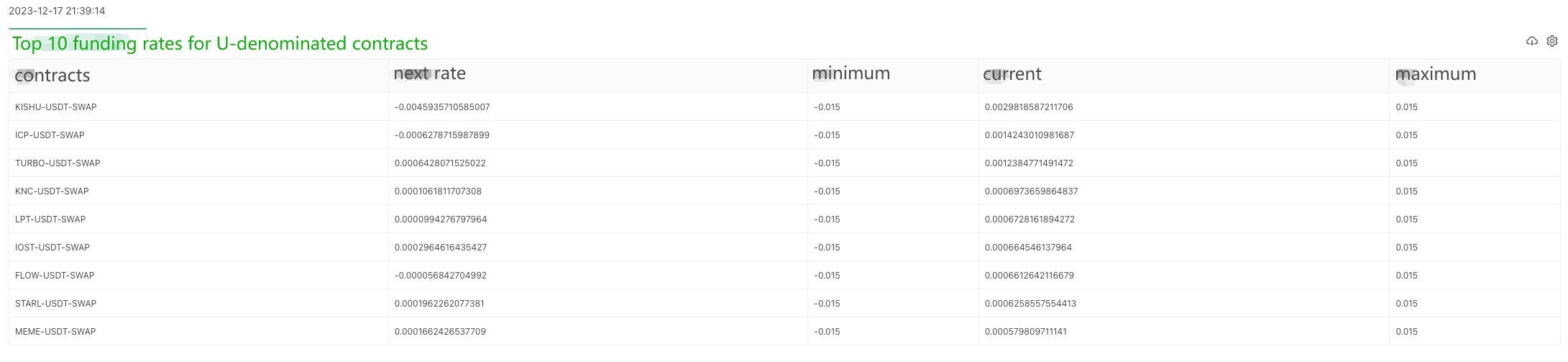
A user has asked for a Python version of the example, and it's for the OKX exchange. Here is an example:
The data returned by the interface ```https://www.okx.com/priapi/v5/public/funding-rate-all?currencyType=1```:
¿ Qué pasa?
Specific code:
solicitudes de importación Importar json de tiempo de importación de sueño desde la hora de fecha hasta la hora de importación
Definición principal:
mientras True:
#https://www.okx.com/priapi/v5/public/funding-rate-all?currencyType=1Prueba:
respuesta = peticiones. obtenerhttps://www.okx.com/priapi/v5/public/funding-rate-all?currencyType=1”)
arr = respuesta.json() [
arr.sort(key=lambda x: float(x["fundingRate"]), reverse=True)
tbl = {
"type": "table",
"title": "Top 10 funding rates for U-denominated contracts",
"cols": ["contracts", "next rate", "minimum", "current", "maximum"],
"rows": []
}
for i in range(min(9, len(arr))):
obj = arr[i]
row = [
obj["instId"],
obj["nextFundingRate"],
obj["minFundingRate"],
obj["fundingRate"],
obj["maxFundingRate"]
]
tbl["rows"].append(row)
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", '`' + json.dumps(tbl) + '`')
except Exception as e:
Log(f"Error: {str(e)}")
sleep(10)
Enlace a la sección
Estos ejemplos proporcionan ideas básicas de diseño y métodos de llamada, el proyecto real puede necesitar hacer cambios y extensiones apropiados basados en las necesidades específicas.
- Cuantificar el análisis fundamental en el mercado de criptomonedas: ¡Deja que los datos hablen por sí mismos!
- La investigación cuantitativa básica del círculo monetario - ¡No confíes más en los profesores de idiomas, los datos hablan objetivamente!
- Una herramienta esencial en el campo del comercio cuantitativo - FMZ Quant Data Exploration Module
- Una herramienta esencial en el campo de la transacción cuantitativa - inventor de módulos de exploración de datos cuantitativos
- Dominarlo todo - Introducción a FMZ Nueva versión de la terminal de negociación (con el código fuente de TRB Arbitrage)
- Conozca todo acerca de la nueva versión del terminal de operaciones de FMZ (con código de código de TRB)
- FMZ Quant: Análisis de ejemplos de diseño de requisitos comunes en el mercado de criptomonedas (II)
- Cómo explotar robots de venta sin cerebro con una estrategia de alta frecuencia en 80 líneas de código
- Cuantificación FMZ: Desarrollo de casos de diseño de necesidades comunes en el mercado de criptomonedas (II)
- Cómo utilizar una estrategia de alta frecuencia de 80 líneas de código para explotar y vender robots sin cerebro
- Cuantificación FMZ: Desarrollo de casos de diseño de necesidades comunes en el mercado de criptomonedas (1)
- WexApp, el FMZ Quant Cryptocurrency Demo Exchange, fue lanzado recientemente.
- Explicación detallada de la optimización del parámetro de la estrategia de la red de contratos perpetuos
- Enseñarle a usar la API ampliada de FMZ para modificar los parámetros del bot
- Le enseñará a usar la API de expansión de FMZ para modificar los parámetros del disco duro en serie
- Parámetros de optimización de la estrategia de la red de contratos permanentes
- Instrucciones para instalar Interactive Brokers IB Gateway en Linux Bash
- Descripción de la seguridad de penetración IB GATEWAY para instalar en Linux bash
- ¿Qué es más adecuado para la pesca de fondo, bajo valor de mercado o bajo precio?
- ¿Cuál es el mejor para copiar: el valor de mercado bajo o el precio bajo?