Inventores de plataformas de intercambio cuantitativas de protocolo general para acceder a intercambios personalizados
El autor:Los inventores cuantifican - sueños pequeños, Creado: 2017-08-24 16:29:56, Actualizado: 2021-06-10 15:33:02Documento de uso del protocolo general
Se puede acceder a cualquier servicio con este protocolo.
APIEl intercambio de transacciones, el protocolo API específico no está limitado, ya searest、websocket、fix... puede acceder y usar.Un ejemplo del protocolo Python general:https://www.fmz.com/strategy/101399
- ### 1, Plugin de protocolo general en marcha, configuración de puertos
La dirección de vigilancia y el puerto de los plugins de protocolo general de Python están bien escritos. Por ejemplo:
http://127.0.0.1:6666/DigitalAsset¿Qué es lo que está pasando?http://127.0.0.1:6666/exchange。¿Por qué poner esto?P.I.、El camino¿Qué es eso? Porque enEl inventor de la cuantificaciónPáginaCentro de controlEl saltoAñadir una bolsaEn la página, seleccione el menú de protocolo general, que muestra excepto
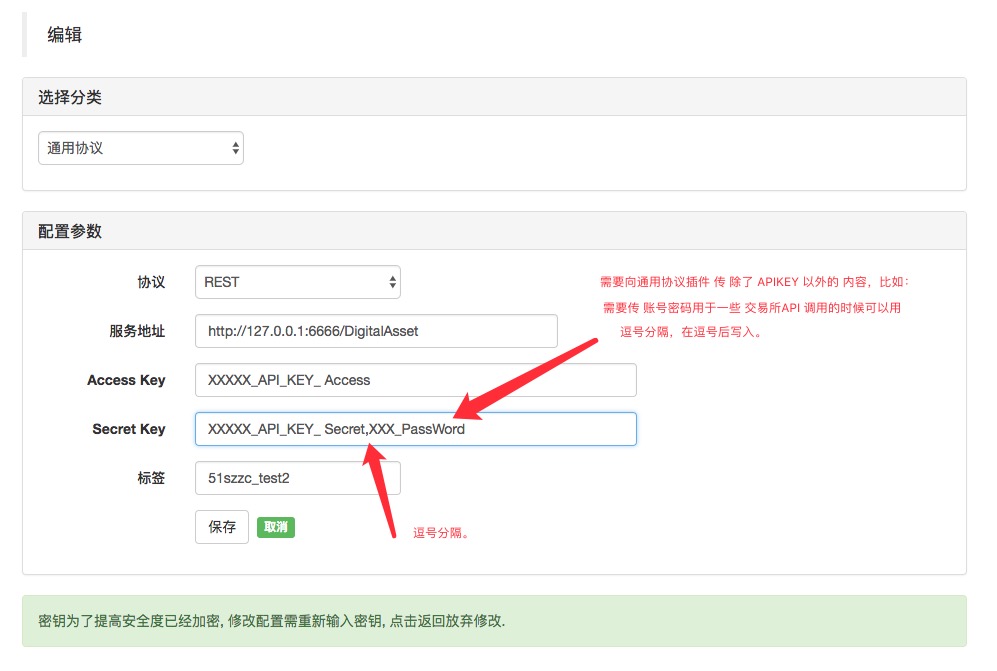
API-KEYTambién hay una barra de direcciones de servidores que le dice al administrador qué IP y puertos debe acceder (el administrador y el plugin del protocolo general no pueden funcionar en el mismo dispositivo).http://127.0.0.1:6666/DigitalAsset。DigitalAssetEste es un nombre auto-definido, sólo un ejemplo.En la página de inventores de agregar cantidades a las bolsas, se ve lo siguiente: Normalmente, la información de configuración de la cuenta de los intercambios solo requiere configurar
access keyysecret keySin embargo, algunas interfaces API de los intercambios requieren la transmisión de la contraseña de la transacción (por ejemplo, las interfaces de bajo costo de algunos intercambios), en este caso, debido a que no hay controles adicionales en las páginas de protocolo general para escribir esta información, cuando encontramos las API de este tipo de intercambios, podemos escribir la información de configuración que se requiere para transmitir la información extra en la página de protocolo general.secret keySi la información no es sensible puede escribirse enaccess keyEn este caso, el código de código es el mismo que el código de código de la aplicación.splitLa operación consiste en separar los datos, como se muestra en el ejemplo de la imagen.
Y luego procesamos en el complemento, y lo conseguimos.
XXX_PassWord¿Qué es esto? Por ejemplo, en el último ejemplo completo de este post, la función newBitgo:func newBitgo(accessKey, secretKey string) *iBitgo { s := new(iBitgo) s.accessKey = accessKey s.secretKey = secretKey // 在此可以分离secretKey中的额外配置信息,可以写成如下注释中的内容 /* arr := strings.SplitN(secretKey, ",", 2) if len(arr) != 2 { panic("配置错误!") } s.secretKey = arr[0] // secret key s.passWord = arr[1] // XXX_PassWord */ s.apiBase = "https://www.bitgo.cn" s.timeout = 20 * time.Second s.timeLocation = time.FixedZone("Asia/Shanghai", 8*60*60) return s }

Plugins de protocolo generalmainEjemplo de función:
```go
func main(){
var addr = flag.String("b", "127.0.0.1:6666", "bing addr") // 设置命令行参数,默认值描述,端口设置6666
flag.Parse() // 解析命令行
if *addr == "" {
flag.Usage() // 显示命令行描述
return
}
basePath := "/DigitalAsset"
log.Println("Running ", fmt.Sprintf("http://%s%s", *addr, basePath), "...") // 打印监听端口信息
http.HandleFunc(basePath, OnPost)
http.ListenAndServe(*addr, nil)
}
- #### # 2, la función de respuesta
El plugin del protocolo de API está constantemente vigilando el puerto designado, si se ha enviado una solicitudrequestUna vez que se realiza una solicitud, se llama a la función de respuesta para ejecutar la respuesta y luego analizar los parámetros de los datos de la solicitud, los datos de la solicitud enviados por el administrador son:
/* request的JSON结构,发明者量化调用GetTicker,托管者发送给通用协议插件情况举例(各个API调用时,params的值可能不一样,此处method为ticker):
{
"access_key" : "XXX", // `json:"access_key"`
"secret_key" : "XXX", // `json:"secret_key"`
"nonce" : "1502345965295519602", // `json:"nonce"`
"method" : "ticker", // `json:"method"`
"params" : { // `json:"params"`
"symbol" : "btc",
...
}, // 各个请求参数略有区别。即在策略中调用不同的 发明者量化 API会有不同的参数, 在下文各个API 有介绍说明。
}
*/
Por lo tanto, de acuerdo con las solicitudes recibidas en los complementos de protocolo general, los cuerpos de datos son estructuras que se obtienen después de la secuenciación de JSON.requestEn el interiorMethod¿Qué podemos hacer con esto?switchPara clasificar las llamadas de las API que tratan la cuantificación de diferentes inventores (es decir, para identificar las llamadas de las políticas que se ejecutan en los hosts de cuál inventor se cuantifican)API¿Qué es lo que está pasando?
```go
switch request.Method { // 此处request.Method的M为大写,通用协议程序接收到的请求主体中为JSON数据,在Go语言中反JSON序列化(Unmarshal)为结构体,字段首字母必须大写
case "accounts" : // 当托管者上的机器人策略中调用了exchange.GetAccount()函数,托管者会发送来请求,其中Body携带的数据中method属性值为accounts
data, err = e.GetAccount(symbol)
case "ticker" :
data, err = e.GetTicker(symbol)
case "depth" :
data, err = e.GetDepth(symbol)
case "trades" :
data, err = e.GetTrades(symbol)
case "trade" :
...
default:
...
Estas ramas escriben los datos devueltos después de su ejecución en una estructura a la que el plugin del protocolo general debe responder, respondiendo a las solicitudes de los administradores.
Ejemplo de lenguaje Go:
defer func(){ // 处理收尾工作
if e := recover(); e != nil { // recover()函数用于捕获panic,e != nil即有错误发生
if ee, ok := e.(error); ok { // 类型推导,推导成功把ee.Error()赋值给e
e = ee.Error() // 调用Error方法获取返回的错误字符串
}
ret = map[string]string{"error": fmt.Sprintf("%v", e)}
}
b, _ := json.Marshal(ret) // 把本次调用获取的结果ret编码,赋值给b,写入响应指针
w.Write(b)
//fmt.Println("after w.Write the b is", string(b)) // 测试
}()
- #### 3 Tipo de llamadas de la API
Los bloggers y los activistas se dividen en dos grandes categorías: En el caso de las aplicaciones de Internet, el usuario puede utilizar las siguientes herramientas:
```GetDepth()```
```GetTrades()```
```GetRecords(period)```
...
2、 需要签名的 用户接口, 如:
```Buy```、```Sell```
```GetOrder(id)```
```GetOrders()```
```GetAccount()```
```CancelOrder(id)```
...
各个交易所的签名方式可能各不相同,需要根据需求具体编写。
- ### 4、发明者量化各个API接口调用时**通用协议插件**和**托管者**交互的数据格式:
> 一些发明者量化的API接口如```GetName()```,```GetLabel()```等函数,调用时不会向**通用协议插件**发送请求。
```exchange.GetName()```通用插件配置的交易所调用时会返回"Exchange"。
- #### 1、GetTicker: **用于获取当前行情数据。**
**托管者**发送给监听响应函数的```request```中的```method```为:```ticker```。
托管者发送参数:```request.Params.symbol```:由托管者根据机器人页面设置的币种发送。
**托管者向通用协议插件请求时请求主体携带的数据格式(JSON)**
```
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // 毫秒时间戳
"method" : "ticker",
"params" : {"symbol" : "ETH_BTC"}, // 以ETH_BTC交易对举例
}
```
**最终发送给托管者的返回值结构:(即通用协议插件请求交易所接口后的数据返回给托管者的格式)**
JSON结构
```
{
"data": {
"time": 1500793319499, // 毫秒时间戳,整型
"buy": 1000, // 以下浮点型
"sell": 1001,
"last": 1005,
"high": 1100,
"low": 980,
"vol": 523,
}
}
```
- #### 2、GetRecords:**用于获取交易所提供的K线数据。(根据托管者请求的参数获取)**
托管者发送给监听响应函数的```request```中的```method```为:```records```
托管者发送参数:```request.Params.period```:值关联```exchange.GetRecords```函数的第一个参数,实际```request.Params.period```为分钟数表示的周期,例如日周期为```60*24```即```1440```、```request.Params.symbol```:托管者根据设置的币种发送。
**托管者向通用协议插件请求时请求主体携带的数据格式**
```
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // 毫秒时间戳
"method" : "records",
"params" : {"symbol" : "ETH_BTC", "period" : "1440"}, // 以ETH_BTC交易对,K线周期为日线举例
}
```
**最终发送给托管者的 返回值结构:**
JSON结构
```
{
"data": [
[1500793319, 1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5], // "Time":1500793319000,"Open":1.1,"High":2.2,"Low":3.3,"Close":4.4,"Volume":5.5
[1500793259, 1.01, 2.02, 3.03, 4.04, 5.05],
...
]
}
```
Go语言测试数据:
```
ret_records = []interface{}{
[6]interface{}{1500793319, 1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5},
[6]interface{}{1500793259, 1.01, 2.02, 3.03, 4.04, 5.05}
}
```
发明者量化平台```Log```显示```records```数据:
```
[
{"Time":1500793319000,"Open":1.1,"High":2.2,"Low":3.3,"Close":4.4,"Volume":5.5},
{"Time":1500793259000,"Open":1.01,"High":2.02,"Low":3.03,"Close":4.04,"Volume":5.05}
]
```
注意:1、第二维数组中的第一个元素是```int```类型,代表时间戳。2、托管者会自动给时间戳乘1000,以上可以见。
- #### 3、GetDepth:**获取交易所的深度信息(订单薄,卖一、卖二...买一、买二...)**
托管者发送给监听响应函数的```request```中的```method```为:```depth```
托管者发送参数:```request.Params.symbol```:由托管者根据策略设置的币种发送
**托管者向通用协议插件请求时请求主体携带的数据格式**
```
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // 毫秒时间戳
"method" : "depth",
"params" : {"symbol" : "ETH_BTC"}, // 以ETH_BTC交易对举例
}
```
**最终发送给托管者的返回值结构:**
JSON结构
```
{
"data" : {
"time" : 1500793319499,
"asks" : [ [1000, 0.5], [1001, 0.23], [1004, 2.1], ... ],
"bids" : [ [999, 0.25], [998, 0.8], [995, 1.4], ... ],
}
}
```
- #### 4、GetTrades:**获取交易所提供的整个交易所一定时间内的交易记录(非自己的交易记录)**
托管者发送给监听响应函数的```request```中的```method```为:```trades```
托管者发送参数:```request.Params.symbol```值为交易币种例如:```btc```,由托管者根据策略设置的币种发送。
**托管者向通用协议插件请求时请求主体携带的数据格式**
```
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // 毫秒时间戳
"method" : "trades",
"params" : {"symbol" : "ETH_BTC"}, // 以ETH_BTC交易对举例
}
```
**最终发送给托管者的返回值结构:**
JSON结构
```
{
"data": [
{
"id": 12232153,
"time" : 1529919412968,
"price": 1000,
"amount": 0.5,
"type": "buy", // "buy"、"sell"
},{
"id": 12545664,
"time" : 1529919412900,
"price": 1001,
"amount": 1,
"type": "sell",
},{
...
}
]
}
```
- #### 5、GetAccount:**获取账户资产信息**
托管者发送给监听响应函数的```request```中的```method```为:```accounts```
托管者发送参数:(需注意!一般是获取账户的所有资产!,具体看交易所接口,是单独获取还是获取总资产信息)
**托管者向通用协议插件请求时请求主体携带的数据格式**
```
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // 毫秒时间戳
"method" : "accounts",
"params" : {},
}
```
**最终发送给托管者的 返回值结构:**
JSON结构
```
{
"data": [
{"currency": "btc", "free": 1.2, "frozen": 0.1},
{"currency": "ltc", "free": 25, "frozen": 2.1},
{"currency": "ltc", "free": 25, "frozen": 2.1},
...
],
"raw" : {...} // 可以写入插件访问交易所时,交易所返回的原始信息(response)
}
```
- #### 6、Buy、Sell:**发送委托单,下单交易。(市价单、限价单)**
托管者发送给监听响应函数的```request```中的```method```为:```trade```
托管者发送参数:```request.Params.type```:托管者根据调用```exchange.Buy```还是```exchange.Sell```发送、```request.Params.price```:策略中调用的```API```函数的第一个参数、```request.Params.amount```:策略中调用的```API```函数的第二个参数、```request.Params.symbol```:托管者根据设置的币种发送。
**托管者向通用协议插件请求时请求主体携带的数据格式**
```
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // 毫秒时间戳
"method" : "trade",
"params" : {
"symbol" : "ETH_BTC",
"type" : "buy",
"price" : "1000",
"amount" : "1"
}, // 以ETH_BTC交易对,"type":"buy"买请求,价格1000,数量1举例
}
```
**最终发送给托管者的返回值结构:**
JSON结构
```
{
"data": {
"id": 125456, // 下单后返回的订单id
// 如果订单id是"asdf346sfasf532"这样的字符串形式
// 此处id也可以是字符串类型
}
}
```
- #### 7、GetOrder:**获取指定订单号的订单信息**
托管者发送给监听响应函数的```request```中的```method```为:```order```
托管者发送参数:```request.Params.id```、```request.Params.symbol```
**托管者向通用协议插件请求时请求主体携带的数据格式**
```
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // 毫秒时间戳
"method" : "order",
"params" : {"symbol" : "ETH_BTC", "id" : "XXX"}, // 以ETH_BTC交易对,订单id为XXX举例,注意有些交易所的订单号是数字形式的订单ID,如123456,有些交易所的订单号是字符串形式的ID,如poimd55sdfheqxv,具体看交易所的订单ID格式
}
```
**最终发送给托管者的返回值结构:**
JSON结构
```
{
"data": {
"id": 2565244,
"amount": 0.15,
"price": 1002,
"status": "open", // "open":挂起状态、"closed":完成关闭状态、"cancelled":已取消
"deal_amount": 0,
"type": "buy", // "buy"、"sell"
"avg_price": 0, // 如果交易所没有提供,在处理时可以赋值为0
}
}
```
- #### 8、GetOrders: **获取所有未完成的订单信息**
托管者发送给监听响应函数的```request```中的method为:```orders```
托管者发送参数:```request.Params.symbol```
**托管者向通用协议插件请求时请求主体携带的数据格式**
```
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // 毫秒时间戳
"method" : "orders",
"params" : {"symbol" : "ETH_BTC"}, // 以ETH_BTC交易对举例
}
```
**最终发送给托管者的返回值结构:**
JSON结构
```
{
"data": [{
"id": 542156,
"amount": 0.25,
"price": 1005,
"deal_amount": 0,
"type": "buy", // "buy"、"sell"
"status": "open", // "open"
},{
...
}]
}
```
- #### 9、CancelOrder: **取消指定订单号的订单委托**
托管者发送给监听响应函数的```request```中的```method```为:```cancel```
托管者发送参数:```request.Params.id```:字符串类型,策略调用的API函数的第一个参数、```request.Params.symbol```:btc(举例)由托管者根据策略设置的币种发送
**托管者向通用协议插件请求时请求主体携带的数据格式**
```
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // 毫秒时间戳
"method" : "cancel",
"params" : {"symbol" : "ETH_BTC", "id" : "XXX"}, // 以ETH_BTC交易对,id为"XXX"(同GetOrder函数的参数id一样),举例
}
```
**最终发送给托管者的返回值结构:**
JSON结构
```
{
"data": true, // true or false
}
```
- #### 10、IO: **调用发明者量化平台的exchange.IO函数**
托管者发送给监听响应函数的```request```中的```method```为以```__api_```开头的的方法名。
**托管者向通用协议插件请求时请求主体携带的数据格式**
```
{
"access_key" : "access_key",
"secret_key" : "secret_key",
"nonce" : "1500793319499", // 毫秒时间戳
"method" : "__api_XXX", // XXX为具体交易所的API接口(不包含基地址)
"params" : {"borrow_id" : "123", "symbol" : "cny"}, // 具体是传入IO函数的参数
}
```
**最终发送给托管者的返回值结构:**
```
{
"data": {...} // 具体的接口调用的返回值
}
```
举例,策略调用:
```
var io_str = exchange.IO("api", "POST", "cancel_borrow", "symbol=cny&borrow_id=123")
```
插件中的测试代码(go语言):
```go
fmt.Println("request.Method:", request.Method, "request.Params:", request.Params)
```
插件命令行 :
2017/08/31 10:19:59 Running http://127.0.0.1:6666/DigitalAsset ...
**插件命令行中打印出的request.Method,request.Params**
托管者发送的请求Body中数据解析后的request中:```request.Method```为:```__api_cancel_borrow```
托管者发送的请求Body中数据解析后的request中:```request.Params```为:```{"borrow_id" : "123", "symbol" : "cny"}```
可自定义处理这些直接访问交易所```API```的```exchange.IO```调用。
```
# 注意:
# 在调用exchange.IO("api", "POST", "/api/v1/getAccount", "symbol=BTC_USDT")时,
# 如果第二个参数不是POST,而是:exchange.IO("api", "GET", "/api/v1/getAccount", "symbol=BTC_USDT")
# 是GET方法,这时在通用协议插件接受到的http请求中头部Http-Method中储存的才是GET,
# 所以在通用协议处理IO函数实现时,需要参考以下范例代码:
// tapiCall函数定义
func (p *iStocksExchange) tapiCall(method string, params map[string]string, httpType string) (js *Json, err error) {
...
}
// 在OnPost函数中
if strings.HasPrefix(request.Method, "__api_") {
var js *Json
js, err = e.tapiCall(request.Method[6:], request.Params, r.Header.Get("Http-Method"))
...
}
```
- ### 对于exchange.GetRawJSON的支持
底层自动处理```exchange.GetRawJSON```的调用,不用在插件中实现。
- ### 对于exchange.Go的支持
底层自动处理```exchange.Go```的调用,不用在插件中处理。
```
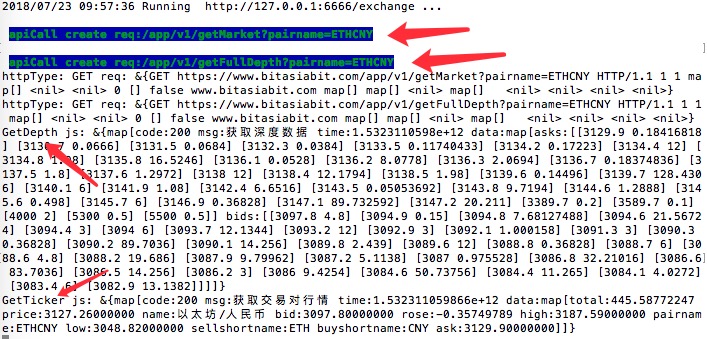
var beginTime = new Date().getTime()
var ret = exchange.Go("GetDepth")
var endTime = new Date().getTime()
Log(endTime - beginTime, "#FF0000")
// Sleep(2000)
beginTime = new Date().getTime()
Log(exchange.GetTicker())
endTime = new Date().getTime()
Log(endTime - beginTime, "#FF0000")
var depth = ret.wait()
Log("depth:", depth)
```
```
# 注意:使用exchange.Go在wait的时候如果指定了超时时间,
# 一定要确保获取到最终的数据,这样申请的并发线程才能回收。
```
- ### 对于期货函数的支持
需要在插件程序中实现具体处理,例如设置杠杆、合约代码、下单方向,可以设置一个本地变量记录,获取持仓需要访问交易所接口获取原始数据并处理为FMZ平台上定义的持仓结构并返回。
当策略中调用以下函数时,插件程序接收到的```Rpc```请求格式与其它接口略有差异,需要注意通用协议插件程序中```RpcRequest```的格式,主要区别为params的值是一个复合结构。
- SetContractType
设置合约代码。
```
{"access_key":"123","method":"io","nonce":1623307269528738000,"params":{"args":["quarter"],"code":2},"secret_key":"123"}
```
- SetDirection
设置期货下单方向。
```
{"access_key":"123","method":"io","nonce":1623308734966484000,"params":{"args":["closesell"],"code":1},"secret_key":"123"}
```
- SetMarginLevel
设置期货杠杆。
```
{"access_key":"123","method":"io","nonce":1623308734966939000,"params":{"args":[12],"code":0},"secret_key":"123"}
```
- GetPosition
获取期货持仓。
当```exchange.GetPosition()```调用时:
```
{"access_key":"123","method":"io","nonce":1623308734967442000,"params":{"args":[],"code":3},"secret_key":"123"}
```
当```exchange.GetPosition("swap")```调用时:
```
{"access_key":"123","method":"io","nonce":1623308734967442000,"params":{"args":["swap"],"code":3},"secret_key":"123"}
```
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- ### 通用协议插件完整的Go语言范例(接入比特购交易所)
```go
/*
GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build -ldflags '-s -w -extldflags -static' rest_bitgo.go
*/
package main
import (
"bytes"
"crypto/md5"
"encoding/hex"
"encoding/json"
"errors"
"flag"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
"net/url"
"sort"
"strconv"
"strings"
"time"
)
func toFloat(s interface{}) float64 {
var ret float64
switch v := s.(type) {
case float64:
ret = v
case float32:
ret = float64(v)
case int64:
ret = float64(v)
case int:
ret = float64(v)
case int32:
ret = float64(v)
case string:
ret, _ = strconv.ParseFloat(strings.TrimSpace(v), 64)
}
return ret
}
func float2str(i float64) string {
return strconv.FormatFloat(i, 'f', -1, 64)
}
func toInt64(s interface{}) int64 {
var ret int64
switch v := s.(type) {
case int:
ret = int64(v)
case float64:
ret = int64(v)
case bool:
if v {
ret = 1
} else {
ret = 0
}
case int64:
ret = v
case string:
ret, _ = strconv.ParseInt(strings.TrimSpace(v), 10, 64)
}
return ret
}
func toString(s interface{}) string {
var ret string
switch v := s.(type) {
case string:
ret = v
case int64:
ret = strconv.FormatInt(v, 10)
case float64:
ret = strconv.FormatFloat(v, 'f', -1, 64)
case bool:
ret = strconv.FormatBool(v)
default:
ret = fmt.Sprintf("%v", s)
}
return ret
}
type Json struct {
data interface{}
}
func NewJson(body []byte) (*Json, error) {
j := new(Json)
err := j.UnmarshalJSON(body)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return j, nil
}
func (j *Json) UnmarshalJSON(p []byte) error {
return json.Unmarshal(p, &j.data)
}
func (j *Json) Get(key string) *Json {
m, err := j.Map()
if err == nil {
if val, ok := m[key]; ok {
return &Json{val}
}
}
return &Json{nil}
}
func (j *Json) CheckGet(key string) (*Json, bool) {
m, err := j.Map()
if err == nil {
if val, ok := m[key]; ok {
return &Json{val}, true
}
}
return nil, false
}
func (j *Json) Map() (map[string]interface{}, error) {
if m, ok := (j.data).(map[string]interface{}); ok {
return m, nil
}
return nil, errors.New("type assertion to map[string]interface{} failed")
}
func (j *Json) Array() ([]interface{}, error) {
if a, ok := (j.data).([]interface{}); ok {
return a, nil
}
return nil, errors.New("type assertion to []interface{} failed")
}
func (j *Json) Bool() (bool, error) {
if s, ok := (j.data).(bool); ok {
return s, nil
}
return false, errors.New("type assertion to bool failed")
}
func (j *Json) String() (string, error) {
if s, ok := (j.data).(string); ok {
return s, nil
}
return "", errors.New("type assertion to string failed")
}
func (j *Json) Bytes() ([]byte, error) {
if s, ok := (j.data).(string); ok {
return []byte(s), nil
}
return nil, errors.New("type assertion to []byte failed")
}
func (j *Json) Int() (int, error) {
if f, ok := (j.data).(float64); ok {
return int(f), nil
}
return -1, errors.New("type assertion to float64 failed")
}
func (j *Json) MustArray(args ...[]interface{}) []interface{} {
var def []interface{}
switch len(args) {
case 0:
case 1:
def = args[0]
default:
log.Panicf("MustArray() received too many arguments %d", len(args))
}
a, err := j.Array()
if err == nil {
return a
}
return def
}
func (j *Json) MustMap(args ...map[string]interface{}) map[string]interface{} {
var def map[string]interface{}
switch len(args) {
case 0:
case 1:
def = args[0]
default:
log.Panicf("MustMap() received too many arguments %d", len(args))
}
a, err := j.Map()
if err == nil {
return a
}
return def
}
func (j *Json) MustString(args ...string) string {
var def string
switch len(args) {
case 0:
case 1:
def = args[0]
default:
log.Panicf("MustString() received too many arguments %d", len(args))
}
s, err := j.String()
if err == nil {
return s
}
return def
}
func (j *Json) MustInt64() int64 {
var ret int64
var err error
switch v := j.data.(type) {
case int:
ret = int64(v)
case int64:
ret = v
case float64:
ret = int64(v)
case string:
if ret, err = strconv.ParseInt(v, 10, 64); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
default:
ret = 0
//panic("type assertion to int64 failed")
}
return ret
}
func (j *Json) MustFloat64() float64 {
var ret float64
var err error
switch v := j.data.(type) {
case int:
ret = float64(v)
case int64:
ret = float64(v)
case float64:
ret = v
case string:
v = strings.Replace(v, ",", "", -1)
if ret, err = strconv.ParseFloat(v, 64); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
default:
ret = 0
//panic("type assertion to float64 failed")
}
return ret
}
type iBitgo struct {
accessKey string
secretKey string
currency string
opCurrency string
baseCurrency string
secret string
secretExpires int64
apiBase string
step int64
newRate float64
timeout time.Duration
timeLocation *time.Location
}
type MapSorter []Item
type Item struct {
Key string
Val string
}
func NewMapSorter(m map[string]string) MapSorter {
ms := make(MapSorter, 0, len(m))
for k, v := range m {
if strings.HasPrefix(k, "!") {
k = strings.Replace(k, "!", "", -1)
}
ms = append(ms, Item{k, v})
}
return ms
}
func (ms MapSorter) Len() int {
return len(ms)
}
func (ms MapSorter) Less(i, j int) bool {
//return ms[i].Val < ms[j].Val // 按值排序
return ms[i].Key < ms[j].Key // 按键排序
}
func (ms MapSorter) Swap(i, j int) {
ms[i], ms[j] = ms[j], ms[i]
}
func encodeParams(params map[string]string, escape bool) string {
ms := NewMapSorter(params)
sort.Sort(ms)
v := url.Values{}
for _, item := range ms {
v.Add(item.Key, item.Val)
}
if escape {
return v.Encode()
}
var buf bytes.Buffer
keys := make([]string, 0, len(v))
for k := range v {
keys = append(keys, k)
}
sort.Strings(keys)
for _, k := range keys {
vs := v[k]
prefix := k + "="
for _, v := range vs {
if buf.Len() > 0 {
buf.WriteByte('&')
}
buf.WriteString(prefix)
buf.WriteString(v)
}
}
return buf.String()
}
func newBitgo(accessKey, secretKey string) *iBitgo {
s := new(iBitgo)
s.accessKey = accessKey
s.secretKey = secretKey
s.apiBase = "https://www.bitgo.cn"
s.timeout = 20 * time.Second
s.timeLocation = time.FixedZone("Asia/Shanghai", 8*60*60)
return s
}
func (p *iBitgo) apiCall(method string) (*Json, error) {
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", fmt.Sprintf("%s/appApi.html?%s", p.apiBase, method), nil)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
resp, err := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
b, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return NewJson(b)
}
func (p *iBitgo) GetTicker(symbol string) (ticker interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.apiCall("action=market&symbol=" + symbol)
if err != nil {
return
}
dic := js.Get("data")
ticker = map[string]interface{}{
"time": js.Get("time").MustInt64(),
"buy": dic.Get("buy").MustFloat64(),
"sell": dic.Get("sell").MustFloat64(),
"last": dic.Get("last").MustFloat64(),
"high": dic.Get("high").MustFloat64(),
"low": dic.Get("low").MustFloat64(),
"vol": dic.Get("vol").MustFloat64(),
}
return
}
func (p *iBitgo) GetDepth(symbol string) (depth interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.apiCall("action=depth&symbol=" + symbol)
if err != nil {
return
}
dic := js.Get("data")
asks := [][2]float64{}
bids := [][2]float64{}
for _, pair := range dic.Get("asks").MustArray() {
arr := pair.([]interface{})
asks = append(asks, [2]float64{toFloat(arr[0]), toFloat(arr[1])})
}
for _, pair := range dic.Get("bids").MustArray() {
arr := pair.([]interface{})
bids = append(bids, [2]float64{toFloat(arr[0]), toFloat(arr[1])})
}
depth = map[string]interface{}{
"time": js.Get("time").MustInt64(),
"asks": asks,
"bids": bids,
}
return
}
func (p *iBitgo) GetTrades(symbol string) (trades interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.apiCall("action=trades&symbol=" + symbol)
if err != nil {
return
}
dic := js.Get("data")
items := []map[string]interface{}{}
for _, pair := range dic.MustArray() {
item := map[string]interface{}{}
arr := pair.(map[string]interface{})
item["id"] = toInt64(arr["id"])
item["price"] = toFloat(arr["price"])
item["amount"] = toFloat(arr["amount"])
// trade.Time = toInt64(arr["time"]) * 1000
if toString(arr["en_type"]) == "bid" {
item["type"] = "buy"
} else {
item["type"] = "sell"
}
items = append(items, item)
}
trades = items
return
}
func (p *iBitgo) GetRecords(step int64, symbol string) (records interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.apiCall(fmt.Sprintf("action=kline&symbol=%s&step=%d", symbol, step*60))
if err != nil {
return
}
items := []interface{}{}
for _, pair := range js.Get("data").MustArray() {
arr := pair.([]interface{})
if len(arr) < 6 {
err = errors.New("response format error")
return
}
item := [6]interface{}{}
item[0] = toInt64(arr[0])
item[1] = toFloat(arr[1])
item[2] = toFloat(arr[2])
item[3] = toFloat(arr[3])
item[4] = toFloat(arr[4])
item[5] = toFloat(arr[5])
items = append(items, item)
}
records = items
return
}
func (p *iBitgo) tapiCall(method string, params map[string]string) (js *Json, err error) {
if params == nil {
params = map[string]string{}
}
params["api_key"] = p.accessKey
h := md5.New()
h.Write([]byte(encodeParams(params, false) + "&secret_key=" + p.secretKey))
params["sign"] = strings.ToUpper(hex.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil)))
params["action"] = method
qs := encodeParams(params, false)
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", fmt.Sprintf("%s/appApi.html?%s", p.apiBase, qs), nil)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
resp, err := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
b, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
js, err = NewJson(b)
if js != nil {
if code := js.Get("code").MustInt64(); code != 200 {
s := js.Get("msg").MustString()
if s == "" {
s = fmt.Sprintf("%v", toString(js.data))
}
return nil, errors.New(s)
}
}
return js, err
}
func (p *iBitgo) GetAccount(symbol string) (account interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.tapiCall("userinfo", nil)
if err != nil {
return
}
mp := js.Get("data")
assets := map[string]map[string]interface{}{}
for k := range mp.MustMap() {
dic := mp.Get(k)
if k == "free" {
for c := range dic.MustMap() {
if _, ok := assets[c]; !ok {
assets[c] = map[string]interface{}{}
}
assets[c]["currency"] = c
assets[c]["free"] = dic.Get(c).MustFloat64()
}
} else if k == "frozen" {
for c := range dic.MustMap() {
if _, ok := assets[c]; !ok {
assets[c] = map[string]interface{}{}
}
assets[c]["currency"] = c
assets[c]["frozen"] = dic.Get(c).MustFloat64()
}
}
}
accounts := []map[string]interface{}{}
for _, pair := range assets {
accounts = append(accounts, pair)
}
account = accounts
return
}
func (p *iBitgo) Trade(side string, price, amount float64, symbol string) (orderId interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.tapiCall("trade", map[string]string{
"symbol": symbol,
"type": side,
"price": float2str(price),
"amount": float2str(amount),
})
if err != nil {
return
}
orderId = map[string]int64{"id": js.Get("orderId").MustInt64()}
return
}
func (p *iBitgo) GetOrders(symbol string) (orders interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.tapiCall("entrust", map[string]string{"symbol": symbol})
if err != nil {
return
}
items := []map[string]interface{}{}
for _, ele := range js.Get("data").MustArray() {
mp := ele.(map[string]interface{})
item := map[string]interface{}{}
item["id"] = toInt64(mp["id"])
item["amount"] = toFloat(mp["count"])
if _, ok := mp["prize"]; ok {
item["price"] = toFloat(mp["prize"])
} else {
item["price"] = toFloat(mp["price"])
}
item["deal_amount"] = toFloat(mp["success_count"])
if toInt64(mp["type"]) == 0 {
item["type"] = "buy"
} else {
item["type"] = "sell"
}
item["status"] = "open"
items = append(items, item)
}
return items, nil
}
func (p *iBitgo) GetOrder(orderId int64, symbol string) (order interface{}, err error) {
var js *Json
js, err = p.tapiCall("order", map[string]string{"id": toString(orderId)})
if err != nil {
return
}
found := false
item := map[string]interface{}{}
for _, ele := range js.Get("data").MustArray() {
mp := ele.(map[string]interface{})
if toInt64(mp["id"]) != orderId {
continue
}
item["id"] = toInt64(mp["id"])
item["amount"] = toFloat(mp["count"])
if _, ok := mp["prize"]; ok {
item["price"] = toFloat(mp["prize"])
} else {
item["price"] = toFloat(mp["price"])
}
item["deal_amount"] = toFloat(mp["success_count"])
if toInt64(mp["type"]) == 0 {
item["type"] = "buy"
} else {
item["type"] = "sell"
}
switch toInt64(mp["status"]) {
case 1, 2:
item["status"] = "open"
case 3:
item["status"] = "closed"
case 4:
item["status"] = "cancelled"
}
found = true
break
}
if !found {
return nil, errors.New("order not found")
}
return item, nil
}
func (p *iBitgo) CancelOrder(orderId int64, symbol string) (ret bool, err error) {
_, err = p.tapiCall("cancel_entrust", map[string]string{"id": strconv.FormatInt(orderId, 10)})
if err != nil {
return
}
ret = true
return
}
type RpcRequest struct { // 结构体里的字段首字母必须大写,否则无法正常解析,结构体有导出和未导出,大写字母开头为导出。
// 在Unmarshal的时候会 根据 json 匹配查找该结构体的tag, 所以此处需要修饰符
AccessKey string `json:"access_key"`
SecretKey string `json:"secret_key"`
Nonce int64 `json:"nonce"`
Method string `json:"method"`
Params map[string]string `json:"params"`
}
func OnPost(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
var ret interface{}
defer func() {
if e := recover(); e != nil {
if ee, ok := e.(error); ok {
e = ee.Error()
}
ret = map[string]string{"error": fmt.Sprintf("%v", e)}
}
b, _ := json.Marshal(ret)
w.Write(b)
}()
b, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
var request RpcRequest
err = json.Unmarshal(b, &request)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
e := newBitgo(request.AccessKey, request.SecretKey)
symbol := request.Params["symbol"]
if s := request.Params["access_key"]; len(s) > 0 {
e.accessKey = s
}
if s := request.Params["secret_key"]; len(s) > 0 {
e.secretKey = s
}
if symbolIdx, ok := map[string]int{
"btc": 1,
"ltc": 2,
"etp": 3,
"eth": 4,
"etc": 5,
"doge": 6,
"bec": 7,
}[strings.Replace(strings.ToLower(symbol), "_cny", "", -1)]; ok {
symbol = toString(symbolIdx)
}
var data interface{}
switch request.Method {
case "ticker":
data, err = e.GetTicker(symbol)
case "depth":
data, err = e.GetDepth(symbol)
case "trades":
data, err = e.GetTrades(symbol)
case "records":
data, err = e.GetRecords(toInt64(request.Params["period"]), symbol)
case "accounts":
data, err = e.GetAccount(symbol)
case "trade":
side := request.Params["type"]
if side == "buy" {
side = "0"
} else {
side = "1"
}
price := toFloat(request.Params["price"])
amount := toFloat(request.Params["amount"])
data, err = e.Trade(side, price, amount, symbol)
case "orders":
data, err = e.GetOrders(symbol)
case "order":
data, err = e.GetOrder(toInt64(request.Params["id"]), symbol)
case "cancel":
data, err = e.CancelOrder(toInt64(request.Params["id"]), symbol)
default:
if strings.HasPrefix(request.Method, "__api_") {
data, err = e.tapiCall(request.Method[6:], request.Params)
} else {
panic(errors.New(request.Method + " not support"))
}
}
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
ret = map[string]interface{}{
"data": data,
}
return
}
func main() {
var addr = flag.String("b", "127.0.0.1:6666", "bind addr")
flag.Parse()
if *addr == "" {
flag.Usage()
return
}
basePath := "/exchange"
log.Println("Running ", fmt.Sprintf("http://%s%s", *addr, basePath), "...")
http.HandleFunc(basePath, OnPost)
http.ListenAndServe(*addr, nil)
}
- Uno de los estudios de la serie de estrategias de comercio de alta frecuencia: Radicalismo bajo la ley de Bayes
- Estrategia y estado
- Investigación sobre la cantidad de operaciones diarias
- ¿Alguien ha usado la versión mejorada del sistema de negociación en la playa BTC?
- Cuadrícula unilateral de la estrategia de deformación de la red (versión de notas)
- ¿Puede agregar 4 horas de datos de línea K?
- El libro de órdenes de alta frecuencia
- ¿Es la velocidad de conexión un poco lenta para acceder a un servidor fuera del país?
- ¿Cómo evitar los puntos débiles?
- Tomé una nota de la información errónea que apareció.
- Inventor cuantificado Nuevo incremento Función de importación e exportación de parámetros de robots de disco real
- ¿Okcoin tiene una API para indicadores tecnológicos como MACD?
- El resultado es que el país está en una situación de crisis.
- ¿Puedo acceder a una API de terceros?
- La API de Bitcoin ha estado haciendo errores
- Bithumb, la bolsa de valores, informó de un error, por favor, a los altos funcionarios.
- La agrupación BTC_PEB está apoyando un error
- ¿Cómo añadir plataformas personalizadas?
- ¿Qué puede hacer el protocolo general cuando se añade una bolsa?
- Las preguntas que surgen cuando se compra una pieza con un precio más bajo en la lista de compras de la pieza.
Las hierbasEjemplos de intercambios personalizados con el protocolo de acceso general de Python https://www.fmz.com/strategy/101399
Las hierbasEjemplos de intercambios personalizados con el protocolo de acceso Python http://www.fmz.com/strategy/101399
- ¿Por qué no?Bitmex ya ha accedido a la plataforma, pero sin importar si usa _C (exchange.GetTicker).Buy o _C (exchange.GetDepth).
Un buen modelo todos los días.Ha ha, escribir un plugin de protocolo general puede ser un paso más para que puedas vincular completamente tu propia API de intercambio, o mejor usar tu propio programa directamente.
Zhchy751¿Hay ejemplos de acceso al protocolo general listo, robots completos / estrategias / configuración de intercambios, etc.?
¿Qué quieres decir?Este código es el plugin del protocolo general, ¿verdad? Este plugin no es similar al modelo de estrategia que puedo llamar directamente? Voy a enviar y obtener datos y analizarlos con py post o get. El código del plugin del protocolo general, es el post implementado, get y descifrado, al mismo tiempo que recibe botvs.api?
el chalieSi tienes Python, está bien, sólo esto.
el jado¿No entiendo completamente... si usar un plugin de programación general significa escribir muchas funciones por sí mismo, por ejemplo, GetAccout)))?
Alanyao¿Por qué no hay un ejemplo de js? ¿Por qué no hay un ejemplo de js? ¿Por qué no hay un ejemplo de GO?
Nxtplayer6 para volar, sin embargo, no lo hace....
Las novias también.El hombre de las calles
Los inventores cuantifican - sueños pequeñosBITMEX es una bolsa de futuros. Para establecer los contratos que desea operar o obtener, consulte el documento de la API exchange.SetContractType.
Un buen modelo todos los días.También lo es.
Los inventores cuantifican - sueños pequeñosPero ¿qué pasa si la estrategia es multi-plataforma? ¡No puedes renunciar a un bosque por un árbol!
Los inventores cuantifican - sueños pequeñosEs decir, se puede compilar en un archivo ejecutable que se puede ejecutar junto con el administrador. No importa qué catálogo sea. No hay ejemplos de python por ahora, pero si tengo tiempo, escribo uno.
¿Qué quieres decir?¿Cómo hace el plugin para que funcione, por ejemplo, escribiendo en formato py y colocándolo directamente en el directorio exe del administrador? ¿Y añadir un camino de referencia al directorio de archivos py del plugin en el programa py local?
Los inventores cuantifican - sueños pequeñosPara BotVS API, estos objetos de intercambio son los mismos (ya sea que BotVS ya esté conectado o que usted mismo haya escrito el protocolo general. Plugin compatible), la política no requiere ningún ajuste. Ver más arriba Documentación: 1, Plugin de protocolo general en marcha, configuración de puertos El contenido es claro.
¿Qué quieres decir?¿Es esto similar a un patrón de estrategia, en el que las bolsas de intercambio que quieren conectar el plugin correspondiente llaman la función aquí, y las otras utilizan la API botvs existente?
Los inventores cuantifican - sueños pequeños- ¿Es el código de este plugin del protocolo general el mismo que el implementado en post, get y descifrado, al mismo tiempo que se conecta al API de botvs? Sí, es cierto. - http://127.0.0.1:6666/DigitalAsset Esta dirección representa un objeto de intercambio al que se envían las solicitudes de los administradores. Los complementos de servicios escuchan las solicitudes de esta dirección y responden, en lugar de los administradores, para acceder al intercambio y devolver los datos solicitados por el administrador (en formato), implementar, estrategiar y bot Compatible con un BotVS que aún no tiene acceso al intercambio.
Los inventores cuantifican - sueños pequeñosLa implementación en Python es la misma, la interfaz y el formato son los mismos. La diferencia es sólo en el lenguaje utilizado.
Los inventores cuantifican - sueños pequeñosEste es un ejemplo de un plugin externo al administrador, cuyo objetivo es escribir un poco de código interactivo de intercambio para acceder a la plataforma BotVS, lo que equivale a un intercambio automático con BotVS. Se puede escribir este tipo de plugins en lenguajes como PHP, node.js, python, Go, etc. Siempre que el formato de datos cumpla con el formato descrito en la documentación anterior, los datos obtenidos por el plugin se pueden conectar a la interfaz API BotVS correspondiente.
Los inventores cuantifican - sueños pequeñosSí, escribir una implementación concreta de estas funciones de interfaz, como BotVS API GetAccount, es como escribir tu propio código de la bolsa de intercambio conectada.
Los inventores cuantifican - sueños pequeñosDe acuerdo con los ejemplos, se puede usar Python, Node.js, PHP y Golang.