Las instrucciones de la API FMZ
El autor:No hay nada, Creado: 2020-04-20 10:19:00, Actualizado: 2023-04-12 14:44:56- ¿ Qué?parameter is set toel signoorel signoTx, theSe requiere el parámetro key```.
function main(){
Log(Encode("md5", "raw", "hex", "hello"))
Log(Encode("sha512", "raw", "base64", "hello"))
Log(Encode("keccak256", "raw", "hex", "unwrapWETH9(uint256,address)"))
Log(Encode("raw", "string", "hex", "example")) // 6578616d706c65
Log(Encode("raw", "hex", "string", "6578616d706c65")) // example
}
def main():
Log(Encode("md5", "raw", "hex", "hello", "", ""))
Log(Encode("sha512", "raw", "base64", "hello", "", ""))
Log(Encode("keccak256", "raw", "hex", "unwrapWETH9(uint256,address)", "", ""))
Log(Encode("raw", "string", "hex", "example", "", ""))
Log(Encode("raw", "hex", "string", "6578616d706c65", "", ""))
void main(){
Log(Encode("md5", "raw", "hex", "hello"));
Log(Encode("sha512", "raw", "base64", "hello"));
Log(Encode("keccak256", "raw", "hex", "unwrapWETH9(uint256,address)"));
Log(Encode("raw", "string", "hex", "example")); // 6578616d706c65
Log(Encode("raw", "hex", "string", "6578616d706c65")); // example
}
El parámetroalgoTambién admite la codificación y decodificación de cadenas, tales comotext.encoder.utf8, text.decoder.utf8, text.encoder.gbkytext.decoder.gbk.
function main(){
var ret1 = Encode("text.encoder.utf8", "raw", "hex", "hello") // e4bda0e5a5bd
Log(ret1)
var ret2 = Encode("text.decoder.utf8", "hex", "string", ret1)
Log(ret2)
var ret3 = Encode("text.encoder.gbk", "raw", "hex", "hello") // c4e3bac3
Log(ret3)
var ret4 = Encode("text.decoder.gbk", "hex", "string", ret3)
Log(ret4)
}
def main():
ret1 = Encode("text.encoder.utf8", "raw", "hex", "hello", "", "") # e4bda0e5a5bd
Log(ret1)
ret2 = Encode("text.decoder.utf8", "hex", "string", ret1, "", "")
Log(ret2)
ret3 = Encode("text.encoder.gbk", "raw", "hex", "hello", "", "") # c4e3bac3
Log(ret3)
ret4 = Encode("text.decoder.gbk", "hex", "string", ret3, "", "")
Log(ret4)
void main(){
auto ret1 = Encode("text.encoder.utf8", "raw", "hex", "hello"); // e4bda0e5a5bd
Log(ret1);
auto ret2 = Encode("text.decoder.utf8", "hex", "string", ret1);
Log(ret2);
auto ret3 = Encode("text.encoder.gbk", "raw", "hex", "hello"); // c4e3bac3
Log(ret3);
auto ret4 = Encode("text.decoder.gbk", "hex", "string", ret3);
Log(ret4);
}
UnixNano (()
UnixNano()devuelve una marca de tiempo de nivel nanosegundo; si necesita obtener la marca de tiempo de nivel milisegundo, puede utilizar el siguiente código:
function main() {
var time = UnixNano() / 1000000
Log(_N(time, 0))
}
def main():
time = UnixNano()
Log(time)
void main() {
auto time = UnixNano();
Log(time);
}
Unix ((()
Unix()devuelve una marca de tiempo en segundos.
function main() {
var t = Unix()
Log(t)
}
def main():
t = Unix()
Log(t)
void main() {
auto t = Unix();
Log(t);
}
¿Qué quieres decir?
GetOS()Devuelve información sobre el sistema donde se encuentra el docker.
function main() {
Log("GetOS:", GetOS())
}
def main():
Log("GetOS:", GetOS())
void main() {
Log("GetOS:", GetOS());
}
La salida de registro del docker ejecutado porMac OSde un ordenador Apple:
- ¿Qué quieres decir?
darwines el nombre deMac OS system.
MD5 (cuadrícula)
MD5(String); valor del parámetro: tipo de cadena.
function main() {
Log("MD5", MD5("hello world"))
}
def main():
Log("MD5", MD5("hello world"))
void main() {
Log("MD5", MD5("hello world"));
}
Producción de registro:
¿Qué es lo que está pasando?
DbExec ((...)
DBExec(), su valor de parámetro podría ser cadena, número o booleano, nulo y otros tipos; valor de retorno: el objeto con los resultados de ejecución en lenguaje SQLite.DBExec(), la función de interfaz de la base de datos, a través de los parámetros de paso, puede ejecutar la base de datos del bot (base de datos SQLite).SQLiteEl sistema en la base de datos de bots guarda tablas incluyendo:kvdb, cfg, log, profitychartNo se utilizarán las tablas mencionadas anteriormente.DBExec()Sólo admite el bot real.
-
Apoya la base de datos de memoria Para los parámetros de funcionamiento
DBExec, si elCuadradola declaración comienza con:, las operaciones en la base de datos de memoria serán más rápidas sin necesidad de escribir archivos.function main() { var strSql = [ ":CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(", "TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,", "HIGH REAL NOT NULL,", "OPEN REAL NOT NULL,", "LOW REAL NOT NULL,", "CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,", "VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)" ].join("") var ret = DBExec(strSql) Log(ret) // Add a piece of data Log(DBExec(":INSERT INTO TEST_TABLE (TS, HIGH, OPEN, LOW, CLOSE, VOLUME) VALUES (1518970320000, 100, 99.1, 90, 100, 12345.6);")) // Query the data Log(DBExec(":SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;")) }def main(): arr = [ ":CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(", "TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,", "HIGH REAL NOT NULL,", "OPEN REAL NOT NULL,", "LOW REAL NOT NULL,", "CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,", "VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)" ] strSql = "" for i in range(len(arr)): strSql += arr[i] ret = DBExec(strSql) Log(ret) # Add a piece of data Log(DBExec(":INSERT INTO TEST_TABLE (TS, HIGH, OPEN, LOW, CLOSE, VOLUME) VALUES (1518970320000, 100, 99.1, 90, 100, 12345.6);")) # Query the data Log(DBExec(":SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;"))void main() { string strSql = ":CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(\ TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,\ HIGH REAL NOT NULL,\ OPEN REAL NOT NULL,\ LOW REAL NOT NULL,\ CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,\ VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)"; auto ret = DBExec(strSql); Log(ret); // Add a piece of data Log(DBExec(":INSERT INTO TEST_TABLE (TS, HIGH, OPEN, LOW, CLOSE, VOLUME) VALUES (1518970320000, 100, 99.1, 90, 100, 12345.6);")); // Query the data Log(DBExec(":SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;")); } -
Crear una tabla
function main() {
var strSql = [
"CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(",
"TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,",
"HIGH REAL NOT NULL,",
"OPEN REAL NOT NULL,",
"LOW REAL NOT NULL,",
"CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,",
"VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)"
].join("")
var ret = DBExec(strSql)
Log(ret)
}
def main():
arr = [
"CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(",
"TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,",
"HIGH REAL NOT NULL,",
"OPEN REAL NOT NULL,",
"LOW REAL NOT NULL,",
"CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,",
"VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)"
]
strSql = ""
for i in range(len(arr)):
strSql += arr[i]
ret = DBExec(strSql)
Log(ret)
void main() {
string strSql = "CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(\
TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,\
HIGH REAL NOT NULL,\
OPEN REAL NOT NULL,\
LOW REAL NOT NULL,\
CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,\
VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)";
auto ret = DBExec(strSql);
Log(ret);
}
- Las operaciones de adición, eliminación, consulta y modificación registradas en el cuadro
function main() {
var strSql = [
"CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(",
"TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,",
"HIGH REAL NOT NULL,",
"OPEN REAL NOT NULL,",
"LOW REAL NOT NULL,",
"CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,",
"VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)"
].join("")
Log(DBExec(strSql))
// Add a piece of data
Log(DBExec("INSERT INTO TEST_TABLE (TS, HIGH, OPEN, LOW, CLOSE, VOLUME) VALUES (1518970320000, 100, 99.1, 90, 100, 12345.6);"))
// Query the data
Log(DBExec("SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;"))
// Modify the data
Log(DBExec("UPDATE TEST_TABLE SET HIGH=? WHERE TS=?", 110, 1518970320000))
// Delete the data
Log(DBExec("DELETE FROM TEST_TABLE WHERE HIGH=?", 110))
}
def main():
arr = [
"CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(",
"TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,",
"HIGH REAL NOT NULL,",
"OPEN REAL NOT NULL,",
"LOW REAL NOT NULL,",
"CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,",
"VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)"
]
strSql = ""
for i in range(len(arr)):
strSql += arr[i]
Log(DBExec(strSql))
# Add a piece of data
Log(DBExec("INSERT INTO TEST_TABLE (TS, HIGH, OPEN, LOW, CLOSE, VOLUME) VALUES (1518970320000, 100, 99.1, 90, 100, 12345.6);"))
# Query the data
Log(DBExec("SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;"))
# Modify the data
Log(DBExec("UPDATE TEST_TABLE SET HIGH=? WHERE TS=?", 110, 1518970320000))
# Delete the data
Log(DBExec("DELETE FROM TEST_TABLE WHERE HIGH=?", 110))
void main() {
string strSql = "CREATE TABLE TEST_TABLE(\
TS INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,\
HIGH REAL NOT NULL,\
OPEN REAL NOT NULL,\
LOW REAL NOT NULL,\
CLOSE REAL NOT NULL,\
VOLUME REAL NOT NULL)";
Log(DBExec(strSql));
// Add a piece of data
Log(DBExec("INSERT INTO TEST_TABLE (TS, HIGH, OPEN, LOW, CLOSE, VOLUME) VALUES (1518970320000, 100, 99.1, 90, 100, 12345.6);"));
// Query the data
Log(DBExec("SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;"));
// Modify the data
Log(DBExec("UPDATE TEST_TABLE SET HIGH=? WHERE TS=?", 110, 1518970320000));
// Delete the data
Log(DBExec("DELETE FROM TEST_TABLE WHERE HIGH=?", 110));
}
UUID (()
UUID(), devuelve un UUID único de 32 bits, esta función solo está disponible para bots reales.
function main() {
var uuid1 = UUID()
var uuid2 = UUID()
Log(uuid1, uuid2)
}
def main():
uuid1 = UUID()
uuid2 = UUID()
Log(uuid1, uuid2)
void main() {
auto uuid1 = UUID();
auto uuid2 = UUID();
Log(uuid1, uuid2);
}
EventLoop (tiempo muerto)
EventLoop(timeout), devuelve después de que haya algúnwebsocketlegible oexchange.Go, HttpQuery_Goy otras tareas concurrentes.timeoutSi el valor de un evento es igual a 0, espere a que ocurra un evento antes de devolverlo. Si es mayor que 0, establezca el tiempo de espera del evento. Si es menor que 0, devuelva el evento más reciente inmediatamente. Si el objeto devuelto no esnull, elEventEsta función sólo está disponible para el comercio de bots reales.
La primera llamada deEventLoopEn el código se inicializa el mecanismo de escucha del evento.EventLoopLa estructura de cola encapsulada por el sistema subyacente almacenará en caché hasta 500 devoluciones de eventos.EventLoopSi no se llama a tiempo para su eliminación durante la ejecución del programa, las llamadas posteriores de eventos más allá de la caché 500 se perderán.EventLoopla función no afectará a la cola de caché dewebsocketEn el sistema subyacente, ni la caché deexchange.GoPara estos caches, todavía necesita utilizar sus propios métodos para recuperar datos.EventLoopfunción devuelve, ningún evento de retorno se generará en elEventLoop function.
El objetivo principal de laEventLoopLa función principal de la red es la de notificar a la capa de estrategia que el sistema subyacente ha recibido nuevos datos de red.EventLoopSi la función devuelve un evento, sólo necesita recorrer todas las fuentes de datos.websocketconexión y objetos creados porexchange.GoPuedes hacer referencia a un diseño de biblioteca de clases de código abierto:Enlace a la biblioteca de clases.
function main() {
var routine_getTicker = exchange.Go("GetTicker")
var routine_getDepth = exchange.Go("GetDepth")
var routine_getTrades = exchange.Go("GetTrades")
// Sleep(2000), if the Sleep statement is used here, the subsequent EventLoop function will miss the previous events, because after waiting for 2 seconds, the concurrent function has received the data, and the EventLoop monitoring mechanism will start later, and these events will be missed
// Unless you start calling EventLoop(-1) on the first line of code, first initialize the listening mechanism of EventLoop, you will not miss these events
// Log("GetDepth:", routine_getDepth.wait()) If the wait function is called in advance to get the result of the concurrent call of the GetDepth function, the event that the GetDepth function receives the request result will not be returned in the EventLoop function
var ts1 = new Date().getTime()
var ret1 = EventLoop(0)
var ts2 = new Date().getTime()
var ret2 = EventLoop(0)
var ts3 = new Date().getTime()
var ret3 = EventLoop(0)
Log("The first concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts1), ret1)
Log("The second concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts2), ret2)
Log("The third concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts3), ret3)
Log("GetTicker:", routine_getTicker.wait())
Log("GetDepth:", routine_getDepth.wait())
Log("GetTrades:", routine_getTrades.wait())
}
import time
def main():
routine_getTicker = exchange.Go("GetTicker")
routine_getDepth = exchange.Go("GetDepth")
routine_getTrades = exchange.Go("GetTrades")
ts1 = time.time()
ret1 = EventLoop(0)
ts2 = time.time()
ret2 = EventLoop(0)
ts3 = time.time()
ret3 = EventLoop(0)
Log("The first concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts1), ret1)
Log("The second concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts2), ret2)
Log("The third concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts3), ret3)
Log("GetTicker:", routine_getTicker.wait())
Log("GetDepth:", routine_getDepth.wait())
Log("GetTrades:", routine_getTrades.wait())
void main() {
auto routine_getTicker = exchange.Go("GetTicker");
auto routine_getDepth = exchange.Go("GetDepth");
auto routine_getTrades = exchange.Go("GetTrades");
auto ts1 = Unix() * 1000;
auto ret1 = EventLoop(0);
auto ts2 = Unix() * 1000;
auto ret2 = EventLoop(0);
auto ts3 = Unix() * 1000;
auto ret3 = EventLoop(0);
Log("The first concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts1), ret1);
Log("The second concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts2), ret2);
Log("The third concurrent task completed was:", _D(ts3), ret3);
Ticker ticker;
Depth depth;
Trades trades;
routine_getTicker.wait(ticker);
routine_getDepth.wait(depth);
routine_getTrades.wait(trades);
Log("GetTicker:", ticker);
Log("GetDepth:", depth);
Log("GetTrades:", trades);
}
Funciones incorporadas
_G(K, V)
_G(K, V), con una función de un diccionario global que se puede guardar, admite tanto backtest como bot. Después de la backtest, los datos guardados se borrarán.
La estructura de los datos esKVCada bot tiene una base de datos separada. Siempre existirá después de reiniciar o cuando el docker salga.Kdebe ser una cadena, que no es sensible a mayúsculas.Vpuede ser cualquierJSONcontenido serializable._G()se llama y no se pasan parámetros en la operación bot, la función_G()devuelve elIDdel bot actual.
function main(){
// Set a global variable num with a value of 1
_G("num", 1)
// Change a global variable num with the value "ok"
_G("num", "ok")
// Delete global variable num
_G("num", null)
// Return the value of the global variable num
Log(_G("num"))
// Delete all global variables
_G(null)
// Return bot ID
var robotId = _G()
}
def main():
_G("num", 1)
_G("num", "ok")
_G("num", None)
Log(_G("num"))
_G(None)
robotId = _G()
void main() {
_G("num", 1);
_G("num", "ok");
_G("num", NULL);
Log(_G("num"));
_G(NULL);
// does not support auto robotId = _G();
}
Nota:
Cuando se utilice el_GLa función de almacenamiento de datos debe utilizarse razonablemente de acuerdo con la memoria y el espacio en disco duro del dispositivo de hardware, y no debe abusar.Desbordamiento de memoria problem.
_D (tiempo, FMT)
_D(Timestamp, Fmt), devuelve las cadenas de tiempo correspondientes de la marca de tiempo especificada. Valor del parámetro:Timestampes un tipo numérico, en milisegundos.Fmtes un tipo de cadena;Fmtpor defecto a:yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss; el valor de retorno: tipo de cadena.
Devuelve la cadena de marca de tiempo especificada ((ms), y devuelve la hora actual sin pasar ningún parámetro; por ejemplo:_D()o bien_D(1478570053241), cuyo formato predeterminado esyyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss.
function main(){
var time = _D()
Log(time)
}
def main():
strTime = _D()
Log(strTime)
void main() {
auto strTime = _D();
Log(strTime);
}
Nota:
Cuando se utiliza_D()En elPythonLa estrategia, debemos prestar atención a que los parámetros transmitidos son las marcas de tiempo en segundo (las marcas de tiempo de nivel milisegundo en elJavaScriptyC ++estrategias, y 1 segundo = 1000 milisegundos).
En el bot, cuando se utiliza la función_D()para analizar una cadena de tiempo con una marca de tiempo legible, usted necesita prestar atención a la zona horaria en el sistema operativo del programa docker._D()analiza una marca de tiempo como una cadena de tiempo legible basada en el tiempo del sistema docker.
Por ejemplo, analizar una marca de tiempo de1574993606000con el código:
function main() {
Log(_D(1574993606000))
}
def main():
# Beijing time server runs: 2019-11-29 10:13:26, and the docker on another server in another region runs this code will get the results: 2019-11-29 02:13:26
Log(_D(1574993606))
void main() {
Log(_D(1574993606000));
}
_N ((Número, Precisión)
_N(Num, Precision), un número con coma flotante con formato. Valor del parámetro:Numes de tipo numérico;Precisiones de tipo entero. Valor devuelto: tipo numérico.
Por ejemplo:_N(3.1415, 2)borrará el valor después de dos decimales de3.1415y regresar3.14.
function main(){
var i = 3.1415
Log(i)
var ii = _N(i, 2)
Log(ii)
}
def main():
i = 3.1415
Log(i)
ii = _N(i, 2)
Log(ii)
void main() {
auto i = 3.1415;
Log(i);
auto ii = _N(i, 2);
Log(ii);
}
Si necesitas cambiar N dígitos a la izquierda del punto decimal a 0, puedes escribir:
function main(){
var i = 1300
Log(i)
var ii = _N(i, -3)
// Checking the log shows that it is 1000
Log(ii)
}
def main():
i = 1300
Log(i)
ii = _N(i, -3)
Log(ii)
void main() {
auto i = 1300;
Log(i);
auto ii = _N(i, -3);
Log(ii);
}
¿Qué es esto?
_C(function, args…)es una función de prueba de nuevo, utilizada para la tolerancia a fallos de las interfaces sobre la obtención de información de mercado y la adquisición de pedidos incompletos, etc.
La interfaz llamará la función especificada continuamente hasta que devuelva con éxito (parámetrofunctiondevuelve el valor nulo cuando se llama la función a la que se hace referencia ofalsePor ejemplo,_ C(exchange. GetTicker), el intervalo de reintentos predeterminado es de 3 segundos, que puede llamar a la función_CDelay (...)para fijar el intervalo de ensayo de nuevo, por ejemplo:_CDelay (1000)significa función de cambio_CIntervalo de repetición de ensayo a 1 segundo.
Para las siguientes funciones:
exchange.GetTicker()exchange.GetDepth()exchange.GetTrades()exchange.GetRecords()exchange.GetAccount()exchange.GetOrders()exchange.GetOrder()exchange.GetPosition()
Todos ellos pueden ser llamados a hacer tolerancia a fallas por función_C(...). La función_C(function, args...)no se limita a la tolerancia a fallos de las funciones enumeradas anteriormente.functionse cita no se llama, y prestar atención a que es_C(exchange.GetTicker), no_C(exchange.GetTicker()).
function main(){
var ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
// Adjust _C() function's retry interval to 2 seconds
_CDelay(2000)
var depth = _C(exchange.GetDepth)
Log(ticker)
Log(depth)
}
def main():
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
_CDelay(2000)
depth = _C(exchange.GetDepth)
Log(ticker)
Log(depth)
void main() {
auto ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker);
_CDelay(2000);
auto depth = _C(exchange.GetDepth);
Log(ticker);
Log(depth);
}
Para funciones con parámetros, cuando se utilice_C(...)para hacer tolerancia a fallas:
function main(){
var records = _C(exchange.GetRecords, PERIOD_D1)
Log(records)
}
def main():
records = _C(exchange.GetRecords, PERIOD_D1)
Log(records)
void main() {
auto records = _C(exchange.GetRecords, PERIOD_D1);
Log(records);
}
También se puede utilizar para el manejo de tolerancia a fallas de funciones personalizadas:
var test = function(a, b){
var time = new Date().getTime() / 1000
if(time % b == 3){
Log("Meet the criteria! ", "#FF0000")
return true
}
Log("Retry!", "#FF0000")
return false
}
function main(){
var ret = _C(test, 1, 5)
Log(ret)
}
import time
def test(a, b):
ts = time.time()
if ts % b == 3:
Log("Meet the criteria!", "#FF0000")
return True
Log("Retry!", "#FF0000")
return False
def main():
ret = _C(test, 1, 5)
Log(ret)
// C++ does not support this method for fault tolerance of custom functions.
_Cruce ((Arr1, Arr2)
_Cross(Arr1, Arr2)devuelve el número de períodos de cruce de las matricesarr1yarr2Un número positivo es el período de alza, y un número negativo es el período de bajada, y 0 significa lo mismo que el precio actual.
Se puede simular un conjunto de datos para probar la función_Cross(Arr1, Arr2):
// Fast line indicator
var arr1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,8,8,9]
// Slow line indicator
var arr2 = [2,3,4,5,6,7,7,7,7]
function main(){
Log("_Cross(arr1, arr2) : ", _Cross(arr1, arr2))
Log("_Cross(arr2, arr1) : ", _Cross(arr2, arr1))
}
arr1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,8,8,9]
arr2 = [2,3,4,5,6,7,7,7,7]
def main():
Log("_Cross(arr1, arr2) : ", _Cross(arr1, arr2))
Log("_Cross(arr2, arr1) : ", _Cross(arr2, arr1))
void main() {
vector<double> arr1 = {1,2,3,4,5,6,8,8,9};
vector<double> arr2 = {2,3,4,5,6,7,7,7,7};
Log("_Cross(arr1, arr2) : ", _Cross(arr1, arr2));
Log("_Cross(arr2, arr1) : ", _Cross(arr2, arr1));
}
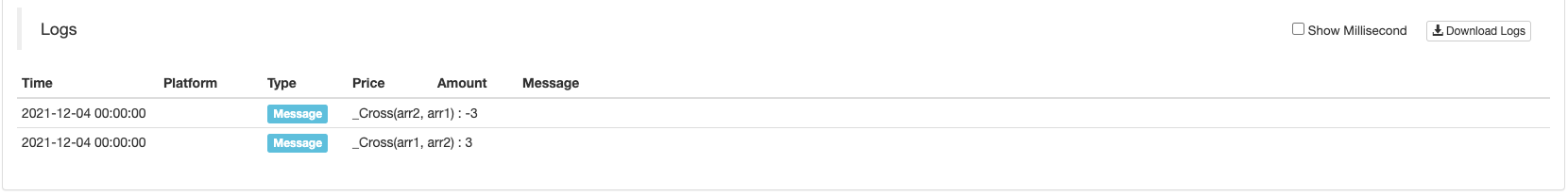
Visualizar los datos simulados para la observación
Instrucciones específicas:Función integrada _Análisis cruzado e instrucciones
JSONParse ((strJson) es el nombre de la aplicación.
JSONParse(strJson), la función se utiliza para analizar cadenas JSON. Las cadenas JSON que contienen números grandes se pueden analizar correctamente, y los números grandes se analizarán en tipos de cadena. El sistema de backtesting no admite esta función.
function main() {
let s1 = '{"num": 8754613216564987646512354656874651651358}'
Log("JSON.parse:", JSON.parse(s1)) // JSON.parse: {"num":8.754613216564988e+39}
Log("JSONParse:", JSONParse(s1)) // JSONParse: {"num":"8754613216564987646512354656874651651358"}
let s2 = '{"num": 123}'
Log("JSON.parse:", JSON.parse(s2)) // JSON.parse: {"num":123}
Log("JSONParse:", JSONParse(s2)) // JSONParse: {"num":123}
}
import json
def main():
s1 = '{"num": 8754613216564987646512354656874651651358}'
Log("json.loads:", json.loads(s1)) # json.loads: map[num:8.754613216564987e+39]
Log("JSONParse:", JSONParse(s1)) # JSONParse: map[num:8754613216564987646512354656874651651358]
s2 = '{"num": 123}'
Log("json.loads:", json.loads(s2)) # json.loads: map[num:123]
Log("JSONParse:", JSONParse(s2)) # JSONParse: map[num:123]
void main() {
auto s1 = "{\"num\":8754613216564987646512354656874651651358}";
Log("json::parse:", json::parse(s1));
// Log("JSONParse:", JSONParse(s1)); // The function is not supported
auto s2 = "{\"num\":123}";
Log("json::parse:", json::parse(s2));
// Log("JSONParse:", JSONParse(s2)); // The function is not supported
}
Color personalizado
Cada cadena de mensajes puede terminar con un valor RGB como:#ff0000, que representa el color de primer plano a mostrar. Si está en un formato como#ff0000112233, las últimas seis caras traseras representan el color de fondo.
function main() {
Log("Red", "#FF0000")
}
def main():
Log("Red", "#FF0000")
void main() {
Log("Red", "#FF0000");
}
Información del registro
Cuando el bot está ejecutando, la información del registro se registra en la base de datos del bot, que adopta elsqlite3Los archivos de base de datos se localizan en el dispositivo con el programa docker, y la ubicación exacta de los archivos está en el diccionario del programa docker (robotPor ejemplo: El archivo de la base de datos de bots con ID130350está en el directorio../logs/storage/130350 (..es el diccionario donde el docker de larobotse encuentra), y el nombre del archivo de la base de datos es130350.db3.
Los registros en el sistema de backtest se pueden descargar haciendo clic en [Descargar registro] botón en la esquina inferior derecha de la página de backtest después de que finalice la backtest.
Cuando necesite transferir el bot a un docker en otro servidor, puede mover los archivos de base de datos del bot (archivos de base de datos con la extensión
Registro de las operaciones
Log(message)significa guardar un mensaje en la lista de registro.messagepuede ser de cualquier tipo.
Si añades el carácter@después de la cadena, el mensaje entrará en la cola de push y será empujado a la cuenta actual de WeChat de la plataforma de comercio de FMZ Quant, y el
Nota:
- Push no está soportado en la
Herramienta de depuración . - Push no está soportado en el
Backtest System .
function main() {
Log("Hello FMZ Quant!@")
Sleep(1000 * 5)
// Add the string to #ff0000, print the log in red, and push the message
Log("Hello, #ff0000@")
}
def main():
Log("Hello FMZ Quant!@")
Sleep(1000 * 5)
Log("Hello, #ff0000@")
void main() {
Log("Hello FMZ Quant!@");
Sleep(1000 * 5);
Log("Hello, #ff0000@");
}
- ¿ Qué pasa?Empuje:
Utilice el programa de servicio DEMO escrito enGolang:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
func Handle (w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
defer func() {
fmt.Println("req:", *r)
}()
}
func main () {
fmt.Println("listen http://localhost:9090")
http.HandleFunc("/data", Handle)
http.ListenAndServe(":9090", nil)
}
Se ha puestoWebHook: http://XXX.XX.XXX.XX:9090/data?data=Hello_FMZ
Después de ejecutar el programa de servicio, ejecutar la estrategia y presionar la información:
function main() {
Log("msg", "@")
}
def main():
Log("msg", "@")
void main() {
Log("msg", "@");
}
Recibe la información de empuje, y el programa de servicio imprime la información:
listen http://localhost:9090
req: {GET /data?data=Hello_FMZ HTTP/1.1 1 1 map[User-Agent:[Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_9_3) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/xx.x.xxxx.xxx Safari/537.36] Accept-Encoding:[gzip]] {} <nil> 0 [] false 1XX.XX.X.XX:9090 map[] map[] <nil> map[] XXX.XX.XXX.XX:4xxx2 /data?data=Hello_FMZ <nil> <nil> <nil> 0xc420056300}
Imprimir elbase64imagen codificadaLa funciónLogadmite la impresión de las imágenes codificadas enbase64, comienza con`, y termina con`, por ejemplo:
function main() {
Log("`data:image/png;base64,AAAA`")
}
def main():
Log("`data:image/png;base64,AAAA`")
void main() {
Log("`data:image/png;base64,AAAA`");
}
LogApoya la impresión de lamatplotlib.pyplotobjetos dePythondirectamente, es decir, siempre y cuando los objetos contienensavefigmétodo, se puede utilizarLogpara imprimir directamente, por ejemplo:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def main():
plt.plot([3,6,2,4,7,1])
Log(plt)
Cambio automático de idioma de los registros impresosLa funciónLogadmite el cambio de idioma; cuando la función emite texto, cambiará automáticamente al idioma correspondiente de acuerdo con la configuración de idioma en la página de la plataforma.
function main() {
Log("[trans]Chinese|abc[/trans]")
}
def main():
Log("[trans]Chinese|abc[/trans]")
void main() {
Log("[trans]Chinese|abc[/trans]");
}
LogProfit (Profito)
LogProfit(Profit)registra el valor de ganancia, imprime el valor de ganancia y dibuja una curva de ganancia de acuerdo con el valor de ganancia.Profitoses de tipo numérico.
Si la función termina con el carácter&, sólo puede realizar el dibujo del gráfico de ganancias, y no la impresión del registro de ganancias, tales como:LogProfit(10, '&').
LogProfitReset (()
LogProfitReset()borra todos los registros de ganancias; puede tomar un parámetro de valor entero para especificar el número de artículos reservados.
function main() {
// Print 30 points on the income chart, then reset, and only retain the last 10 points
for(var i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
LogProfit(i)
Sleep(500)
}
LogProfitReset(10)
}
def main():
for i in range(30):
LogProfit(i)
Sleep(500)
LogProfitReset(10)
void main() {
for(int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
LogProfit(i);
Sleep(500);
}
LogProfitReset(10);
}
LogStatus (Msg)
LogStatus(Msg), la información no se guarda en la lista de registro, solo se actualiza la información de estado actual del bot; se muestra por encima del registro y se puede llamar varias veces para actualizar el estado. Valor del parámetro:Msgpuede ser de cualquier tipo.
function main() {
LogStatus('This is a normal status prompt')
LogStatus('This is a status prompt in red font # ff0000')
LogStatus('This is a multi-line status message \n I am the second line')
}
def main():
LogStatus('This is a normal status prompt')
LogStatus('This is a status prompt in red font # ff0000')
LogStatus('This is a multi-line status message \nI am the second line')
void main() {
LogStatus("This is a normal status prompt");
LogStatus("This is a status prompt in red font # ff0000");
LogStatus("This is a multi-line status message \nI am the second line");
}
LogStatus(Msg)soporta la impresiónbase64Imágenes codificadas, comenzando con`y terminando con`, como por ejemplo:LogStatus("`data:image/png;base64,AAAA`").
LogStatus(Msg)apoya la importación directa dePython¿ Qué?matplotlib.pyplotobjeto, siempre y cuando el objeto contenga elsavefigmétodo, se puede pasar en la funciónLogStatus(Msg), como por ejemplo:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def main():
plt.plot([3,6,2,4,7,1])
LogStatus(plt)
El ejemplo de salida de datos en la barra de estado:
function main() {
var table = {type: 'table', title: 'Position Information', cols: ['Column1', 'Column2'], rows: [ ['abc', 'def'], ['ABC', 'support color #ff0000']]}
// After the JSON order is serialized, add the character "`" on both sides, which is regarded as a complex message format (currently supporting tables)
LogStatus('`' + JSON.stringify(table) + '`')
// Table information can also appear in multiple lines
LogStatus('First line message\n`' + JSON.stringify(table) + '`\nThird line message')
// That supports multiple tables displayed at the same time, and that will be displayed in a group with TAB
LogStatus('`' + JSON.stringify([table, table]) + '`')
// You can also construct a button in the table, and the strategy uses "GetCommand" to receive the content of the cmd attribute
var table = {
type: 'table',
title: 'Position operation',
cols: ['Column1', 'Column2', 'Action'],
rows: [
['abc', 'def', {'type':'button', 'cmd': 'coverAll', 'name': 'close position'}]
]
}
LogStatus('`' + JSON.stringify(table) + '`')
// Or create a separate button
LogStatus('`' + JSON.stringify({'type':'button', 'cmd': 'coverAll', 'name': 'close position'}) + '`')
// You can customize the button style (button attribute of bootstrap)
LogStatus('`' + JSON.stringify({'type':'button', 'class': 'btn btn-xs btn-danger', 'cmd': 'coverAll', 'name': 'close position'}) + '`')
}
import json
def main():
table = {"type": "table", "title": "Position Information", "cols": ["Column1", "Column2"], "rows": [["abc", "def"], ["ABC", "support color #ff0000"]]}
LogStatus('`' + json.dumps(table) + '`')
LogStatus('First line message\n`' + json.dumps(table) + '`\nThird line message')
LogStatus('`' + json.dumps([table, table]) + '`')
table = {
"type" : "table",
"title" : "Position operation",
"cols" : ["Column1", "Column2", "Action"],
"rows" : [
["abc", "def", {"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close position"}]
]
}
LogStatus('`' + json.dumps(table) + '`')
LogStatus('`' + json.dumps({"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close position"}) + '`')
LogStatus('`' + json.dumps({"type": "button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-danger", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close position"}) + '`')
void main() {
json table = R"({"type": "table", "title": "Position Information", "cols": ["Column1", "Column2"], "rows": [["abc", "def"], ["ABC", "support color #ff0000"]]})"_json;
LogStatus("`" + table.dump() + "`");
LogStatus("First line message\n`" + table.dump() + "`\nThird line message");
json arr = R"([])"_json;
arr.push_back(table);
arr.push_back(table);
LogStatus("`" + arr.dump() + "`");
table = R"({
"type" : "table",
"title" : "Position operation",
"cols" : ["Column1", "Column2", "Action"],
"rows" : [
["abc", "def", {"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close position"}]
]
})"_json;
LogStatus("`" + table.dump() + "`");
LogStatus("`" + R"({"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close position"})"_json.dump() + "`");
LogStatus("`" + R"({"type": "button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-danger", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close position"})"_json.dump() + "`");
}
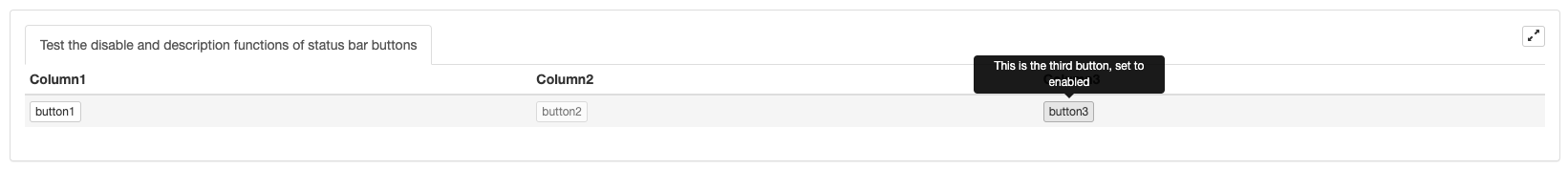
Configurar las funciones de desactivación y descripción de los botones de la barra de estado:
function main() {
var table = {
type: "table",
title: "Test the disable and description functions of status bar buttons",
cols: ["Column1", "Column2", "Column3"],
rows: []
}
var button1 = {"type": "button", "name": "button1", "cmd": "button1", "description": "This is the first button"}
var button2 = {"type": "button", "name": "button2", "cmd": "button2", "description": "This is the second button, set to disabled", "disabled": true}
var button3 = {"type": "button", "name": "button3", "cmd": "button3", "description": "This is the third button, set to enabled", "disabled": false}
table.rows.push([button1, button2, button3])
LogStatus("`" + JSON.stringify(table) + "`")
}
import json
def main():
table = {
"type": "table",
"title": "Test the disable and description functions of status bar buttons",
"cols": ["Column1", "Column2", "Column3"],
"rows": []
}
button1 = {"type": "button", "name": "button1", "cmd": "button1", "description": "This is the first button"}
button2 = {"type": "button", "name": "button2", "cmd": "button2", "description": "This is the second button, set to disabled", "disabled": True}
button3 = {"type": "button", "name": "button3", "cmd": "button3", "description": "This is the third button, set to enabled", "disabled": False}
table["rows"].append([button1, button2, button3])
LogStatus("`" + json.dumps(table) + "`")
void main() {
json table = R"({
"type": "table",
"title": "Test the disable and description functions of status bar buttons",
"cols": ["Column1", "Column2", "Column3"],
"rows": []
})"_json;
json button1 = R"({"type": "button", "name": "button1", "cmd": "button1", "description": "This is the first button"})"_json;
json button2 = R"({"type": "button", "name": "button2", "cmd": "button2", "description": "This is the second button, set to disabled", "disabled": true})"_json;
json button3 = R"({"type": "button", "name": "button3", "cmd": "button3", "description": "This is the third button, set to enabled", "disabled": false})"_json;
json arr = R"([])"_json;
arr.push_back(button1);
arr.push_back(button2);
arr.push_back(button3);
table["rows"].push_back(arr);
LogStatus("`" + table.dump() + "`");
}
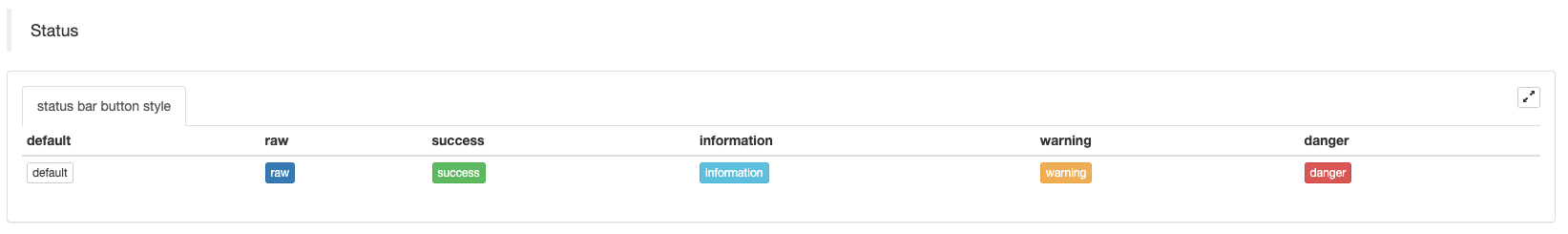
Establecer el estilo de los botones de la barra de estado:
function main() {
var table = {
type: "table",
title: "status bar button style",
cols: ["default", "raw", "success", "information", "warning", "danger"],
rows: [
[
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-default", "name": "default"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-primary", "name": "raw"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-success", "name": "success"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-info", "name": "information"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-warning", "name": "warning"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-danger", "name": "danger"}
]
]
}
LogStatus("`" + JSON.stringify(table) + "`")
}
import json
def main():
table = {
"type": "table",
"title": "status bar button style",
"cols": ["default", "raw", "success", "information", "warning", "danger"],
"rows": [
[
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-default", "name": "default"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-primary", "name": "raw"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-success", "name": "success"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-info", "name": "information"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-warning", "name": "warning"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-danger", "name": "danger"}
]
]
}
LogStatus("`" + json.dumps(table) + "`")
void main() {
json table = R"({
"type": "table",
"title": "status bar button style",
"cols": ["default", "raw", "success", "information", "warning", "danger"],
"rows": [
[
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-default", "name": "default"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-primary", "name": "raw"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-success", "name": "success"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-info", "name": "information"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-warning", "name": "warning"},
{"type":"button", "class": "btn btn-xs btn-danger", "name": "danger"}
]
]
})"_json;
LogStatus("`" + table.dump() + "`");
}
Combinar la funciónGetCommand()para construir la función interactiva de los botones de la barra de estado:
function test1() {
Log("Call a custom function")
}
function main() {
while (true) {
var table = {
type: 'table',
title: 'operation',
cols: ['Column1', 'Column2', 'Action'],
rows: [
['a', '1', {
'type': 'button',
'cmd': "CoverAll",
'name': 'close position'
}],
['b', '1', {
'type': 'button',
'cmd': 10,
'name': 'Send value'
}],
['c', '1', {
'type': 'button',
'cmd': _D(),
'name': 'Call a function'
}],
['d', '1', {
'type': 'button',
'cmd': 'test1',
'name': 'Call a custom function'
}]
]
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", '`' + JSON.stringify(table) + '`')
var str_cmd = GetCommand()
if (str_cmd) {
Log("Received interactive data str_cmd:", "Types of:", typeof(str_cmd), "Value:", str_cmd)
if(str_cmd == "test1") {
test1()
}
}
Sleep(500)
}
}
import json
def test1():
Log("Call a custom function")
def main():
while True:
table = {
"type": "table",
"title": "Operation",
"cols": ["Column1", "Column2", "Action"],
"rows": [
["a", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": "CoverAll",
"name": "close position"
}],
["b", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": 10,
"name": "Send value"
}],
["c", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": _D(),
"name": "Call a function"
}],
["d", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": "test1",
"name": "Call a custom function"
}]
]
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + json.dumps(table) + "`")
str_cmd = GetCommand()
if str_cmd:
Log("Received interactive data str_cmd", "Types:", type(str_cmd), "Value:", str_cmd)
if str_cmd == "test1":
test1()
Sleep(500)
void test1() {
Log("Call a custom function");
}
void main() {
while(true) {
json table = R"({
"type": "table",
"title": "Operation",
"cols": ["Column1", "Column2", "Action"],
"rows": [
["a", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": "CoverAll",
"name": "close position"
}],
["b", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": 10,
"name": "Send value"
}],
["c", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": "",
"name": "Call a function"
}],
["d", "1", {
"type": "button",
"cmd": "test1",
"name": "Call a custom function"
}]
]
})"_json;
table["rows"][2][2]["cmd"] = _D();
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + table.dump() + "`");
auto str_cmd = GetCommand();
if(str_cmd != "") {
Log("Received interactive data str_cmd", "Type:", typeid(str_cmd).name(), "Value:", str_cmd);
if(str_cmd == "test1") {
test1();
}
}
Sleep(500);
}
}
Cuando se construye un botón de la barra de estado para la interacción, los datos de entrada también son compatibles, y el comando interactivo es finalmente capturado por elGetCommand()la función.
Para añadir uninputelemento a la estructura de datos de un botón de control en la barra de estado, por ejemplo, añadir"input": {"name": "Number of opening orders", "type": "number", "defValue": 1}En el{"type": "button", "cmd": "open", "name": "open position"}, puede hacer que el botón aparezca un cuadro de diálogo con un control de cuadro de entrada cuando se hace clic (El valor predeterminado en el cuadro de entrada es 1, que es establecido por los datos de 111en el cuadro de entrada y haciendo clic en GetCommandLa función capturará el mensaje:open:111.
function main() {
var tbl = {
type: "table",
title: "operation",
cols: ["column 1", "column2"],
rows: [
["Open position operation", {"type": "button", "cmd": "open", "name": "open position", "input": {"name": "number of opening positions", "type": "number", "defValue": 1}}],
["Close position operation", {"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close all positions"}]
]
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`")
while (true) {
var cmd = GetCommand()
if (cmd) {
Log("cmd:", cmd)
}
Sleep(1000)
}
}
import json
def main():
tbl = {
"type": "table",
"title": "operation",
"cols": ["column 1", "column 2"],
"rows": [
["Open position operation", {"type": "button", "cmd": "open", "name": "open position", "input": {"name": "number of opening positions", "type": "number", "defValue": 1}}],
["Close position operation", {"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close all positions"}]
]
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + json.dumps(tbl) + "`")
while True:
cmd = GetCommand()
if cmd:
Log("cmd:", cmd)
Sleep(1000)
void main() {
json tbl = R"({
"type": "table",
"title": "operation",
"cols": ["column 1", "column 2"],
"rows": [
["Open position operation", {"type": "button", "cmd": "open", "name": "open position", "input": {"name": "number of opening positions", "type": "number", "defValue": 1}}],
["Close position operation", {"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close all positions"}]
]
})"_json;
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + tbl.dump() + "`");
while(true) {
auto cmd = GetCommand();
if(cmd != "") {
Log("cmd:", cmd);
}
Sleep(1000);
}
}
Combinar las celdas del cuadro dibujado por elLogStatus(Msg)Función:
-
Fusión horizontal
function main() { var table = { type: 'table', title: 'position operation', cols: ['Column1', 'Column2', 'Action'], rows: [ ['abc', 'def', {'type':'button', 'cmd': 'coverAll', 'name': 'close position'}] ] } var ticker = exchange.GetTicker() // Add a row of data, merge the first and second cells, and output the ticker variable in the merged cell table.rows.push([{body : JSON.stringify(ticker), colspan : 2}, "abc"]) LogStatus('`' + JSON.stringify(table) + '`') }import json def main(): table = { "type" : "table", "title" : "position operation", "cols" : ["Column1", "Column2", "Action"], "rows" : [ ["abc", "def", {"type": "button", "cmd": "coverAll", "name": "close position"}] ] } ticker = exchange.GetTicker() table["rows"].append([{"body": json.dumps(ticker), "colspan": 2}, "abc"]) LogStatus("`" + json.dumps(table) + "`")void main() { json table = R"({ "type" : "table", "title" : "position operation", "cols" : ["Column1", "Column2", "Action"], "rows" : [
- ¿Hay ejemplos de combinación de macd en el diagrama de tiempo interno?
- ¡Pregúntenme cómo está la red de las API de los intercambios de monedas!
- Huobi reportó un error en el contrato
- ¿Pueden los administradores implementar el robot en la fundación de la nube de IBM gratis?
- Cómo instalar la base de datos de pandas en el administrador
- Comprobar los errores con el Exchange.IO
- Pregunta sobre el número de comandos bk, sk, etc. en my
- El problema de los indicadores del cinturón de Bryn
- ¿Cómo debo hacer el debugging si encuentro un error en los parámetros de la orden?
- Regreso de errores de datos personalizados
- ¿El IP del administrador está bloqueado y afecta el funcionamiento normal?
- ¿Por qué las líneas K de los futuros de OKex parecen estar obteniendo sólo 49 en estos días?
- La pregunta sobre cómo asignar la primera
- ¿Por qué no se puede acceder a los datos de K-Line de Binance?
- Prueba de nuevo si el origen de datos personalizados es compatible con otros intercambios
- La fórmula del indicador RSI que escribí, hay un error, por favor guíame.
- ¿Hay algún incidente que haya sido desencadenado en la transacción de la orden de compra de la moneda digital?
- Historia de los juegos de Binance
- ¿Se puede establecer dinámicamente el número de cuentas y monedas en la función init ()) al revisar?
- No se puede usar un contrato permanente