FMZ Quant: Une analyse des exemples de conception des exigences communes sur le marché des crypto-monnaies (I)
Auteur:FMZ~Lydia, Créé: 2023-12-19 16:02:58, Mis à jour: 2024-11-06 21:19:16
Dans l'espace de négociation d'actifs de crypto-monnaie, l'obtention et l'analyse de données de marché, les taux de requête et la surveillance des mouvements d'actifs de compte sont toutes des opérations critiques.
1. Comment écrire le code pour obtenir la monnaie avec la plus forte augmentation en 4 heures sur Binance Spot?
Lorsque vous écrivez un programme de stratégie de trading quantitative sur la plateforme FMZ, la première chose que vous devez faire lorsque vous rencontrez une exigence est de l'analyser.
- Quel langage de programmation utiliser? Le plan est d'utiliser Javascript pour le mettre en œuvre.
- Exige des cotations au comptant en temps réel dans toutes les devises
La première chose que nous avons faite lorsque nous avons vu l'exigence était de chercher le document de l'API de Binance pour savoir s'il y avait des cotations agrégées (il est préférable d'avoir des cotations agrégées, il faut beaucoup de travail pour chercher une par une).
Nous avons trouvé l'interface des citations agrégées:
GET https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/priceJe suis désolée. Sur la plateforme FMZ, utilisez leHttpQueryune fonction permettant d'accéder à l'interface du ticker d'échange (interface publique ne nécessitant pas de signature). - Besoin de compter les données pour une période de fenêtre mobile de 4 heures Conceptualiser comment concevoir la structure du programme statistique.
- Calculer les fluctuations de prix et les trier
En pensant à l'algorithme des fluctuations de prix, est-ce:
price fluctuations (%) = (current price - initial price) / initial price * 100dans% .
Après avoir résolu le problème et défini le programme, nous avons commencé à concevoir le programme.
Conception du code
var dictSymbolsPrice = {}
function main() {
while (true) {
// GET https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price
try {
var arr = JSON.parse(HttpQuery("https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price"))
if (!Array.isArray(arr)) {
Sleep(5000)
continue
}
var ts = new Date().getTime()
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
var symbolPriceInfo = arr[i]
var symbol = symbolPriceInfo.symbol
var price = symbolPriceInfo.price
if (typeof(dictSymbolsPrice[symbol]) == "undefined") {
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol] = {name: symbol, data: []}
}
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data.push({ts: ts, price: price})
}
} catch(e) {
Log("e.name:", e.name, "e.stack:", e.stack, "e.message:", e.message)
}
// Calculate price fluctuations
var tbl = {
type : "table",
title : "Price fluctuations",
cols : ["trading pair", "current price", "price 4 hours ago", "price fluctuations", "data length", "earliest data time", "latest data time"],
rows : []
}
for (var symbol in dictSymbolsPrice) {
var data = dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data
if (data[data.length - 1].ts - data[0].ts > 1000 * 60 * 60 * 4) {
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data.shift()
}
data = dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].percentageChange = (data[data.length - 1].price - data[0].price) / data[0].price * 100
}
var entries = Object.entries(dictSymbolsPrice)
entries.sort((a, b) => b[1].percentageChange - a[1].percentageChange)
for (var i = 0; i < entries.length; i++) {
if (i > 9) {
break
}
var name = entries[i][1].name
var data = entries[i][1].data
var percentageChange = entries[i][1].percentageChange
var currPrice = data[data.length - 1].price
var currTs = _D(data[data.length - 1].ts)
var prePrice = data[0].price
var preTs = _D(data[0].ts)
var dataLen = data.length
tbl.rows.push([name, currPrice, prePrice, percentageChange + "%", dataLen, preTs, currTs])
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`")
Sleep(5000)
}
}
Analyse du code
- 1. Structure des données
- 2. Main function main()
2.1. Infinite loop
pendant (vrai) { - Je ne sais pas. Je ne sais pas.
The program continuously monitors the Binance API trading pair prices through an infinite loop.
2.2. Get price information
Var arr = JSON.parse ((HttpQuery))https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price”))
Get the current price information of the trading pair via Binance API. If the return is not an array, wait for 5 seconds and retry.
2.3. Update price data
pour (var i = 0; i < arr.longueur; i++) { - Je ne sais pas. Je ne sais pas.
Iterate through the array of obtained price information and update the data in dictSymbolsPrice. For each trading pair, add the current timestamp and price to the corresponding data array.
2.4. Exception processing
Je sais pas.
Log ((
Catch exceptions and log the exception information to ensure that the program can continue to execute.
2.5. Calculate the price fluctuations
pour (symbole de variation dans dictSymbolsPrice) { - Je ne sais pas. Je ne sais pas.
Iterate through dictSymbolsPrice, calculate the price fluctuations of each trading pair, and remove the earliest data if it is longer than 4 hours.
2.6. Sort and generate tables
les entrées var = Objet.entrées ((dictSymbolsPrice) les entrées.sort (((a, b) => b[1].pourcentageModifier - a[1].pourcentageModifier)
pour (var i = 0; i < entrées.longueur; i++) { - Je ne sais pas. Je ne sais pas.
Sort the trading pairs in descending order of their price fluctuations and generate a table containing information about the trading pairs.
2.7. Log output and delay
LogStatus ((_D(), " + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "
Output the table and the current time in the form of a log and wait for 5 seconds to continue the next round of the loop.
The program obtains the real-time price information of the trading pair through Binance API, then calculates the price fluctuations, and outputs it to the log in the form of a table. The program is executed in a continuous loop to realize the function of real-time monitoring of the prices of trading pairs. Note that the program includes exception processing to ensure that the execution is not interrupted by exceptions when obtaining price information.
### Live Trading Running Test
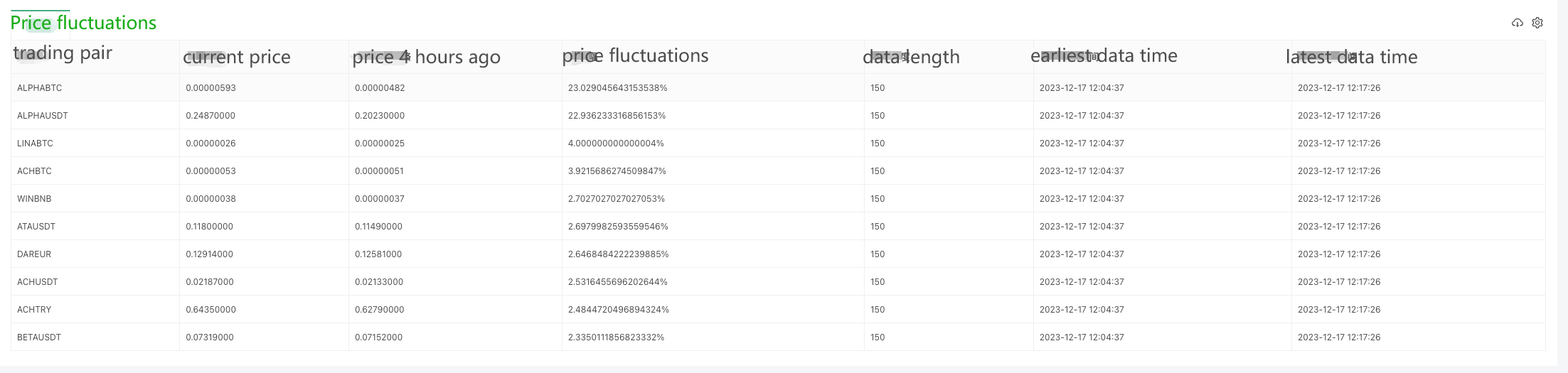
Since data can only be collected bit by bit at the beginning, it is not possible to calculate the price fluctuations on a rolling basis without collecting enough data for a 4-hour window. Therefore, the initial price is used as the base for calculation, and after collecting enough data for 4 hours, the oldest data will be eliminated in order to maintain the 4-hour window for calculating the price fluctuations.
## 2. Check the full variety of funding rates for Binance U-denominated contracts
Checking the funding rate is similar to the above code, first of all, we need to check the Binance API documentation to find the funding rate related interface. Binance has several interfaces that allow us to query the rate of funds, here we take the interface of the U-denominated contract as an example:
GEThttps://fapi.binance.com/fapi/v1/premiumIndex
### Code Implementation
Since there are so many contracts, we're exporting the top 10 largest funding rates here.
fonction principale pendant (vrai) { // GEThttps://fapi.binance.com/fapi/v1/premiumIndexJe vais essayer Var arr = JSON.parse ((HttpQuery))https://fapi.binance.com/fapi/v1/premiumIndex”)) si (!Array.isArray(arr)) { Le sommeil Je continue Je ne sais pas.
arr.sort((a, b) => parseFloat(b.lastFundingRate) - parseFloat(a.lastFundingRate))
var tbl = {
type: "table",
title: "Top 10 funding rates for U-denominated contracts",
cols: ["contracts", "funding rate", "marked price", "index price", "current rate time", "next rate time"],
rows: []
}
for (var i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
var obj = arr[i]
tbl.rows.push([obj.symbol, obj.lastFundingRate, obj.markPrice, obj.indexPrice, _D(obj.time), _D(obj.nextFundingTime)])
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`")
} catch(e) {
Log("e.name:", e.name, "e.stack:", e.stack, "e.message:", e.message)
}
Sleep(1000 * 10)
}
}
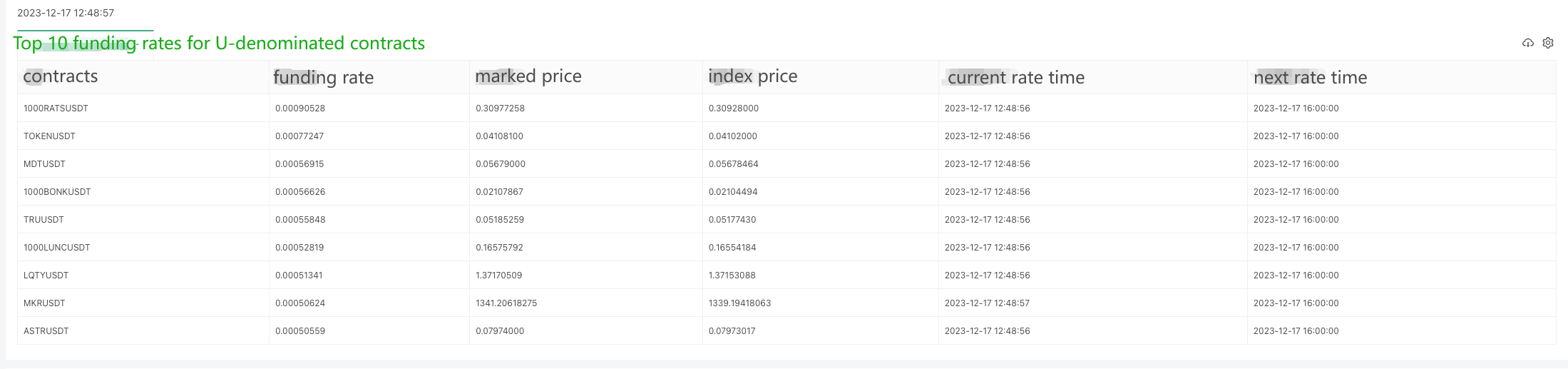
The returned data structure is as follows, and check the Binance documentation, it shows that lastFundingRate is the funding rate we want.
Je ne sais pas.
Live trading running test:
### Getting OKX exchange contract funding rates of Python version
A user has asked for a Python version of the example, and it's for the OKX exchange. Here is an example:
The data returned by the interface ```https://www.okx.com/priapi/v5/public/funding-rate-all?currencyType=1```:
Je ne sais pas.
Specific code:
demandes d'importation Importer le fichier json de l'importation du temps de sommeil à partir de l'heure de la date date de l'importation
Définition principale:
alors que True:
Je suis désolé.https://www.okx.com/priapi/v5/public/funding-rate-all?currencyType=1Essayez ceci:
réponse = requêtes.get(
arr.sort(key=lambda x: float(x["fundingRate"]), reverse=True)
tbl = {
"type": "table",
"title": "Top 10 funding rates for U-denominated contracts",
"cols": ["contracts", "next rate", "minimum", "current", "maximum"],
"rows": []
}
for i in range(min(9, len(arr))):
obj = arr[i]
row = [
obj["instId"],
obj["nextFundingRate"],
obj["minFundingRate"],
obj["fundingRate"],
obj["maxFundingRate"]
]
tbl["rows"].append(row)
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", '`' + json.dumps(tbl) + '`')
except Exception as e:
Log(f"Error: {str(e)}")
sleep(10)
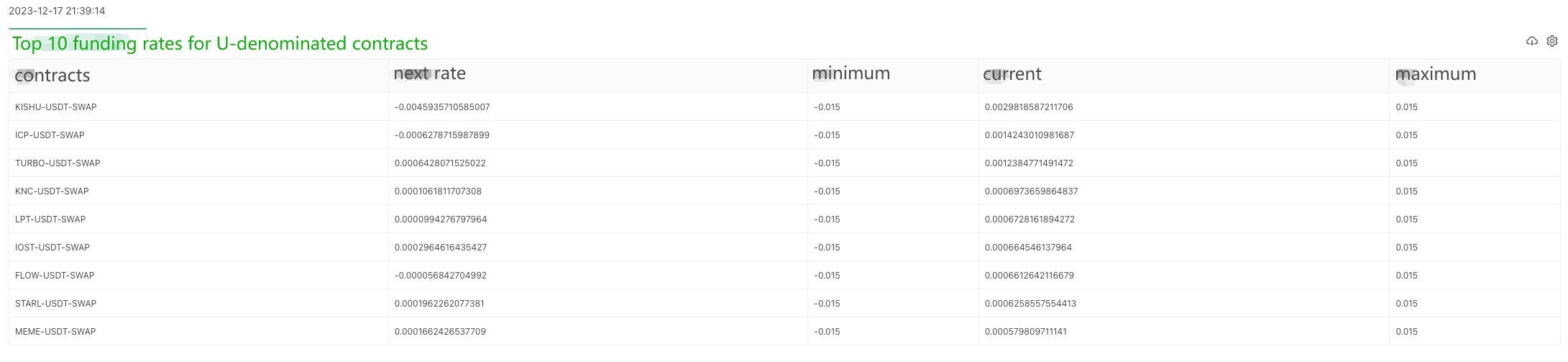
Résultats
Ces exemples fournissent des idées de conception de base et des méthodes d'appel, le projet réel peut devoir apporter des modifications et des extensions appropriées en fonction des besoins spécifiques.
- Quantifier l'analyse fondamentale sur le marché des crypto-monnaies: laissez les données parler d'elles-mêmes!
- Les fondements de la recherche quantifiée dans le cercle monétaire - ne croyez plus à tous les professeurs de mathématiques, les données sont objectives!
- Un outil essentiel dans le domaine du trading quantitatif - FMZ Quant Data Exploration Module
- Un outil indispensable dans le domaine de la quantification des transactions - l'inventeur du module de recherche de données quantifiées
- Maîtriser tout - Introduction à FMZ Nouvelle version du terminal de négociation (avec le code source TRB Arbitrage)
- Tout savoir sur la nouvelle version du terminal de trading FMZ (source code TRB)
- FMZ Quant: Une analyse des exemples de conception des exigences communes sur le marché des crypto-monnaies (II)
- Comment exploiter les robots de vente sans cerveau avec une stratégie de haute fréquence en 80 lignes de code
- Quantification FMZ: analyse de l'exemple de conception des besoins courants sur le marché des crypto-monnaies (II)
- Comment exploiter les robots sans cerveau pour les vendre avec une stratégie de haute fréquence de 80 lignes de code
- Quantification FMZ: analyse de l'exemple de conception des besoins courants sur le marché des crypto-monnaies (1)
- WexApp, la plateforme de démonstration de crypto-monnaie FMZ Quant, est récemment lancée.
- Explication détaillée de l'optimisation des paramètres de la stratégie de la grille de contrats perpétuels
- Apprenez à utiliser l'API étendue FMZ pour modifier les paramètres du bot
- Apprenez à modifier les paramètres du disque dur en masse à l'aide de l'API FMZ Extension
- Optimisation des paramètres stratégiques de la grille de contrats permanents
- Instructions pour l'installation de la passerelle IB Interactive Brokers dans Linux Bash
- Comment installer le GATEWAY pour les titres de pénétration sous Linux bash
- Qu'est-ce qui est le plus approprié pour la pêche au fond, la faible valeur marchande ou le faible prix?
- La valeur de marché est basse et le prix bas, lequel est le meilleur pour la traduction?