एफएमजेड क्वांटः क्रिप्टोकरेंसी बाजार में सामान्य आवश्यकताओं के डिजाइन उदाहरणों का विश्लेषण (I)
लेखक:FMZ~Lydia, बनाया गयाः 2023-12-19 16:02:58, अद्यतनः 2024-11-06 21:19:16
क्रिप्टोक्यूरेंसी परिसंपत्ति व्यापार अंतरिक्ष में, बाजार डेटा प्राप्त करना और उनका विश्लेषण करना, क्वेरी दरें, और खाता परिसंपत्ति आंदोलनों की निगरानी करना सभी महत्वपूर्ण संचालन हैं। नीचे कुछ सामान्य आवश्यकताओं के लिए कार्यान्वयन के कोड उदाहरण दिए गए हैं।
1. मैं कैसे Binance स्पॉट पर 4 घंटे में उच्चतम वृद्धि के साथ मुद्रा पाने के बारे में कोड लिखने के लिए?
जब आप एफएमजेड प्लेटफॉर्म पर एक मात्रात्मक ट्रेडिंग रणनीति प्रोग्राम लिखते हैं, तो पहली चीज जो आपको करने की आवश्यकता है जब आप किसी आवश्यकता का सामना करते हैं तो इसका विश्लेषण करना है। इसलिए आवश्यकताओं के आधार पर, हमने निम्नलिखित सामग्री का विश्लेषण कियाः
- कौन सी प्रोग्रामिंग भाषा का प्रयोग करें? योजना इसे लागू करने के लिए जावास्क्रिप्ट का उपयोग करना है।
- सभी मुद्राओं में वास्तविक समय में स्पॉट उद्धरणों की आवश्यकता होती है
जब हमने आवश्यकता देखी तो हमने सबसे पहले यह पता लगाने के लिए बिनेंस एपीआई दस्तावेज़ देखा कि क्या कोई एकत्रित उद्धरण थे (एक साथ एकत्रित उद्धरण होना सबसे अच्छा है, एक-एक करके देखना बहुत काम है) ।
हमने संकलित उद्धरण इंटरफ़ेस पाया:
GET https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price. एफएमजेड प्लेटफॉर्म पर,HttpQueryएक्सचेंज टिकर इंटरफेस (सार्वजनिक इंटरफेस जिसके लिए हस्ताक्षर की आवश्यकता नहीं है) तक पहुँचने के लिए कार्य। - 4 घंटे की रोलिंग विंडो अवधि के लिए डेटा गिनने की आवश्यकता है सांख्यिकीय कार्यक्रम की संरचना को कैसे डिजाइन किया जाए, इसकी कल्पना करें।
- मूल्य उतार-चढ़ाव की गणना करें और उन्हें क्रमबद्ध करें
मूल्य उतार-चढ़ाव एल्गोरिथ्म के बारे में सोच, यह हैः
price fluctuations (%) = (current price - initial price) / initial price * 100% में।
समस्या का पता लगाने के बाद, साथ ही कार्यक्रम को परिभाषित करने के बाद, हम कार्यक्रम को डिजाइन करने के व्यवसाय में उतर आए।
कोड डिजाइन
var dictSymbolsPrice = {}
function main() {
while (true) {
// GET https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price
try {
var arr = JSON.parse(HttpQuery("https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price"))
if (!Array.isArray(arr)) {
Sleep(5000)
continue
}
var ts = new Date().getTime()
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
var symbolPriceInfo = arr[i]
var symbol = symbolPriceInfo.symbol
var price = symbolPriceInfo.price
if (typeof(dictSymbolsPrice[symbol]) == "undefined") {
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol] = {name: symbol, data: []}
}
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data.push({ts: ts, price: price})
}
} catch(e) {
Log("e.name:", e.name, "e.stack:", e.stack, "e.message:", e.message)
}
// Calculate price fluctuations
var tbl = {
type : "table",
title : "Price fluctuations",
cols : ["trading pair", "current price", "price 4 hours ago", "price fluctuations", "data length", "earliest data time", "latest data time"],
rows : []
}
for (var symbol in dictSymbolsPrice) {
var data = dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data
if (data[data.length - 1].ts - data[0].ts > 1000 * 60 * 60 * 4) {
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data.shift()
}
data = dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].percentageChange = (data[data.length - 1].price - data[0].price) / data[0].price * 100
}
var entries = Object.entries(dictSymbolsPrice)
entries.sort((a, b) => b[1].percentageChange - a[1].percentageChange)
for (var i = 0; i < entries.length; i++) {
if (i > 9) {
break
}
var name = entries[i][1].name
var data = entries[i][1].data
var percentageChange = entries[i][1].percentageChange
var currPrice = data[data.length - 1].price
var currTs = _D(data[data.length - 1].ts)
var prePrice = data[0].price
var preTs = _D(data[0].ts)
var dataLen = data.length
tbl.rows.push([name, currPrice, prePrice, percentageChange + "%", dataLen, preTs, currTs])
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`")
Sleep(5000)
}
}
कोड विश्लेषण
- 1. डेटा संरचना
- 2. Main function main()
2.1. Infinite loop
जबकि (सही) { //... }
The program continuously monitors the Binance API trading pair prices through an infinite loop.
2.2. Get price information
var arr = JSON.parse(HttpQuery(
Get the current price information of the trading pair via Binance API. If the return is not an array, wait for 5 seconds and retry.
2.3. Update price data
के लिए (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { //... }
Iterate through the array of obtained price information and update the data in dictSymbolsPrice. For each trading pair, add the current timestamp and price to the corresponding data array.
2.4. Exception processing
पकड़ना
लॉग ((
Catch exceptions and log the exception information to ensure that the program can continue to execute.
2.5. Calculate the price fluctuations
के लिए (DictSymbolsPrice में var प्रतीक) { //... }
Iterate through dictSymbolsPrice, calculate the price fluctuations of each trading pair, and remove the earliest data if it is longer than 4 hours.
2.6. Sort and generate tables
var प्रविष्टियाँ = Object.entries ((dictSymbolsPrice) entries.sort (((a, b) => b[1].percentageChange - a[1].percentageChange)
for (var i = 0; i < entries.length; i++) { //... }
Sort the trading pairs in descending order of their price fluctuations and generate a table containing information about the trading pairs.
2.7. Log output and delay
लॉगस्टेटस ((_D(), " + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "
Output the table and the current time in the form of a log and wait for 5 seconds to continue the next round of the loop.
The program obtains the real-time price information of the trading pair through Binance API, then calculates the price fluctuations, and outputs it to the log in the form of a table. The program is executed in a continuous loop to realize the function of real-time monitoring of the prices of trading pairs. Note that the program includes exception processing to ensure that the execution is not interrupted by exceptions when obtaining price information.
### Live Trading Running Test
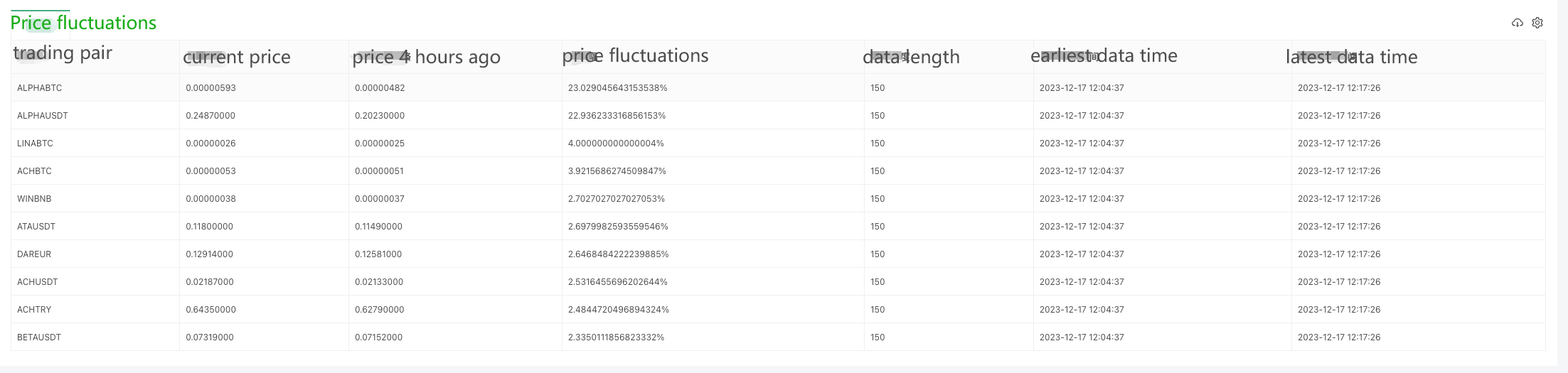
Since data can only be collected bit by bit at the beginning, it is not possible to calculate the price fluctuations on a rolling basis without collecting enough data for a 4-hour window. Therefore, the initial price is used as the base for calculation, and after collecting enough data for 4 hours, the oldest data will be eliminated in order to maintain the 4-hour window for calculating the price fluctuations.
## 2. Check the full variety of funding rates for Binance U-denominated contracts
Checking the funding rate is similar to the above code, first of all, we need to check the Binance API documentation to find the funding rate related interface. Binance has several interfaces that allow us to query the rate of funds, here we take the interface of the U-denominated contract as an example:
GEThttps://fapi.binance.com/fapi/v1/premiumIndex
### Code Implementation
Since there are so many contracts, we're exporting the top 10 largest funding rates here.
main() {
जबकि (सही) {
// प्राप्त करेंhttps://fapi.binance.com/fapi/v1/premiumIndexकोशिश करो
var arr = JSON.parse(HttpQuery(
arr.sort((a, b) => parseFloat(b.lastFundingRate) - parseFloat(a.lastFundingRate))
var tbl = {
type: "table",
title: "Top 10 funding rates for U-denominated contracts",
cols: ["contracts", "funding rate", "marked price", "index price", "current rate time", "next rate time"],
rows: []
}
for (var i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
var obj = arr[i]
tbl.rows.push([obj.symbol, obj.lastFundingRate, obj.markPrice, obj.indexPrice, _D(obj.time), _D(obj.nextFundingTime)])
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`")
} catch(e) {
Log("e.name:", e.name, "e.stack:", e.stack, "e.message:", e.message)
}
Sleep(1000 * 10)
}
}
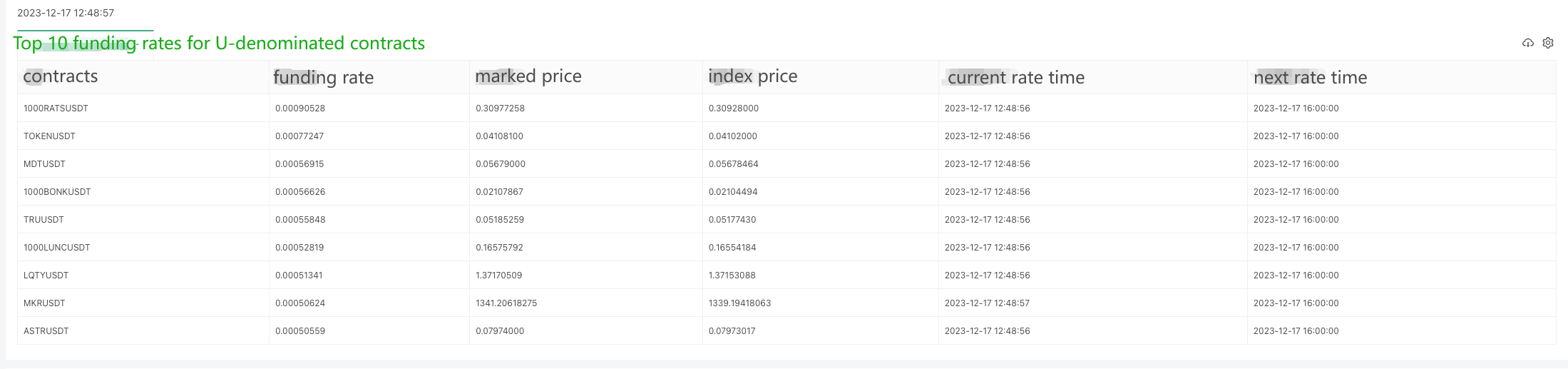
The returned data structure is as follows, and check the Binance documentation, it shows that lastFundingRate is the funding rate we want.
{
Live trading running test:
### Getting OKX exchange contract funding rates of Python version
A user has asked for a Python version of the example, and it's for the OKX exchange. Here is an example:
The data returned by the interface ```https://www.okx.com/priapi/v5/public/funding-rate-all?currencyType=1```:
{
Specific code:
आयात अनुरोध json आयात करें समय आयात नींद से दिनांक समय से आयात दिनांक समय
मुख्य परिभाषाः
जबकि True:
#https://www.okx.com/priapi/v5/public/funding-rate-all?currencyType=1कोशिश करो:
प्रतिक्रिया = अनुरोध. प्राप्त करेंhttps://www.okx.com/priapi/v5/public/funding-rate-all?currencyType=1”)
arr = response.json() [
arr.sort(key=lambda x: float(x["fundingRate"]), reverse=True)
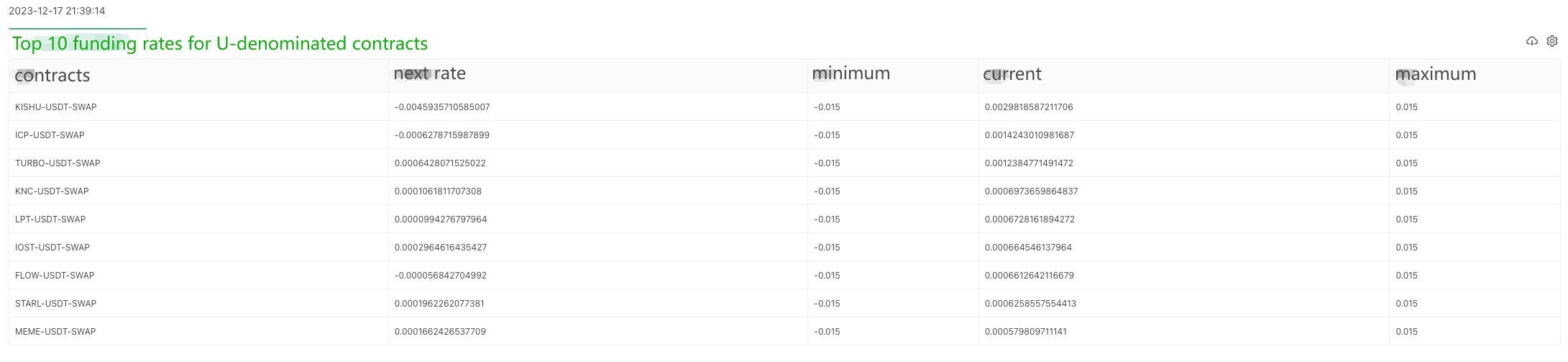
tbl = {
"type": "table",
"title": "Top 10 funding rates for U-denominated contracts",
"cols": ["contracts", "next rate", "minimum", "current", "maximum"],
"rows": []
}
for i in range(min(9, len(arr))):
obj = arr[i]
row = [
obj["instId"],
obj["nextFundingRate"],
obj["minFundingRate"],
obj["fundingRate"],
obj["maxFundingRate"]
]
tbl["rows"].append(row)
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", '`' + json.dumps(tbl) + '`')
except Exception as e:
Log(f"Error: {str(e)}")
sleep(10)
अंत
इन उदाहरणों में बुनियादी डिजाइन विचार और कॉलिंग विधियां प्रदान की गई हैं, वास्तविक परियोजना को विशिष्ट आवश्यकताओं के आधार पर उचित परिवर्तन और विस्तार करने की आवश्यकता हो सकती है। उम्मीद है, ये कोड आपको क्रिप्टोक्यूरेंसी डिजिटल परिसंपत्ति व्यापार में विभिन्न आवश्यकताओं को बेहतर ढंग से पूरा करने में मदद कर सकते हैं।
- क्रिप्टोक्यूरेंसी बाजार में मौलिक विश्लेषण की मात्राः डेटा को खुद के लिए बोलने दें!
- मौद्रिक सर्कल के मूलभूत मात्रात्मक अनुसंधान - अब हर तरह के जादूगरों पर भरोसा न करें, डेटा निष्पक्ष रूप से बोलते हैं!
- मात्रात्मक व्यापार के क्षेत्र में एक आवश्यक उपकरण - FMZ क्वांट डेटा एक्सप्लोरेशन मॉड्यूल
- क्वांटिफाइड ट्रेडिंग के लिए आवश्यक उपकरण - आविष्कारक क्वांटिफाइड डेटा एक्सप्लोरर मॉड्यूल
- सब कुछ में महारत हासिल करना - एफएमजेड ट्रेडिंग टर्मिनल का नया संस्करण (टीआरबी आर्बिट्रेज स्रोत कोड के साथ)
- सब कुछ जानने के लिए FMZ के नए संस्करण के लिए ट्रेडिंग टर्मिनल का परिचय (अनुदानित TRB सूट स्रोत कोड)
- एफएमजेड क्वांटः क्रिप्टोकरेंसी बाजार में सामान्य आवश्यकताओं के डिजाइन उदाहरणों का विश्लेषण (II)
- 80 पंक्तियों के कोड में उच्च आवृत्ति रणनीति के साथ मस्तिष्क रहित बिक्री बॉट्स का शोषण कैसे करें
- एफएमजेड क्वांटिकेशनः क्रिप्टोक्यूरेंसी बाजार में आम जरूरतों के डिजाइन उदाहरण का विश्लेषण
- 80 लाइनों के कोड के साथ उच्च आवृत्ति रणनीतियों का उपयोग करके बेचने के लिए मस्तिष्क रहित रोबोट का शोषण कैसे करें
- एफएमजेड क्वांटिकेशनः क्रिप्टोक्यूरेंसी बाजार में आम जरूरतों के डिजाइन उदाहरण का विश्लेषण (1)
- एफएमजेड क्वांट क्रिप्टोक्यूरेंसी डेमो एक्सचेंज, वेक्सऐप, हाल ही में लॉन्च किया गया है
- स्थायी अनुबंध ग्रिड रणनीति पैरामीटर अनुकूलन का विस्तृत स्पष्टीकरण
- बॉट के पैरामीटर को बैच संशोधित करने के लिए FMZ विस्तारित एपीआई का उपयोग करने के लिए आपको सिखाएं
- आपको FMZ विस्तार एपीआई का उपयोग करके थोक डिस्क पैरामीटर को संशोधित करने के लिए सिखाता है
- स्थायी अनुबंध ग्रिड रणनीति पैरामीटर अनुकूलन विवरण
- लिनक्स बैश में इंटरएक्टिव ब्रोकर आईबी गेटवे स्थापित करने के लिए निर्देश
- लिनक्स बैश के तहत इंस्टॉल करने के लिए घुसपैठ के लिए प्रतिभूति आईबी गेटवे
- निचली मछली पकड़ने के लिए कौन सा अधिक उपयुक्त है, कम बाजार मूल्य या कम कीमत?
- कम बाजार मूल्य और कम कीमत, कौन सा बेहतर है?