FMZ Quant: Analisis Contoh Desain Persyaratan Umum di Pasar Cryptocurrency (I)
Penulis:FMZ~Lydia, Dibuat: 2023-12-19 16:02:58, Diperbarui: 2024-11-06 21:19:16
Dalam ruang perdagangan aset cryptocurrency, memperoleh dan menganalisis data pasar, menanyakan tingkat, dan memantau pergerakan aset akun adalah semua operasi penting.
Bagaimana saya menulis kode untuk mendapatkan mata uang dengan kenaikan tertinggi dalam 4 jam di Binance Spot?
Ketika menulis program strategi perdagangan kuantitatif di platform FMZ, hal pertama yang perlu Anda lakukan ketika Anda menemukan persyaratan adalah menganalisisnya.
- Bahasa pemrograman apa yang harus digunakan? Rencananya adalah menggunakan JavaScript untuk menerapkannya.
- Membutuhkan kutipan real-time spot di semua mata uang
Hal pertama yang kami lakukan ketika kami melihat persyaratan adalah mencari dokumen API Binance untuk mengetahui apakah ada kutipan agregat (yang terbaik adalah memiliki kutipan agregat, itu banyak pekerjaan untuk mencari satu per satu).
Kami menemukan antarmuka kutipan agregat:
GET https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/priceAku tidak tahu. Di platform FMZ, gunakanHttpQueryfungsi untuk mengakses antarmuka ticker pertukaran (antarmuka publik yang tidak memerlukan tanda tangan). - Perlu menghitung data untuk periode jendela bergulir 4 jam Konsepsi bagaimana merancang struktur program statistik.
- Menghitung fluktuasi harga dan menyortirnya
Berpikir tentang algoritma fluktuasi harga, adalah:
price fluctuations (%) = (current price - initial price) / initial price * 100dalam% .
Setelah mencari tahu masalah, serta mendefinisikan program, kami kemudian turun ke bisnis merancang program.
Desain Kode
var dictSymbolsPrice = {}
function main() {
while (true) {
// GET https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price
try {
var arr = JSON.parse(HttpQuery("https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price"))
if (!Array.isArray(arr)) {
Sleep(5000)
continue
}
var ts = new Date().getTime()
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
var symbolPriceInfo = arr[i]
var symbol = symbolPriceInfo.symbol
var price = symbolPriceInfo.price
if (typeof(dictSymbolsPrice[symbol]) == "undefined") {
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol] = {name: symbol, data: []}
}
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data.push({ts: ts, price: price})
}
} catch(e) {
Log("e.name:", e.name, "e.stack:", e.stack, "e.message:", e.message)
}
// Calculate price fluctuations
var tbl = {
type : "table",
title : "Price fluctuations",
cols : ["trading pair", "current price", "price 4 hours ago", "price fluctuations", "data length", "earliest data time", "latest data time"],
rows : []
}
for (var symbol in dictSymbolsPrice) {
var data = dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data
if (data[data.length - 1].ts - data[0].ts > 1000 * 60 * 60 * 4) {
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data.shift()
}
data = dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].percentageChange = (data[data.length - 1].price - data[0].price) / data[0].price * 100
}
var entries = Object.entries(dictSymbolsPrice)
entries.sort((a, b) => b[1].percentageChange - a[1].percentageChange)
for (var i = 0; i < entries.length; i++) {
if (i > 9) {
break
}
var name = entries[i][1].name
var data = entries[i][1].data
var percentageChange = entries[i][1].percentageChange
var currPrice = data[data.length - 1].price
var currTs = _D(data[data.length - 1].ts)
var prePrice = data[0].price
var preTs = _D(data[0].ts)
var dataLen = data.length
tbl.rows.push([name, currPrice, prePrice, percentageChange + "%", dataLen, preTs, currTs])
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`")
Sleep(5000)
}
}
Analisis Kode
- 1. Struktur data
- 2. Main function main()
2.1. Infinite loop
sementara (benar) { /... {\cH00FFFF}
The program continuously monitors the Binance API trading pair prices through an infinite loop.
2.2. Get price information
var arr = JSON.parse ((HttpQuery(
Get the current price information of the trading pair via Binance API. If the return is not an array, wait for 5 seconds and retry.
2.3. Update price data
untuk (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) /... {\cH00FFFF}
Iterate through the array of obtained price information and update the data in dictSymbolsPrice. For each trading pair, add the current timestamp and price to the corresponding data array.
2.4. Exception processing
{\cH00FFFF}menangkapnya.
Log ((
Catch exceptions and log the exception information to ensure that the program can continue to execute.
2.5. Calculate the price fluctuations
untuk (simbol var dalam dictSymbolsPrice) { /... {\cH00FFFF}
Iterate through dictSymbolsPrice, calculate the price fluctuations of each trading pair, and remove the earliest data if it is longer than 4 hours.
2.6. Sort and generate tables
var entries = Object.entries ((dictSymbolsPrice) entries.sort (((a, b) => b[1].percentageChange - a[1].percentageChange)
untuk (var i = 0; i < entries.length; i++) { /... {\cH00FFFF}
Sort the trading pairs in descending order of their price fluctuations and generate a table containing information about the trading pairs.
2.7. Log output and delay
LogStatus ((_D(), " + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "
Output the table and the current time in the form of a log and wait for 5 seconds to continue the next round of the loop.
The program obtains the real-time price information of the trading pair through Binance API, then calculates the price fluctuations, and outputs it to the log in the form of a table. The program is executed in a continuous loop to realize the function of real-time monitoring of the prices of trading pairs. Note that the program includes exception processing to ensure that the execution is not interrupted by exceptions when obtaining price information.
### Live Trading Running Test
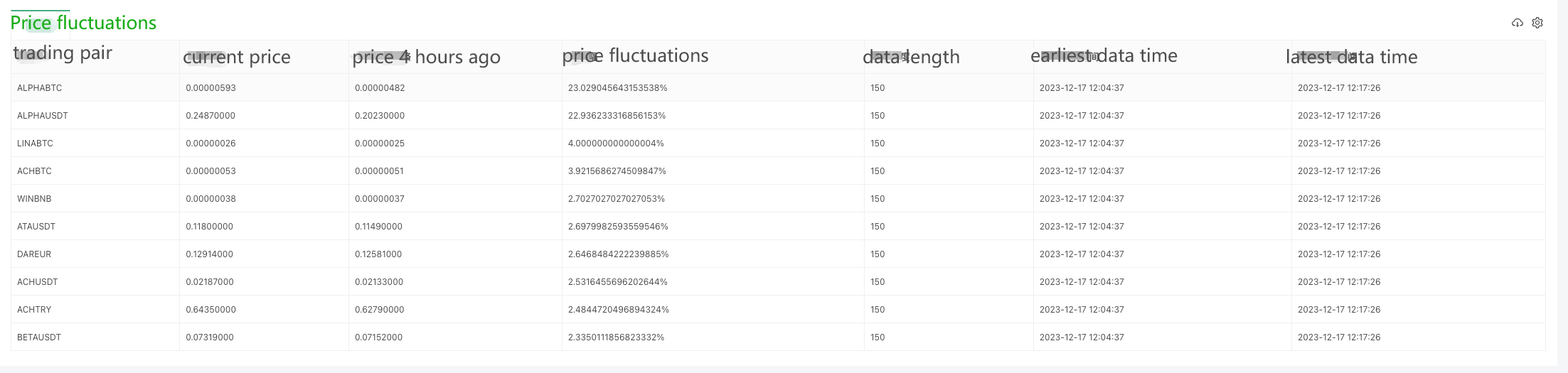
Since data can only be collected bit by bit at the beginning, it is not possible to calculate the price fluctuations on a rolling basis without collecting enough data for a 4-hour window. Therefore, the initial price is used as the base for calculation, and after collecting enough data for 4 hours, the oldest data will be eliminated in order to maintain the 4-hour window for calculating the price fluctuations.
## 2. Check the full variety of funding rates for Binance U-denominated contracts
Checking the funding rate is similar to the above code, first of all, we need to check the Binance API documentation to find the funding rate related interface. Binance has several interfaces that allow us to query the rate of funds, here we take the interface of the U-denominated contract as an example:
GEThttps://fapi.binance.com/fapi/v1/premiumIndex
### Code Implementation
Since there are so many contracts, we're exporting the top 10 largest funding rates here.
Fungsi utama
sementara (benar) {
// Dapatkanhttps://fapi.binance.com/fapi/v1/premiumIndexCobalah
var arr = JSON.parse ((HttpQuery(
arr.sort((a, b) => parseFloat(b.lastFundingRate) - parseFloat(a.lastFundingRate))
var tbl = {
type: "table",
title: "Top 10 funding rates for U-denominated contracts",
cols: ["contracts", "funding rate", "marked price", "index price", "current rate time", "next rate time"],
rows: []
}
for (var i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
var obj = arr[i]
tbl.rows.push([obj.symbol, obj.lastFundingRate, obj.markPrice, obj.indexPrice, _D(obj.time), _D(obj.nextFundingTime)])
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`")
} catch(e) {
Log("e.name:", e.name, "e.stack:", e.stack, "e.message:", e.message)
}
Sleep(1000 * 10)
}
}
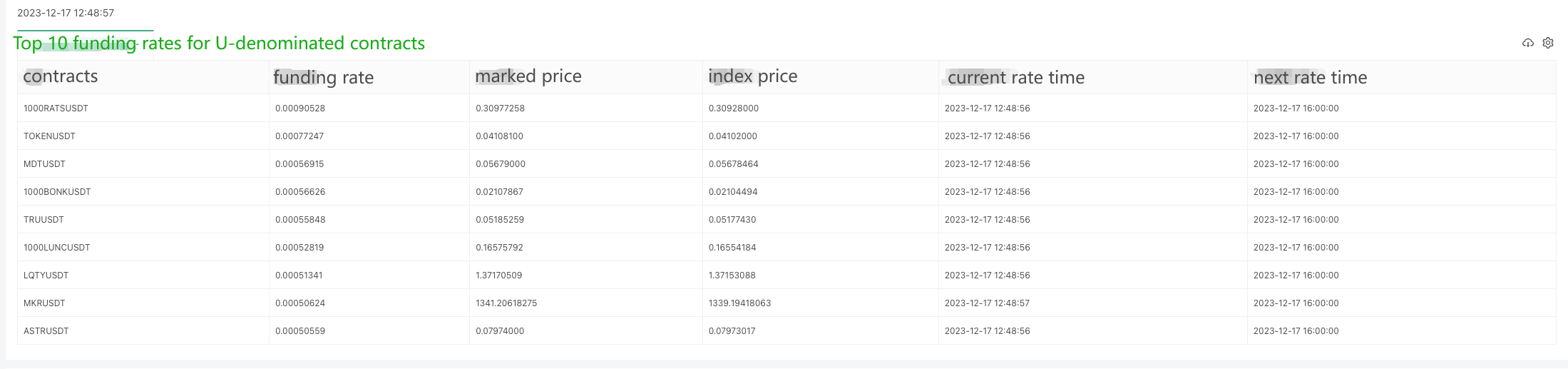
The returned data structure is as follows, and check the Binance documentation, it shows that lastFundingRate is the funding rate we want.
{\cH00FFFF}
Live trading running test:
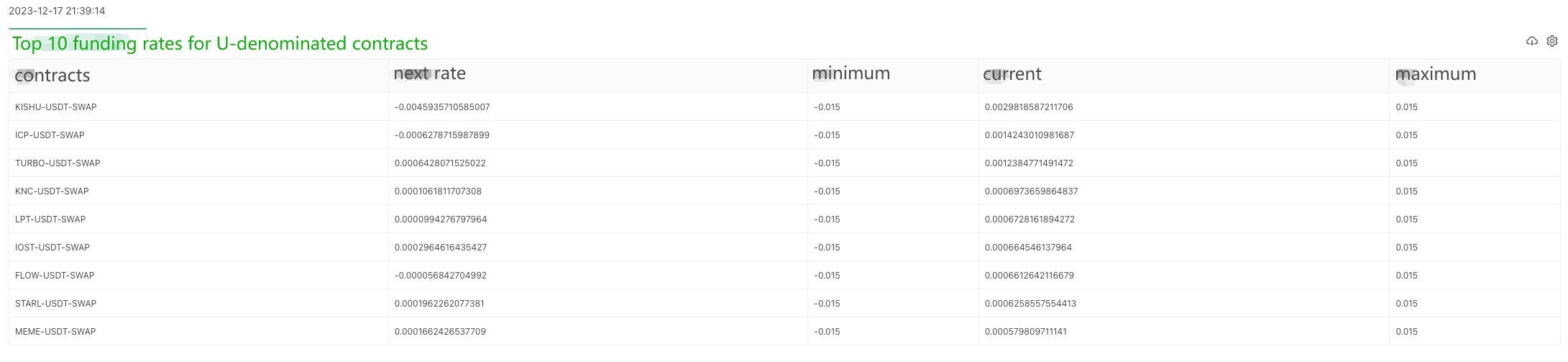
### Getting OKX exchange contract funding rates of Python version
A user has asked for a Python version of the example, and it's for the OKX exchange. Here is an example:
The data returned by the interface ```https://www.okx.com/priapi/v5/public/funding-rate-all?currencyType=1```:
{\cH00FFFF}
Specific code:
permintaan impor mengimpor json dari waktu impor tidur dari waktu tanggal waktu impor
Definisi utama:
sementara True:
#https://www.okx.com/priapi/v5/public/funding-rate-all?currencyType=1Cobalah:
respon = permintaan.get(
arr.sort(key=lambda x: float(x["fundingRate"]), reverse=True)
tbl = {
"type": "table",
"title": "Top 10 funding rates for U-denominated contracts",
"cols": ["contracts", "next rate", "minimum", "current", "maximum"],
"rows": []
}
for i in range(min(9, len(arr))):
obj = arr[i]
row = [
obj["instId"],
obj["nextFundingRate"],
obj["minFundingRate"],
obj["fundingRate"],
obj["maxFundingRate"]
]
tbl["rows"].append(row)
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", '`' + json.dumps(tbl) + '`')
except Exception as e:
Log(f"Error: {str(e)}")
sleep(10)
Penghentian
Contoh-contoh ini memberikan ide-ide desain dasar dan metode panggilan, proyek sebenarnya mungkin perlu membuat perubahan dan ekstensi yang sesuai berdasarkan kebutuhan spesifik.
- Mengkuantifikasi Analisis Fundamental di Pasar Cryptocurrency: Biarkan Data Berbicara Sendiri!
- Di sini, saya akan membahas beberapa hal yang sangat penting tentang penelitian kuantitatif dasar dalam lingkaran mata uang - jangan percaya lagi pada guru-guru sihir yang bodoh, data berbicara secara obyektif!
- Sebuah alat penting dalam bidang perdagangan kuantitatif - FMZ Quant Data Exploration Module
- Alat penting dalam bidang transaksi kuantitatif - inventor modul eksplorasi data kuantitatif
- Menguasai Semuanya - Pendahuluan ke FMZ Versi Baru Terminal Trading (dengan TRB Arbitrage Source Code)
- Untuk mengetahui semua tentang FMZ, silahkan kunjungi situs resmi FMZ.
- FMZ Quant: Analisis Contoh Desain Persyaratan Umum di Pasar Cryptocurrency (II)
- Cara Mengeksploitasi Robot Penjual Tanpa Otak dengan Strategi Frekuensi Tinggi dalam 80 Baris Kode
- FMZ Kuantitas: Perencanaan Contoh Desain Permintaan Umum di Pasar Cryptocurrency (II)
- Cara Mengeksploitasi Robot Tanpa Otak untuk Dijual dengan Strategi Frekuensi Tinggi 80 Baris Kode
- Kuantitas FMZ: Perbedaan antara permintaan umum pasar cryptocurrency dan contoh desain (1)
- WexApp, FMZ Quant Cryptocurrency Demo Exchange, Baru Diluncurkan
- Penjelasan Rincian Optimasi Parameter Strategi Grid Kontrak Perpetual
- Ajarkan Anda untuk menggunakan FMZ diperluas API untuk Batch Modify Parameter dari bot
- Mengajarkan Anda menggunakan FMZ Extension API untuk mengubah parameter disk secara massal
- Parameter Optimasi Strategi Jaringan Kontrak Langsung
- Instruksi untuk menginstal Interactive Brokers IB Gateway di Linux Bash
- Panduan untuk menginstal Penetration Securities IB GATEWAY di Linux bash
- Yang mana yang lebih cocok untuk memancing dasar, nilai pasar rendah atau harga rendah?
- Jika Anda ingin membeli sebuah buku dengan nilai pasar rendah atau harga rendah, mana yang lebih cocok?