取引の原則を分析するために研究環境を使用することを学びます
作者: リン・ハーンFMZ~リディア, 作成日:2022-12-27 16:33:51, 更新日:2023-09-20 09:17:27
より良いツールで良い仕事をする 取引の原則を分析するために研究環境を使用することを学ぶ
"ヘジング"という用語は,定量取引とプログラム取引の分野における非常に基本的な概念である.デジタル通貨の定量取引では,しばしば使用されるヘジング戦略は,基本的には価格差のための取引であるフューチャースポットヘジング,クロス期間のヘジング,スポットヘジングである.おそらく,ヘジングの概念,原則,詳細に関しては,定量取引の分野に入ってきた多くの学生がまだ非常に明確ではない.それは問題ではありません.この知識を簡単に学び,マスターするために,FMZ取引プラットフォームが提供する"QuantAnalyze"ツールを使用しましょう.
FMZ Quant プラットフォームのダッシュボードで,ツールページへジャンプするために"分析"をクリックします.
分析ファイルを直接アップロードします.
この分析文書は,バックテスト中に先物先物先のヘッジポジションを開設および閉じるプロセスを分析します.先物先取引所はOKX先物先物で,契約は先物先の取引所です.quarter取引対は,OKXの通貨対通貨取引であり,取引対は,OKXの通貨対通貨取引であり,取引対はOKXの通貨対通貨取引であり,取引対はOKXの通貨対通貨取引であり,取引対はOKXの通貨対通貨取引であり,取引対はOKXの通貨対通貨取引である.BTC_USDT. フューチャー・スポット・ヘジングの動作プロセスを分析するには,次の特定の研究環境ファイルを見ることができます. Python言語バージョン,JavaScript言語バージョンで書かれています.
研究環境 Python 言語ファイル
フューチャー・スポット・ヘージングの原則に関する分析.ipynb [1] において
from fmz import *
task = VCtx('''backtest
start: 2019-09-19 00:00:00
end: 2019-09-28 12:00:00
period: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_OKCoin","currency":"BTC_USD", "stocks":1}, {"eid":"OKX","currency":"BTC_USDT","balance":10000,"stocks":0}]
''')
# Create backtesting environment
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Import the plot library matplotlib and library numpy
[2] において
exchanges[0].SetContractType("quarter") # The first exchange object OKX Futures (eid: Futures_OKCoin) calls the function to set the current contract as a quarterly contract
initQuarterAcc = exchanges[0].GetAccount() # The initial account information of OKX Futures Exchange is recorded in the variable initQuarterAcc
initQuarterAcc
アウト[2]:
{
[3] において
initSpotAcc = exchanges[1].GetAccount() # The initial account information of the OKX Spot Exchange is recorded in the variable initSpotAcc
initSpotAcc
アウト[3]:
{
[4] において
quarterTicker1 = exchanges[0].GetTicker() # Get the futures exchange ticker, recorded in the variable quarterTicker1
quarterTicker1
アウト[4]:
タイム1568851210000
[5] において
spotTicker1 = exchanges[1].GetTicker() # Get the spot exchange ticker, recorded in the variable spotTicker1
spotTicker1
アウト[5]:
タイム1568851210000
[6] において
quarterTicker1.Buy - spotTicker1.Sell # The price difference between going short on futures and going long on spot.
アウト[6]: 284.6499999799999985
[7]:
exchanges[0].SetDirection("sell") # Set up a futures exchange and trade in the direction of going short
quarterId1 = exchanges[0].Sell(quarterTicker1.Buy, 10) # Futures go short to place orders. The order quantity is 10 contracts. The returned order ID is recorded in the variable quarterId1.
exchanges[0].GetOrder(quarterId1) # Check the details of the order with futures order ID quarterId1.
アウト[7]:
{cH00ffff}1つ目
[8] で:
spotAmount = 10 * 100 / quarterTicker1.Buy # Calculate the currency equivalent of 10 contracts as the order quantity of the spot.
spotId1 = exchanges[1].Buy(spotTicker1.Sell, spotAmount) # Place orders on the spot exchange
exchanges[1].GetOrder(spotId1) # Check the order details of the spot order ID of spotId1
アウト[8]:
{cH00ffff}1つ目
価格: 10156.60000002
オーダーQuarterId1とSpotId1が完全に満たされていることがわかります.つまり,オープンポジションのヘッジが完了しています.
[9]:
Sleep(1000 * 60 * 60 * 24 * 7) # Hold the position for a while and wait for the price difference to become smaller to close the position.
待機時間後,ポジションを閉じる準備. 現在のティッカーを取得quarterTicker2, spotTicker2プリントして
フューチャー取引対象の取引方向は,ショートポジションを閉じるように設定されます.exchanges[0].SetDirection("closesell")ポジションを閉じる命令を出す.
閉じるポジションオーダーの詳細を印刷し,閉じるオーダーが完了し,閉じるポジションが完了したことを示す.
[10] で:
quarterTicker2 = exchanges[0].GetTicker() # Get the current futures exchange ticker, recorded in the variable quarterTicker2
quarterTicker2
アウト[10]:
1569456010000 時間
[11] で:
spotTicker2 = exchanges[1].GetTicker() # Get the current ticker of the spot exchange, recorded in the variable spotTicker2
spotTicker2
アウト[11]:
{
[12] で:
quarterTicker2.Sell - spotTicker2.Buy # The price difference between closing a short futures position and closing a long spot position.
アウト[12]: 52.5000200100003
[13]では:
exchanges[0].SetDirection("closesell") # Set the current trading direction of the futures exchange to close short positions.
quarterId2 = exchanges[0].Buy(quarterTicker2.Sell, 10) # The futures exchange places an order to close a position and records the order ID to the variable quarterId2.
exchanges[0].GetOrder(quarterId2) # Check futures close out order details
アウト[13]:
2つ目,この3つを
[14] では:
spotId2 = exchanges[1].Sell(spotTicker2.Buy, spotAmount) # The spot exchange places an order to close a position and records the order ID, which is recorded to the variable spotId2.
exchanges[1].GetOrder(spotId2) # Check spot close out order details
アウト[14]:
2つ目で2つ目で2つ目で3つ目で4つ目で5つ目で5つ目で5つ目で5つ目で5つ目で5つ目で5つ目で5つ目で5つ目です
価格: 8444.69999999,
[15] について
nowQuarterAcc = exchanges[0].GetAccount() # Get the current futures exchange account information, recorded in the variable nowQuarterAcc.
nowQuarterAcc
アウト[15]:
{
[16]:
nowSpotAcc = exchanges[1].GetAccount() # Get the current spot exchange account information, recorded in the variable nowSpotAcc.
nowSpotAcc
アウト[16]:
余計は9834.74705446
初期口座と経常口座を比較することで,ヘージングオペレーションの利益と損失を計算する.
[17]:
diffStocks = abs(nowQuarterAcc.Stocks - initQuarterAcc.Stocks)
diffBalance = nowSpotAcc.Balance - initSpotAcc.Balance
if nowQuarterAcc.Stocks - initQuarterAcc.Stocks > 0 :
print("profits:", diffStocks * spotTicker2.Buy + diffBalance)
else :
print("profits:", diffBalance - diffStocks * spotTicker2.Buy)
アウト[17]: 利益: 18.72350977580652
フレームワークを図に描いてみましょう. フューチャー価格は青い線,スポット価格はオレンジ線です. 両方の価格が下がっています. フューチャー価格はスポット価格よりも速く下がっています.
[18]:
xQuarter = [1, 2]
yQuarter = [quarterTicker1.Buy, quarterTicker2.Sell]
xSpot = [1, 2]
ySpot = [spotTicker1.Sell, spotTicker2.Buy]
plt.plot(xQuarter, yQuarter, linewidth=5)
plt.plot(xSpot, ySpot, linewidth=5)
plt.show()
アウト[18]:
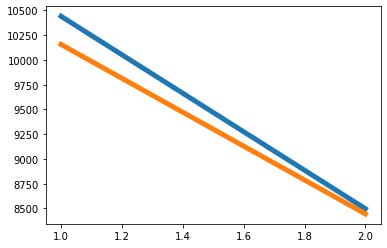
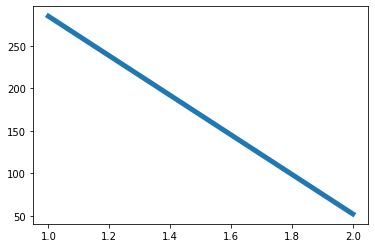
価格差の変化を見てみましょう.価格差は,ヘッジ開始ポジション (すなわち,先物がショートになり,スポットがロングになる) の時点で284から,閉店ポジション (先物ショートポジションが閉鎖され,スポットロングポジションが閉鎖される) の時点で52に及ぶ.価格差は,大きくて小さくなります.
[19]:
xDiff = [1, 2]
yDiff = [quarterTicker1.Buy - spotTicker1.Sell, quarterTicker2.Sell - spotTicker2.Buy]
plt.plot(xDiff, yDiff, linewidth=5)
plt.show()
アウト[19]:
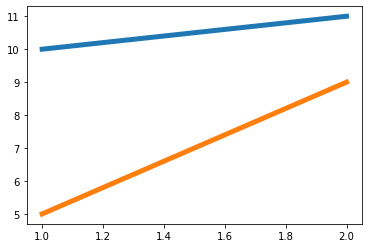
例えば,a1は時間1の先物価格,b1は時間1の即時価格.A2は時間2の先物価格,b2は時間2の即時価格です.フューチャーズ・スポット・価格差が時間1 (a1-b1) が時間2 (a2-b2) のフューチャーズ・スポット・価格差よりも大きい限り,a1 - a2>b1 - b2が導入できる. 3つの状況があります (先物と即時ポジションの量は同じ)
-
a1 - a2 は 0 より大きい.b1 - b2 は 0 より大きい. a1 - a2は先物利益の価格差を指し,b1 - b2は即時損失の価格差を指す (スポットがロングになったため,開始価格はポジションを閉じるための販売価格よりも高いので,お金は失われる).しかし先物利益は即時損失よりも大きい.したがって,全体として有利である.この状況はステップインのチャートに対応する [8].
-
a1 - a2 は 0 より大きい.b1 - b2 は 0 より小さい. a1 - a2は先物利得の価格差で,b1 - b2は即時利得の価格差 (b1 - b2は0未満で,b2はb1より大きいことを示します.つまり,開設と購入の価格が低く,売却と閉じる価格が高く,利便性があります).
-
a1 - a2 0未満 b1 - b2 0未満 a1 - a2は先物損失の価格差であり,b1 - b2は即時利益の価格差である.a1 - a2 > b1 - b2であるため,a1 - a2の絶対値はb1 - b2の絶対値よりも小さいし,即時利益は先物損失よりも大きい.全体として利益がある.
A1 - a2 > b1 - b2 が定義されているため,a1 - a2 が 0 未満で,b1 - b2 が 0 未満であるケースは存在しない.同様に,a1 - a2 が 0 に等しい場合,a1 - a2 > b1 - b2 が定義されているため,b1 - b2 は 0 未満でなければならない.したがって,ショート・フューチャーとロング・スポットのヘッジ方法が a1 - b1 > a2 - b2 の条件を満たす限り,ポジションの開設と閉じる操作は利益ヘッジである.
例えば,次のモデルは,次のケースの1つです.
[20]:
a1 = 10
b1 = 5
a2 = 11
b2 = 9
# a1 - b1 > a2 - b2 launches: a1 - a2 > b1 - b2
xA = [1, 2]
yA = [a1, a2]
xB = [1, 2]
yB = [b1, b2]
plt.plot(xA, yA, linewidth=5)
plt.plot(xB, yB, linewidth=5)
plt.show()
アウト[20]:
検索環境 JavaScript 言語ファイル
研究環境はPythonだけでなく JavaScriptもサポートしています JavaScript の研究環境の例も挙げます
フューチャー・スポット・ヘージングの原則の分析 (JavaScript).ipynb [1] において
// Import the required package, click "Save settings" on the FMZ's "Strategy editing page" to get the string configuration and convert it to an object.
var fmz = require("fmz") // Import the talib, TA, and plot libraries automatically after import
var task = fmz.VCtx({
start: '2019-09-19 00:00:00',
end: '2019-09-28 12:00:00',
period: '15m',
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_OKCoin","currency":"BTC_USD","stocks":1},{"eid":"OKX","currency":"BTC_USDT","balance":10000,"stocks":0}]
})
[2] において
exchanges[0].SetContractType("quarter") // The first exchange object OKX Futures (eid: Futures_OKCoin) calls the function to set the current contract as a quarterly contract.
var initQuarterAcc = exchanges[0].GetAccount() // The initial account information of OKX Futures Exchange is recorded in the variable initQuarterAcc.
initQuarterAcc
アウト[2]: { 収支: 0 凍結 収支: 0 備蓄: 1 凍結 備蓄: 0 }
[3] において
var initSpotAcc = exchanges[1].GetAccount() // The initial account information of the OKX Spot Exchange is recorded in the variable initSpotAcc.
initSpotAcc
アウト[3]: { 収支: 10000, 凍結 収支: 0, 収支: 0, 凍結 収支: 0 }
[4] において
var quarterTicker1 = exchanges[0].GetTicker() // Get the futures exchange ticker, recorded in the variable quarterTicker1.
quarterTicker1
アウト[4]: { 時間: 1568851210000, 高さ: 10441.25002 10441.25. 低かった 売る 10441.25002 10441.25. 買って 最後の10441.25001号 第1772巻 オープン・インテレスト: 0 }
[5] において
var spotTicker1 = exchanges[1].GetTicker() // Get the spot exchange ticker, recorded in the variable spotTicker1.
spotTicker1
アウト[5]: { 時間: 1568851210000, 高さ: 10156.60000002 低値: 10156.6 売る 10156.60000002 10156.6で買える 最後の10156.60000001 7.4443 巻 オープン・インテレスト: 0 }
[6] において
quarterTicker1.Buy - spotTicker1.Sell // The price difference between going short on futures and going long on spot.
アウト[6]: 284.6499999799999985 [7]:
exchanges[0].SetDirection("sell") // Set up a futures exchange and trade in the direction of going short
var quarterId1 = exchanges[0].Sell(quarterTicker1.Buy, 10) // Go short futures to place orders. The order quantity is 10 contracts. The returned order ID is recorded in the variable quarterId1.
exchanges[0].GetOrder(quarterId1) // Check the details of the order with futures order ID quarterId1.
アウト[7]:
{ アイデンティティ: 1,
価格: 10441.25,
額: 10
取引金額: 10
平均価格: 10441.25,
タイプ: 1
オフセット: 0
状況: 1
契約型:
[8] で:
var spotAmount = 10 * 100 / quarterTicker1.Buy // Calculate the currency equivalent of 10 contracts as the order quantity of the spot.
var spotId1 = exchanges[1].Buy(spotTicker1.Sell, spotAmount) // Place orders on the spot exchange.
exchanges[1].GetOrder(spotId1) // Check the order details of the spot order ID of spotId1.
アウト[8]:
{ アイデンティティ: 1,
価格: 10156.60000002
額:0.0957
取引金額: 0.0957
平均価格: 10156.60000002
タイプ: 0
オフセット: 0
状況: 1
契約型:
quarterId1 と spotId1 の注文が完全に満たされ,つまり開設ポジションのヘッジが完了していることがわかります.
[9]:
Sleep(1000 * 60 * 60 * 24 * 7) // Hold the position for a while and wait for the price difference to become smaller to close the position.
待機時間後,ポジションを閉じる準備. 現在のティッカーを取得quarterTicker2, spotTicker2プリントして
フューチャー取引対象の取引方向は,ショートポジションを閉じるように設定されます.exchanges[0].SetDirection("closesell")ポジションを閉じる命令を出す.
閉じるポジションオーダーの詳細を印刷し,閉じるオーダーが完了し,閉じるポジションが完了したことを示す.
[10] で:
var quarterTicker2 = exchanges[0].GetTicker() // Get the current futures exchange ticker, recorded in the variable quarterTicker2.
quarterTicker2
アウト[10]: { 時間: 1569456010000, 高さ: 8497.20002 低値: 8497.2 売る: 8497.20002 買って 8497.2 最後の番号: 8497.20001 巻: 4311 オープン・インテレスト: 0 }
[11] で:
var spotTicker2 = exchanges[1].GetTicker() // Get the current ticker of the spot exchange, recorded in the variable spotTicker2.
spotTicker2
アウト[11]: { 時間: 1569456114600, 高さ: 8444.70000001 8444.69999999 低かった 売る: 8444.70000001 8444.69999999 購入する 最後の8444.7 78.6273巻 オープン・インテレスト: 0 }
[12] で:
quarterTicker2.Sell - spotTicker2.Buy // The price difference between closing short position of futures and closing long position of spot.
アウト[12]: 52.5000200100003
[13]では:
exchanges[0].SetDirection("closesell") // Set the current trading direction of the futures exchange to close short positions.
var quarterId2 = exchanges[0].Buy(quarterTicker2.Sell, 10) // The futures exchange places an order to close the position, and records the order ID to the variable quarterId2.
exchanges[0].GetOrder(quarterId2) // Check futures closing position order details.
アウト[13]:
{ID: 2} オーケー オーケー
価格: 8497.20002,
額: 10件
取引金額: 10
平均価格: 8493.95335,
タイプ: 0
オフセット: 1
状況: 1
契約型:
[14] では:
var spotId2 = exchanges[1].Sell(spotTicker2.Buy, spotAmount) // The spot exchange places an order to close the position, and records the order ID to the variable spotId2.
exchanges[1].GetOrder(spotId2) // Check spot closing position order details.
アウト[14]:
{ID: 2} リストは
価格: 8444.69999999,
額:0.0957
取引金額: 0.0957
平均価格: 8444.69999999,
タイプ: 1
オフセット: 0
状況: 1
契約型:
[15] について
var nowQuarterAcc = exchanges[0].GetAccount() // Get the current futures exchange account information, recorded in the variable nowQuarterAcc.
nowQuarterAcc
アウト[15]: {残高: 0, フローズン バランス: 0 ストック: 1.021786026184 フローズンストック: 0 }
[16]:
var nowSpotAcc = exchanges[1].GetAccount() // Get the current spot exchange account information, recorded in the variable nowSpotAcc.
nowSpotAcc
アウト[16]: {残高: 9834.74705446, フローズン バランス: 0 ストック: 0 フローズンストック: 初期口座と経常口座を比較することで,ヘージング事業の利益と損失を計算する.
[17]:
var diffStocks = Math.abs(nowQuarterAcc.Stocks - initQuarterAcc.Stocks)
var diffBalance = nowSpotAcc.Balance - initSpotAcc.Balance
if (nowQuarterAcc.Stocks - initQuarterAcc.Stocks > 0) {
console.log("profits:", diffStocks * spotTicker2.Buy + diffBalance)
} else {
console.log("profits:", diffBalance - diffStocks * spotTicker2.Buy)
}
アウト[17]: 利益: 18.72350977580652
フレームワークを図に描いてみましょう. フューチャー価格は青い線,スポット価格はオレンジ線です. 両方の価格が下がっています. フューチャー価格はスポット価格よりも速く下がっています.
[18]:
var objQuarter = {
"index" : [1, 2], // The index is 1, that is, the first time, the opening time, and 2 is the closing time.
"arrPrice" : [quarterTicker1.Buy, quarterTicker2.Sell],
}
var objSpot = {
"index" : [1, 2],
"arrPrice" : [spotTicker1.Sell, spotTicker2.Buy],
}
plot([{name: 'quarter', x: objQuarter.index, y: objQuarter.arrPrice}, {name: 'spot', x: objSpot.index, y: objSpot.arrPrice}])
アウト[18]: 価格差の変化を見てみましょう. 価格差は,開設ポジションをヘッジする時に284 (つまり先物がショートになり,スポットがロングになった) から閉じる時に52 (先物でショートポジションを閉じ,スポットでロングポジションを閉じ) まであります. 価格差は大きくて小さくなります.
[19]:
var arrDiffPrice = [quarterTicker1.Buy - spotTicker1.Sell, quarterTicker2.Sell - spotTicker2.Buy]
plot(arrDiffPrice)
アウト[19]:例えば,a1は時間1の先物価格,b1は時間1の即時価格.A2は時間2の先物価格,b2は時間2の即時価格です.フューチャーズ・スポット・価格差が時間1 (a1-b1) が時間2 (a2-b2) のフューチャーズ・スポット・価格差よりも大きい限り,a1 - a2>b1 - b2が導入できる. 3つの状況があります (先物と即時ポジションの量は同じ)
-
a1 - a2 は 0 より大きい.b1 - b2 は 0 より大きい. a1 - a2は先物利益の価格差を指し,b1 - b2は即時損失の価格差を指す (スポットがロングになったため,開始価格はポジションを閉じるための販売価格よりも高いので,お金は失われる).しかし先物利益は即時損失よりも大きい.したがって,全体として有利である.この状況はステップインのチャートに対応する [8].
-
a1 - a2 は 0 より大きい.b1 - b2 は 0 より小さい. a1 - a2は先物利得の価格差で,b1 - b2は即時利得の価格差 (b1 - b2は0未満で,b2はb1より大きいことを示します.つまり,開設と購入の価格が低く,売却と閉じる価格が高く,利便性があります).
-
a1 - a2 0未満 b1 - b2 0未満 a1 - a2は先物損失の価格差であり,b1 - b2は即時利益の価格差である.a1 - a2 > b1 - b2であるため,a1 - a2の絶対値はb1 - b2の絶対値よりも小さいし,即時利益は先物損失よりも大きい.全体として利益がある.
A1 - a2 > b1 - b2 が定義されているため,a1 - a2 が 0 未満で,b1 - b2 が 0 未満であるケースは存在しない.同様に,a1 - a2 が 0 に等しい場合,a1 - a2 > b1 - b2 が定義されているため,b1 - b2 は 0 未満でなければならない.したがって,ショート・フューチャーとロング・スポットのヘッジ方法が a1 - b1 > a2 - b2 の条件を満たす限り,ポジションの開設と閉じる操作は利益ヘッジである.
例えば,次のモデルは,次のケースの1つです.
[20]:
var a1 = 10
var b1 = 5
var a2 = 11
var b2 = 9
// a1 - b1 > a2 - b2 launches: a1 - a2 > b1 - b2
var objA = {
"index" : [1, 2],
"arrPrice" : [a1, a2],
}
var objB = {
"index" : [1, 2],
"arrPrice" : [b1, b2],
}
plot([{name : "a", x : objA.index, y : objA.arrPrice}, {name : "b", x : objB.index, y : objB.arrPrice}])
アウト[20]:
試して!
- 暗号通貨におけるリード・ラグ・アービトラージへの導入 (2)
- デジタル通貨におけるリード-ラグ套路の紹介 (2)
- FMZプラットフォームの外部信号受信に関する議論: 戦略におけるHttpサービス内蔵の信号受信のための完全なソリューション
- FMZプラットフォームの外部信号受信に関する探求:戦略内蔵Httpサービス信号受信の完全な方案
- 暗号通貨におけるリード・ラグ・アービトラージへの導入 (1)
- デジタル通貨におけるリード-ラグ套路の紹介 (1)
- FMZプラットフォームの外部信号受信に関する議論:拡張API VS戦略内蔵HTTPサービス
- FMZプラットフォームの外部信号受信に関する探究:拡張API vs 戦略内蔵HTTPサービス
- ランダム・ティッカー・ジェネレーターに基づく戦略テスト方法に関する議論
- ランダム市場生成器に基づく戦略テスト方法について
- FMZ Quant の新しい機能: _Serve 機能を使用して HTTP サービスを簡単に作成する
- Python での価格動向分析による定量的な取引戦略
- Python で デジタル 通貨 の 量 的な 取引 戦略 を 実行 する
- Linux docker のインストールとアップグレードの最良の方法
- 長期・短期ポジションのバランスのとれた株式戦略を順序よく調整する
- タイムシリーズデータ分析とTickデータバックテスト
- デジタル通貨市場の定量分析
- データ駆動技術に基づくペア取引
- 機械学習技術の取引への応用
- 研究環境を利用して,三角型ヘッジの詳細と,ヘッジ可能な価格差に対する処理手数料の影響を分析する.
- デリビットの先物取引APIを改革し,オプションの定量取引に適応する
- ブロックチェーン資産の量的な取引におけるクロス通貨ヘッジ戦略
- FMexのデジタル通貨戦略ガイドを FMZ Quantで入手する
- MyLanguageの戦略を移植します (高度)
- MyLanguageの戦略を移植する
- 戦略にマルチチャートサポートを追加することを教える
- PythonのバージョンでK線合成関数を書くことを教える
- 研究環境におけるドンキアン・チャネル戦略の分析
- FMZがChatGPTに出くわしたとき,AIを使って量的な取引を学ぶのを助ける試みを記してください.
- デジタル通貨オプションの定量取引ツール
- Python バージョンのシンプルなグリッド戦略