FMZ Quant: Análise de Exemplos de Design de Requisitos Comuns no Mercado de Criptomoedas (I)
Autora:FMZ~Lydia, Criado: 2023-12-19 16:02:58, Atualizado: 2024-11-06 21:19:16
No espaço de negociação de ativos de criptomoedas, a obtenção e análise de dados de mercado, as taxas de consulta e o monitoramento dos movimentos de ativos da conta são operações críticas.
1. Como escrevo o código para obter a moeda com o maior aumento em 4 horas no Binance Spot?
Ao escrever um programa de estratégia quantitativa de negociação na plataforma FMZ, a primeira coisa que você precisa fazer quando você encontrar um requisito é analisá-lo.
- Que linguagem de programação usar? O plano é usar o Javascript para implementá-lo.
- Requer cotações em tempo real em todas as moedas
A primeira coisa que fizemos quando vimos o requisito foi procurar o documento da API da Binance para descobrir se havia alguma cotação agregada (é melhor ter cotações agregadas, é muito trabalho procurar uma por uma).
Encontrámos a interface de citações agregadas:
GET https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price- Não. Na plataforma FMZ, use oHttpQueryFunção para aceder à interface do ticker de troca (interface pública que não requer uma assinatura). - Necessidade de contar dados para um período de janela rotativa de 4 horas Conceptualizar como conceber a estrutura do programa estatístico.
- Calcular as flutuações de preços e classificá-las
Pensando no algoritmo de flutuações de preços, é:
price fluctuations (%) = (current price - initial price) / initial price * 100em% .
Depois de resolvermos o problema e definirmos o programa, começámos a trabalhar no projeto.
Projeto de código
var dictSymbolsPrice = {}
function main() {
while (true) {
// GET https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price
try {
var arr = JSON.parse(HttpQuery("https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price"))
if (!Array.isArray(arr)) {
Sleep(5000)
continue
}
var ts = new Date().getTime()
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
var symbolPriceInfo = arr[i]
var symbol = symbolPriceInfo.symbol
var price = symbolPriceInfo.price
if (typeof(dictSymbolsPrice[symbol]) == "undefined") {
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol] = {name: symbol, data: []}
}
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data.push({ts: ts, price: price})
}
} catch(e) {
Log("e.name:", e.name, "e.stack:", e.stack, "e.message:", e.message)
}
// Calculate price fluctuations
var tbl = {
type : "table",
title : "Price fluctuations",
cols : ["trading pair", "current price", "price 4 hours ago", "price fluctuations", "data length", "earliest data time", "latest data time"],
rows : []
}
for (var symbol in dictSymbolsPrice) {
var data = dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data
if (data[data.length - 1].ts - data[0].ts > 1000 * 60 * 60 * 4) {
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data.shift()
}
data = dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].percentageChange = (data[data.length - 1].price - data[0].price) / data[0].price * 100
}
var entries = Object.entries(dictSymbolsPrice)
entries.sort((a, b) => b[1].percentageChange - a[1].percentageChange)
for (var i = 0; i < entries.length; i++) {
if (i > 9) {
break
}
var name = entries[i][1].name
var data = entries[i][1].data
var percentageChange = entries[i][1].percentageChange
var currPrice = data[data.length - 1].price
var currTs = _D(data[data.length - 1].ts)
var prePrice = data[0].price
var preTs = _D(data[0].ts)
var dataLen = data.length
tbl.rows.push([name, currPrice, prePrice, percentageChange + "%", dataLen, preTs, currTs])
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`")
Sleep(5000)
}
}
Análise do código
- 1. Estrutura dos dados
- 2. Main function main()
2.1. Infinite loop
enquanto (verdadeiro) { - Não. - Não.
The program continuously monitors the Binance API trading pair prices through an infinite loop.
2.2. Get price information
var arr = JSON.parse ((HttpQuery(
Get the current price information of the trading pair via Binance API. If the return is not an array, wait for 5 seconds and retry.
2.3. Update price data
para (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { - Não. - Não.
Iterate through the array of obtained price information and update the data in dictSymbolsPrice. For each trading pair, add the current timestamp and price to the corresponding data array.
2.4. Exception processing
- Não, não.
Registo ((
Catch exceptions and log the exception information to ensure that the program can continue to execute.
2.5. Calculate the price fluctuations
para (símbolo var em dictSymbolsPrice) { - Não. - Não.
Iterate through dictSymbolsPrice, calculate the price fluctuations of each trading pair, and remove the earliest data if it is longer than 4 hours.
2.6. Sort and generate tables
Var entries = Object.entries ((dictSymbolsPrice) entries.sort (((a, b) => b[1].percentagemMudança - a[1].percentagemMudança)
para (var i = 0; i < entries.length; i++) { - Não. - Não.
Sort the trading pairs in descending order of their price fluctuations and generate a table containing information about the trading pairs.
2.7. Log output and delay
LogStatus(_D(), " + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "
Output the table and the current time in the form of a log and wait for 5 seconds to continue the next round of the loop.
The program obtains the real-time price information of the trading pair through Binance API, then calculates the price fluctuations, and outputs it to the log in the form of a table. The program is executed in a continuous loop to realize the function of real-time monitoring of the prices of trading pairs. Note that the program includes exception processing to ensure that the execution is not interrupted by exceptions when obtaining price information.
### Live Trading Running Test
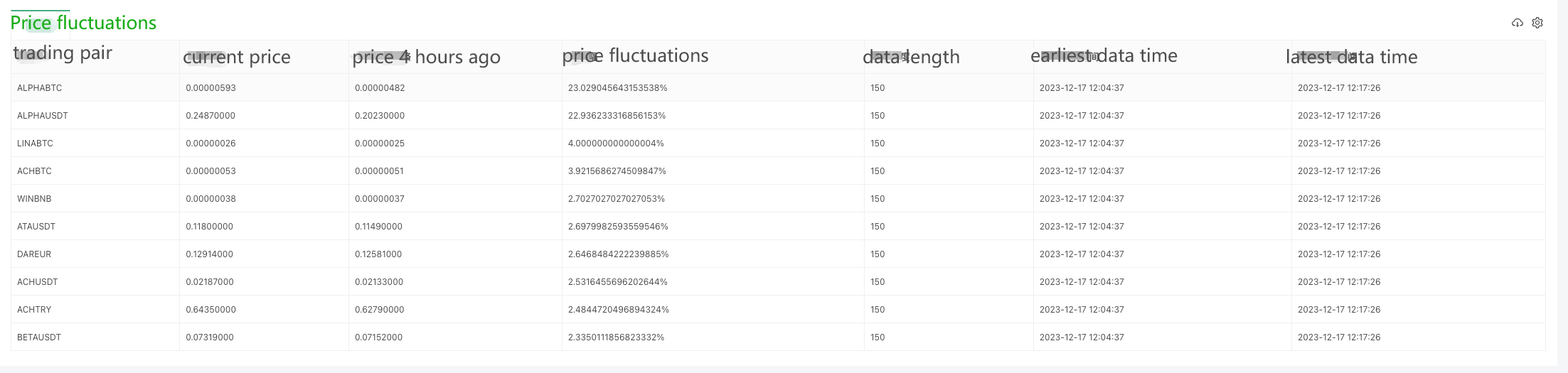
Since data can only be collected bit by bit at the beginning, it is not possible to calculate the price fluctuations on a rolling basis without collecting enough data for a 4-hour window. Therefore, the initial price is used as the base for calculation, and after collecting enough data for 4 hours, the oldest data will be eliminated in order to maintain the 4-hour window for calculating the price fluctuations.
## 2. Check the full variety of funding rates for Binance U-denominated contracts
Checking the funding rate is similar to the above code, first of all, we need to check the Binance API documentation to find the funding rate related interface. Binance has several interfaces that allow us to query the rate of funds, here we take the interface of the U-denominated contract as an example:
GEThttps://fapi.binance.com/fapi/v1/premiumIndex
### Code Implementation
Since there are so many contracts, we're exporting the top 10 largest funding rates here.
função principal (() {
enquanto (verdadeiro) {
// GEThttps://fapi.binance.com/fapi/v1/premiumIndexTente.
var arr = JSON.parse ((HttpQuery(
arr.sort((a, b) => parseFloat(b.lastFundingRate) - parseFloat(a.lastFundingRate))
var tbl = {
type: "table",
title: "Top 10 funding rates for U-denominated contracts",
cols: ["contracts", "funding rate", "marked price", "index price", "current rate time", "next rate time"],
rows: []
}
for (var i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
var obj = arr[i]
tbl.rows.push([obj.symbol, obj.lastFundingRate, obj.markPrice, obj.indexPrice, _D(obj.time), _D(obj.nextFundingTime)])
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`")
} catch(e) {
Log("e.name:", e.name, "e.stack:", e.stack, "e.message:", e.message)
}
Sleep(1000 * 10)
}
}
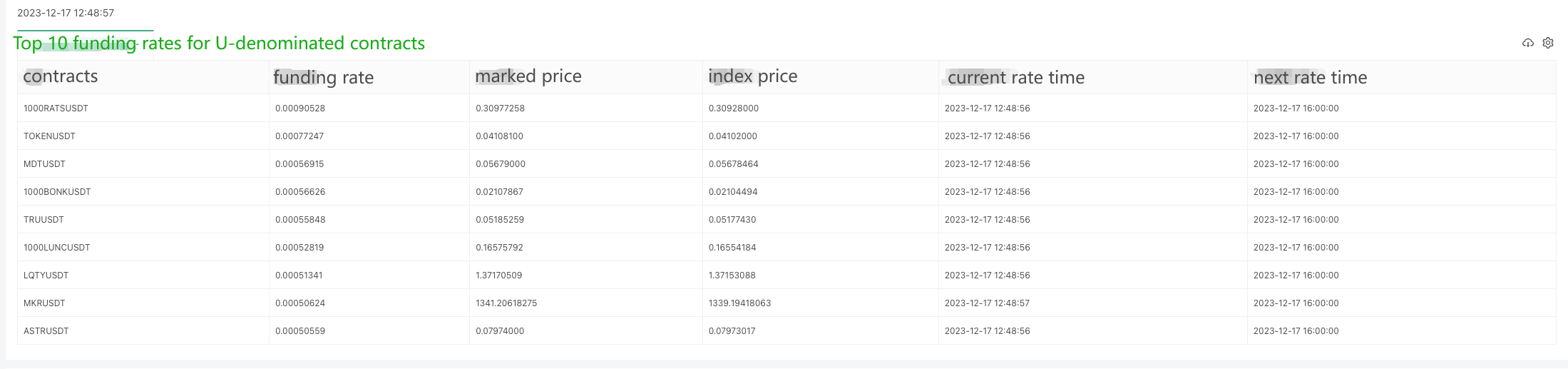
The returned data structure is as follows, and check the Binance documentation, it shows that lastFundingRate is the funding rate we want.
- O quê?
Live trading running test:
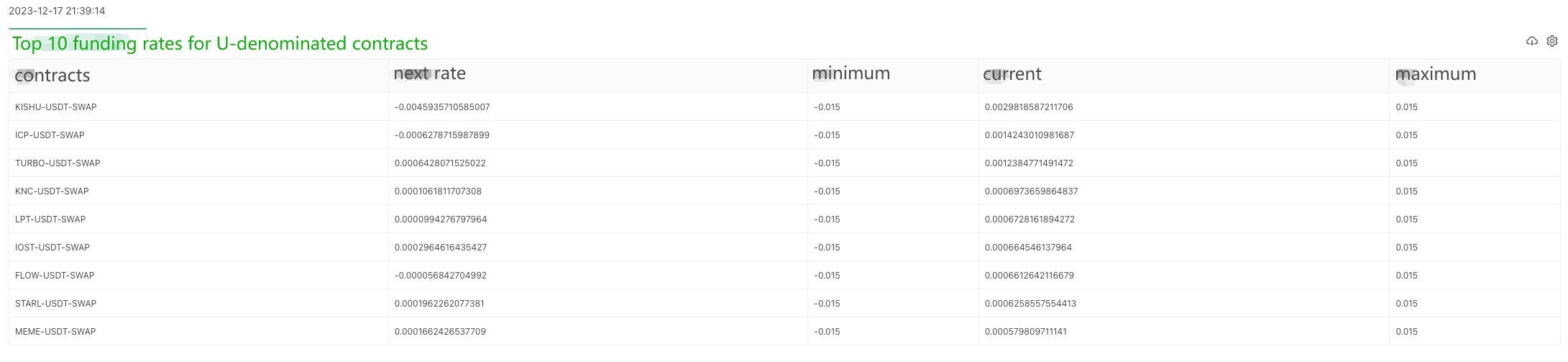
### Getting OKX exchange contract funding rates of Python version
A user has asked for a Python version of the example, and it's for the OKX exchange. Here is an example:
The data returned by the interface ```https://www.okx.com/priapi/v5/public/funding-rate-all?currencyType=1```:
- O quê?
Specific code:
Pedidos de importação importar json do tempo importado do sono a partir da data-hora da importação data-hora
def main (():
enquanto True:
#https://www.okx.com/priapi/v5/public/funding-rate-all?currencyType=1Tente:
resposta = solicitações.get(
arr.sort(key=lambda x: float(x["fundingRate"]), reverse=True)
tbl = {
"type": "table",
"title": "Top 10 funding rates for U-denominated contracts",
"cols": ["contracts", "next rate", "minimum", "current", "maximum"],
"rows": []
}
for i in range(min(9, len(arr))):
obj = arr[i]
row = [
obj["instId"],
obj["nextFundingRate"],
obj["minFundingRate"],
obj["fundingRate"],
obj["maxFundingRate"]
]
tbl["rows"].append(row)
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", '`' + json.dumps(tbl) + '`')
except Exception as e:
Log(f"Error: {str(e)}")
sleep(10)
Fim de ano
Esses exemplos fornecem ideias básicas de design e métodos de chamada, o projeto real pode precisar fazer alterações e extensões apropriadas com base nas necessidades específicas.
- Quantificar a análise fundamental no mercado de criptomoedas: deixe os dados falarem por si mesmos!
- A pesquisa quantitativa básica do círculo monetário - deixe de acreditar em todos os professores de matemática loucos, os dados são objetivos!
- Uma ferramenta essencial no domínio da negociação quantitativa - FMZ Quant Data Exploration Module
- Uma ferramenta indispensável no campo da transação quantitativa - inventor do módulo de exploração de dados quantitativos
- Dominar tudo - Introdução ao FMZ Nova versão do Terminal de Negociação (com TRB Arbitrage Source Code)
- Conheça tudo sobre a nova versão do terminal de negociação da FMZ
- FMZ Quant: Análise de Exemplos de Design de Requisitos Comuns no Mercado de Criptomoedas (II)
- Como explorar robôs de venda sem cérebro com uma estratégia de alta frequência em 80 linhas de código
- Quantificação FMZ: Análise de casos de design de necessidades comuns do mercado de criptomoedas (II)
- Como usar estratégias de 80 linhas de código de alta frequência para explorar robôs sem cérebro para venda
- Quantificação FMZ: Análise de casos de design de necessidades comuns do mercado de criptomoedas (I)
- WexApp, a FMZ Quant Cryptocurrency Demo Exchange, é recém-lançada
- Explicação detalhada da otimização do parâmetro de estratégia da rede de contratos perpétuos
- Ensine-o a usar a FMZ Extended API para Batch Modify Parameters do Bot
- Aprenda a modificar os parâmetros do disco físico em massa usando a FMZ Extension API
- Parâmetros de otimização da estratégia de rede de contratos permanentes
- Instruções para instalar o Interactive Brokers IB Gateway no Linux Bash
- Introdução ao IB GATEWAY para instalação de títulos de penetração no Linux bash
- O que é mais adequado para a pesca de fundo, baixo valor de mercado ou baixo preço?
- O que é mais adequado para transcrição: baixo valor de mercado ou baixo preço?