Função integrada_Análise cruzada e instruções
Autora:Ninabadass, Criado: 2022-03-23 08:56:29, Atualizado: 2022-03-24 16:54:30Função integrada_Análise cruzada e instruções
A função _Cross na coluna de funções globais da documentação API é utilizada para calcular o estado cruzado das duas linhas de indicadores
-
Códigos como os seguintes são implementados pela função:
Deve notar-se que, quando
arr1é definido como uma matriz de indicadores de linha rápida, earr2é definido como uma matriz de indicadores de linha lenta, o valor devolvido pelo_Crossfunção é um número positivo, ou seja, de acordo com o contexto da documentaçãoa positive number is the upswing period, a negative number indicates the downswing period, and 0 means it is the same as the current price- Não. Pode-se ver que neste momento,arr1Ele cruzouarr2durante n ciclos, ou seja, a linha rápida cruzou a linha lenta, indicando cruz de ouro. Da mesma forma, se o_CrossFunção retorna um número negativo, significa cruz de morte.Se ` `arr1
is defined as an array of slow line indicators, andarr2as an array of fast line indicators, the situation will be opposite. If the value returned by the_Cruzadafunction is a positive number, it means death cross. If the value returned by theA função cruz é um número negativo, significa cruz de ouro.
// Return the number of upswing periods; a positive number represents the number of upswing periods, and a negative number represents the number of downswing periods, and 0 means it is the same as the current price
$.Cross = function(arr1, arr2) { // The number of parameters is 2. As you can see from the parameter names, these two parameters should be of array type.
// The array is like a line segment in the coordinate system where the X axis is the array index value and the Y axis is the index value. The function is to determine the intersection of two lines
if (arr1.length !== arr2.length) { // First, judge whether the lengths of the two compared arrays are equal
throw "array length not equal"; // If they are not equal, raise an error, for the unequal indicator lines cannot judge if crossed or not
}
var n = 0; // Declare the variable n to record the cross-status; its initial value is 0, indicating not crossed
for (var i = arr1.length-1; i >= 0; i--) { // Traverse arr1,from the last element to the front
if (typeof(arr1[i]) !== 'number' || typeof(arr2[i]) !== 'number') { // when arr1 or arr2 is non-numeric type (namely invalid indicators), break the traversing loop
break; // break the loop
}
if (arr1[i] < arr2[i]) { // If arr1 < arr2, the n-- will record the comparative status of arr1 and arr2 from the beginning (that is, at the beginning, n will adjust automatically according to the comparative value of arr1[i] and arr2[i]; once the comparison relation between arr1[i] and arr2[i] opposite to n happens, it means the two lines crossed).
if (n > 0) {
break;
}
n--;
} else if (arr1[i] > arr2[i]) { // If arr1 > arr2, then n++
if (n < 0) {
break;
}
n++;
} else { // arr1[i] == arr2[i], then break immediately
break;
}
}
return n; // Return n, indicating the number of periods with cross, 0 means equal indicator values
};
-
Simulamos uma matriz de dados e passamos para ver os resultados
var arr1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,8,8,9] // Fast line indicator
var arr2 = [2,3,4,5,6,7,7,7,7] // Slow line indicator
function main(){
Log("_Cross(arr1, arr2) : ", _Cross(arr1, arr2))
Log("_Cross(arr2, arr1) : ", _Cross(arr2, arr1))
}
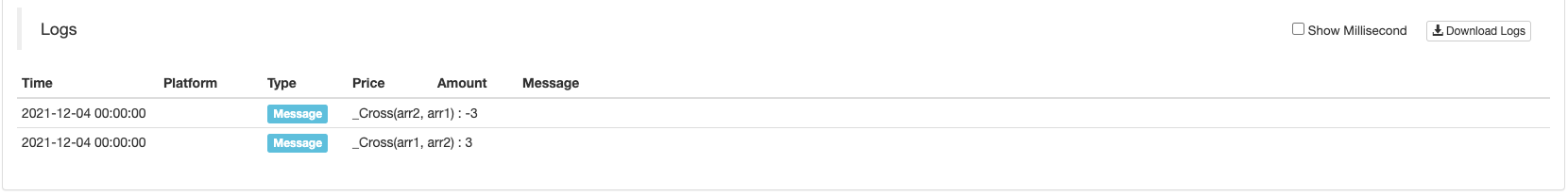
Você pode ver os resultados são 3 e -3.
A localização do cruzamento é em frente a três barras de linha K.
- Interface de mercado de chamadas
- Como escrever o botão de posicionamento manual em MY?
- Pedimos ajuda, o Bitmex fez um erro no pedido
- Descrição do mecanismo de ensaio posterior de nível de simulação quântica FMZ
- Descrição do mecanismo de ensaio de retrocesso FMZ
- Etapas de instalação e atualização do Linux Docker
- Iniciação rápida para Python
- Iniciação Rápida para JavaScript
- Futures_Kraken link
- Futures_Bybit Link
- Como especificar diferentes versões de dados para a estratégia alugada por seus metadados de código de aluguel
- Qual é o quadro técnico usado para a estratégia de alta frequência?
- Binance obtém o comprimento de linha k, não pode ultrapassar 1000 interfaces com a plataforma
- Tutorial avançado para a plataforma FMZ Quant
- Erro: Futures_OP 3: 400: {"code":"50004","data":[],"msg":"Endpoint request timeout "}
- Ema, como esses indicadores podem calcular dados autodeterminados como parâmetros?
- Relatar um suspeito de bug que pode causar emoji no código da política e impedir a conservação
- A plataforma pode apoiar as próximas grandes exchanges do mercado?
- A estratégia do tubarão foi visualizada no ano passado.
- A velocidade de retestamento é lenta.