Python versão estratégia da comissão iceberg
Autora:Bem-estar, Criado: 2020-07-21 10:21:10, Atualizado: 2023-10-26 20:08:29
Este artigo traz duas estratégias clássicas para o transplante: Iceberg comissão (comprar/vender).https://www.fmz.com/square/s:Iceberg/1
Citando a versão JavaScript da Iceberg comissão estratégia de negociação introdução:
A comissão Iceberg refere-se ao fato de que, quando os investidores realizam transações de grande valor, a fim de evitar um impacto excessivo no mercado, a comissão de grande ordem é automaticamente dividida em várias comissões, com base no último preço atual de compra / venda 1 e no preço definido pelo comerciante. A estratégia automaticamente comissão de uma pequena ordem. Quando a última comissão é completamente transacionada ou o último preço se desvia significativamente do preço atual de comissão, a operação de comissão é reiniciada automaticamente.
Muitas páginas de negociação de câmbio vêm com ferramentas de comissionamento de iceberg, que têm funções ricas, mas se você quiser personalizar algumas funções ou modificar algumas funções de acordo com suas próprias necessidades, você precisa de uma ferramenta mais flexível. A plataforma FMZ foi projetada para resolver esse problema corretamente. Nossa estratégia quadrada não tem muitas estratégias de negociação Python. Alguns comerciantes que querem usar a linguagem Python para escrever ferramentas e estratégias de negociação precisam se referir a exemplos. Portanto, a estratégia clássica de comissionamento de iceberg foi portada para a versão Python.
Comissão Iceberg para Python - Compra
import random # Import random number library
def CancelPendingOrders(): # The function of CancelPendingOrders is to cancel all pending orders of the current transaction.
while True: # Loop detection, call GetOrders function to detect the current pending order, if orders is an empty array, that is, len(orders) is equal to 0, indicating that all orders have been cancelled, you can exit the function and call return to exit.
orders = _C(exchange.GetOrders)
if len(orders) == 0 :
return
for j in range(len(orders)): # Traverse the current array of pending orders, and call CancelOrder to cancel the orders one by one.
exchange.CancelOrder(orders[j]["Id"])
if j < len(orders) - 1: # Except for the last order, execute Sleep every time and let the program wait for a while to avoid canceling orders too frequently.
Sleep(Interval)
LastBuyPrice = 0 # Set a global variable to record the the latest buying price.
InitAccount = None # Set a global variable to record the initial account asset information.
def dispatch(): # Main functions of iceberg commission logic
global InitAccount, LastBuyPrice # Reference global variables
account = None # Declare a variable to record the account information obtained in real time for comparison calculation.
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker) # Declare a variable to record the latest market quotes.
LogStatus(_D(), "ticker:", ticker) # Output time and latest quotation in the status bar
if LastBuyPrice > 0: # When LastBuyPrice is greater than 0, that is, when the commission has started, the code in the if condition is executed.
if len(_C(exchange.GetOrders)) > 0: # Call the exchange.GetOrders function to get all current pending orders, determine that there are pending orders, and execute the code in the if condition.
if ticker["Last"] > LastBuyPrice and ((ticker["Last"] - LastBuyPrice) / LastBuyPrice) > (2 * (EntrustDepth / 100)): # Detect the degree of deviation, if the condition is triggered, execute the code in the if, and cancel the order.
Log("Too much deviation, the latest transaction price:", ticker["Last"], "Commission price", LastBuyPrice)
CancelPendingOrders()
else :
return True
else : # If there is no pending order, it proves that the order is completely filled.
account = _C(exchange.GetAccount) # Get current account asset information.
Log("The buying order is completed, the cumulative cost:", _N(InitAccount["Balance"] - account["Balance"]), "Average buying price:", _N((InitAccount["Balance"] - account["Balance"]) / (account["Stocks"] - InitAccount["Stocks"]))) # Print transaction information.
LastBuyPrice = 0 # Reset LastBuyPrice to 0
BuyPrice = _N(ticker["Buy"] * (1 - EntrustDepth / 100)) # Calculate the price of pending orders based on current market conditions and parameters.
if BuyPrice > MaxBuyPrice: # Determine whether the maximum price set by the parameter is exceeded
return True
if not account: # If account is null, execute the code in the if statement to retrieve the current asset information and copy it to account
account = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
if (InitAccount["Balance"] - account["Balance"]) >= TotalBuyNet: # Determine whether the total amount of money spent on buying exceeds the parameter setting.
return False
RandomAvgBuyOnce = (AvgBuyOnce * ((100.0 - FloatPoint) / 100.0)) + (((FloatPoint * 2) / 100.0) * AvgBuyOnce * random.random()) # random number 0~1
UsedMoney = min(account["Balance"], RandomAvgBuyOnce, TotalBuyNet - (InitAccount["Balance"] - account["Balance"]))
BuyAmount = _N(UsedMoney / BuyPrice) # Calculate the buying quantity
if BuyAmount < MinStock: # Determine whether the buying quantity is less than the minimum buying quantity limit on the parameter.
return False
LastBuyPrice = BuyPrice # Record the price of this order and assign it to LastBuyPrice
exchange.Buy(BuyPrice, BuyAmount, "spend:¥", _N(UsedMoney), "Last transaction price", ticker["Last"]) # Place orders
return True
def main():
global LoopInterval, InitAccount # Refer to LoopInterval, InitAccount global variables
CancelPendingOrders() # Cancel all pending orders when starting to run
InitAccount = _C(exchange.GetAccount) # Account assets at the beginning of the initial record
Log(InitAccount) # Print initial account information
if InitAccount["Balance"] < TotalBuyNet: # If the initial assets are insufficient, an error will be thrown and the program will stop
raise Exception("Insufficient account balance")
LoopInterval = max(LoopInterval, 1) # Set LoopInterval to at least 1
while dispatch(): # The main loop, the iceberg commission logic function dispatch is called continuously, and the loop stops when the dispatch function returns false.
Sleep(LoopInterval * 1000) # Pause each cycle to control the polling frequency.
Log("委托全部完成", _C(exchange.GetAccount)) # When the loop execution jumps out, the current account asset information is printed.
Comissão Iceberg para Python - Venda
A lógica estratégica é a mesma que a da compra, com apenas uma ligeira diferença.
import random
def CancelPendingOrders():
while True:
orders = _C(exchange.GetOrders)
if len(orders) == 0:
return
for j in range(len(orders)):
exchange.CancelOrder(orders[j]["Id"])
if j < len(orders) - 1:
Sleep(Interval)
LastSellPrice = 0
InitAccount = None
def dispatch():
global LastSellPrice, InitAccount
account = None
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
LogStatus(_D(), "ticker:", ticker)
if LastSellPrice > 0:
if len(_C(exchange.GetOrders)) > 0:
if ticker["Last"] < LastSellPrice and ((LastSellPrice - ticker["Last"]) / ticker["Last"]) > (2 * (EntrustDepth / 100)):
Log("Too much deviation, the latest transaction price:", ticker["Last"], "Commission price", LastSellPrice)
CancelPendingOrders()
else :
return True
else :
account = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
Log("The buy order is completed, and the accumulated selling:", _N(InitAccount["Stocks"] - account["Stocks"]), "Average selling price:", _N((account["Balance"] - InitAccount["Balance"]) / (InitAccount["Stocks"] - account["Stocks"])))
LastSellPrice = 0
SellPrice = _N(ticker["Sell"] * (1 + EntrustDepth / 100))
if SellPrice < MinSellPrice:
return True
if not account:
account = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
if (InitAccount["Stocks"] - account["Stocks"]) >= TotalSellStocks:
return False
RandomAvgSellOnce = (AvgSellOnce * ((100.0 - FloatPoint) / 100.0)) + (((FloatPoint * 2) / 100.0) * AvgSellOnce * random.random())
SellAmount = min(TotalSellStocks - (InitAccount["Stocks"] - account["Stocks"]), RandomAvgSellOnce)
if SellAmount < MinStock:
return False
LastSellPrice = SellPrice
exchange.Sell(SellPrice, SellAmount, "Last transaction price", ticker["Last"])
return True
def main():
global InitAccount, LoopInterval
CancelPendingOrders()
InitAccount = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
Log(InitAccount)
if InitAccount["Stocks"] < TotalSellStocks:
raise Exception("Insufficient account currency")
LoopInterval = max(LoopInterval, 1)
while dispatch():
Sleep(LoopInterval)
Log("All commissioned", _C(exchange.GetAccount))
Operação estratégica
Use o WexApp para simular o teste de troca:
Compra:
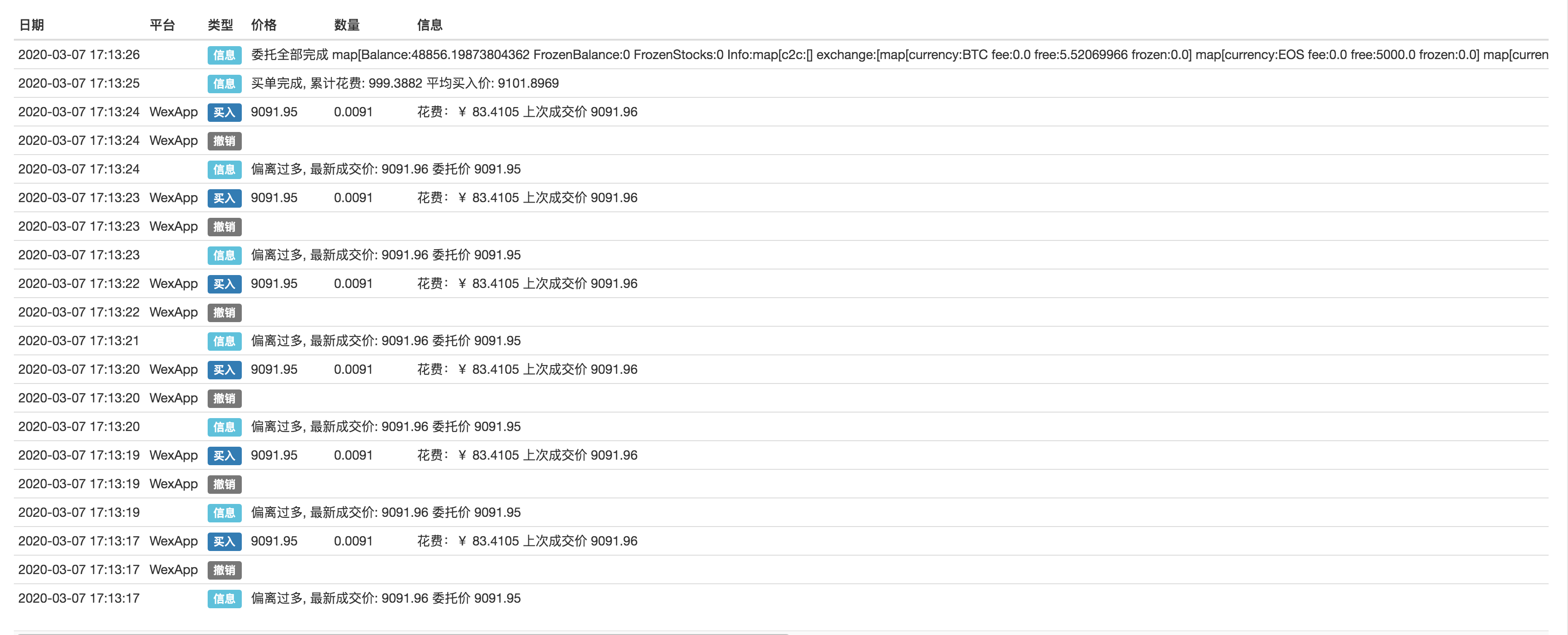
Venda:

A lógica da estratégia não é complicada. Quando a estratégia é executada, ela irá dinamicamente colocar e cancelar ordens com base nos parâmetros da estratégia e no preço atual do mercado. Quando o valor da transação / número de moeda atinge ou se aproxima do número de configuração do parâmetro, a estratégia para. O código da estratégia é muito simples e adequado para iniciantes. Os leitores interessados podem modificá-lo e projetar uma estratégia que se adapte ao seu estilo de negociação.
- Novo recurso do FMZ Quant: Use a função _Serve para criar serviços HTTP facilmente
- Inventores quantificam novas funcionalidades: criar serviços HTTP facilmente com a função _Serve
- FMZ Quant Trading Platform Guia de acesso ao protocolo personalizado
- Estratégia de aquisição e acompanhamento da taxa de financiamento da FMZ
- Estratégias de captação e monitoramento de taxas de financiamento da FMZ
- Um modelo de estratégia permite que você use o WebSocket Market sem problemas
- Um modelo de estratégia para usar o WebSocket sem problemas
- Guia de acesso ao Protocolo Geral para Inventores de Plataformas de Negociação Quantificadas
- Como construir uma estratégia de negociação multi-moeda universal rapidamente após a atualização da FMZ
- Como construir rapidamente uma estratégia de negociação multicurrency geral após a atualização do FMZ
- Negociação de DCA: Uma estratégia quantitativa amplamente utilizada