Negociação quantitativa de criptomoedas para iniciantes - aproximando-o da negociação quantitativa de criptomoedas (6)
Autora:FMZ~Lydia, Criado: 2022-08-05 17:13:26, Atualizado: 2024-12-04 21:36:07
No último artigo, fizemos uma estratégia de grade simples juntos. Neste artigo, atualizamos e expandimos essa estratégia em uma estratégia de grade de pontos de várias espécies, e deixamos essa estratégia ser testada na prática. O objetivo não é encontrar um "santo graal", mas discutir vários problemas e soluções ao projetar estratégias. Este artigo explicará algumas de minhas experiências na concepção dessa estratégia. O conteúdo deste artigo é um pouco complicado e requer uma certa base em programação.
Pensamento de conceção baseado em necessidades estratégicas
Este artigo, tal como o anterior, continua a discutir o projecto baseado no FMZ Quant (FMZ.COM).
-
Espécies múltiplas Para ser franco, penso que esta estratégia de rede não só pode
BTC_USDT, mas tambémLTC_USDT/EOS_USDT/DOGE_USDT/ETC_USDT/ETH_USDTDe qualquer forma, os pares de negociação spot e as variedades que querem correr são todos negociados na grade ao mesmo tempo.É bom capturar o mercado volátil de várias espécies. O requisito parece muito simples, e o problema surge quando se desenha.
-
- Em primeiro lugar, as cotações de mercado de várias variedades são obtidas. Este é o primeiro problema a ser resolvido. Após consultar a documentação API da bolsa, descobri que a maioria das bolsas fornece interfaces de mercado agregadas. OK, use a interface de mercado agregada para obter dados.
-
- O segundo problema encontrado são os ativos da conta. Como é uma estratégia de várias espécies, é necessário considerar a gestão de cada par de ativos de negociação separadamente. E precisamos obter dados para todos os ativos de uma só vez e registrá-los. Por que precisamos obter os dados dos ativos da conta? Por que precisamos separar os registros de cada par? Porque é preciso avaliar os activos disponíveis quando se faz uma encomenda. E você precisa calcular os lucros, é também necessário registrar um dado de ativos conta inicial primeiro, em seguida, obter os dados de ativos conta corrente e compará-lo com o inicial para calcular o lucro e perda? Felizmente, a interface de conta de ativos da bolsa normalmente retorna todos os dados de ativos de moeda, só precisamos obtê-lo uma vez, e depois processar os dados.
-
- Design de parâmetros de estratégia. O design de parâmetros de múltiplas espécies é bastante diferente do design de parâmetros de uma única variedade, embora a lógica de negociação de cada variedade de múltiplas variedades seja a mesma, é possível que os parâmetros durante a negociação sejam diferentes. Por exemplo, na estratégia de grade, você pode querer negociar 0,01 BTC cada vez que fizer o par de negociação BTC_USDT, mas é obviamente inapropriado usar esse parâmetro (negociar 0,01 moedas) quando fizer DOGE_USDT. Claro, você também pode lidar com o montante USDT. Mas ainda haverá problemas. E se você quiser negociar 1000U para BTC_USDT e 10U para DOGE_USDT? A demanda nunca pode ser satisfeita.
Pode haver alguém que vai pensar sobre este problema e, em seguida, perguntar:
Eu posso definir vários conjuntos de parâmetros para controlar os parâmetros de diferentes pares de negociação a ser feito separadamente. Isso ainda não é flexível o suficiente para atender às necessidades, quantos conjuntos de parâmetros são bons para definir? Três conjuntos de parâmetros são definidos, e se eu quiser fazer 4 variedades? Tenho que modificar a estratégia e aumentar os parâmetros?.. Portanto, ao projetar os parâmetros da estratégia multiespécie, é necessário considerar plenamente as necessidades de tais parâmetros diferenciados. Por exemplo:
ETHUSDT:100:0.002|LTCUSDT:20:0.1Entre eles,
gaman divide os dados de cada espécie, o que significa que ETHUSDT:100:0.002controla o par de negociação ETH_USDT, eLTCUSDT:20:0.1O par de negociação LTC_USDT é controlado pelo par de negociação LTC_USDT. O par de negociação LTC_USDT é controlado pelo par de negociação LTC_USDT.ETHUSDT:100:0.002, onde ETHUSDT indica qual o par de negociação que você deseja fazer, 100 é o espaçamento da grade, 0,002 é o número de moedas ETH negociadas em cada grade, e o: é para dividir esses dados (é claro, essas regras de parâmetros são feitas pelo designer de estratégia, você pode projetar qualquer coisa de acordo com suas necessidades). Essas cadeias contêm as informações de parâmetros de cada espécie que você deseja fazer. Analise essas cadeias na estratégia e atribua valores às variáveis da estratégia para controlar a lógica de negociação de cada espécie. Como analisá-lo? Ainda use o exemplo acima. function main() { var net = [] // The recorded grid parameters, use the data when running to the grid trading logic var params = "ETHUSDT:100:0.002|LTCUSDT:20:0.1" var arrPair = params.split("|") _.each(arrPair, function(pair) { var arr = pair.split(":") var symbol = arr[0] // Trading pair name var diff = parseFloat(arr[1]) // Grid spacing var amount = parseFloat(arr[2]) // Grid order volume net.push({symbol : symbol, diff : diff, amount : amount}) }) Log("Grid parameter data:", net) }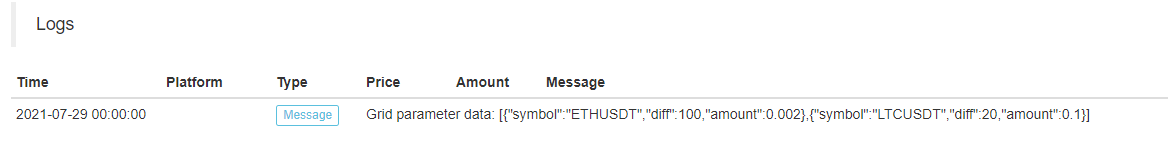
Olhando para isso, os parâmetros são analisados.
function main() { var params = '[{"symbol":"ETHUSDT","diff":100,"amount":0.002},{"symbol":"LTCUSDT","diff":20,"amount":0.1}]' var net = JSON.parse(params) // The recorded grid parameters, use the data when running to the grid trading logic _.each(net, function(pair) { Log("Trading pairs:", pair.symbol, pair) }) }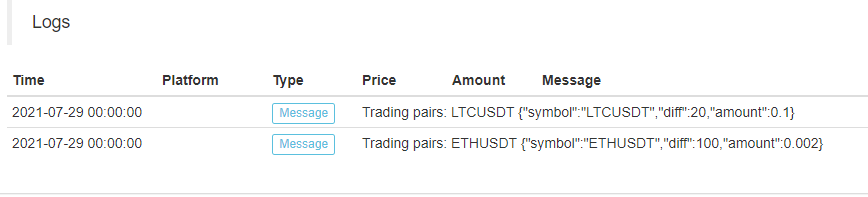
- Design de parâmetros de estratégia. O design de parâmetros de múltiplas espécies é bastante diferente do design de parâmetros de uma única variedade, embora a lógica de negociação de cada variedade de múltiplas variedades seja a mesma, é possível que os parâmetros durante a negociação sejam diferentes. Por exemplo, na estratégia de grade, você pode querer negociar 0,01 BTC cada vez que fizer o par de negociação BTC_USDT, mas é obviamente inapropriado usar esse parâmetro (negociar 0,01 moedas) quando fizer DOGE_USDT. Claro, você também pode lidar com o montante USDT. Mas ainda haverá problemas. E se você quiser negociar 1000U para BTC_USDT e 10U para DOGE_USDT? A demanda nunca pode ser satisfeita.
Pode haver alguém que vai pensar sobre este problema e, em seguida, perguntar:
-
- Durabilidade dos dados
Há também uma grande diferença entre as estratégias que podem ser aplicadas na prática e as estratégias tutoriais. As estratégias tutoriais no artigo anterior são apenas um teste preliminar de lógica e design de estratégia, e há mais questões a serem consideradas quando se trata do mundo real. No bot real, é possível iniciar e parar a negociação real. Neste momento, todos os dados durante a operação do bot real serão perdidos. Então, como fazer o bot real reiniciar para continuar funcionando no status anterior depois de parar?
Aqui, é necessário salvar os dados-chave persistentemente quando o bot real está sendo executado, para que os dados possam ser lidos e continuarem a ser executados quando reiniciados.
Pode usar o
_G()função na plataforma de negociação quantitativa FMZ, ou utilizar a função de operação da base de dadosDBExec(), e você pode verificar a documentação FMZ API para detalhes.
Por exemplo, nós projetar uma função de varredura de cauda e usar o
_G()Função de armazenamento de dados de rede.var net = null function main() { // Strategy main functions // Read the stored net first net = _G("net") // ... } function onExit() { _G("net", net) Log("Perform tail-sweeping processing and save data", "#FF0000") } function onexit() { // The exit sweep function defined by the platform system, triggered the execution when the real bot is clicked to stop onExit() } function onerror() { // The abnormal exit function defined by the platform system, triggered the execution when the program is abnormal onExit() } - Durabilidade dos dados
Há também uma grande diferença entre as estratégias que podem ser aplicadas na prática e as estratégias tutoriais. As estratégias tutoriais no artigo anterior são apenas um teste preliminar de lógica e design de estratégia, e há mais questões a serem consideradas quando se trata do mundo real. No bot real, é possível iniciar e parar a negociação real. Neste momento, todos os dados durante a operação do bot real serão perdidos. Então, como fazer o bot real reiniciar para continuar funcionando no status anterior depois de parar?
Aqui, é necessário salvar os dados-chave persistentemente quando o bot real está sendo executado, para que os dados possam ser lidos e continuarem a ser executados quando reiniciados.
Pode usar o
-
- Limites tais como precisão da quantidade de encomenda, precisão do preço da encomenda, quantidade mínima de encomenda e montante mínimo de encomenda, etc.
O sistema de backtesting não impõe restrições tão rígidas sobre o valor do pedido e a precisão do pedido, mas cada exchange pode ter padrões rigorosos para o preço e o valor do pedido ao colocar um pedido no bot real, e essas restrições não são as mesmas em diferentes exchanges.
Para casos de várias espécies, este requisito é mais complicado. Para uma estratégia de uma única espécie, você pode projetar um parâmetro para especificar informações como precisão, mas ao projetar uma estratégia de várias espécies, é óbvio que escrever essa informação nos parâmetros fará com que os parâmetros fiquem muito inchados.
Neste momento, você precisa verificar a documentação da API da bolsa para ver se há informações de interface relacionadas a pares de negociação na documentação da bolsa. Se houver, você pode projetar uma interface de acesso automático na estratégia para obter informações como precisão e configurá-la nas informações de pares de negociação envolvidas na negociação (em suma, a precisão ou algo é obtida da bolsa automaticamente e, em seguida, adaptada às variáveis relacionadas aos parâmetros da estratégia).
-
- Adaptação a diferentes bolsas Por que colocar esta pergunta no final? Porque as soluções para estes problemas que falamos acima vai trazer o último problema, porque nossa estratégia planeja usar a interface de mercado agregada, acesso à precisão do par de negociação de câmbio e outros dados adaptativos, acesso a informações da conta para lidar com cada par de negociação separadamente, estas soluções podem variar muito de câmbio para câmbio. Existem diferenças nas chamadas de interface e mecanismos. Para as exchanges spot, a diferença é menor se a estratégia de grade for estendida para a versão de futuros. As diferenças no mecanismo de várias trocas são ainda maiores. Uma solução é projetar uma biblioteca de classes de modelos FMZ. Escreva o projeto na biblioteca de classes para implementar essas diferenças. Reduzir o acoplamento entre a própria estratégia e a troca. A desvantagem disso é que você precisa escrever uma biblioteca de classes de modelo e implementá-la especificamente para cada diferença de troca neste modelo.
-
Projetar uma biblioteca de classes de modelo
Com base na análise acima, uma biblioteca de classes modelo foi concebida para reduzir a ligação entre a estratégia e o mecanismo e interface de troca.
Podemos projetar esta biblioteca de classes modelo assim (parte do código é omitido):
function createBaseEx(e, funcConfigure) {
var self = {}
self.e = e
self.funcConfigure = funcConfigure
self.name = e.GetName()
self.type = self.name.includes("Futures_") ? "Futures" : "Spot"
self.label = e.GetLabel()
// Interfaces to be implemented
self.interfaceGetTickers = null // Create a function to asynchronously obtain a thread of aggregated market data
self.interfaceGetAcc = null // Create a function that asynchronously obtains account data thread
self.interfaceGetPos = null // Get a position
self.interfaceTrade = null // Create concurrent orders
self.waitTickers = null // Waiting for concurrent market data
self.waitAcc = null // Waiting for account concurrent data
self.waitTrade = null // Waiting for order concurrent data
self.calcAmount = null // Calculate the order volume based on data such as trading pair accuracy
self.init = null // Initialization work, obtaining data such as accuracy
// Execute the configuration function to configure the object
funcConfigure(self)
// Check whether the interfaces agreed by configList are implemented
_.each(configList, function(funcName) {
if (!self[funcName]) {
throw "interface" + funcName + "unimplemented"
}
})
return self
}
$.createBaseEx = createBaseEx
$.getConfigureFunc = function(exName) {
dicRegister = {
"Futures_OKCoin" : funcConfigure_Futures_OKCoin, // Implementation of OK futures
"Huobi" : funcConfigure_Huobi,
"Futures_Binance" : funcConfigure_Futures_Binance,
"Binance" : funcConfigure_Binance,
"WexApp" : funcConfigure_WexApp, // Implementation of wexApp
}
return dicRegister
}
No modelo, ele é escrito para trocas específicas, tome o bot simulado do FMZ
function funcConfigure_WexApp(self) {
var formatSymbol = function(originalSymbol) {
// BTC_USDT
var arr = originalSymbol.split("_")
var baseCurrency = arr[0]
var quoteCurrency = arr[1]
return [originalSymbol, baseCurrency, quoteCurrency]
}
self.interfaceGetTickers = function interfaceGetTickers() {
self.routineGetTicker = HttpQuery_Go("https://api.wex.app/api/v1/public/tickers")
}
self.waitTickers = function waitTickers() {
var ret = []
var arr = JSON.parse(self.routineGetTicker.wait()).data
_.each(arr, function(ele) {
ret.push({
bid1: parseFloat(ele.buy),
bid1Vol: parseFloat(-1),
ask1: parseFloat(ele.sell),
ask1Vol: parseFloat(-1),
symbol: formatSymbol(ele.market)[0],
type: "Spot",
originalSymbol: ele.market
})
})
return ret
}
self.interfaceGetAcc = function interfaceGetAcc(symbol, updateTS) {
if (self.updateAccsTS != updateTS) {
self.routineGetAcc = self.e.Go("GetAccount")
}
}
self.waitAcc = function waitAcc(symbol, updateTS) {
var arr = formatSymbol(symbol)
var ret = null
if (self.updateAccsTS != updateTS) {
ret = self.routineGetAcc.wait().Info
self.bufferGetAccRet = ret
} else {
ret = self.bufferGetAccRet
}
if (!ret) {
return null
}
var acc = {symbol: symbol, Stocks: 0, FrozenStocks: 0, Balance: 0, FrozenBalance: 0, originalInfo: ret}
_.each(ret.exchange, function(ele) {
if (ele.currency == arr[1]) {
// baseCurrency
acc.Stocks = parseFloat(ele.free)
acc.FrozenStocks = parseFloat(ele.frozen)
} else if (ele.currency == arr[2]) {
// quoteCurrency
acc.Balance = parseFloat(ele.free)
acc.FrozenBalance = parseFloat(ele.frozen)
}
})
return acc
}
self.interfaceGetPos = function interfaceGetPos(symbol, price, initSpAcc, nowSpAcc) {
var symbolInfo = self.getSymbolInfo(symbol)
var sumInitStocks = initSpAcc.Stocks + initSpAcc.FrozenStocks
var sumNowStocks = nowSpAcc.Stocks + nowSpAcc.FrozenStocks
var diffStocks = _N(sumNowStocks - sumInitStocks, symbolInfo.amountPrecision)
if (Math.abs(diffStocks) < symbolInfo.min / price) {
return []
}
return [{symbol: symbol, amount: diffStocks, price: null, originalInfo: {}}]
}
self.interfaceTrade = function interfaceTrade(symbol, type, price, amount) {
var tradeType = ""
if (type == self.OPEN_LONG || type == self.COVER_SHORT) {
tradeType = "bid"
} else {
tradeType = "ask"
}
var params = {
"market": symbol,
"side": tradeType,
"amount": String(amount),
"price" : String(-1),
"type" : "market"
}
self.routineTrade = self.e.Go("IO", "api", "POST", "/api/v1/private/order", self.encodeParams(params))
}
self.waitTrade = function waitTrade() {
return self.routineTrade.wait()
}
self.calcAmount = function calcAmount(symbol, type, price, amount) {
// Obtain trading pair information
var symbolInfo = self.getSymbolInfo(symbol)
if (!symbol) {
throw symbol + ", the trading pair information cannot be checked"
}
var tradeAmount = null
var equalAmount = null // Number of coins recorded
if (type == self.OPEN_LONG || type == self.COVER_SHORT) {
tradeAmount = _N(amount * price, parseFloat(symbolInfo.pricePrecision))
// Check the minimum trading volume
if (tradeAmount < symbolInfo.min) {
Log(self.name, " tradeAmount:", tradeAmount, "less than", symbolInfo.min)
return false
}
equalAmount = tradeAmount / price
} else {
tradeAmount = _N(amount, parseFloat(symbolInfo.amountPrecision))
// Check the minimum trading volume
if (tradeAmount < symbolInfo.min / price) {
Log(self.name, " tradeAmount:", tradeAmount, "less than", symbolInfo.min / price)
return false
}
equalAmount = tradeAmount
}
return [tradeAmount, equalAmount]
}
self.init = function init() { // Functions that deal with conditions such as accuracy automatically
var ret = JSON.parse(HttpQuery("https://api.wex.app/api/v1/public/markets"))
_.each(ret.data, function(symbolInfo) {
self.symbolsInfo.push({
symbol: symbolInfo.pair,
amountPrecision: parseFloat(symbolInfo.basePrecision),
pricePrecision: parseFloat(symbolInfo.quotePrecision),
multiplier: 1,
min: parseFloat(symbolInfo.minQty),
originalInfo: symbolInfo
})
})
}
}
Então usar este modelo em uma estratégia é simples:
function main() {
var fuExName = exchange.GetName()
var fuConfigureFunc = $.getConfigureFunc()[fuExName]
var ex = $.createBaseEx(exchange, fuConfigureFunc)
var arrTestSymbol = ["LTC_USDT", "ETH_USDT", "EOS_USDT"]
var ts = new Date().getTime()
// Test to get tickers
ex.goGetTickers()
var tickers = ex.getTickers()
Log("tickers:", tickers)
// Test to obtain account information
ex.goGetAcc(symbol, ts)
_.each(arrTestSymbol, function(symbol) {
_.each(tickers, function(ticker) {
if (symbol == ticker.originalSymbol) {
// print ticker data
Log(symbol, ticker)
}
})
// print asset data
var acc = ex.getAcc(symbol, ts)
Log("acc:", acc.symbol, acc)
})
}
Estratégia real bot
É muito simples projetar e escrever uma estratégia baseada no modelo acima.
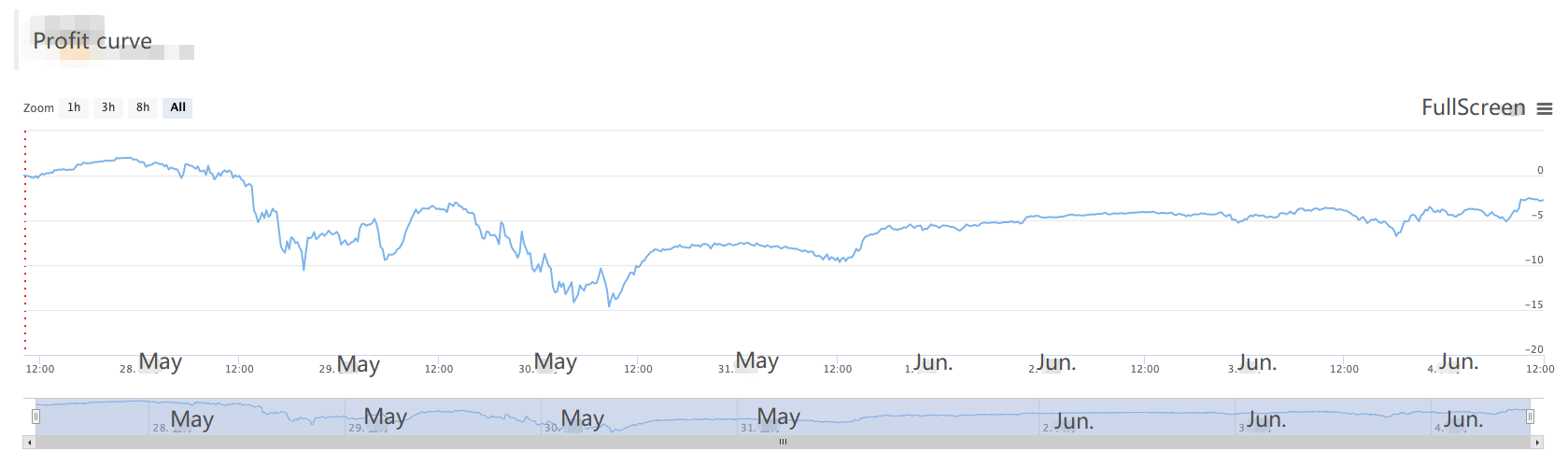
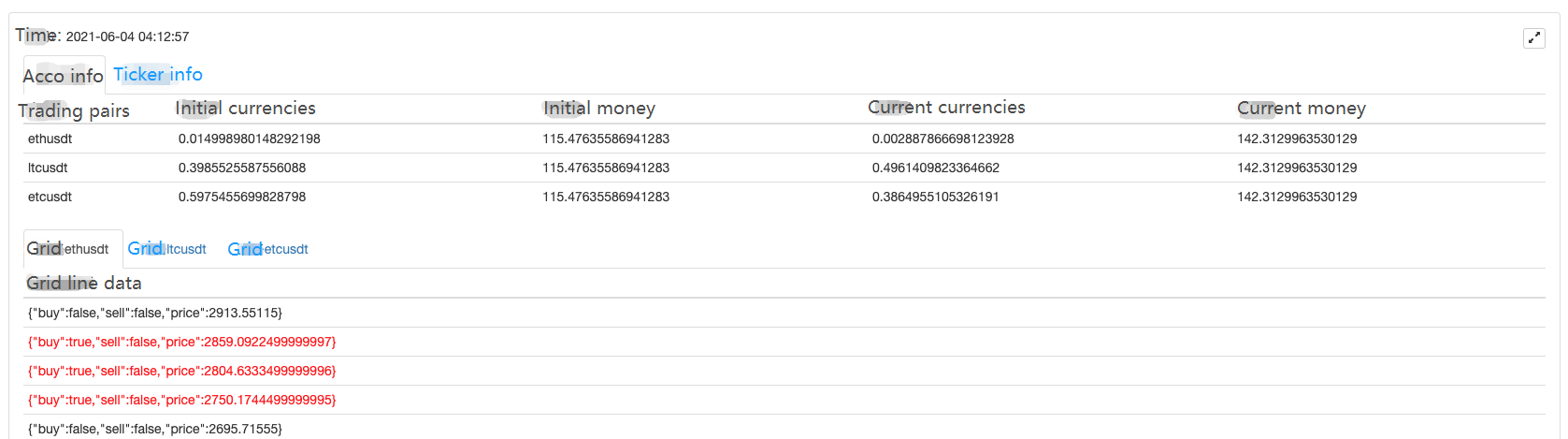
Está a perder dinheiro neste momento.T_T, o código fonte não será divulgado por enquanto.
Aqui estão alguns códigos de registro, se você estiver interessado, você pode usar o wexApp para tentar:
Buy address: https://www.fmz.com/m/s/284507
Registration code:
adc7a2e0a2cfde542e3ace405d216731
f5db29d05f57266165ce92dc18fd0a30
1735dca92794943ddaf277828ee04c27
0281ea107935015491cda2b372a0997d
1d0d8ef1ea0ea1415eeee40404ed09cc
Pouco mais de 200 U, quando comecei a correr, encontrei um grande mercado unilateral, mas recuperei-me lentamente. A estabilidade não é má, não foi modificada desde 27 de Maio, e a rede de futuros não ousou tentar temporariamente.
- Práticas de quantificação da DEX exchange ((1) -- dYdX v4 Guia de uso
- Introdução ao conjunto de Lead-Lag na moeda digital (3)
- Introdução à arbitragem de lead-lag em criptomoedas (2)
- Introdução ao suporte de Lead-Lag na moeda digital (2)
- Discussão sobre a recepção de sinais externos da plataforma FMZ: uma solução completa para receber sinais com serviço HTTP em estratégia
- Discussão da recepção de sinais externos da plataforma FMZ: estratégias para o sistema completo de recepção de sinais do serviço HTTP embutido
- Introdução à arbitragem de lead-lag em criptomoedas (1)
- Introdução ao suporte de Lead-Lag na moeda digital
- Discussão sobre a recepção de sinais externos da plataforma FMZ: API estendida VS estratégia Serviço HTTP integrado
- Exploração da recepção de sinais externos da plataforma FMZ: API de extensão vs estratégia de serviços HTTP embutidos
- Discussão sobre o método de teste de estratégia baseado no gerador de tickers aleatórios
- Modelo de Fator de Moeda Digital
- A estratégia de dupla EMA equilátera é do YouTube.
- Escrever uma ferramenta de negociação semi-automática usando o linguagem Pine
- Modelo de fatores de moeda digital
- Seja seu próprio salvador no negócio.
- Estratégia de cobertura de futuros e spot manuais de criptomoedas
- Conceção de uma estratégia de cobertura spot de criptomoedas (1)
- Uma estratégia de equilíbrio perpétuo adequada para um mercado de baixa
- Negociação Quantitativa de Criptomoedas para iniciantes - Levá-lo mais perto da Quantitativa de Criptomoedas (8)
- Negociação Quantitativa de Criptomoedas para iniciantes - Levá-lo mais perto de Criptomoeda Quantitativa (7)
- Visão geral e arquitetura da interface principal da plataforma de negociação quântica FMZ
- Projeto de estratégia Martingale para futuros de criptomoedas
- Negociação Quantitativa de Criptomoedas para iniciantes - Levá-lo mais perto da Criptomoeda Quantitativa (5)
- Negociação quantitativa de criptomoedas para iniciantes - aproximando-o da negociação quantitativa de criptomoedas (4)
- Negociação Quantitativa de Criptomoedas para iniciantes - Levá-lo mais perto da Criptomoeda Quantitativa (3)
- Negociação Quantitativa de Criptomoedas para iniciantes - Levá-lo mais perto de Criptomoeda Quantitativa (2)
- Negociação Quantitativa de Criptomoedas para iniciantes - Levá-lo mais perto de Criptomoeda Quantitativa (1)
- Projeto de estratégia de cobertura spot de criptomoedas (2)
- Exemplo de contrato de acesso ao protocolo geral na FMZ
- Compartilhamento lógico de estratégias de arbitragem de spread spot de várias bolsas