FMZ Quant: Phân tích các ví dụ thiết kế yêu cầu chung trong thị trường tiền điện tử (I)
Tác giả:FMZ~Lydia, Tạo: 2023-12-19 16:02:58, Cập nhật: 2024-11-06 21:19:16
Trong không gian giao dịch tài sản tiền điện tử, thu thập và phân tích dữ liệu thị trường, truy vấn tỷ lệ và theo dõi chuyển động tài sản tài khoản đều là các hoạt động quan trọng.
Làm thế nào để tôi viết mã để có được đồng tiền tăng cao nhất trong 4 giờ trên Binance Spot?
Khi viết một chương trình chiến lược giao dịch định lượng trên nền tảng FMZ, điều đầu tiên bạn cần làm khi bạn gặp một yêu cầu là phân tích nó.
- Tôi nên sử dụng ngôn ngữ lập trình nào? Kế hoạch là sử dụng JavaScript để thực hiện nó.
- Yêu cầu báo giá tại chỗ trong thời gian thực trong tất cả các loại tiền tệ
Điều đầu tiên chúng tôi đã làm khi chúng tôi thấy yêu cầu là tìm kiếm tài liệu API Binance để tìm hiểu xem có bất kỳ báo giá tổng hợp nào không (tốt nhất là có báo giá tổng hợp, nó là rất nhiều công việc để tìm kiếm từng cái một).
Chúng tôi tìm thấy giao diện trích dẫn tổng hợp:
GET https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price. Trên nền tảng FMZ, sử dụngHttpQuerychức năng để truy cập giao diện ticker trao đổi (công thức giao diện công khai không yêu cầu chữ ký). - Cần đếm dữ liệu cho một thời gian cửa sổ lăn 4 giờ Xác định khái niệm về cách thiết kế cấu trúc của chương trình thống kê.
- Tính toán biến động giá và sắp xếp chúng
Suy nghĩ về thuật toán biến động giá, nó là:
price fluctuations (%) = (current price - initial price) / initial price * 100trong% .
Sau khi giải quyết vấn đề, cũng như xác định chương trình, chúng tôi bắt đầu thiết kế chương trình.
Thiết kế mã
var dictSymbolsPrice = {}
function main() {
while (true) {
// GET https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price
try {
var arr = JSON.parse(HttpQuery("https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price"))
if (!Array.isArray(arr)) {
Sleep(5000)
continue
}
var ts = new Date().getTime()
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
var symbolPriceInfo = arr[i]
var symbol = symbolPriceInfo.symbol
var price = symbolPriceInfo.price
if (typeof(dictSymbolsPrice[symbol]) == "undefined") {
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol] = {name: symbol, data: []}
}
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data.push({ts: ts, price: price})
}
} catch(e) {
Log("e.name:", e.name, "e.stack:", e.stack, "e.message:", e.message)
}
// Calculate price fluctuations
var tbl = {
type : "table",
title : "Price fluctuations",
cols : ["trading pair", "current price", "price 4 hours ago", "price fluctuations", "data length", "earliest data time", "latest data time"],
rows : []
}
for (var symbol in dictSymbolsPrice) {
var data = dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data
if (data[data.length - 1].ts - data[0].ts > 1000 * 60 * 60 * 4) {
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data.shift()
}
data = dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].data
dictSymbolsPrice[symbol].percentageChange = (data[data.length - 1].price - data[0].price) / data[0].price * 100
}
var entries = Object.entries(dictSymbolsPrice)
entries.sort((a, b) => b[1].percentageChange - a[1].percentageChange)
for (var i = 0; i < entries.length; i++) {
if (i > 9) {
break
}
var name = entries[i][1].name
var data = entries[i][1].data
var percentageChange = entries[i][1].percentageChange
var currPrice = data[data.length - 1].price
var currTs = _D(data[data.length - 1].ts)
var prePrice = data[0].price
var preTs = _D(data[0].ts)
var dataLen = data.length
tbl.rows.push([name, currPrice, prePrice, percentageChange + "%", dataLen, preTs, currTs])
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`")
Sleep(5000)
}
}
Phân tích mã
- 1. Cấu trúc dữ liệu
- 2. Main function main()
2.1. Infinite loop
trong khi (true) { - Không. }
The program continuously monitors the Binance API trading pair prices through an infinite loop.
2.2. Get price information
var arr = JSON.parse ((HttpQuery))https://api.binance.com/api/v3/ticker/price”))
Get the current price information of the trading pair via Binance API. If the return is not an array, wait for 5 seconds and retry.
2.3. Update price data
cho (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { - Không. }
Iterate through the array of obtained price information and update the data in dictSymbolsPrice. For each trading pair, add the current timestamp and price to the corresponding data array.
2.4. Exception processing
♪ bắt được ♪
Log ((
Catch exceptions and log the exception information to ensure that the program can continue to execute.
2.5. Calculate the price fluctuations
cho (vár biểu tượng trong dictSymbolsPrice) { - Không. }
Iterate through dictSymbolsPrice, calculate the price fluctuations of each trading pair, and remove the earliest data if it is longer than 4 hours.
2.6. Sort and generate tables
var entry = Object.entries ((dictSymbolsPrice) entry.sort (((a, b) => b[1].percentageChange - a[1].percentageChange)
cho (var i = 0; i < các mục.length; i++) { - Không. }
Sort the trading pairs in descending order of their price fluctuations and generate a table containing information about the trading pairs.
2.7. Log output and delay
LogStatus(_D(), " + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "
Output the table and the current time in the form of a log and wait for 5 seconds to continue the next round of the loop.
The program obtains the real-time price information of the trading pair through Binance API, then calculates the price fluctuations, and outputs it to the log in the form of a table. The program is executed in a continuous loop to realize the function of real-time monitoring of the prices of trading pairs. Note that the program includes exception processing to ensure that the execution is not interrupted by exceptions when obtaining price information.
### Live Trading Running Test
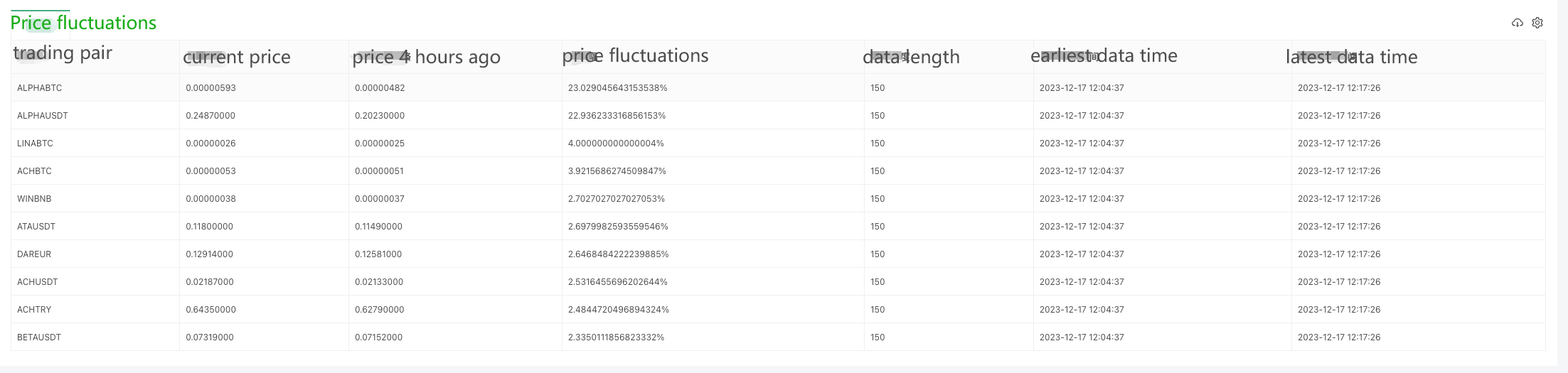
Since data can only be collected bit by bit at the beginning, it is not possible to calculate the price fluctuations on a rolling basis without collecting enough data for a 4-hour window. Therefore, the initial price is used as the base for calculation, and after collecting enough data for 4 hours, the oldest data will be eliminated in order to maintain the 4-hour window for calculating the price fluctuations.
## 2. Check the full variety of funding rates for Binance U-denominated contracts
Checking the funding rate is similar to the above code, first of all, we need to check the Binance API documentation to find the funding rate related interface. Binance has several interfaces that allow us to query the rate of funds, here we take the interface of the U-denominated contract as an example:
GEThttps://fapi.binance.com/fapi/v1/premiumIndex
### Code Implementation
Since there are so many contracts, we're exporting the top 10 largest funding rates here.
chức năng chính (() { trong khi (true) { // GEThttps://fapi.binance.com/fapi/v1/premiumIndexThử đi. var arr = JSON.parse ((HttpQuery))https://fapi.binance.com/fapi/v1/premiumIndex”)) if (!Array.isArray(arr)) { Giấc ngủ ((5000) tiếp tục }
arr.sort((a, b) => parseFloat(b.lastFundingRate) - parseFloat(a.lastFundingRate))
var tbl = {
type: "table",
title: "Top 10 funding rates for U-denominated contracts",
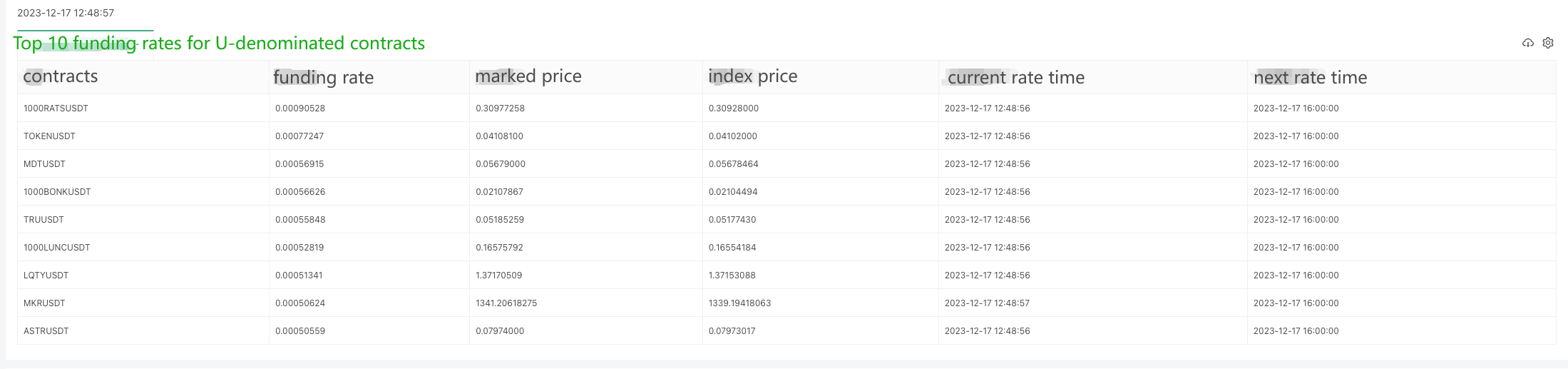
cols: ["contracts", "funding rate", "marked price", "index price", "current rate time", "next rate time"],
rows: []
}
for (var i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
var obj = arr[i]
tbl.rows.push([obj.symbol, obj.lastFundingRate, obj.markPrice, obj.indexPrice, _D(obj.time), _D(obj.nextFundingTime)])
}
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`")
} catch(e) {
Log("e.name:", e.name, "e.stack:", e.stack, "e.message:", e.message)
}
Sleep(1000 * 10)
}
}
The returned data structure is as follows, and check the Binance documentation, it shows that lastFundingRate is the funding rate we want.
♪
Live trading running test:
### Getting OKX exchange contract funding rates of Python version
A user has asked for a Python version of the example, and it's for the OKX exchange. Here is an example:
The data returned by the interface ```https://www.okx.com/priapi/v5/public/funding-rate-all?currencyType=1```:
♪
Specific code:
Yêu cầu nhập khẩu nhập json từ thời gian nhập giấc ngủ từ thời điểm nhập khẩu đến thời điểm nhập khẩu
defin main (():
trong khi True:
#https://www.okx.com/priapi/v5/public/funding-rate-all?currencyType=1Hãy thử:
response = requests.get ((
arr.sort(key=lambda x: float(x["fundingRate"]), reverse=True)
tbl = {
"type": "table",
"title": "Top 10 funding rates for U-denominated contracts",
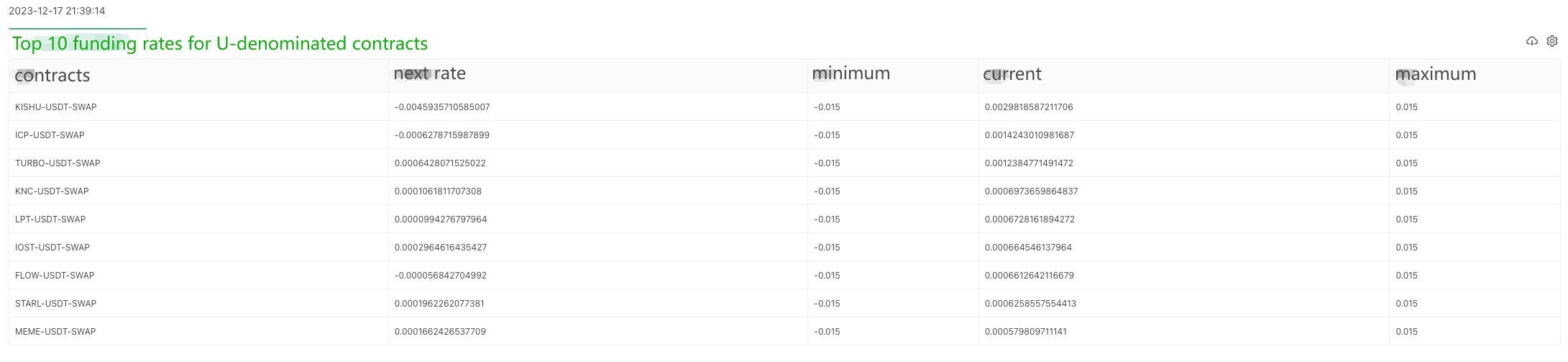
"cols": ["contracts", "next rate", "minimum", "current", "maximum"],
"rows": []
}
for i in range(min(9, len(arr))):
obj = arr[i]
row = [
obj["instId"],
obj["nextFundingRate"],
obj["minFundingRate"],
obj["fundingRate"],
obj["maxFundingRate"]
]
tbl["rows"].append(row)
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", '`' + json.dumps(tbl) + '`')
except Exception as e:
Log(f"Error: {str(e)}")
sleep(10)
Kết thúc
Những ví dụ này cung cấp các ý tưởng thiết kế cơ bản và phương pháp gọi, dự án thực tế có thể cần phải thực hiện các thay đổi và mở rộng thích hợp dựa trên nhu cầu cụ thể. Hy vọng, các mã này có thể giúp bạn đáp ứng tốt hơn các nhu cầu khác nhau trong giao dịch tài sản kỹ thuật số tiền điện tử.
- Xác định số lượng phân tích cơ bản trong thị trường tiền điện tử: Hãy để dữ liệu nói cho chính nó!
- Các nghiên cứu định lượng cơ bản của vòng đồng tiền - đừng tin vào những giáo viên mờ nhạt, nói khách quan về dữ liệu!
- Một công cụ thiết yếu trong lĩnh vực giao dịch định lượng - FMZ Quant Data Exploration Module
- Một công cụ thiết yếu trong lĩnh vực giao dịch định lượng - nhà phát minh mô-đun khám phá dữ liệu định lượng
- Kiểm soát mọi thứ - giới thiệu về FMZ Phiên bản mới của Terminal giao dịch (với mã nguồn TRB Arbitrage)
- Có tất cả các thông tin về FMZ phiên bản mới của giao dịch đầu cuối (được thêm mã nguồn TRB)
- FMZ Quant: Phân tích các ví dụ thiết kế yêu cầu chung trong thị trường tiền điện tử (II)
- Làm thế nào để khai thác robot bán hàng không có não với một chiến lược tần số cao trong 80 dòng mã
- FMZ định lượng: Phân tích các trường hợp thiết kế nhu cầu phổ biến của thị trường tiền điện tử (II)
- Cách khai thác robot vô trí tuệ để bán bằng chiến lược tần số cao 80 dòng mã
- FMZ định lượng: Các nhu cầu phổ biến của thị trường tiền điện tử
- WexApp, FMZ Quant Cryptocurrency Demo Exchange, vừa được ra mắt
- Giải thích chi tiết về tối ưu hóa tham số chiến lược lưới hợp đồng vĩnh viễn
- Dạy bạn sử dụng FMZ Extended API để Batch Modify Parameters của bot
- Dạy bạn sử dụng FMZ Extension API để thay đổi số lượng các tham số ổ đĩa
- Phương pháp tối ưu hóa các tham số lưới hợp đồng bền vững
- Hướng dẫn cài đặt Interactive Brokers IB Gateway trong Linux Bash
- Định hướng cài đặt chứng khoán xâm nhập IB GATEWAY trên Linux bash
- Điều gì phù hợp hơn cho việc đánh cá dưới đáy, giá trị thị trường thấp hay giá thấp?
- Giá trị thị trường thấp hay giá thấp, cái nào thích hợp hơn?