Chiến lược chỉ số động lực tương đối
Tác giả:ChaoZhang, Ngày: 2023-11-02 17:21:45Tags:
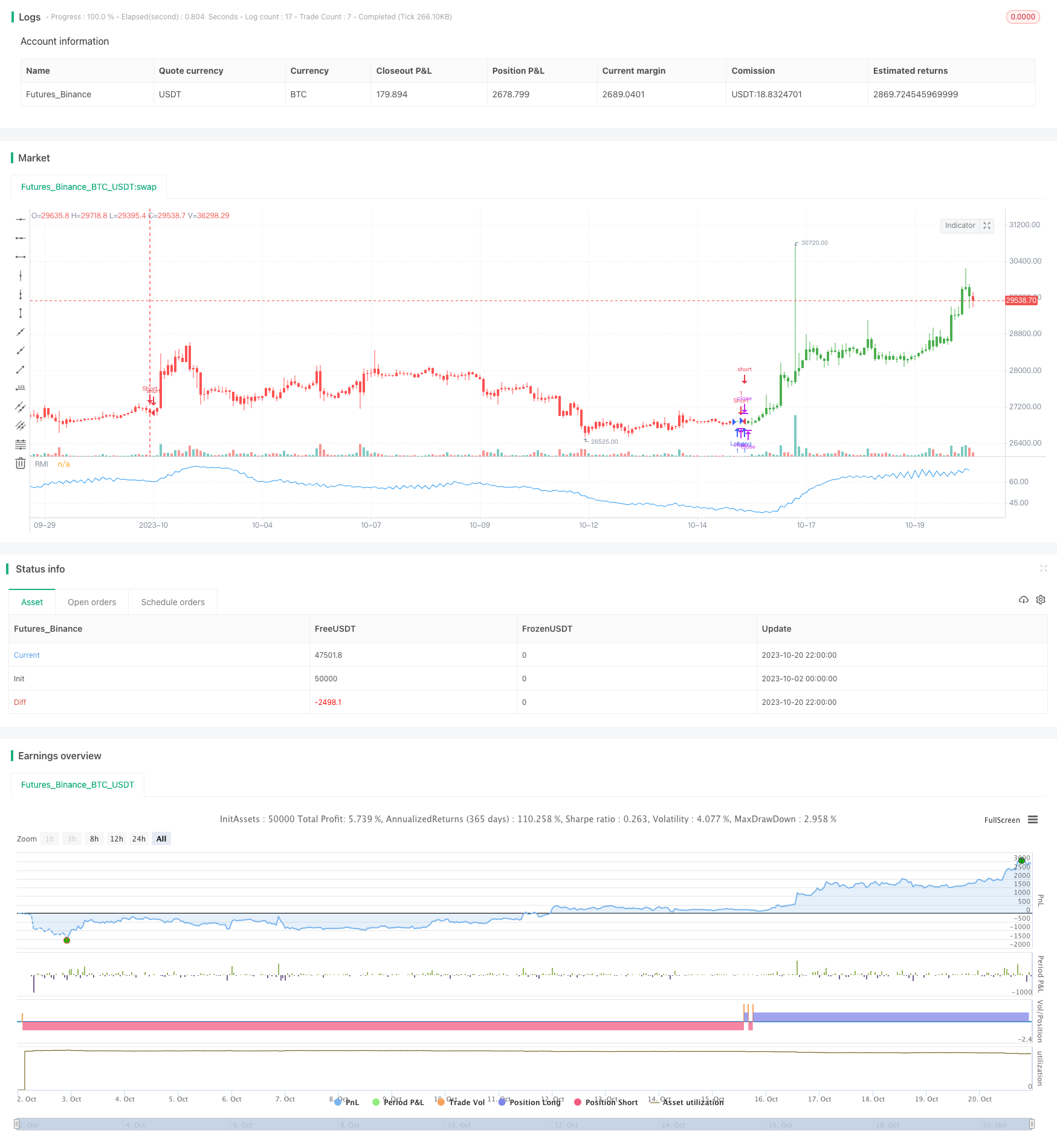
Tổng quan
Chiến lược chỉ số động lượng tương đối (RMI) là một phiên bản cải tiến dựa trên chỉ số động lực. Nó tính toán động lực giá trong một khoảng thời gian để xác định xem thị trường có mua quá nhiều hay bán quá nhiều, để nắm bắt các cơ hội đảo ngược.
Chiến lược logic
Công thức tính toán RMI là như sau:
xMom = xPrice - xPrice[Length] // Price change over Length periods
xMU = If xMom >= 0: previous xMU minus xMU/Length plus xMom; else: previous xMU
xMD = If xMom <= 0: previous xMD minus xMD/Length plus absolute value of xMom; else: 0
RM = xMU / xMD
RMI = 100 * (RM / (1 + RM))
Đầu tiên tính toán sự thay đổi giá xMom trong thời gian dài. Nếu xMom>=0, nghĩa là giá tăng, tích lũy nó vào xMU; nếu xMom<0, nghĩa là giá giảm, tích lũy giá trị tuyệt đối của nó vào xMD. RM là tỷ lệ giữa xMU và xMD, đại diện cho đà tăng và giảm. RMI bình thường hóa RM vào khoảng 0-100.
Khi RMI cao hơn ngưỡng SellZone, thị trường bị mua quá mức, đi ngắn. Khi RMI thấp hơn BuyZone, thị trường bị bán quá mức, đi dài.
Ưu điểm
- So với RSI, RMI nhạy cảm hơn và có thể nắm bắt các cơ hội đảo ngược sớm hơn.
- RMI đo đạc đà tăng và giảm, ít bị ảnh hưởng bởi hợp nhất.
- Dựa trên động lực, RMI có thể xác định tốt hơn tình trạng mua quá mức / bán quá mức.
Rủi ro
- Giống như các chiến lược đảo ngược khác, RMI có nguy cơ bị dừng lại bởi các xu hướng mạnh.
- Các thông số RMI cần được tối ưu hóa cho các sản phẩm khác nhau, nếu không kết quả có thể kém.
- Các ngưỡng mua/bán quá mức cần phải được thiết lập hợp lý, nếu không có thể xảy ra quá nhiều tín hiệu sai.
Rủi ro có thể được giảm bằng cách mở rộng dừng lỗ, tối ưu hóa các tham số, kết hợp với các chiến lược xu hướng vv.
Cải thiện
Chiến lược RMI có thể được cải thiện từ các khía cạnh sau:
- Tối ưu hóa tham số Length để tối đa hóa lợi nhuận.
- Tối ưu hóa ngưỡng mua quá mức / bán quá mức để giảm tín hiệu sai.
- Thêm stop loss để kiểm soát single loss.
- Kết hợp với các chiến lược theo xu hướng hoặc trung bình động để tăng tỷ lệ thắng.
- Chọn các phiên giao dịch phù hợp dựa trên các đặc điểm của sản phẩm để cải thiện sự ổn định.
Kết luận
Chiến lược RMI nắm bắt các cơ hội rút lui ngắn hạn bằng cách đo lường sự thay đổi động lực giá. So với RSI, RMI nhạy cảm và mạnh mẽ hơn đối với việc hợp nhất. Nhưng rủi ro bị dừng lại tồn tại. Các thông số cần được tối ưu hóa và kết hợp với các chiến lược xu hướng để tối đa hóa hiệu suất.
/*backtest
start: 2023-10-02 00:00:00
end: 2023-10-21 00:00:00
period: 2h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=2
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Copyright by HPotter v1.0 19/10/2017
// The Relative Momentum Index (RMI) was developed by Roger Altman. Impressed
// with the Relative Strength Index's sensitivity to the number of look-back
// periods, yet frustrated with it's inconsistent oscillation between defined
// overbought and oversold levels, Mr. Altman added a momentum component to the RSI.
// As mentioned, the RMI is a variation of the RSI indicator. Instead of counting
// up and down days from close to close as the RSI does, the RMI counts up and down
// days from the close relative to the close x-days ago where x is not necessarily
// 1 as required by the RSI). So as the name of the indicator reflects, "momentum" is
// substituted for "strength".
//
// You can change long to short in the Input Settings
// WARNING:
// - For purpose educate only
// - This script to change bars colors.
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
strategy(title="Relative Momentum Index", shorttitle="RMI")
xPrice = close
Length = input(20, minval=1)
BuyZone = input(40, minval=1)
SellZone = input(70, minval=1)
reverse = input(false, title="Trade reverse")
// hline(0, color=gray, linestyle=dashed)
// hline(SellZone, color=red, linestyle=line)
// hline(BuyZone, color=green, linestyle=line)
xMom = xPrice - xPrice[Length]
xMU = iff(xMom >= 0, nz(xMU[1], 1) - (nz(xMU[1],1) / Length) + xMom, nz(xMU[1], 1))
xMD = iff(xMom <= 0, nz(xMD[1], 1) - (nz(xMD[1],1) / Length) + abs(xMom), nz(xMD[1], 0))
RM = xMU / xMD
nRes = 100 * (RM / (1+RM))
pos = iff(nRes < BuyZone, 1,
iff(nRes > SellZone, -1, nz(pos[1], 0)))
possig = iff(reverse and pos == 1, -1,
iff(reverse and pos == -1, 1, pos))
if (possig == 1)
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
if (possig == -1)
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)
barcolor(possig == -1 ? red: possig == 1 ? green : blue )
plot(nRes, color=blue, title="RMI")
- Chiến lược theo dõi xu hướng Breakout Moving Average
- Chiến lược theo dõi xu hướng dựa trên dao động khối lượng
- Xu hướng theo chiến lược dài hạn dựa trên siêu xu hướng và biến đổi Fisher
- Chiến lược giao dịch đảo ngược Golden Cross kép
- Fibonacci rút lại kịch bản chiến lược giao dịch
- RSI-BB Momentum Breakout chiến lược
- Breakout Band Fixed Stop Loss chiến lược
- Chiến lược giao dịch hai hướng dựa trên RSI và SuperTrend
- EMA 13 48 Xu hướng theo chiến lược
- Chiến lược tích lũy / phân phối Williams (Williams AD)
- Hệ thống theo dõi xu hướng hộp kép
- Chiến lược Martingale với phạm vi trung bình động mở rộng cho giao dịch chứng khoán
- Chiến lược cân bằng bò và gấu
- Chiến lược giao dịch đường sắt kép của Oma và Apollo
- Chiến lược chéo giữa hai mức trung bình động
- Chiến lược theo dõi xu hướng hai tín hiệu
- Xu hướng sau chiến lược SMA
- Chiến lược cân bằng vết nứt sư tử
- Chiến lược giao dịch trung bình động ATR thích nghi
- Chiến lược đảo ngược hai hướng