কৌশল অনুসরণ করে সাধারণ প্রবণতা
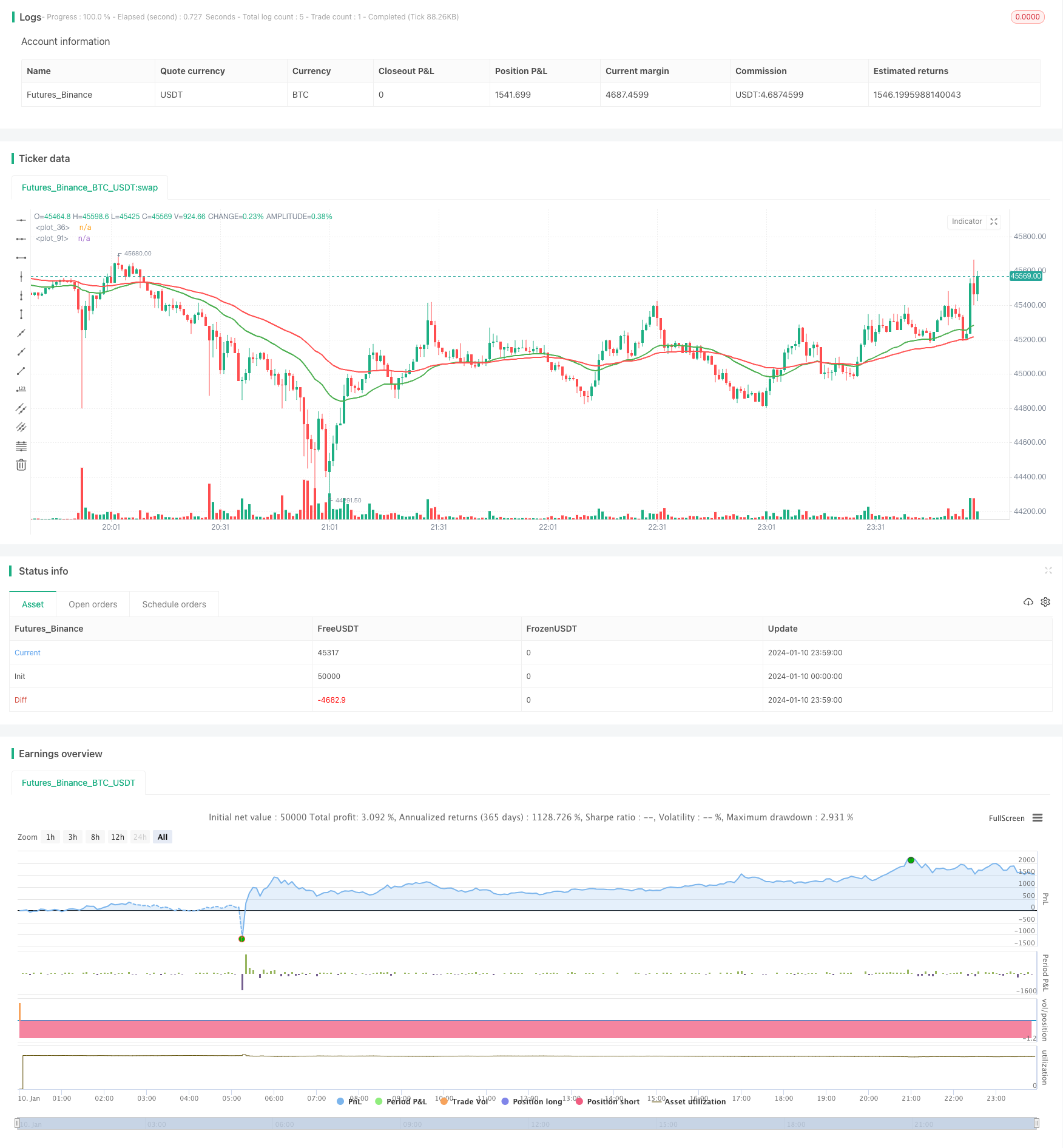
ওভারভিউ
ডাবল ইয়ারেজ লাইন ক্রসিং কৌশল একটি প্রচলিত ট্রেন্ড ট্র্যাকিং কৌশল। এটি দুটি ভিন্ন পিরিয়ডের ইএমএ গড় ব্যবহার করে, দামের প্রবণতার একটি বিপরীত পয়েন্ট ধরার জন্য দীর্ঘমেয়াদী গড়ের উপরে দীর্ঘমেয়াদী গড় অতিক্রম করার সময় এবং দীর্ঘমেয়াদী গড়ের নীচে দীর্ঘমেয়াদী গড় অতিক্রম করার সময় খালি করে।
কৌশল নীতি
এই কৌশলটির কেন্দ্রীয় সূচক দুটি ইএমএ গড় লাইন, যথাক্রমে 30 এবং 60 পিরিয়ড। কোডটিতে একটি কাস্টম ফাংশন ব্যবহার করে দুটি ইএমএ গড় লাইন গণনা করা হয়েছেঃ
emaLen1 = emaFuncOne(close, lenMA1)
emaLen2 = emaFuncTwo(close, lenMA2)
কৌশলটির ট্রেডিং সিগন্যাল আসে দুটি ইএমএ সমান্তরালের ক্রস থেকেঃ
currentState = if emaLen2 > emaLen1
0
else
1
previousState = if emaLastLen2 > emaLastLen1
0
else
1
convergence = if currentState != previousState
1
else
0
যখন একটি স্বল্পমেয়াদী ইএমএ একটি দীর্ঘমেয়াদী ইএমএ পরা হয়, বর্তমান রাষ্ট্রটি পূর্ববর্তী রাষ্ট্রের সাথে সমান নয়, ক্রস সংকেত উপস্থিত হয়। এই সময়ে আরও কিছু করুন। যখন স্বল্পমেয়াদী ইএমএ দীর্ঘমেয়াদী ইএমএ অতিক্রম করে, বর্তমান রাষ্ট্রটি পূর্ববর্তী রাষ্ট্রের সাথে সমান নয়, একটি ক্রস সংকেত দেখা দেয়। এই সময় খালি।
সামর্থ্য বিশ্লেষণ
এই কৌশলটির সুবিধাগুলো হলঃ
- কৌশলগুলি সহজ, স্বজ্ঞাত, সহজে বোঝা যায় এবং বাস্তবায়িত হয়
- ইএমএ সমতলতার মসৃণ বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি ব্যবহার করে বাজারের শব্দকে কার্যকরভাবে ফিল্টার করুন
- স্বয়ংক্রিয় ট্রেন্ড ট্র্যাকিং, সহজেই মিস করা যায় না
ঝুঁকি বিশ্লেষণ
এই কৌশলটির কিছু ঝুঁকিও রয়েছেঃ
- ডাবল-ইয়ারলাইন ক্রস সিগন্যালটি দেরিতে যেতে পারে, সময়মত পাল্টাতে ব্যর্থ হতে পারে
- ভূমিকম্পের সময় একাধিক ত্রুটিপূর্ণ সংকেত হতে পারে
- প্যারামিটার সেটিং ভুল হলে এটি সংবেদনশীল বা বিলম্বিত হতে পারে
EMA চক্রের পরিবর্তন বা ফিল্টারিং শর্ত যোগ করে অপ্টিমাইজ করা যেতে পারে।
অপ্টিমাইজেশান দিক
এই কৌশলটি নিম্নলিখিত দিকগুলি থেকে উন্নত করা যেতে পারেঃ
- বিভিন্ন দৈর্ঘ্যের EMA চক্রের সমন্বয় পরীক্ষা করা
- ভুয়া সংকেত ফিল্টার করার জন্য ট্রানজিট বা ওভাররাইডিং হার বাড়ানো
- অন্যান্য সূচকের সাথে মিলিত ট্রেন্ড নিশ্চিতকরণ, যেমন MACD
- তহবিল ব্যবস্থাপনা অপ্টিমাইজ করুন, স্টপ লস স্টপ সেট করুন
সারসংক্ষেপ
ডাবল ইক্যুয়ালাইন ক্রস কৌশল সামগ্রিকভাবে একটি সহজ ব্যবহারিক প্রবণতা অনুসরণ কৌশল। এটি সোজা-ফরওয়ার্ড, বাস্তবায়ন করা সহজ এবং স্বয়ংক্রিয়ভাবে প্রবণতা অনুসরণ করতে পারে। তবে কিছু পিছিয়ে পড়া এবং মিথ্যা সংকেতের ঝুঁকিও রয়েছে। প্যারামিটার অপ্টিমাইজেশন এবং ফিল্টারিংয়ের শর্তগুলি যুক্ত করে এটি আরও উন্নত করা যেতে পারে, এটি পরিমাপযোগ্য ব্যবসায়ের অন্যতম মৌলিক কৌশল।
/*backtest
start: 2024-01-10 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-11 00:00:00
period: 1m
basePeriod: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=2
strategy("ParkerMAStrat", overlay=true)
lenMA1=input(title="Length 1", defval=30)
lenMA2=input(title="Length 2", defval=60)
x = 0
checkLines(current, last) =>
if current > last
x = 1
else
x = 0
x
//plot ema based on len1
emaFuncOne(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[1])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
emaLen1 = emaFuncOne(close, lenMA1)
plot(emaLen1, color=green, transp=0, linewidth=2)
// now we plot the _10_period_ema
//plot ema based on len2
emaFuncTwo(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[1])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
//plot ema based on len2
emaFuncOneLast(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[0])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
//plot ema based on len2
emaFuncTwoLast(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[0])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
emaLastLen1 = emaFuncOneLast(close, lenMA1)
emaLastLen2 = emaFuncTwoLast(close, lenMA2)
emaLen2 = emaFuncTwo(close, lenMA2)
plot(emaLen2, color=red, transp=30, linewidth=2)
// now we plot the _10_period_ema
//now we compare the two and when green crosses red we buy/sell (line1 vs line2)
previousState = if emaLastLen2 > emaLastLen1
0
else
1
currentState = if emaLen2 > emaLen1
0
else
1
convergence = if currentState != previousState
1
else
0
lineCheck = if convergence == 1
checkLines(currentState, previousState)
if lineCheck == 1
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
else
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)