Diese Strategie ist eine bidirektionale Adaptivbereich Filterung Impulsverfolgung Strategie
Schriftsteller:ChaoZhang, Datum: 2024-01-24 11:31:51Tags:
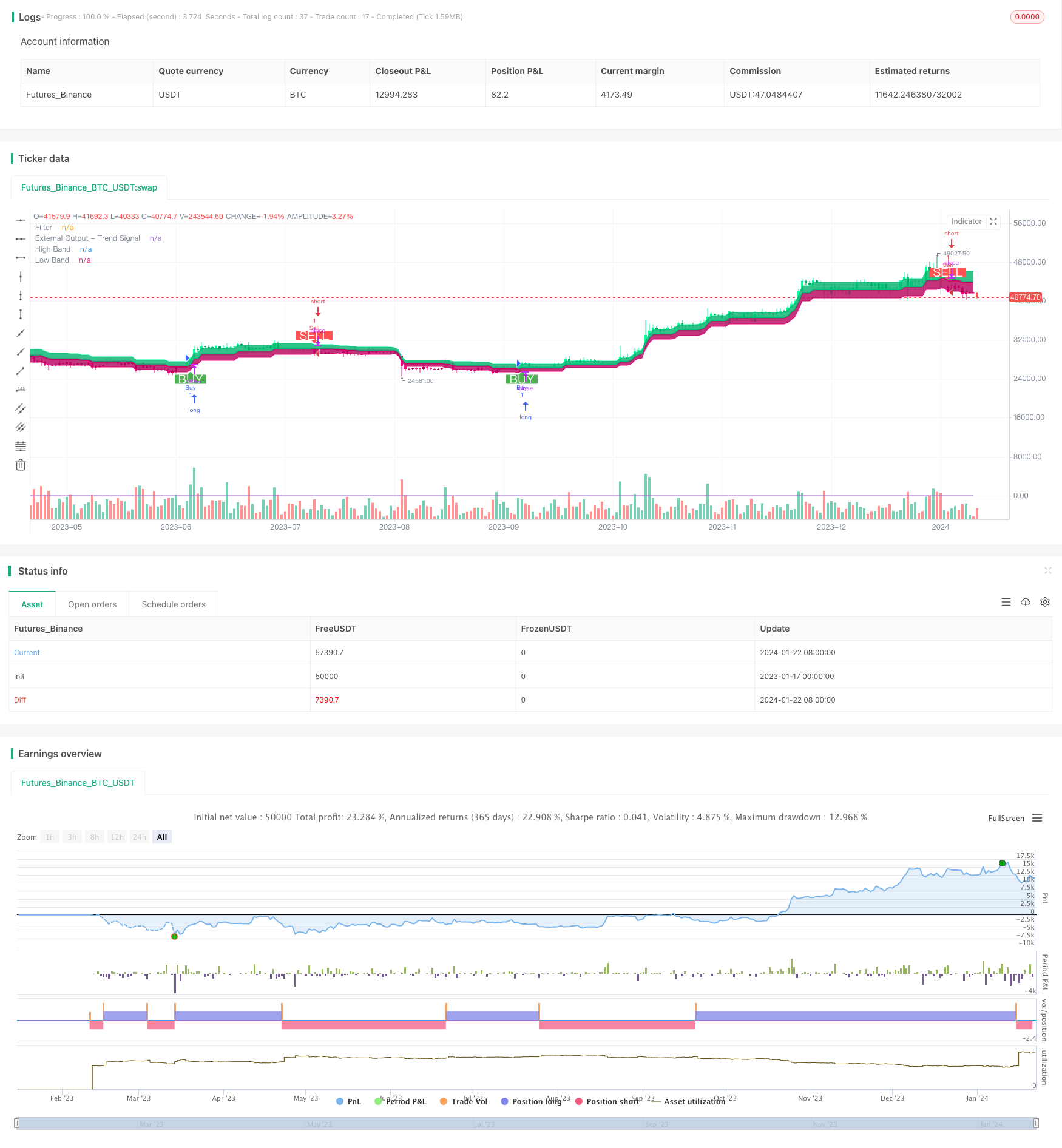
Übersicht
Diese Strategie ist eine bidirektionale dynamische Anpassungs-Range-Filterungs-Tracking-Strategie. Sie verwendet einen anpassungsfähigen Range-Filter, um Preisschwankungen zu verfolgen, und kombiniert Volumenindikatoren, um die Wertrichtung zu bestimmen, um niedrige Käufe und hohe Verkäufe zu implementieren.
Strategieprinzipien
-
Die Größe des Filters wird entsprechend der vom Benutzer definierten Spanne, Menge und Größenordnung anpassungsfähig angepasst.
-
Es gibt zwei Arten von Filtern: Typ 1 und Typ 2. Typ 1 ist ein Standard-Range-Tracking-Typ, und Typ 2 ist ein Stufen-Rundungstyp.
-
Die Kursschwankung wird anhand des Verhältnisses zwischen dem Filter und dem Schlusskurs bestimmt.
-
In Kombination mit dem Anstieg und Fall des Schlusskurses im Vergleich zum Vortag, bestimmen Sie die Kursrichtung.
-
Ausgabe eines Kaufsignals, wenn der Preis die obere Spur durchbricht und der Wert steigt; Ausgabe eines Verkaufssignals, wenn der Preis die untere Spur durchbricht und der Wert fällt.
Analyse der Vorteile
-
Der adaptive Bereichsfilter kann Marktschwankungen genau erfassen.
-
Zwei Arten von Filtern können unterschiedliche Handelspräferenzen erfüllen.
-
Durch die Kombination von Volumenindikatoren kann die Wertrichtung wirksam ermittelt werden.
-
Die Strategie ist flexibel und die Parameter können an die Marktbedingungen angepasst werden.
-
Anpassbare Handelsbedingungen Logik.
Risikoanalyse
-
Eine falsche Einstellung der Parameter kann zu Über- oder fehlenden Trades führen.
-
Die Breakout-Signale haben eine gewisse Verzögerung.
-
Die Volumenindikatoren haben ein gewisses Risiko für eine Verzögerung.
-
Range Breaks sind anfällig für Fallen.
Risikoprävention:
-
Wählen Sie geeignete Parameterkombinationen aus und passen Sie diese rechtzeitig an.
-
Kombinieren Sie andere Indikatoren, um Trends zu erkennen.
-
Handel vorsichtig um Schlüsselniveaus und Trendumkehrungen.
Optimierungsrichtlinien
-
Versuche verschiedene Kombinationen von Bereichsgrößen und Glättungszyklen, um die optimale Kombination zu finden.
-
Probieren Sie verschiedene Filterarten aus und wählen Sie Ihren bevorzugten Typ.
-
Versuch mit anderen Volumenindikatoren oder Hilfstechnischen Indikatoren.
-
Optimierung und Anpassung der Handelsbedingungenlogik, um den irrationalen Handel zu reduzieren.
-
Einbeziehung von Marktsatz zur Anpassung der Positionsgröße.
/*backtest
start: 2023-01-17 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-23 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=4
strategy("Range Filter [DW] & Labels", shorttitle="RF [DW] & Labels", overlay=true)
//Conditional Sampling EMA Function
Cond_EMA(x, cond, n)=>
var val = array.new_float(0)
var ema_val = array.new_float(1)
if cond
array.push(val, x)
if array.size(val) > 1
array.remove(val, 0)
if na(array.get(ema_val, 0))
array.fill(ema_val, array.get(val, 0))
array.set(ema_val, 0, (array.get(val, 0) - array.get(ema_val, 0))*(2/(n + 1)) + array.get(ema_val, 0))
EMA = array.get(ema_val, 0)
EMA
//Conditional Sampling SMA Function
Cond_SMA(x, cond, n)=>
var vals = array.new_float(0)
if cond
array.push(vals, x)
if array.size(vals) > n
array.remove(vals, 0)
SMA = array.avg(vals)
SMA
//Standard Deviation Function
Stdev(x, n)=>
sqrt(Cond_SMA(pow(x, 2), 1, n) - pow(Cond_SMA(x, 1, n), 2))
//Range Size Function
rng_size(x, scale, qty, n)=>
ATR = Cond_EMA(tr(true), 1, n)
AC = Cond_EMA(abs(x - x[1]), 1, n)
SD = Stdev(x, n)
rng_size = scale=="Pips" ? qty*0.0001 : scale=="Points" ? qty*syminfo.pointvalue : scale=="% of Price" ? close*qty/100 : scale=="ATR" ? qty*ATR :
scale=="Average Change" ? qty*AC : scale=="Standard Deviation" ? qty*SD : scale=="Ticks" ? qty*syminfo.mintick : qty
//Two Type Range Filter Function
rng_filt(h, l, rng_, n, type, smooth, sn, av_rf, av_n)=>
rng_smooth = Cond_EMA(rng_, 1, sn)
r = smooth ? rng_smooth : rng_
var rfilt = array.new_float(2, (h + l)/2)
array.set(rfilt, 1, array.get(rfilt, 0))
if type=="Type 1"
if h - r > array.get(rfilt, 1)
array.set(rfilt, 0, h - r)
if l + r < array.get(rfilt, 1)
array.set(rfilt, 0, l + r)
if type=="Type 2"
if h >= array.get(rfilt, 1) + r
array.set(rfilt, 0, array.get(rfilt, 1) + floor(abs(h - array.get(rfilt, 1))/r)*r)
if l <= array.get(rfilt, 1) - r
array.set(rfilt, 0, array.get(rfilt, 1) - floor(abs(l - array.get(rfilt, 1))/r)*r)
rng_filt1 = array.get(rfilt, 0)
hi_band1 = rng_filt1 + r
lo_band1 = rng_filt1 - r
rng_filt2 = Cond_EMA(rng_filt1, rng_filt1 != rng_filt1[1], av_n)
hi_band2 = Cond_EMA(hi_band1, rng_filt1 != rng_filt1[1], av_n)
lo_band2 = Cond_EMA(lo_band1, rng_filt1 != rng_filt1[1], av_n)
rng_filt = av_rf ? rng_filt2 : rng_filt1
hi_band = av_rf ? hi_band2 : hi_band1
lo_band = av_rf ? lo_band2 : lo_band1
[hi_band, lo_band, rng_filt]
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Inputs
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Filter Type
f_type = input(defval="Type 1", options=["Type 1", "Type 2"], title="Filter Type")
//Movement Source
mov_src = input(defval="Close", options=["Wicks", "Close"], title="Movement Source")
//Range Size Inputs
rng_qty = input(defval=2.618, minval=0.0000001, title="Range Size")
rng_scale = input(defval="Average Change", options=["Points", "Pips", "Ticks", "% of Price", "ATR", "Average Change", "Standard Deviation", "Absolute"], title="Range Scale")
//Range Period
rng_per = input(defval=14, minval=1, title="Range Period (for ATR, Average Change, and Standard Deviation)")
//Range Smoothing Inputs
smooth_range = input(defval=true, title="Smooth Range")
smooth_per = input(defval=27, minval=1, title="Smoothing Period")
//Filter Value Averaging Inputs
av_vals = input(defval=true, title="Average Filter Changes")
av_samples = input(defval=2, minval=1, title="Number Of Changes To Average")
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Definitions
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//High And Low Values
h_val = mov_src=="Wicks" ? high : close
l_val = mov_src=="Wicks" ? low : close
//Range Filter Values
[h_band, l_band, filt] = rng_filt(h_val, l_val, rng_size((h_val + l_val)/2, rng_scale, rng_qty, rng_per), rng_per, f_type, smooth_range, smooth_per, av_vals, av_samples)
//Direction Conditions
var fdir = 0.0
fdir := filt > filt[1] ? 1 : filt < filt[1] ? -1 : fdir
upward = fdir==1 ? 1 : 0
downward = fdir==-1 ? 1 : 0
//Colors
filt_color = upward ? #05ff9b : downward ? #ff0583 : #cccccc
bar_color = upward and (close > filt) ? (close > close[1] ? #05ff9b : #00b36b) :
downward and (close < filt) ? (close < close[1] ? #ff0583 : #b8005d) : #cccccc
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Outputs
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//Filter Plot
filt_plot = plot(filt, color=filt_color, transp=0, linewidth=3, title="Filter")
//Band Plots
h_band_plot = plot(h_band, color=#05ff9b, transp=100, title="High Band")
l_band_plot = plot(l_band, color=#ff0583, transp=100, title="Low Band")
//Band Fills
fill(h_band_plot, filt_plot, color=#00b36b, transp=85, title="High Band Fill")
fill(l_band_plot, filt_plot, color=#b8005d, transp=85, title="Low Band Fill")
//Bar Color
barcolor(bar_color)
//External Trend Output
plot(fdir, transp=100, editable=false, display=display.none, title="External Output - Trend Signal")
// Trading Conditions Logic
longCond = close > filt and close > close[1] and upward > 0 or close > filt and close < close[1] and upward > 0
shortCond = close < filt and close < close[1] and downward > 0 or close < filt and close > close[1] and downward > 0
CondIni = 0
CondIni := longCond ? 1 : shortCond ? -1 : CondIni[1]
longCondition = longCond and CondIni[1] == -1
shortCondition = shortCond and CondIni[1] == 1
// Strategy Entry and Exit
strategy.entry("Buy", strategy.long, when = longCondition)
strategy.entry("Sell", strategy.short, when = shortCondition)
strategy.close("Buy", when = shortCondition)
strategy.close("Sell", when = longCondition)
// Plot Buy and Sell Labels
plotshape(longCondition, title = "Buy Signal", text ="BUY", textcolor = color.white, style=shape.labelup, size = size.normal, location=location.belowbar, color = color.green, transp = 0)
plotshape(shortCondition, title = "Sell Signal", text ="SELL", textcolor = color.white, style=shape.labeldown, size = size.normal, location=location.abovebar, color = color.red, transp = 0)
// Alerts
alertcondition(longCondition, title="Buy Alert", message = "BUY")
alertcondition(shortCondition, title="Sell Alert", message = "SELL")
- RSI und Breakout-Strategie für gleitende Durchschnitte
- EMA-Verfolgungsstrategie
- Trend nach einer auf gleitenden Durchschnitten basierenden Strategie
- SMA Crossover Ichimoku Markttiefe Volumenbasierte quantitative Handelsstrategie
- Trendverfolgung Stop Loss Take Profit Strategie
- Zwei-richtungs-Null-Achsen-Übergang Qstick-Indikator Backteststrategie
- Strategie für den Crossover-Handel mit gleitendem Durchschnitt
- Strategie für die Divergenz des gleitenden Durchschnitts
- Umkehrung der Hochfrequenz-Handelsstrategie auf Basis der Schattenlinie
- Quantitative Handelsstrategie auf der Grundlage von linearen Regressions-RSI
- Strategie zur Beobachtung der Trendentwicklung durch zwei gleitende Durchschnittswerte
- Durchbruchsstrategie
- RSI CCI Williams%R Quantitative Handelsstrategie
- Dynamische Risikobereinigte Handelsstrategie
- Momentum Moving Average Crossover-Handelsstrategie
- Bollinger Band Limit Market Maker-Strategie
- Langfristige Strategie des gleitenden Durchschnitts im Kreuzverlauf von Renko
- Binance-Nachrichten überwachen Online-Transaktionen
- Zwei-Richtungs-Trend-Tracking-Renko-Handelsstrategie
- Kombinierte Strategie für eine bewegte und unendliche Impulsresponslinie