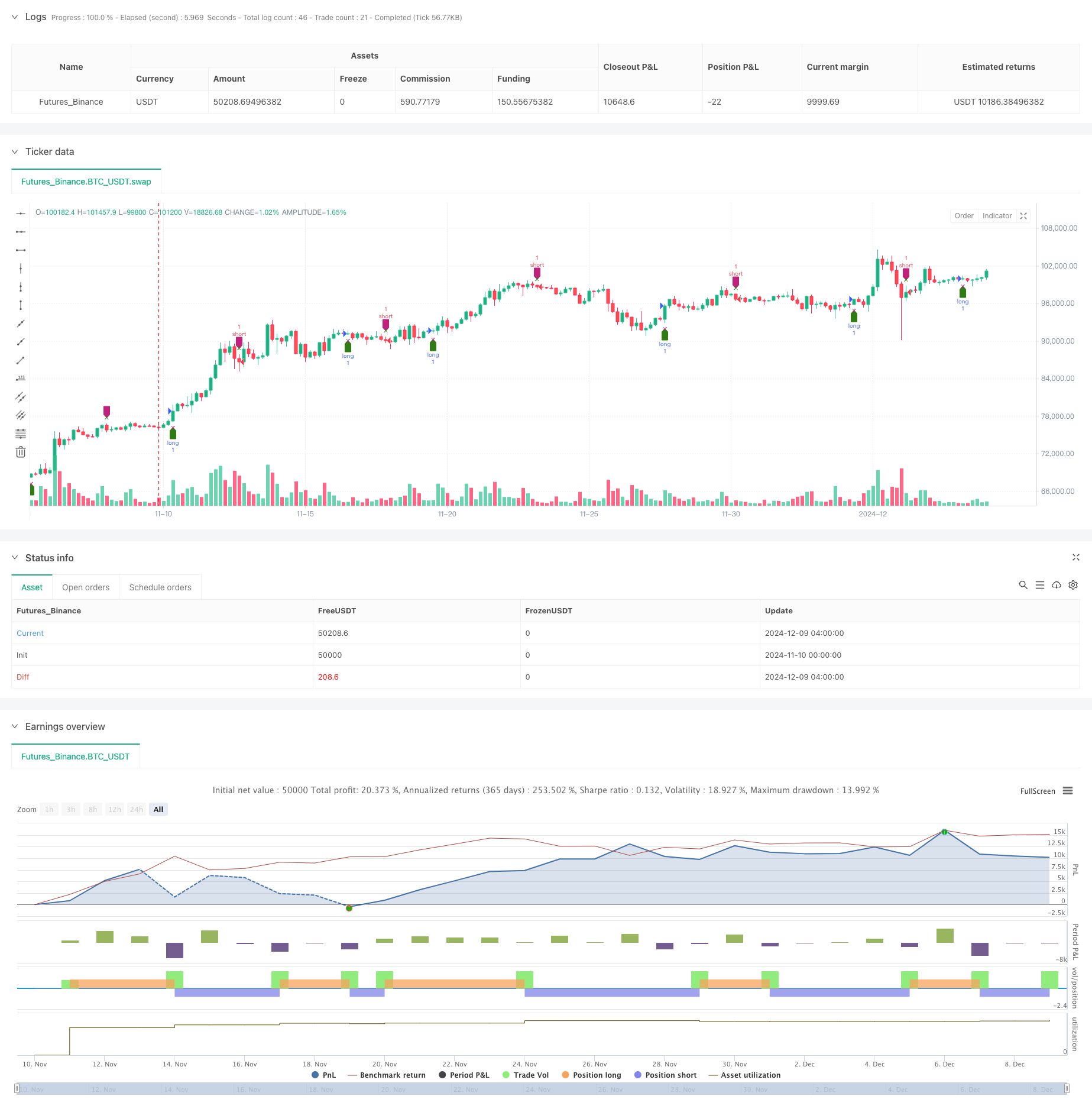
Die Strategie ist ein quantitatives Handelssystem, das auf einem dynamischen RSI-Oszillator basiert. Durch die Durchführung einer multivariaten Anpassung und einer Zeitreihenanalyse der RSI-Indikatoren wird die Veränderungsrate des RSI berechnet, um die Marktdynamik zu erfassen. Die Strategie verwendet fortgeschrittene mathematische Methoden wie die QR-Auflösung für die Signalverarbeitung und für die Handelsentscheidung in Verbindung mit einem linearen System.
Strategieprinzip
Der Delta-RSI-Obsolver steht im Mittelpunkt der Strategie und wird in folgenden Schritten umgesetzt:
- Zuerst berechnen Sie den traditionellen RSI als Basis
- RSI wird mit einer multiplen Anpassung glatter und geräuscharmer bearbeitet
- Berechnen Sie die Zeitvariablen des RSI mit Delta-RSI, die die Veränderungsrate des RSI widerspiegeln
- Vergleiche des Delta-RSI mit seinem Moving Average erzeugt Handelssignale
- Bewertung und Filterung der Anpassungsklasse mittels der gleichmäßigen Quadratwurzel-Fehler (RMSE)
Die Handelssignale können auf drei Arten erzeugt werden:
- Null-Linien-Kreuzung: Delta-RSI ist positiver als negativ und null als negativ
- Signallinien kreuzen sich: Delta-RSI überschreitet/unterschreitet seinen Moving Average und macht Plus/Lose
- Richtungsänderung: Delta-RSI ist zu hoch, wenn der Negativbereich zu steigen beginnt, und zu niedrig, wenn der Positivbereich zu sinken beginnt
Strategische Vorteile
- Die mathematische Basis ist solide. Die Signalverarbeitung erfolgt mittels fortgeschrittener mathematischer Methoden, wie z.B. der QR-Auflösung. Die theoretische Basis ist zuverlässig.
- Signalglättung: Multi-Punkt-Einfügung filtert effektiv Marktlärm und verbessert die Signalqualität
- Flexibilität: Verschiedene Signalgenerierungsmethoden und Parameteroptionen für verschiedene Marktumgebungen
- Risikokontrolle: Ein RMSE-Filtermechanismus, der zuverlässige Signale auswählt
- Hohe Rechenleistung: Die Matrix-Berechnungen werden durch optimierte Algorithmen effizienter ausgeführt
Strategisches Risiko
- Parameter-sensibel: Mehrere Schlüsselparameter müssen sorgfältig angepasst werden, und die falsche Parameterwahl kann die Strategie-Performance erheblich beeinträchtigen
- Verzögerung: Die glatte Verarbeitung des Signals führt zu einer gewissen Verzögerung und kann zu schnellen Verzögerungen führen.
- Falsche Durchbrüche: Falsche Signale können in den turbulenten Märkten entstehen, was die Kosten erhöht.
- Komplexe Berechnungen: Es sind mehr Matrix-Berechnungen erforderlich, und es kann zu Leistungsschwierigkeiten beim Hochfrequenz-Handel kommen.
- Überpassung: Vorsicht bei der Optimierung von Parametern, um eine Überpassung der historischen Daten zu vermeiden
Richtung der Strategieoptimierung
- Anpassungsparameter: RSI-Zyklen und Anpassungsstufen können entsprechend der Dynamik der Marktfluktuation angepasst werden
- Mehrzeit-Zyklus: Signal mit mehr Zeit-Zyklen zu überprüfen
- Fluktuationsratefilterung: Signalfilterung mit Fluktuationsrateindikatoren wie ATR
- Marktklassifizierung: unterschiedliche Signalgenerationsregeln für verschiedene Marktzustände ((Trend/Schwankungen)
- Stop-Loss-Optimierung: Hinzufügung von intelligenten Stop-Loss-Mechanismen, wie beispielsweise dynamische Stop-Loss-Basis auf unterstützenden Widerstandspunkten
Zusammenfassen
Es handelt sich um eine strukturierte, theoretisch solide und quantitativ ausgerichtete Handelsstrategie. Durch die Analyse der dynamischen Eigenschaften des RSI und die Signalverarbeitung in Verbindung mit modernen mathematischen Methoden ist es möglich, die Markttrends besser zu erfassen. Obwohl es einige Probleme mit der Parameterempfindlichkeit und der Rechenkomplexität gibt, hat die Strategie durch die vernünftige Auswahl und Optimierung von Parametern einen guten Anwendungswert.
/*backtest
start: 2024-11-10 00:00:00
end: 2024-12-09 08:00:00
period: 4h
basePeriod: 4h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © tbiktag
//
// Delta-RSI Oscillator Strategy
//
// A strategy that uses Delta-RSI Oscillator (© tbiktag) as a stand-alone indicator:
// https://www.tradingview.com/script/OXQVFTQD-Delta-RSI-Oscillator/
//
// Delta-RSI is a smoothed time derivative of the RSI, plotted as a histogram
// and serving as a momentum indicator.
//
// Input parameters:
// RSI Length: The timeframe of the RSI that serves as an input to D-RSI.
// Length: The length of the lookback frame used for local regression.
// Polynomial Order: The order of the local polynomial function used to interpolate the RSI.
// Signal Length: The length of a EMA of the D-RSI series that is used as a signal line.
// Trade signals are generated based on three optional conditions:
// - Zero-crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses zero from negative to positive values (bearish otherwise)
// - Signal Line Crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses from below to above the signal line (bearish otherwise)
// - Direction Change: bullish when D-RSI was negative and starts ascending (bearish otherwise)
//
// Since D-RSI oscillator is based on polynomial fitting of the RSI curve, there is also an option
// to filter trade signal by means of the root mean-square error of the fit (normalized by the sample average).
//
//@version=5
strategy(title='Delta-RSI Oscillator Strategy-QuangVersion', shorttitle='D-RSI-Q', overlay=true)
// ---Subroutines---
matrix_get(_A, _i, _j, _nrows) =>
// Get the value of the element of an implied 2d matrix
//input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _i :: integer: row number
// _j :: integer: column number
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in the implied 2d matrix
array.get(_A, _i + _nrows * _j)
matrix_set(_A, _value, _i, _j, _nrows) =>
// Set a value to the element of an implied 2d matrix
//input:
// _A :: array, changed on output: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _value :: float: the new value to be set
// _i :: integer: row number
// _j :: integer: column number
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in the implied 2d matrix
array.set(_A, _i + _nrows * _j, _value)
transpose(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns) =>
// Transpose an implied 2d matrix
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumns :: integer: number of columns in _A
// output:
// _AT :: array: pseudo 2d matrix with implied dimensions: _ncolums x _nrows
var _AT = array.new_float(_nrows * _ncolumns, 0)
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
for j = 0 to _ncolumns - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_AT, matrix_get(_A, i, j, _nrows), j, i, _ncolumns)
_AT
multiply(_A, _B, _nrowsA, _ncolumnsA, _ncolumnsB) =>
// Calculate scalar product of two matrices
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix
// _B :: array: pseudo 2d matrix
// _nrowsA :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumnsA :: integer: number of columns in _A
// _ncolumnsB :: integer: number of columns in _B
// output:
// _C:: array: pseudo 2d matrix with implied dimensions _nrowsA x _ncolumnsB
var _C = array.new_float(_nrowsA * _ncolumnsB, 0)
int _nrowsB = _ncolumnsA
float elementC = 0.0
for i = 0 to _nrowsA - 1 by 1
for j = 0 to _ncolumnsB - 1 by 1
elementC := 0
for k = 0 to _ncolumnsA - 1 by 1
elementC += matrix_get(_A, i, k, _nrowsA) * matrix_get(_B, k, j, _nrowsB)
elementC
matrix_set(_C, elementC, i, j, _nrowsA)
_C
vnorm(_X, _n) =>
//Square norm of vector _X with size _n
float _norm = 0.0
for i = 0 to _n - 1 by 1
_norm += math.pow(array.get(_X, i), 2)
_norm
math.sqrt(_norm)
qr_diag(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns) =>
//QR Decomposition with Modified Gram-Schmidt Algorithm (Column-Oriented)
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumns :: integer: number of columns in _A
// output:
// _Q: unitary matrix, implied dimenstions _nrows x _ncolumns
// _R: upper triangular matrix, implied dimansions _ncolumns x _ncolumns
var _Q = array.new_float(_nrows * _ncolumns, 0)
var _R = array.new_float(_ncolumns * _ncolumns, 0)
var _a = array.new_float(_nrows, 0)
var _q = array.new_float(_nrows, 0)
float _r = 0.0
float _aux = 0.0
//get first column of _A and its norm:
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
array.set(_a, i, matrix_get(_A, i, 0, _nrows))
_r := vnorm(_a, _nrows)
//assign first diagonal element of R and first column of Q
matrix_set(_R, _r, 0, 0, _ncolumns)
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_Q, array.get(_a, i) / _r, i, 0, _nrows)
if _ncolumns != 1
//repeat for the rest of the columns
for k = 1 to _ncolumns - 1 by 1
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
array.set(_a, i, matrix_get(_A, i, k, _nrows))
for j = 0 to k - 1 by 1
//get R_jk as scalar product of Q_j column and A_k column:
_r := 0
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
_r += matrix_get(_Q, i, j, _nrows) * array.get(_a, i)
_r
matrix_set(_R, _r, j, k, _ncolumns)
//update vector _a
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
_aux := array.get(_a, i) - _r * matrix_get(_Q, i, j, _nrows)
array.set(_a, i, _aux)
//get diagonal R_kk and Q_k column
_r := vnorm(_a, _nrows)
matrix_set(_R, _r, k, k, _ncolumns)
for i = 0 to _nrows - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_Q, array.get(_a, i) / _r, i, k, _nrows)
[_Q, _R]
pinv(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns) =>
//Pseudoinverse of matrix _A calculated using QR decomposition
// Input:
// _A:: array: implied as a (_nrows x _ncolumns) matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(_ncolumns-1)]]
// Output:
// _Ainv:: array implied as a (_ncolumns x _nrows) matrix _A = [[row_0],[row_1],...,[row_(_nrows-1)]]
// ----
// First find the QR factorization of A: A = QR,
// where R is upper triangular matrix.
// Then _Ainv = R^-1*Q^T.
// ----
[_Q, _R] = qr_diag(_A, _nrows, _ncolumns)
_QT = transpose(_Q, _nrows, _ncolumns)
// Calculate Rinv:
var _Rinv = array.new_float(_ncolumns * _ncolumns, 0)
float _r = 0.0
matrix_set(_Rinv, 1 / matrix_get(_R, 0, 0, _ncolumns), 0, 0, _ncolumns)
if _ncolumns != 1
for j = 1 to _ncolumns - 1 by 1
for i = 0 to j - 1 by 1
_r := 0.0
for k = i to j - 1 by 1
_r += matrix_get(_Rinv, i, k, _ncolumns) * matrix_get(_R, k, j, _ncolumns)
_r
matrix_set(_Rinv, _r, i, j, _ncolumns)
for k = 0 to j - 1 by 1
matrix_set(_Rinv, -matrix_get(_Rinv, k, j, _ncolumns) / matrix_get(_R, j, j, _ncolumns), k, j, _ncolumns)
matrix_set(_Rinv, 1 / matrix_get(_R, j, j, _ncolumns), j, j, _ncolumns)
//
_Ainv = multiply(_Rinv, _QT, _ncolumns, _ncolumns, _nrows)
_Ainv
norm_rmse(_x, _xhat) =>
// Root Mean Square Error normalized to the sample mean
// _x. :: array float, original data
// _xhat :: array float, model estimate
// output
// _nrmse:: float
float _nrmse = 0.0
if array.size(_x) != array.size(_xhat)
_nrmse := na
_nrmse
else
int _N = array.size(_x)
float _mse = 0.0
for i = 0 to _N - 1 by 1
_mse += math.pow(array.get(_x, i) - array.get(_xhat, i), 2) / _N
_mse
_xmean = array.sum(_x) / _N
_nrmse := math.sqrt(_mse) / _xmean
_nrmse
_nrmse
diff(_src, _window, _degree) =>
// Polynomial differentiator
// input:
// _src:: input series
// _window:: integer: wigth of the moving lookback window
// _degree:: integer: degree of fitting polynomial
// output:
// _diff :: series: time derivative
// _nrmse:: float: normalized root mean square error
//
// Vandermonde matrix with implied dimensions (window x degree+1)
// Linear form: J = [ [z]^0, [z]^1, ... [z]^degree], with z = [ (1-window)/2 to (window-1)/2 ]
var _J = array.new_float(_window * (_degree + 1), 0)
for i = 0 to _window - 1 by 1
for j = 0 to _degree by 1
matrix_set(_J, math.pow(i, j), i, j, _window)
// Vector of raw datapoints:
var _Y_raw = array.new_float(_window, na)
for j = 0 to _window - 1 by 1
array.set(_Y_raw, j, _src[_window - 1 - j])
// Calculate polynomial coefficients which minimize the loss function
_C = pinv(_J, _window, _degree + 1)
_a_coef = multiply(_C, _Y_raw, _degree + 1, _window, 1)
// For first derivative, approximate the last point (i.e. z=window-1) by
float _diff = 0.0
for i = 1 to _degree by 1
_diff += i * array.get(_a_coef, i) * math.pow(_window - 1, i - 1)
_diff
// Calculates data estimate (needed for rmse)
_Y_hat = multiply(_J, _a_coef, _window, _degree + 1, 1)
float _nrmse = norm_rmse(_Y_raw, _Y_hat)
[_diff, _nrmse]
/// --- main ---
degree = input.int(title='Polynomial Order', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar1', defval=2, minval=1)
rsi_l = input.int(title='RSI Length', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar1', defval=21, minval=1, tooltip='The period length of RSI that is used as input.')
window = input.int(title='Length ( > Order)', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar2', defval=21, minval=2)
signalLength = input.int(title='Signal Length', group='Model Parameters:', inline='linepar2', defval=9, tooltip='The signal line is a EMA of the D-RSI time series.')
islong = input.bool(title='Buy', group='Show Signals:', inline='lineent', defval=true)
isshort = input.bool(title='Sell', group='Show Signals:', inline='lineent', defval=true)
showendlabels = input.bool(title='Exit', group='Show Signals:', inline='lineent', defval=true)
buycond = input.string(title='Buy', group='Entry and Exit Conditions:', inline='linecond', defval='Zero-Crossing', options=['Zero-Crossing', 'Signal Line Crossing', 'Direction Change'])
sellcond = input.string(title='Sell', group='Entry and Exit Conditions:', inline='linecond', defval='Zero-Crossing', options=['Zero-Crossing', 'Signal Line Crossing', 'Direction Change'])
endcond = input.string(title='Exit', group='Entry and Exit Conditions:', inline='linecond', defval='Zero-Crossing', options=['Zero-Crossing', 'Signal Line Crossing', 'Direction Change'])
usenrmse = input.bool(title='', group='Filter by Means of Root-Mean-Square Error of RSI Fitting:', inline='linermse', defval=false)
rmse_thrs = input.float(title='RSI fitting Error Threshold, %', group='Filter by Means of Root-Mean-Square Error of RSI Fitting:', inline='linermse', defval=10, minval=0.0) / 100
src = ta.rsi(close, rsi_l)
[drsi, nrmse] = diff(src, window, degree)
signalline = ta.ema(drsi, signalLength)
// Conditions and filters
filter_rmse = usenrmse ? nrmse < rmse_thrs : true
dirchangeup = drsi > drsi[1] and drsi[1] < drsi[2] and drsi[1] < 0.0
dirchangedw = drsi < drsi[1] and drsi[1] > drsi[2] and drsi[1] > 0.0
crossup = ta.crossover(drsi, 0.0)
crossdw = ta.crossunder(drsi, 0.0)
crosssignalup = ta.crossover(drsi, signalline)
crosssignaldw = ta.crossunder(drsi, signalline)
//Signals
golong = (buycond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangeup : buycond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossup : crosssignalup) and filter_rmse
goshort = (sellcond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangedw : sellcond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossdw : crosssignaldw) and filter_rmse
endlong = (endcond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangedw : endcond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossdw : crosssignaldw) and filter_rmse
endshort = (endcond == 'Direction Change' ? dirchangeup : endcond == 'Zero-Crossing' ? crossup : crosssignalup) and filter_rmse
plotshape(golong and islong ? low : na, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.labelup, color=color.new(#2E7C13, 0), size=size.small, title='Buy')
plotshape(goshort and isshort ? high : na, location=location.abovebar, style=shape.labeldown, color=color.new(#BF217C, 0), size=size.small, title='Sell')
plotshape(showendlabels and endlong and islong ? high : na, location=location.abovebar, style=shape.xcross, color=color.new(#2E7C13, 0), size=size.tiny, title='Exit Long')
plotshape(showendlabels and endshort and isshort ? low : na, location=location.belowbar, style=shape.xcross, color=color.new(#BF217C, 0), size=size.tiny, title='Exit Short')
alertcondition(golong, title='Long Signal', message='D-RSI: Long Signal')
alertcondition(goshort, title='Short Signal', message='D-RSI: Short Signal')
alertcondition(endlong, title='Exit Long Signal', message='D-RSI: Exit Long')
alertcondition(endshort, title='Exit Short Signal', message='D-RSI: Exit Short')
strategy.entry('long', strategy.long, when=golong and islong)
strategy.entry('short', strategy.short, when=goshort and isshort)
strategy.close('long', when=endlong and islong)
strategy.close('short', when=endshort and isshort)