1.1 Understand what is a quantitative transaction, a programmatic transaction
Author: Inventors quantify - small dreams, Created: 2016-11-03 20:00:44, Updated: 2017-10-11 10:15:23In this article, we will discuss how to understand quantitative trading, programmatic trading and how to understand quantitative trading.
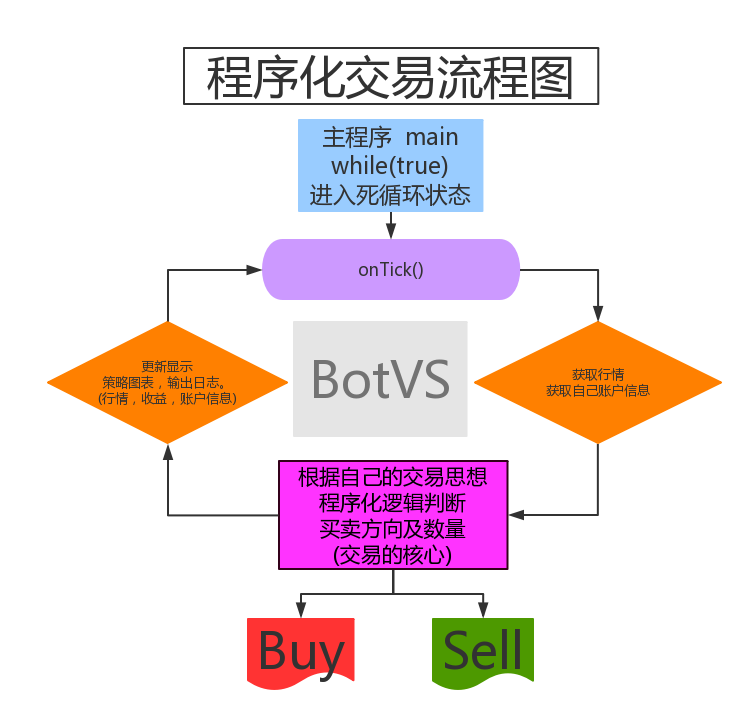
-
The concept
Quantitative trading refers to subjective judgments that are replaced by advanced mathematical models, using computer technology to develop strategies for the multiple volatile probability derivatives that can yield excessive returns from the vast amount of historical data, greatly reducing the impact of investor sentiment fluctuations and avoiding irrational investment decisions in extreme market frenzy or pessimism.
-
Characteristics
Quantitative investing and traditional qualitative investing are essentially the same, both based on theoretical foundations of market inefficiency or weak effectiveness. The difference between the two is that quantitative investment management is a quantitative application of the concept of qualitative thinking, with a stronger tone of data. Quantitative trading has several characteristics:
-
1, Discipline. Decision-making based on the results of the model's operation, rather than on feelings. Discipline can both curb weaknesses in human nature such as greed, fear, and narcissism, and overcome cognitive biases, and can be tracked.
-
2. systematic. It is a multi-layered approach, including large asset allocations, industry selection, and selection of specific assets. It is multi-layered, with the core idea of quantitative investing including macro cycles, market structure, valuation, growth, profitability, analyst profitability forecasts, market sentiment, and many other aspects.
-
3.Successful thinking. Quantitative investing captures the opportunities of mispricing and mispricing through a comprehensive and systematic scanning, so as to find valuation gaps and profit by buying undervalued assets and selling overvalued assets.
-
4. Probability of winning. Quantitative investing continuously extracts and exploits expected patterns of repetition from historical data.
-
The strategy of quantification
Quantitative strategy refers to the use of a computer as a tool to analyze, judge, and make decisions through a fixed set of logic. What does a complete quantification strategy encompass? A complete strategy needs to include inputs, strategy processing logic, and output; strategy processing logic needs to consider factors such as stock selection, timing, position management, and stop-loss.
-
Selected shares Quantitative options are those options that are used to quantify the selection of a certain portfolio in the expectation that the investment portfolio will generate a return that exceeds the big picture. Common options include multi-factor options, industry rotation options, trend tracking options, etc.
- 1 Multi-factor options Multi-factor stock selection is the most classic stock selection method, which uses a series of factors (e.g. market cap, market net, market selling rate, etc.) as the criteria for selecting a stock. Stocks that satisfy these factors are bought and those that do not are sold. Value investors like Buffett, for example, buy stocks with low PE and sell stocks when the PE returns.
- 2 Styles of rolling stock Style rolling stock is an investment that takes advantage of the characteristics of the market style, the market at one time favours large-disc stocks, at another time favours small-disc stocks, if the laws of market switching preference are discovered and the early intervention in the style shift can be obtained.
- 3 Sector rotating stock By discovering these patterns, we can buy the latter after the first one starts and get a higher return, which may produce different characteristics of the sector rotation under different macroeconomic stages and monetary policies.
- 4 Flow of capital The stock market is a voting machine in the short-term, and a weighting machine in the long-term. Short-term investors' trades are a voting act, and the so-called votes are money. If money flows, stocks should go up, if money flows out, stocks should go down.
- 5 Dynamic reversal of stock Dynamic reversal stock selection is a method of building portfolios using the characteristics of the investor's investment behavior. The so-called anti-corporeal theory of Soros emphasizes that the positive feedback effect of rising prices will cause investors to continue to buy, which is the basic basis of dynamic reversal stock selection. Dynamic reversal is that the previously strong stock continues to be strong for some time to come.
- 6 Strategies for tracking trends When the stock price is bought when there is an uptrend, and sold when there is a downtrend, it is essentially a chase-and-kill strategy, and many markets have more trends due to the herd-use. If you can control the amount of good losses when you can hold on to the trend, you can get additional gains in the long run.
-
When to Choose Quantification refers to the use of a quantified method to determine the point of purchase and sale. If the judgment is up, then buy hold; if the judgment is down, then sell clear; if the judgment is shocked, then high and low suck. Commonly used timing methods include: trend quantification, market sentiment quantification, effective capital quantification, SVM quantification, and so on.
-
Position management Position management is the technique of deciding how to segment the entry and stop the exit of a portfolio of stocks when you decide to invest in it. Commonly used positions management methods include: pipeline position management, rectangular position management, pyramid position management, etc.
-
Stop the damage Stop-loss, as the name implies, is the timely sale of shares at the time of earnings and profit; stop-loss, the timely sale of shares at the time of stock losses and avoid greater losses. Timely stop-loss is an effective way to get steady returns.
-
Strategy life cycle A strategy often goes through several stages of idea generation, implementation, testing, execution, and failure.
-
Creating ideas Anyone can come up with a strategic idea at any time, based on their own investment experience or the success of others.
-
Implementing the strategy What does a complete quantitative strategy contain? What does a complete quantitative strategy contain? What does a quantitative strategy contain?
-
Testing policy After the strategy is implemented, it is necessary to review the historical data and test the simulated transactions, which is also a key link before the real-world, to filter out the quality strategies and eliminate the inferior ones.
-
Real-time trading Investing money, taking risks and earning returns through the effectiveness of market testing strategies.
-
Strategy Failed The market is volatile and requires real-time monitoring of the effectiveness of the strategy, and if the strategy fails, the strategy needs to be stopped or further optimized.
-
Potentially risky editors
Quantitative trading is generally tested by means such as big data simulation testing and simulation operations, and positions and funds are allocated according to certain risk management algorithms to minimize risk and maximize returns, but there are often certain potential risks, including:
-
1, the integrity of historical data; incomplete market data may lead to model mismatches with market data; the market data itself may change in style and may also lead to model failures, such as transaction liquidity, price fluctuation magnitude, price fluctuation frequency, etc., which is currently difficult to overcome in quantitative trading.
-
2. The model design does not take into account the position and the allocation of funds, and there is no safe risk assessment and precautions, which can lead to mismatches between funds, positions and models, and the phenomenon of bursting.
-
Network disruptions and hardware failures can also affect quantitative transactions.
-
4 The risk posed by competitive trading phenomena in homogeneous models.
-
5. The unpredictable risks associated with a single investment variety.
Strategies for avoiding or minimizing the potential risk of quantitative transactions include: ensuring the integrity of historical data; adjusting model parameters online; choosing model types online; monitoring and avoiding risks online.
Source from Baidu
- 2.7 Use of indicators
- 2.5 Interface showing API policy interaction
- 2.4 Get order information, cancel orders, and get all unfinished orders
- 2.3 List of market prices
- 2.2 Lower price lists
- 2.1 Use the API to access account information, market data, K-line data, and market depth
- Other functions
- 1.3.4 Robots and strategies
- 1.3.2 Getting to Know the Trustee
- 1.3.1 Overview and architecture of the main interface
- Quantified must read: What exactly is Tick data and why is it so hard to find reliable transaction data?
- Why is there no poloniiex option???
- The Alpha Dog's Tricks: Monte Carlo algorithm, read it and you'll understand!
- Can you run over a gorilla with an SVM vector machine?
- Simple SVM classification algorithms
- There is a problem with the real disk tick.
- Interfaces for trading software
- Modifications of Python 2.x.x with Python 3.x.x & Methods of converting Python 2.x.x to Python 3.x.x
- Ice and Fire: Live and retest
- Dry goods - how is high-frequency trading making money?
teacherMaYou're being rude, brother.
gaojinha OK
A leaf of knowledge nice!
McGee !!!
indexroot GOOD
:) 201807140321