Easy introduction to web3 development based on Ethereum with FMZ
Author: Inventors quantify - small dreams, Created: 2023-03-28 13:32:48, Updated: 2024-11-11 22:28:24“fromBlock” : fromBlock, “toBlock” : toBlock, “address” : self.contractAddress, “topics” : [self.eventHash] } // Log(“fromBlockNumber:”, self.fromBlockNumber, “, currBlockNumber:”, currBlockNumber, “#FF0000”)
var logs = exchange.IO("api", "eth", "eth_getLogs", params)
if (!logs) {
return
}
for (var i = 0; i < logs.length; i++) {
if (toAmount(logs[i].blockNumber, 0) > self.latestBlockNumber) {
/* TODO: test
if (self.isFirst) {
self.firstBlockNumber = toAmount(logs[i].blockNumber, 0)
Log("firstBlockNumber:", self.firstBlockNumber)
self.isFirst = false
}
*/
callBack(logs[i])
}
}
self.latestBlockNumber = currBlockNumber
self.fromBlockNumber = self.latestBlockNumber - 1
}
self.latestBlockNumber = self.getBlockNumber()
self.fromBlockNumber = self.latestBlockNumber - 1
return self
}
var listener = null function main() { var event = “Transfer(address,address,uint256)” var contractAddress = “0xdac17f958d2ee523a2206206994597c13d831ec7” var decimals = exchange.IO("api", contractAddress, “decimals”) Log(exchange.IO("api", contractAddress, “name”), " decimals:", decimals)
listener = addEventListener(contractAddress, event, function(log) {
var fromAddress = "0x" + exchange.IO("encodePacked", "address", log.topics[1])
var toAddress = "0x" + exchange.IO("encodePacked", "address", log.topics[2])
Log("Transfer:", fromAddress, "->", toAddress, ", value:", toAmount(log.data, decimals), ", blockNumber:", toAmount(log.blockNumber, 0))
/* TODO: test
arrLog.push(log)
*/
})
while (true) {
listener.run()
Sleep(5000)
}
}
/* TODO: test This is a list of all the different ways var arrLog = [] is credited in the database. function onexit ((() { Log (the log that completes the run, the log that verifies the run) var firstBlockNumber = listener.firstBlockNumber var endBlockNumber = listener.latestBlockNumber is the last block number
Log("getLogs, from:", firstBlockNumber, " -> to:", endBlockNumber)
var fromBlock = "0x" + (firstBlockNumber).toString(16)
var toBlock = "0x" + (endBlockNumber).toString(16)
var params = {
"fromBlock" : fromBlock,
"toBlock" : toBlock,
"topics" : ["0xddf252ad1be2c89b69c2b068fc378daa952ba7f163c4a11628f55a4df523b3ef"],
"address" : "0xdac17f958d2ee523a2206206994597c13d831ec7"
}
var logs = exchange.IO("api", "eth", "eth_getLogs", params)
Log("arrLog:", arrLog.length)
Log("logs:", logs.length)
if (arrLog.length != logs.length) {
Log("长度不等!")
return
}
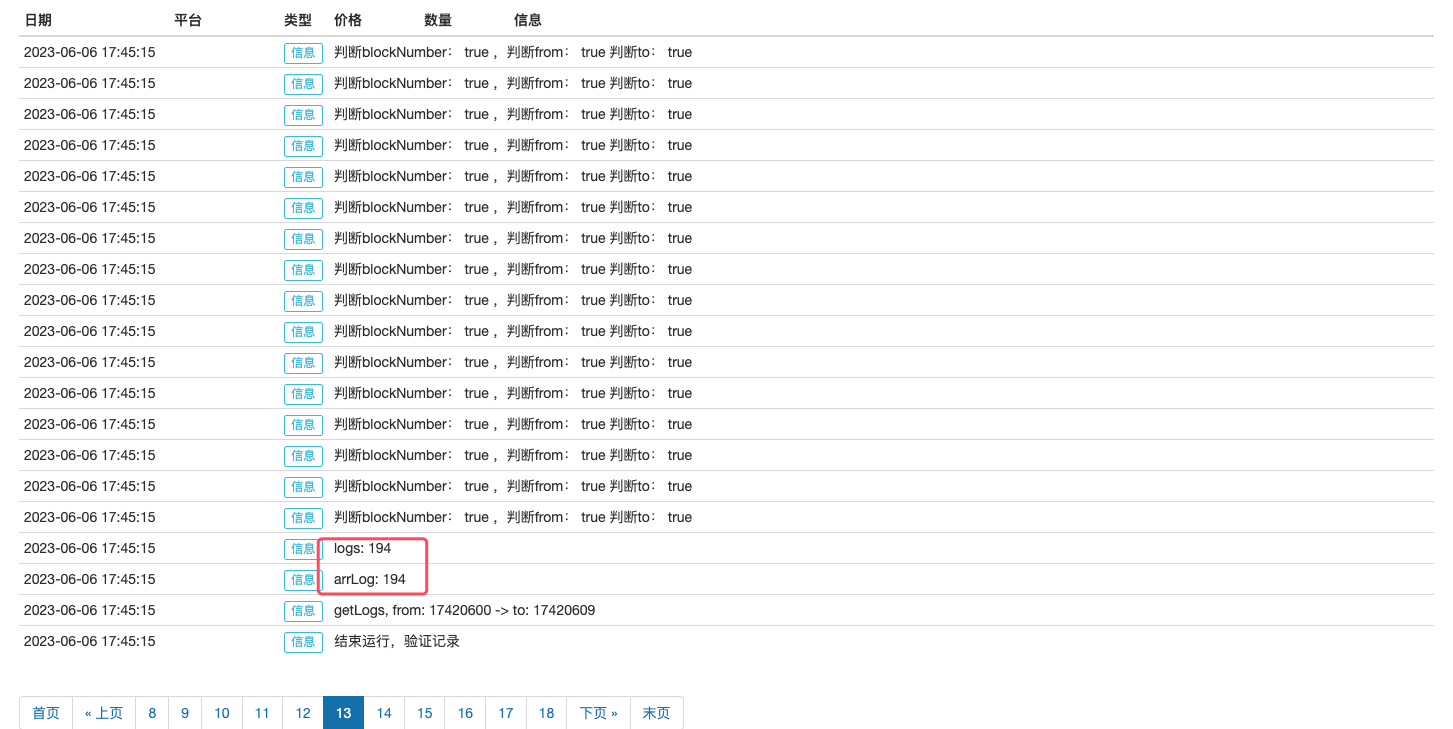
for (var i = 0; i < arrLog.length; i++) {
Log("判断blockNumber:", logs[i].blockNumber == arrLog[i].blockNumber, ",判断from:", logs[i].topics[1] == arrLog[i].topics[1],
"判断to:", logs[i].topics[2] == arrLog[i].topics[2])
}
} */
实盘运行:

对于执行结果,代码中也编写了验证部分(TODO: test)。经过简单验证可以看到持续监控USDT合约的```Transfer```事件并且记录数据,用这个数据和一次性获取的事件数据对比可以观察出数据一致:
### 事件过滤
在上一节课程「监听合约事件」的基础上,我们拓展一下,在监听的过程中增加过滤器,监听指定地址的转入转出。当智能合约创建日志时(即释放事件),日志数据中```topics```最多包含4条信息。所以我们设计一个过滤规则,以```[[A1, A2, ...An], null, [C1], D]```为例子。
1、```[A1, A2, ...An]```对应```topics[0]```位置的数据。
2、```null```对应```topics[1]```位置的数据。
3、```[C1]```对应```topics[2]```位置的数据。
4、```D```对应```topics[3]```位置的数据。
- 如果条件结构中的元素设置```null```表示不被过滤,例如```null```对应```topics[1]```,任何值都匹配。
- 如果条件结构中的元素设置单个值表示该位置必须匹配,例如```[C1]```对应```topics[2]```或者```D```对应```topics[3]```,不匹配的日志被过滤。
- 如果条件结构中的元素是一个数组,表示数组中的元素至少有一个要匹配,例如```[A1, A2, ...An]```对应```topics[0]```,```[A1, A2, ...An]```中有任意一个和```topics[0]```匹配,则日志不会被过滤。
**监听交易所的USDT转账**
监控从币安交易所转出、转入币安交易所```USDT```的交易:
```javascript
function toAmount(s, decimals) {
return Number((BigDecimal(BigInt(s)) / BigDecimal(Math.pow(10, decimals))).toString())
}
function toInnerAmount(n, decimals) {
return (BigDecimal(n) * BigDecimal(Math.pow(10, decimals))).toFixed(0)
}
function addEventListener(contractAddress, event, callBack) {
var self = {}
self.eventHash = "0x" + Encode("keccak256", "string", "hex", event)
self.contractAddress = contractAddress
self.latestBlockNumber = 0
self.fromBlockNumber = 0
self.firstBlockNumber = 0
self.filters = []
self.setFilter = function(filterCondition) {
if (filterCondition.length > 4) {
throw "filterCondition error"
}
self.filters.push(filterCondition)
Log("设置过滤条件:", filterCondition)
}
self.getTokenBalanceOfWallet = function(walletAddress, tokenAddress, tokenDecimals) {
var balance = exchange.IO("api", tokenAddress, "balanceOf", walletAddress)
if (balance) {
return toAmount(balance, tokenDecimals)
}
return null
}
self.getBlockNumber = function() {
var maxTry = 10
for (var i = 0; i < maxTry; i++) {
var ret = exchange.IO("api", "eth", "eth_blockNumber")
if (ret) {
return toAmount(ret, 0)
}
Sleep(5000)
}
throw "getBlockNumber failed"
}
self.run = function() {
var currBlockNumber = self.getBlockNumber()
var fromBlock = "0x" + self.fromBlockNumber.toString(16)
var toBlock = "0x" + currBlockNumber.toString(16)
var params = {
"fromBlock" : fromBlock,
"toBlock" : toBlock,
"address" : self.contractAddress,
"topics" : [self.eventHash]
}
var logs = exchange.IO("api", "eth", "eth_getLogs", params)
if (!logs) {
return
}
for (var i = 0; i < logs.length; i++) {
if (toAmount(logs[i].blockNumber, 0) > self.latestBlockNumber) {
// 检查过滤条件,设置了过滤条件则执行判断
if (self.filters.length != 0) {
// 初始过滤标记
var isFilter = true
// 遍历过滤条件设置
for (var j = 0; j < self.filters.length; j++) {
// 取一个过滤设置,例如:[[A1, A2, ...An], null, [C1], D]
var cond = self.filters[j]
// 遍历这个过滤设置
var final = true
for (var topicsIndex = 0; topicsIndex < cond.length; topicsIndex++) {
// 拿到这个过滤设置中的某一个条件,如果是第一个条件:即要和topics[0]对比的数据
var condValue = cond[topicsIndex]
// 日志中的数据
if (topicsIndex > logs[i].topics.length - 1) {
continue
}
var topicsEleValue = logs[i].topics[topicsIndex]
// 如果是Transfer事件,需要处理from和to
if (logs[i].topics[0] == "0xddf252ad1be2c89b69c2b068fc378daa952ba7f163c4a11628f55a4df523b3ef") {
if (topicsIndex == 1 || topicsIndex == 2) {
topicsEleValue = "0x" + exchange.IO("encodePacked", "address", topicsEleValue)
}
}
// 如果condValue类型是数组,表示该位置的对比条件有多个,多个条件对比是逻辑或关系
if (Array.isArray(condValue) && condValue.length > 1) {
// 判断 condValue[0] == topicsEleValue || condValue[1] == topicsEleValue
final = final && condValue.some(element => element === topicsEleValue)
}else if (condValue === null) {
final = final && true
} else {
final = final && (condValue === topicsEleValue)
}
}
if (final) {
isFilter = false
}
}
if (isFilter) {
continue
}
}
callBack(logs[i])
}
}
self.latestBlockNumber = currBlockNumber
self.fromBlockNumber = self.latestBlockNumber - 1
}
self.latestBlockNumber = self.getBlockNumber()
self.fromBlockNumber = self.latestBlockNumber - 1
return self
}
var listener = null
function main() {
// 初始清理日志
LogReset(1)
LogProfitReset()
var event = "Transfer(address,address,uint256)" // 监听事件
var contractAddress = "0xdac17f958d2ee523a2206206994597c13d831ec7" // USDT合约地址
var decimals = exchange.IO("api", contractAddress, "decimals") // 获取USDT token的精度信息
var accountBinanceAddress = "0x28C6c06298d514Db089934071355E5743bf21d60" // Binance 热钱包地址
accountBinanceAddress = accountBinanceAddress.toLowerCase() // 地址处理为小写
Log(exchange.IO("api", contractAddress, "name"), " decimals:", decimals)
// 创建监听对象
listener = addEventListener(contractAddress, event, function(log) {
var fromAddress = "0x" + exchange.IO("encodePacked", "address", log.topics[1])
var toAddress = "0x" + exchange.IO("encodePacked", "address", log.topics[2])
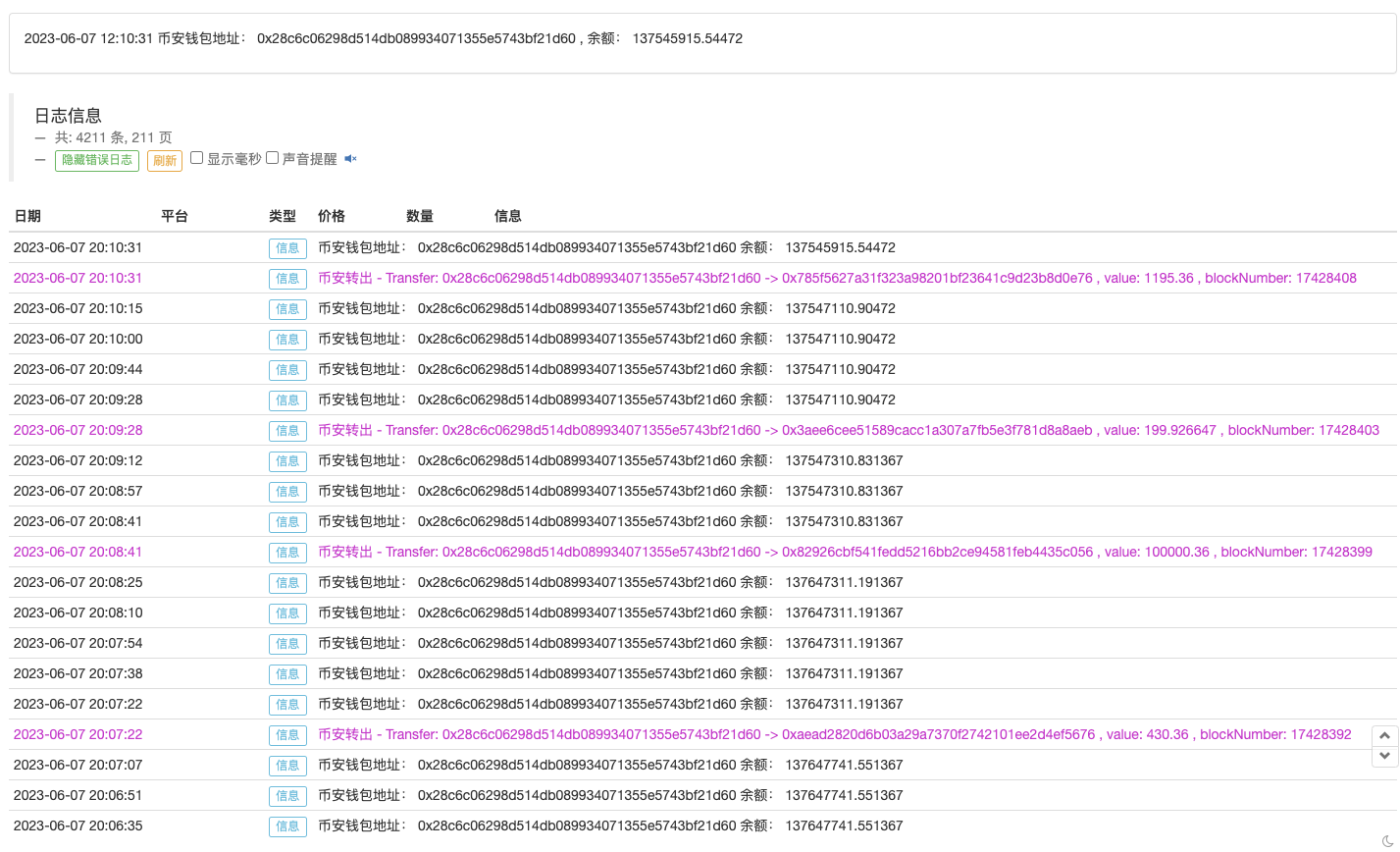
if (fromAddress == accountBinanceAddress) {
Log("币安转出 - ", " Transfer:", fromAddress, "->", toAddress, ", value:", toAmount(log.data, decimals), ", blockNumber:", toAmount(log.blockNumber, 0), "#CD32CD")
} else if (toAddress == accountBinanceAddress) {
Log("转入币安 - ", " Transfer:", fromAddress, "->", toAddress, ", value:", toAmount(log.data, decimals), ", blockNumber:", toAmount(log.blockNumber, 0), "#FF0000")
}
})
// 设置事件过滤
listener.setFilter([null, accountBinanceAddress, null]) // Binance -> USDT
listener.setFilter([null, null, accountBinanceAddress]) // USDT -> Binance
var preBalance = 0
while (true) {
listener.run()
var balance = listener.getTokenBalanceOfWallet(accountBinanceAddress, contractAddress, decimals)
if (balance) {
var direction = ""
if (preBalance != 0 && preBalance > balance) {
direction = " ↓ " + (preBalance - balance) + "#CD32CD"
} else if (preBalance != 0 && preBalance < balance) {
direction = " ↑ " + (balance - preBalance) + "#FF0000"
}
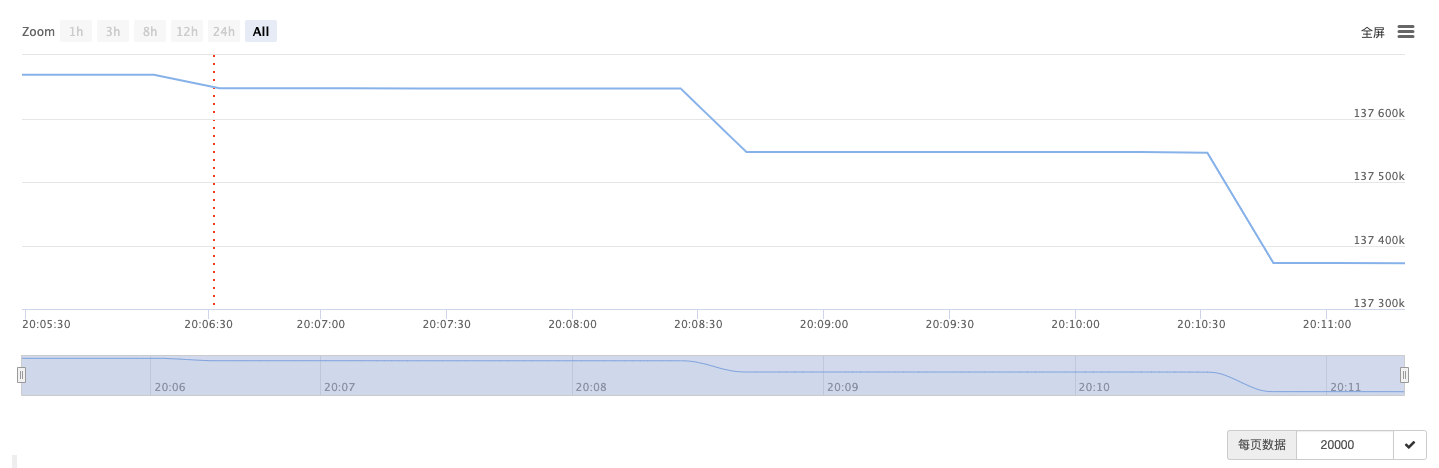
Log("币安钱包地址:", accountBinanceAddress, " 余额:", balance, direction)
LogProfit(balance, "&") // 只画图,不打印日志
preBalance = balance
}
LogStatus(_D(), "币安钱包地址:", accountBinanceAddress, ", 余额:", balance)
Sleep(5000 * 3)
}
}
The above code runs on the hard disk:
In this section, we show how to design an event filter and use it to listen in on Bitcoin exchange hot wallets.USDTTransactions. You can modify or extend this paradigm to listen to any event you're interested in and see if you can.smart moneyWhat new deals have been made?NFTWhat are the new projects that the dam has flooded and so on.
Unit conversion
In many Ethereum-related calculations, the numerical value exceeds theJavaScriptMaximum safe integers in the language. Therefore, there is a need for some methods to handle large numbers on inventor quantized trading platforms, which we have also used specifically in previous courses, without explaining in detail.
PrintingJavaScriptThe maximum safe integer defined in the language is:
function main() {
Log("Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER:", Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER)
}
The results:
Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER: 9007199254740991
BigInt
The smallest unit defined in Ethereum is1wei, defined1Gweiis equal to1000000000 wei。1GweiIn Ethereum-related calculations, it's not really a big number, some data are much bigger than it.Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER: 9007199254740991。
Inventors quantify trading platforms, we use platforms that have a lot of data.BigIntObjects represent these super-large integer data. Use constructor functions.BigInt()to constructBigIntObjects. Use numeric, hexadecimal numeric strings as constructions of argumentsBigIntObjects ─ useBigIntThe objecttoString()The method outputs the data represented by the object in the form of a string.
BigIntOperations supported by objects:
- The multiplication operation:
+ - Subtraction from the law:
- - The multiplication operation:
* - Except for the calculation:
/ - This is the first time I've seen it.
% - I'm going to do the math:
**
See the following code examples:
function main() {
// 1Gwei的十进制表示
var oneGwei = 1000000000
// 1Gwei的十进制转换为十六进制表示
var oneGweiForHex = "0x" + oneGwei.toString(16)
Log("oneGwei : ", oneGwei)
Log("oneGweiForHex : ", oneGweiForHex)
// 构造BigInt对象
Log("1Gwei / 1Gwei : ", (BigInt(oneGwei) / BigInt(oneGweiForHex)).toString(10))
Log("1Gwei * 1Gwei : ", (BigInt(oneGwei) * BigInt(oneGweiForHex)).toString(10))
Log("1Gwei - 1Gwei : ", (BigInt(oneGwei) - BigInt(oneGweiForHex)).toString(10))
Log("1Gwei + 1Gwei : ", (BigInt(oneGwei) + BigInt(oneGweiForHex)).toString(10))
Log("(1Gwei + 1) % 1Gwei : ", (BigInt(oneGwei + 1) % BigInt(oneGweiForHex)).toString(10))
Log("1Gwei ** 2 : ", (BigInt(oneGwei) ** BigInt(2)).toString(10))
Log("100 的平方根 : ", (BigInt(100) ** BigFloat(0.5)).toString(10))
Log("Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER : ", BigInt(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER).toString(10))
Log("Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER * 2 : ", (BigInt(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER) * BigInt("2")).toString(10))
}
Debugging tool testing:
2023-06-08 11:39:50 信息 Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER * 2 : 18014398509481982
2023-06-08 11:39:50 信息 Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER : 9007199254740991
2023-06-08 11:39:50 信息 100 的平方根 : 10
2023-06-08 11:39:50 信息 1Gwei ** 2 : 1000000000000000000
2023-06-08 11:39:50 信息 (1Gwei + 1) % 1Gwei : 1
2023-06-08 11:39:50 信息 1Gwei + 1Gwei : 2000000000
2023-06-08 11:39:50 信息 1Gwei - 1Gwei : 0
2023-06-08 11:39:50 信息 1Gwei * 1Gwei : 1000000000000000000
2023-06-08 11:39:50 信息 1Gwei / 1Gwei : 1
2023-06-08 11:39:50 信息 oneGweiForHex : 0x3b9aca00
2023-06-08 11:39:50 信息 oneGwei : 1000000000
BigFloat
BigFloatObjects andBigIntObjects are used similarly, to represent floating point numbers with larger numerical values, and also support multiplication operations.BigFloatObject supporttoFixed()How to do it.
See the following code examples:
function main() {
var pi = 3.14
var oneGwei = "1000000000"
var oneGweiForHex = "0x3b9aca00"
Log("pi + oneGwei : ", (BigFloat(pi) + BigFloat(oneGwei)).toFixed(2))
Log("pi - oneGweiForHex : ", (BigFloat(pi) - BigFloat(oneGweiForHex)).toFixed(2))
Log("pi * 2.0 : ", (BigFloat(pi) * BigFloat(2.0)).toFixed(2))
Log("pi / 2.0 : ", (BigFloat(pi) / BigFloat(2.0)).toFixed(2))
}
Debugging tool testing:
2023-06-08 13:56:44 信息 pi / 2.0 : 1.57
2023-06-08 13:56:44 信息 pi * 2.0 : 6.28
2023-06-08 13:56:44 信息 pi - oneGweiForHex : -999999996.86
2023-06-08 13:56:44 信息 pi + oneGwei : 1000000003.14
BigDecimal
BigDecimalObjects are compatible with integer values, floating point values, support forBigIntThe object.BigFloatObject initialization, also supports addition subtraction multiplication operations.
See the following code examples:
function main() {
var pi = 3.1415
var oneGwei = 1000000000
var oneGweiForHex = "0x3b9aca00"
Log("pi : ", BigDecimal(pi).toFixed(2))
Log("oneGwei : ", BigDecimal(oneGwei).toString())
Log("oneGweiForHex : ", BigDecimal(BigInt(oneGweiForHex)).toString())
Log("BigInt(oneGwei) : ", BigDecimal(BigInt(oneGwei)).toString())
Log("BigFloat(pi) : ", BigDecimal(BigFloat(pi)).toFixed(4))
Log("oneGwei + pi : ", (BigDecimal(oneGwei) + BigDecimal(pi)).toString())
Log("oneGwei - pi : ", (BigDecimal(oneGwei) - BigDecimal(pi)).toString())
Log("2.0 * pi : ", (BigDecimal(2.0) * BigDecimal(pi)).toString())
Log("pi / pi : ", (BigDecimal(pi) / BigDecimal(pi)).toString())
}
The debugger tool runs on:
2023-06-08 14:52:53 信息 pi / pi : 1
2023-06-08 14:52:53 信息 2.0 * pi : 6.283
2023-06-08 14:52:53 信息 oneGwei - pi : 999999996.8585
2023-06-08 14:52:53 信息 oneGwei + pi : 1000000003.1415
2023-06-08 14:52:53 信息 BigFloat(pi) : 3.1415
2023-06-08 14:52:53 信息 BigInt(oneGwei) : 1e+9
2023-06-08 14:52:53 信息 oneGweiForHex : 1e+9
2023-06-08 14:52:53 信息 oneGwei : 1e+9
2023-06-08 14:52:53 信息 pi : 3.14
Unit conversion
The following two functions:toAmount()、toInnerAmount()We've used these two functions many times in previous lessons, mainly for data precision conversion.
function toAmount(s, decimals) {
return Number((BigDecimal(BigInt(s)) / BigDecimal(Math.pow(10, decimals))).toString())
}
function toInnerAmount(n, decimals) {
return (BigDecimal(n) * BigDecimal(Math.pow(10, decimals))).toFixed(0)
}
toAmount()So the function is going to change a variable.sThe precision parametersdecimalsIn actual web3 development, it is often necessary to process some hexadecimal data on chains.
So we've seen this in our previous courses, and we've seen this in our previous courses, and we've seen this in our previous courses, and we've seen this in our previous courses, and we've seen this in our previous classes, and we've seen this in our previous classes, and we've seen this in our previous classes, and we've seen this in our previous classes, and we've seen this in our previous classes.Transfer(address,address,uint256)In the eventdataThe field data:
{
"data": "0x00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001c1a55000000000",
"topics": ["0xddf252ad1be2c89b69c2b068fc378daa952ba7f163c4a11628f55a4df523b3ef", "0x0000000000000000000000006b75d8af000000e20b7a7ddf000ba900b4009a80", "0x000000000000000000000000bcb095c1f9c3dc02e834976706c87dee5d0f1fb6"],
"transactionHash": "0x27f9bf5abe3148169b4b85a83e1de32bd50eb81ecc52e5af006157d93353e4c4",
"transactionIndex": "0x0",
"removed": false,
"address": "0xc02aaa39b223fe8d0a0e5c4f27ead9083c756cc2",
"blockHash": "0x847be24a7b159c292bda030a011dfec89487b70e71eed486969b032d6ef04bad",
"blockNumber": "0x109b1cc",
"logIndex": "0x0"
}
Processing of data"data": "0x00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001c1a55000000000"This time, usetoAmount()Functions. This kind of processing design can be very useful.dataThe field data is converted to a readable value.
function toAmount(s, decimals) {
return Number((BigDecimal(BigInt(s)) / BigDecimal(Math.pow(10, decimals))).toString())
}
function main() {
var data = "0x00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001c1a55000000000"
Log(toAmount(data, 18)) // 打印出 0.12656402755905127
}
One ETH token we know is1e18 weiSo if we get aweiData by unit126564027559051260How to convert to ETH tokens?
UsetoAmount(, 18)The function can be converted very easily.toInnerAmount()So the function istoAmount()Reverse operation of the function (according to precision, magnification) makes it convenient to convert data using these two functions.
Note that the integer security range in the JavaScript language isNumber.MAX_SAFE_INTEGERThe following example illustrates a problem that is more subtle when converting data:
function toAmount(s, decimals) {
return Number((BigDecimal(BigInt(s)) / BigDecimal(Math.pow(10, decimals))).toString())
}
function toInnerAmount(n, decimals) {
return (BigDecimal(n) * BigDecimal(Math.pow(10, decimals))).toFixed(0)
}
function main() {
var amount = 0.01
var innerAmount = Number(toInnerAmount(amount, 18))
Log("Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER:", Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER) // 9007199254740991
Log("innerAmount:", innerAmount) // 10000000000000000
Log("typeof(innerAmount):", typeof(innerAmount), ", innerAmount:", innerAmount)
// 十进制数值 10000000000000000 -> 十六进制数值 0x2386f26fc10000
Log("转换", innerAmount, "为十六进制:", innerAmount.toString(16))
Log("转换", BigInt(10000000000000000).toString(10), "为十六进制:", BigInt(10000000000000000).toString(16))
Log("0x" + BigInt(10000000000000000).toString(16), "转换为10进制:", toAmount("0x" + BigInt(10000000000000000).toString(16), 0))
}
It can be run in the following debug tools:
2023-06-15 16:21:40 信息 0x2386f26fc10000 转换为10进制: 10000000000000000
2023-06-15 16:21:40 信息 转换 10000000000000000 为十六进制: 2386f26fc10000
2023-06-15 16:21:40 信息 转换 10000000000000000 为十六进制: 10000000000000000
2023-06-15 16:21:40 信息 typeof(innerAmount): number , innerAmount: 10000000000000000
2023-06-15 16:21:40 信息 innerAmount: 10000000000000000
2023-06-15 16:21:40 信息 Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER: 9007199254740991
The following is a list of some of the most common causes of blindness:
Log("转换", innerAmount, "为十六进制:", innerAmount.toString(16))
The log output corresponding to this code line is:转换 10000000000000000 为十六进制: 10000000000000000The reason for this is that the number of translations is not correct.Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER。
But when the decimal is within the safe range, it's less thanNumber.MAX_SAFE_INTEGERI'm not going to lie.toString(16)Functional conversion is normal, for example:
function main() {
var value = 1000
Log("把value转换为十六进制:", "0x" + value.toString(16)) // 0x3e8
Log("把0x3e8转换为十进制:", Number("0x3e8")) // 1000
}
In the blockchain space, even0.01The exchange rate for ETH is:weiThe numerical value of the unit10000000000000000It's going to go beyondNumber.MAX_SAFE_INTEGERIn the case of the following, the safest conversion for such situations is:BigInt(10000000000000000).toString(16)。
Simulated Calling
It's a great way to get started with Ethereum and get started with the process of executing transactions and calling smart contracts.WriteMethods consume a certain amount of gas and sometimes have a risk of failure. It is important to know which transactions are likely to fail before sending transactions or calling them.
eth_call
Ethereum's RPC methodeth_call: can simulate a transaction and return possible transaction outcomes, but does not actually execute the transaction on the blockchain.
eth_callThe method has two parameters, the first parameter is a dictionary structure, and the second one is a dictionary structure.transactionObject:
// transactionObject
{
"from" : ..., // The address from which the transaction is sent
"to" : ..., // The address to which the transaction is addressed
"gas" : ..., // The integer of gas provided for the transaction execution
"gasPrice" : ..., // The integer of gasPrice used for each paid gas encoded as hexadecimal
"value" : ..., // The integer of value sent with this transaction encoded as hexadecimal
"data" : ..., // The hash of the method signature and encoded parameters. For more information, see the Contract ABI description in the Solidity documentation
}
The second parameter isblockNumberLabels can be passed:latest/pending/earliestAnd so on and so forth.
/* blockNumber
The block number in hexadecimal format or the string latest, earliest, pending, safe or
finalized (safe and finalized tags are only supported on Ethereum, Gnosis, Arbitrum,
Arbitrum Nova and Avalanche C-chain), see the default block parameter description in
the official Ethereum documentation
*/
The next thing we'll do is use tokens.DAIThe smart contract methodologyapprove、transferThe following test environment is the Ethereum network.
Approve the analogue call
The ERC20 contractsapproveThe method is familiar to all of us, and we have practiced it in previous courses. Since ERC20 contracts are built into FMZ platform ABI, you do not need to register the ABI for which you want to simulate the call.
function main() {
var contractAddressUniswapV3SwapRouterV2 = "0x68b3465833fb72A70ecDF485E0e4C7bD8665Fc45"
var contractAddress_DAI = "0x6b175474e89094c44da98b954eedeac495271d0f"
var wallet = exchange.IO("address")
// encode approve
var data = exchange.IO("encode", contractAddress_DAI, "approve(address,uint256)",
contractAddressUniswapV3SwapRouterV2, "0xffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff")
Log("ERC20 token DAI approve encode, data:", data)
var transactionObject = {
"from" : wallet,
"to" : contractAddress_DAI,
// "gasPrice" : "0x" + parseInt("21270894680").toString(16),
// "gas" : "0x" + parseInt("21000").toString(16),
"data" : "0x" + data,
}
var blockNumber = "latest"
var ret = exchange.IO("api", "eth", "eth_call", transactionObject, blockNumber)
Log("ret:", ret)
}
The code in the example will first beapprove(address,uint256)The method, the parameters are encoded.approveParameter value of method0xffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffIndicates maximum number of authorizations. Authorization to smart contract, address0x68b3465833fb72A70ecDF485E0e4C7bD8665Fc45That is,Uniswap V3The routing contract. Last call of the Ethereum RPC methodeth_callSimulations. You can seetransactionObjectIn the parametersgasPrice、gasThe fields can be omitted.
Debugging tool running, simulated call approve method authorization successful (but not actually authorized):
2023-06-09 11:58:39 信息 ret: 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001
2023-06-09 11:58:39 信息 ERC20 token DAI approve encode, data: 095ea7b300000000000000000000000068b3465833fb72a70ecdf485e0e4c7bd8665fc45ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff
We can also simulate some failure scenarios, and when we adjust, we can simulate some failure scenarios.gasPriceandgasThe parameter returns an error if the ETH in the wallet is not enough to pay for gas:
insufficient funds
When the gas price is set too low, the error message is:
intrinsic gas too low: have 21000, want 21944 (supplied gas 21000)
Simulated call transfer
For the ERC20transferThe method we are not familiar with is to transfer ERC20 tokens to a wallet address, and we try to simulate transferring 1000 DAI to V.
function toInnerAmount(n, decimals) {
return (BigDecimal(n) * BigDecimal(Math.pow(10, decimals))).toFixed(0)
}
function main() {
var walletVitalik = "0xd8dA6BF26964aF9D7eEd9e03E53415D37aA96045"
var contractAddress_DAI = "0x6b175474e89094c44da98b954eedeac495271d0f"
var wallet = exchange.IO("address")
// 转账给V神
var decimals_DAI = exchange.IO("api", contractAddress_DAI, "decimals")
var transferAmount = toInnerAmount(1000, decimals_DAI)
Log("转账金额:", 1000, "DAI, 使用 toInnerAmount 转换为:", transferAmount)
// encode transfer
var data = exchange.IO("encode", contractAddress_DAI, "transfer(address,uint256)",
walletVitalik, transferAmount)
var transactionObject = {
"from" : wallet,
"to" : contractAddress_DAI,
"data" : "0x" + data,
}
var blockNumber = "latest"
var ret = exchange.IO("api", "eth", "eth_call", transactionObject, blockNumber)
return ret
}
Since my test wallet doesn't have a DAI token, the results I expected from running the debugger were wrong:
execution reverted: Dai/insufficient-balance
Check out the address of this wallet of V-God:0xd8dA6BF26964aF9D7eEd9e03E53415D37aA96045So let's align the transfer direction of the analogue call, and let's say that V God is transferring 1000 DAI to us.
I've changed the code, and I've written a comment in the place where it was changed:
function toInnerAmount(n, decimals) {
return (BigDecimal(n) * BigDecimal(Math.pow(10, decimals))).toFixed(0)
}
function main() {
var walletVitalik = "0xd8dA6BF26964aF9D7eEd9e03E53415D37aA96045"
var contractAddress_DAI = "0x6b175474e89094c44da98b954eedeac495271d0f"
var wallet = exchange.IO("address")
var decimals_DAI = exchange.IO("api", contractAddress_DAI, "decimals")
var transferAmount = toInnerAmount(1000, decimals_DAI)
Log("转账金额:", 1000, "DAI, 使用 toInnerAmount 转换为:", transferAmount)
// encode transfer
var data = exchange.IO("encode", contractAddress_DAI, "transfer(address,uint256)",
wallet, transferAmount) // 使用wallet变量作为参数,转账接收方地址改为我自己
var transactionObject = {
"from" : walletVitalik, // 使用walletVitalik变量作为from字段的值,模拟这个调用是由V神钱包地址发出
"to" : contractAddress_DAI,
"data" : "0x" + data,
}
var blockNumber = "latest"
var ret = exchange.IO("api", "eth", "eth_call", transactionObject, blockNumber)
Log(ret)
}
Debugging tool testing:
2023-06-09 13:34:31 信息 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001
2023-06-09 13:34:31 信息 转账金额: 1000 DAI, 使用 toInnerAmount 转换为: 1000000000000000000000
Using the inventor's quantified trading platform, it is easy to simulate the outcome of a transaction and avoid sending a potentially unsuccessful transaction resulting in unnecessary gas cost losses. We use the example code in this chapter course to simulate a transfer to the V-Wallet, a call from the V-Wallet to a transfer to us.eth_callThere are many more ways to do this. Use your imagination and you'll get the most out of it.eth_callWhere is the method used?
Identify the ERC721 contract
We know that tokens like ETH and BTC are homogeneous tokens, and the token you have in your hand is no different from the token I have in my hand. But there are many things in the world that are heterogeneous, such as real estate, antiques, virtual artwork, etc., that cannot be represented in an abstract way with homogeneous tokens. So how do we identify which of the many smart contracts deployed on Ethereum are ERC721 smart contracts?
To identify ERC721, you first need to understand the ERC165 standard.
ERC165
Through the ERC165 standard, a smart contract can declare the interfaces it supports for other contracts to check.supportsInterface(bytes4 interfaceId), the parametersinterfaceIdThe interface id to be queried. If the contract implements the interface id returns a true Boolean value, otherwise a false value.
We're going to talk about this below.interfaceIdIn this article, we'll look at how to calculate, code, and use these tools.
The ERC165 standardHere's an example:
pragma solidity ^0.4.20;
interface Solidity101 {
function hello() external pure;
function world(int) external pure;
}
contract Selector {
function calculateSelector() public pure returns (bytes4) {
Solidity101 i;
return i.hello.selector ^ i.world.selector;
}
}
For the function signature of the interface (which consists of a list of function names and parameter types) is odd or calculated, for an ERC165 interface contract that contracts only one function:
pragma solidity ^0.4.20;
interface ERC165 {
/// @notice Query if a contract implements an interface
/// @param interfaceID The interface identifier, as specified in ERC-165
/// @dev Interface identification is specified in ERC-165. This function
/// uses less than 30,000 gas.
/// @return `true` if the contract implements `interfaceID` and
/// `interfaceID` is not 0xffffffff, `false` otherwise
function supportsInterface(bytes4 interfaceID) external view returns (bool);
}
The interface identifier for this interface is 0x01ffc9a7. You can calculate this by running bytes4(keccak256(‘supportsInterface(bytes4)’)); or using the Selector contract above.
So if you just compute the function signature directly, and you take the first four bytes of it, you getinterfaceId。
function main() {
var ret = Encode("keccak256", "string", "hex", "supportsInterface(bytes4)")
Log("supportsInterface(bytes4) interfaceId:", "0x" + ret.slice(0, 8))
}
The following tests can be run in the Debug Tool:
2023-06-13 14:53:35 信息 supportsInterface(bytes4) interfaceId: 0x01ffc9a7
You can see the results of the calculations andThe ERC165 standardThe documentation is consistent.
ERC721
Next, we look at the interface definitions of the ERC721 contract standard:
interface ERC721 /* is ERC165 */ {
event Transfer(address indexed _from, address indexed _to, uint256 indexed _tokenId);
event Approval(address indexed _owner, address indexed _approved, uint256 indexed _tokenId);
event ApprovalForAll(address indexed _owner, address indexed _operator, bool _approved);
function balanceOf(address _owner) external view returns (uint256);
function ownerOf(uint256 _tokenId) external view returns (address);
function safeTransferFrom(address _from, address _to, uint256 _tokenId, bytes data) external payable;
function safeTransferFrom(address _from, address _to, uint256 _tokenId) external payable;
function transferFrom(address _from, address _to, uint256 _tokenId) external payable;
function approve(address _approved, uint256 _tokenId) external payable;
function setApprovalForAll(address _operator, bool _approved) external;
function getApproved(uint256 _tokenId) external view returns (address);
function isApprovedForAll(address _owner, address _operator) external view returns (bool);
}
If we want to judge whether a smart contract is an ERC721 contract, we first need to know what the ERC721 contract is.interfaceIdAnd then try using it.supportsInterface(bytes4 interfaceId)Methodology, in previous lessons we have been familiar with some of the concepts and calculations of the ERC165 standardinterfaceIdThe algorithm we write directly in the code calculates:
function calcSelector(arrSelector) {
var ret = null
if (Array.isArray(arrSelector)) {
if (arrSelector.length == 1) {
ret = Encode("keccak256", "string", "hex", arrSelector[0])
} else if (arrSelector.length == 0) {
throw "错误:数组中元素个数为0"
} else {
var viewEncodeData = null
for (var i = 0; i < arrSelector.length; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
ret = new Uint8Array(Encode("keccak256", "string", "raw", arrSelector[i]))
} else {
viewData = new Uint8Array(Encode("keccak256", "string", "raw", arrSelector[i]))
if (viewData.length != ret.length) {
throw "错误:TypeArray view长度不同"
}
for (var index = 0; index < ret.length; index++) {
ret[index] ^= viewData[index]
}
}
}
ret = Encode("raw", "raw", "hex", ret.buffer)
}
} else {
throw "错误:参数需要数组类型。"
}
return "0x" + ret.slice(0, 8)
}
function main() {
// supportsInterface(bytes4): 0x01ffc9a7
// var ret = calcSelector(["supportsInterface(bytes4)"])
// ERC721Metadata: 0x5b5e139f
/*
var arrSelector = [
"name()",
"symbol()",
"tokenURI(uint256)"
]
var ret = calcSelector(arrSelector)
*/
// ERC721: 0x80ac58cd
// /*
var arrSelector = [
"balanceOf(address)",
"ownerOf(uint256)",
"safeTransferFrom(address,address,uint256,bytes)",
"safeTransferFrom(address,address,uint256)",
"transferFrom(address,address,uint256)",
"approve(address,uint256)",
"setApprovalForAll(address,bool)",
"getApproved(uint256)",
"isApprovedForAll(address,address)",
]
var ret = calcSelector(arrSelector)
// */
Log(ret)
}
It's used in code.Encode()Function for calculating the function signaturekeccak256Algorithm), for the calculation in the above code example, specifyEncode()The output of the function is"raw"So this function returnsJavaScriptThe languageArrayBufferI'm not sure what you mean.
So if you want to do two.ArrayBufferObject carried out^(Different) operations, based onArrayBufferObject creationTypedArrayView, then scroll through the data in it, and perform a separation or calculation one at a time.
The debugger tool runs on:
2023-06-13 15:04:09 信息 0x80ac58cd
You can see the results of the calculations andeip-721The consistency described in the article.
pragma solidity ^0.4.20;
/// @title ERC-721 Non-Fungible Token Standard
/// @dev See https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-721
/// Note: the ERC-165 identifier for this interface is 0x80ac58cd.
interface ERC721 /* is ERC165 */ {
/// @dev This emits when ownership of any NFT changes by any mechanism.
/// This event emits when NFTs are created (`from` == 0) and destroyed
/// (`to` == 0). Exception: during contract creation, any number of NFTs
/// may be created and assigned without emitting Transfer. At the time of
/// any transfer, the approved address for that NFT (if any) is reset to none.
event Transfer(address indexed _from, address indexed _to, uint256 indexed _tokenId);
...
With an ERC721 interface ID, we can judge whether a contract is an ERC721 standard contract.BAYCTo test, this is a contract that follows ERC721, first we need to register the ABI, and since we only call the following three methods, only these three methods can be registered:
- supportsInterface(interfaceId)
- symbol()
- name()
The specific codes are:
function main() {
// ERC721的合约地址,这里用的BAYC
var testContractAddress = "0xbc4ca0eda7647a8ab7c2061c2e118a18a936f13d"
var testABI = `[{
"inputs": [{
"internalType": "bytes4",
"name": "interfaceId",
"type": "bytes4"
}],
"name": "supportsInterface",
"outputs": [{
"internalType": "bool",
"name": "",
"type": "bool"
}],
"stateMutability": "view",
"type": "function"
}, {
"inputs": [],
"name": "symbol",
"outputs": [{
"internalType": "string",
"name": "",
"type": "string"
}],
"stateMutability": "view",
"type": "function"
}, {
"inputs": [],
"name": "name",
"outputs": [{
"internalType": "string",
"name": "",
"type": "string"
}],
"stateMutability": "view",
"type": "function"
}]`
// ERC721接口Id,在之前的课程中计算得出
var interfaceId = "0x80ac58cd"
// 注册ABI
exchange.IO("abi", testContractAddress, testABI)
// 调用supportsInterface方法
var isErc721 = exchange.IO("api", testContractAddress, "supportsInterface", interfaceId)
// 输出信息
Log("合约地址:", testContractAddress)
Log("合约名称:", exchange.IO("api", testContractAddress, "name"))
Log("合约代号:", exchange.IO("api", testContractAddress, "symbol"))
Log("合约是否为ERC721标准:", isErc721)
}
The following tests can be run in the Debug Tool:
2023-06-13 16:32:57 信息 合约是否为ERC721标准: true
2023-06-13 16:32:57 信息 合约代号: BAYC
2023-06-13 16:32:57 信息 合约名称: BoredApeYachtClub
2023-06-13 16:32:57 信息 合约地址: 0xbc4ca0eda7647a8ab7c2061c2e118a18a936f13d
Determine the address0xbc4ca0eda7647a8ab7c2061c2e118a18a936f13dThe contract is based on the ERC721 standard.
In this article, we've explained how to judge an ERC721 contract, but ERC20 contracts that don't support the ERC165 standard have to be identified in a different way.
Code for calldata
What is it?calldataIn the author's understanding, the simplest and most common description here is:
"Calldata" is the encoding of a function call or parameter in Ethereum, "calldata" is encoded according to the contractual ABI (Application Binary Interface) specification.
For example, we can use the ERC20 contracts that we learned in the previous lesson.balanceOf、transferThe method calls, along with the parameters when called, are encoded as acalldata◦ In some application scenarios, for example:Interaction between contractsThis is the kind of scenario that would be useful.calldataThere are, of course, many other scenarios of application, which I have listed here.
How to code a smart contract function call and getcalldata?
Inventors can use a quantitative trading platformexchange.IO("encode", ...)It is very simple to use and coded for smart contract function calls.exchange.IO("encode", ...)The first parameter of the function is a fixed string."encode"; the second parameter is the address of the smart contract; the third parameter is the name of the smart contract method to be encoded; the remaining parameters are passed to the specific parameter value of the smart contract method to be encoded.
eth_sendRawTransaction
When we code a call to a smart contract method and generate the correspondingcalldataIn data, if this smart contract method is a Write method (i.e. write operation), we need to generate thecalldataData as a data field for transactions, then using Ethereum's RPC methodeth_sendRawTransactionA request for raw data containing the transaction is sent to the Ethereum network.
eth_sendRawTransactionThe method has only one parameter.data:
data: The signed transaction (typically signed with a library, using your private key)
This onedataA parameter is a transaction data after the signature has been calculated. The transaction data structure of Ethereum consists mainly of the following fields:
{
"nonce": "0x1", // 交易发送方的账户交易次数
"gasPrice": "0x12a05f200", // 交易的Gas价格
"gasLimit": "0x5208", // 交易的Gas限制
"to": "0xAb8483F64d9C6d1EcF9b849Ae677dD3315835cb2", // 目标合约地址或接收方地址
"value": "0x4563918244F40000", // 转账的以太币数量
"data": "0x0123456789ABCDEF", // 要发送给合约的数据
}
How do you sign up for an Ethereum transaction?
Inventors quantify the trading platforms we useEncode()A function to perform signature computation, a specific example of which we wrote in the next lesson "Write method calldata".
Execute the Read method calldata
For the Read methodcalldataWe're going to do it using the RPC methodology we've learned before:eth_callWe're going to do it, and we've explained it before.eth_callThis RPC method of Ethereum is just doing smart contracts.WriteDemonstration of methods used in this chaptercalldataLet's demonstrate how to execute a call to the smart contract Read method.balanceOfHow to read the current wallet's WETH token balance.
We used debugging tools to test the Ethereum network:
function toAmount(s, decimals) {
return Number((BigDecimal(BigInt(s)) / BigDecimal(Math.pow(10, decimals))).toString())
}
function main() {
// WETH合约的ABI
var abiWETH = `[{"constant":true,"inputs":[],"name":"name","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"string"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"constant":false,"inputs":[{"name":"guy","type":"address"},{"name":"wad","type":"uint256"}],"name":"approve","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"bool"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"nonpayable","type":"function"},{"constant":true,"inputs":[],"name":"totalSupply","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"uint256"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"constant":false,"inputs":[{"name":"src","type":"address"},{"name":"dst","type":"address"},{"name":"wad","type":"uint256"}],"name":"transferFrom","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"bool"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"nonpayable","type":"function"},{"constant":false,"inputs":[{"name":"wad","type":"uint256"}],"name":"withdraw","outputs":[],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"nonpayable","type":"function"},{"constant":true,"inputs":[],"name":"decimals","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"uint8"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"constant":true,"inputs":[{"name":"","type":"address"}],"name":"balanceOf","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"uint256"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"constant":true,"inputs":[],"name":"symbol","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"string"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"constant":false,"inputs":[{"name":"dst","type":"address"},{"name":"wad","type":"uint256"}],"name":"transfer","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"bool"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"nonpayable","type":"function"},{"constant":false,"inputs":[],"name":"deposit","outputs":[],"payable":true,"stateMutability":"payable","type":"function"},{"constant":true,"inputs":[{"name":"","type":"address"},{"name":"","type":"address"}],"name":"allowance","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"uint256"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"payable":true,"stateMutability":"payable","type":"fallback"},{"anonymous":false,"inputs":[{"indexed":true,"name":"src","type":"address"},{"indexed":true,"name":"guy","type":"address"},{"indexed":false,"name":"wad","type":"uint256"}],"name":"Approval","type":"event"},{"anonymous":false,"inputs":[{"indexed":true,"name":"src","type":"address"},{"indexed":true,"name":"dst","type":"address"},{"indexed":false,"name":"wad","type":"uint256"}],"name":"Transfer","type":"event"},{"anonymous":false,"inputs":[{"indexed":true,"name":"dst","type":"address"},{"indexed":false,"name":"wad","type":"uint256"}],"name":"Deposit","type":"event"},{"anonymous":false,"inputs":[{"indexed":true,"name":"src","type":"address"},{"indexed":false,"name":"wad","type":"uint256"}],"name":"Withdrawal","type":"event"}]`
// WETH合约地址
var wethAddress = "0xc02aaa39b223fe8d0a0e5c4f27ead9083c756cc2"
// 注册WETH合约的ABI
exchange.IO("abi", wethAddress, abiWETH)
// 当前配置的交易所对象的钱包地址
var walletAddress = exchange.IO("address")
// 编码WETH合约的deposit方法调用
var calldataForDeposit = exchange.IO("encode", wethAddress, "balanceOf(address)", walletAddress)
Log("calldataForDeposit:", "0x" + calldataForDeposit)
// 构造transaction,作为eth_call的第一个参数
var transaction = {
"from" : walletAddress,
"to" : wethAddress,
"data" : "0x" + calldataForDeposit,
}
// eth_call的第二个参数
var blockNumber = "latest"
// 使用eth_call调用
var ret = exchange.IO("api", "eth", "eth_call", transaction, blockNumber)
var wethBalance = exchange.IO("decode", "uint256", ret) // 可以使用exchange.IO("decode", ...) 函数解码
Log("wethBalance:", toAmount(wethBalance, 18)) // 从以wei为单位,换算成WETH个数为单位
}
The debugger tool runs on:
2023-06-15 11:51:31 信息 wethBalance: 0.015
2023-06-15 11:51:31 信息 calldataForDeposit: 0x70a082310000000000000000000000006b3f11d807809b0b1e5e3243df04a280d9f94bf4
If the smart contract method has a return value, it can be used.exchange.IO("decode", ...)Function decoding.calldataThis is the way to call a smart contract directly.balanceOfThe method is the same, I have a WETH balance of 0.015 WETH in my test wallet.
Execute the write method calldata
For the calldata execution of the Write method, the RPC method is required:eth_sendRawTransactionI'm not sure.
We used debugging tools to test the Ethereum network:
function toAmount(s, decimals) {
return Number((BigDecimal(BigInt(s)) / BigDecimal(Math.pow(10, decimals))).toString())
}
function toInnerAmount(s, decimals) {
return (BigDecimal(s)*BigDecimal(Math.pow(10, decimals))).toFixed(0)
}
function main() {
// WETH合约的ABI
var abiWETH = `[{"constant":true,"inputs":[],"name":"name","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"string"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"constant":false,"inputs":[{"name":"guy","type":"address"},{"name":"wad","type":"uint256"}],"name":"approve","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"bool"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"nonpayable","type":"function"},{"constant":true,"inputs":[],"name":"totalSupply","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"uint256"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"constant":false,"inputs":[{"name":"src","type":"address"},{"name":"dst","type":"address"},{"name":"wad","type":"uint256"}],"name":"transferFrom","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"bool"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"nonpayable","type":"function"},{"constant":false,"inputs":[{"name":"wad","type":"uint256"}],"name":"withdraw","outputs":[],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"nonpayable","type":"function"},{"constant":true,"inputs":[],"name":"decimals","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"uint8"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"constant":true,"inputs":[{"name":"","type":"address"}],"name":"balanceOf","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"uint256"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"constant":true,"inputs":[],"name":"symbol","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"string"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"constant":false,"inputs":[{"name":"dst","type":"address"},{"name":"wad","type":"uint256"}],"name":"transfer","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"bool"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"nonpayable","type":"function"},{"constant":false,"inputs":[],"name":"deposit","outputs":[],"payable":true,"stateMutability":"payable","type":"function"},{"constant":true,"inputs":[{"name":"","type":"address"},{"name":"","type":"address"}],"name":"allowance","outputs":[{"name":"","type":"uint256"}],"payable":false,"stateMutability":"view","type":"function"},{"payable":true,"stateMutability":"payable","type":"fallback"},{"anonymous":false,"inputs":[{"indexed":true,"name":"src","type":"address"},{"indexed":true,"name":"guy","type":"address"},{"indexed":false,"name":"wad","type":"uint256"}],"name":"Approval","type":"event"},{"anonymous":false,"inputs":[{"indexed":true,"name":"src","type":"address"},{"indexed- Explore the new functions of FMZ strategy editor: How ChatGPT improves your quantitative productivity significantly
- Explore the new features of the FMZ Strategy Editor: How ChatGPT dramatically improves your quantitative productivity
- Digital Currency High-Frequency Strategy Detailed Introduction
- Introduction to Detailed High-Frequency Trading Strategies for Cryptocurrencies