Python iceberg delegation policy
Author: Inventors quantify - small dreams, Created: 2020-03-06 15:26:43, Updated: 2023-10-11 19:57:53
Python iceberg delegation policy
This article presents two classic strategies for porting: Ice Mountain commissioning (buy/sell); strategy porting from the inventor of the Quantitative Trading Platform Classic strategy JavaScript version Ice Mountain commissioning, strategy address:https://www.fmz.com/square/s:%E5%86%B0%E5%B1%B1%E5%A7%94%E6%89%98⁄1 。
The following is a description of the JavaScript version policy:
Ice Mountain order refers to the investor in the case of large-scale transactions, in order to avoid causing too much shock to the market, to order the large order automatically split into several orders, according to the current latest buy/sell price and the price strategy set by the customer, automatically re-order the order when the previous order is fully completed or the latest price deviates significantly from the current order price.
Many trading pages come with an iceberg commissioning tool with a wealth of functionality, but if you want to customize some features or change some functions according to your needs, you need a more flexible tool. The inventors of the quantified trading platform solved this problem very well. There are not many Python strategies on the strategy square, some traders who want to write trading tools and strategies in Python language need a reference example.
Python Iceberg commission - purchase Policy code and annotations
import random # 导入随机数库
def CancelPendingOrders(): # CancelPendingOrders 函数作用是取消当前交易对所有挂单。
while True: # 循环检测,调用GetOrders 函数,检测当前挂单,如果orders 为空数组,即len(orders) 等于0,说明订单全部取消了,可以退出函数,调用return 退出。
orders = _C(exchange.GetOrders)
if len(orders) == 0 :
return
for j in range(len(orders)): # 遍历当前挂单数组,调用取消订单的函数CancelOrder,逐个取消挂单。
exchange.CancelOrder(orders[j]["Id"])
if j < len(orders) - 1: # 除了最后一个订单,每次都执行Sleep 让程序等待一会儿,避免撤单过于频繁。
Sleep(Interval)
LastBuyPrice = 0 # 设置一个全局变量,记录最近一次买入的价格。
InitAccount = None # 设置一个全局变量,记录初始账户资产信息。
def dispatch(): # 冰山委托逻辑的主要函数
global InitAccount, LastBuyPrice # 引用全局变量
account = None # 声明一个变量,记录实时获取的账户信息,用于对比计算。
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker) # 声明一个变量,记录最近行情。
LogStatus(_D(), "ticker:", ticker) # 在状态栏输出时间,最新行情
if LastBuyPrice > 0: # 当LastBuyPrice大于0时,即已经委托开始时,执行if条件内代码。
if len(_C(exchange.GetOrders)) > 0: # 调用exchange.GetOrders 函数获取当前所有挂单,判断有挂单,执行if条件内代码。
if ticker["Last"] > LastBuyPrice and ((ticker["Last"] - LastBuyPrice) / LastBuyPrice) > (2 * (EntrustDepth / 100)): # 检测偏离程度,如果触发该条件,执行if内代码,撤单。
Log("偏离过多, 最新成交价:", ticker["Last"], "委托价", LastBuyPrice)
CancelPendingOrders()
else :
return True
else : # 如果没有挂单,证明订单完全成交了。
account = _C(exchange.GetAccount) # 获取当前账户资产信息。
Log("买单完成, 累计花费:", _N(InitAccount["Balance"] - account["Balance"]), "平均买入价:", _N((InitAccount["Balance"] - account["Balance"]) / (account["Stocks"] - InitAccount["Stocks"]))) # 打印交易信息。
LastBuyPrice = 0 # 重置 LastBuyPrice为0
BuyPrice = _N(ticker["Buy"] * (1 - EntrustDepth / 100)) # 通过当前行情和参数,计算挂单价格。
if BuyPrice > MaxBuyPrice: # 判断是否超过参数设置的最大价格
return True
if not account: # 如果 account 为 null ,执行if 语句内代码,重新获取当前资产信息,复制给account
account = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
if (InitAccount["Balance"] - account["Balance"]) >= TotalBuyNet: # 判断买入所花费的总钱数,是不是超过参数设置。
return False
RandomAvgBuyOnce = (AvgBuyOnce * ((100.0 - FloatPoint) / 100.0)) + (((FloatPoint * 2) / 100.0) * AvgBuyOnce * random.random()) # 随机数 0~1
UsedMoney = min(account["Balance"], RandomAvgBuyOnce, TotalBuyNet - (InitAccount["Balance"] - account["Balance"]))
BuyAmount = _N(UsedMoney / BuyPrice) # 计算买入数量
if BuyAmount < MinStock: # 判断买入数量是否小于 参数上最小买入量限制。
return False
LastBuyPrice = BuyPrice # 记录本次下单价格,赋值给LastBuyPrice
exchange.Buy(BuyPrice, BuyAmount, "花费:¥", _N(UsedMoney), "上次成交价", ticker["Last"]) # 下单
return True
def main():
global LoopInterval, InitAccount # 引用 LoopInterval, InitAccount 全局变量
CancelPendingOrders() # 开始运行时,取消所有挂单
InitAccount = _C(exchange.GetAccount) # 初始记录 开始时的账户资产
Log(InitAccount) # 打印初始账户信息
if InitAccount["Balance"] < TotalBuyNet: # 如果初始时资产不足,则抛出错误,停止程序
raise Exception("账户余额不足")
LoopInterval = max(LoopInterval, 1) # 设置LoopInterval至少为1
while dispatch(): # 主要循环,不停调用 冰山委托逻辑函数 dispatch ,当dispatch函数 return false 时才停止循环。
Sleep(LoopInterval * 1000) # 每次循环都暂停一下,控制轮询频率。
Log("委托全部完成", _C(exchange.GetAccount)) # 当循环执行跳出时,打印当前账户资产信息。
Python version of Iceberg commissioned - sold
You can try reading the code of "Python Iceberg Commissioning - Selling", the strategy logic is the same as buying, only slightly different.
import random
def CancelPendingOrders():
while True:
orders = _C(exchange.GetOrders)
if len(orders) == 0:
return
for j in range(len(orders)):
exchange.CancelOrder(orders[j]["Id"])
if j < len(orders) - 1:
Sleep(Interval)
LastSellPrice = 0
InitAccount = None
def dispatch():
global LastSellPrice, InitAccount
account = None
ticker = _C(exchange.GetTicker)
LogStatus(_D(), "ticker:", ticker)
if LastSellPrice > 0:
if len(_C(exchange.GetOrders)) > 0:
if ticker["Last"] < LastSellPrice and ((LastSellPrice - ticker["Last"]) / ticker["Last"]) > (2 * (EntrustDepth / 100)):
Log("偏离过多,最新成交价:", ticker["Last"], "委托价", LastSellPrice)
CancelPendingOrders()
else :
return True
else :
account = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
Log("买单完成,累计卖出:", _N(InitAccount["Stocks"] - account["Stocks"]), "平均卖出价:", _N((account["Balance"] - InitAccount["Balance"]) / (InitAccount["Stocks"] - account["Stocks"])))
LastSellPrice = 0
SellPrice = _N(ticker["Sell"] * (1 + EntrustDepth / 100))
if SellPrice < MinSellPrice:
return True
if not account:
account = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
if (InitAccount["Stocks"] - account["Stocks"]) >= TotalSellStocks:
return False
RandomAvgSellOnce = (AvgSellOnce * ((100.0 - FloatPoint) / 100.0)) + (((FloatPoint * 2) / 100.0) * AvgSellOnce * random.random())
SellAmount = min(TotalSellStocks - (InitAccount["Stocks"] - account["Stocks"]), RandomAvgSellOnce)
if SellAmount < MinStock:
return False
LastSellPrice = SellPrice
exchange.Sell(SellPrice, SellAmount, "上次成交价", ticker["Last"])
return True
def main():
global InitAccount, LoopInterval
CancelPendingOrders()
InitAccount = _C(exchange.GetAccount)
Log(InitAccount)
if InitAccount["Stocks"] < TotalSellStocks:
raise Exception("账户币数不足")
LoopInterval = max(LoopInterval, 1)
while dispatch():
Sleep(LoopInterval)
Log("委托全部完成", _C(exchange.GetAccount))
The strategy works
WexApp is a simulated exchange that is used to test:
Buying in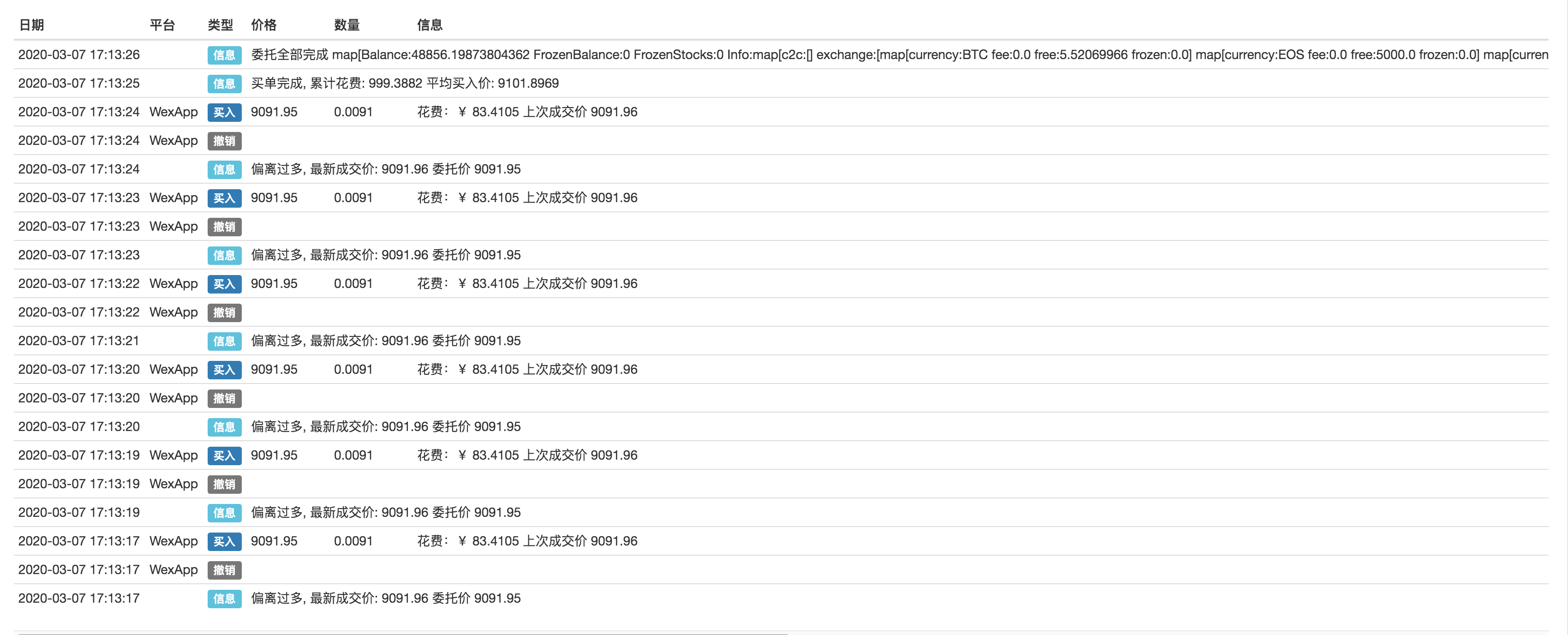
Sold
The strategy logic is not complicated, and when executed, the strategy is based on the strategy parameters, the market price at the time, the dynamic hanging order, withdrawal. When the transaction amount/coin number is reached, the strategy stops when it is close to the number of parameters set. The strategy code is very simple, suitable for beginners. Interested students can modify it to design a strategy to suit their own trading style. The strategy is educational in nature and practical.
- Quantitative Practice of DEX Exchanges (2) -- Hyperliquid User Guide
- DEX exchange quantitative practices ((2) -- Hyperliquid user guide
- Quantitative Practice of DEX Exchanges (1) -- dYdX v4 User Guide
- Introduction to Lead-Lag Arbitrage in Cryptocurrency (3)
- DEX exchange quantitative practice ((1) -- dYdX v4 user guide
- Introduction to the Lead-Lag suite in digital currency (3)
- Introduction to Lead-Lag Arbitrage in Cryptocurrency (2)
- Introduction to the Lead-Lag suite in the digital currency (2)
- Discussion on External Signal Reception of FMZ Platform: A Complete Solution for Receiving Signals with Built-in Http Service in Strategy
- Discussing FMZ platform external signal reception: a complete set of strategies for the reception of signals from built-in HTTP services
- Introduction to Lead-Lag Arbitrage in Cryptocurrency (1)
- Expanded API to enable TradingView alarm signal trading using inventor's quantified trading platform (recommended)
- JavaScript version SuperTrend strategy
- SuperTrend V.1 - Supertrend line system
- JavaScript version of the SuperTrend policy
- [Millennium War] Currency exchange multi-currency hedging strategies Recent recaps and results of the minute-level K-line review ((Part 4)
- Hands-on teaches you how to implement a data collector
- [Millennium War] Bitcoin futures do nothing and do more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more]
- [Millennium War] Bitcoin futures do nothing and do more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more and more.
- [Millennium War] Research on multi-currency hedging strategies in the field of currency exchange (part 1)
- 98 undergraduate coins and the way to quantify
- Dynamic balancing strategies based on digital currency
- Use a trading terminal plug-in to facilitate manual transactions
- Python version of the MACD graph example
- The strategy of cross-currency arbitrage based on the Brin Belt
- Timing start or stop widgets for quantified trading robots using Python
- Corrupt Sisters Speak at the First Session of the General Assembly
- Quantitative fractional rate trading strategy
- The Python spreadsheet platform balancing strategy
- The old farmer's journey to the pit
- The story of a post-95 coin collector
mcmcSo, what's the meaning of this calculation? RandomAvgBuyOnce = (AvgBuyOnce * ((100.0 - FloatPoint) / 100.0)) + (((FloatPoint * 2) / 100.0) * AvgBuyOnce * random.random))) # random number 0 to 1
Inventors quantify - small dreamsThe JS version has this, directly ported.