Diseño de una estrategia de cobertura al contado de criptomonedas (2)
El autor:FMZ~Lydia, Creado: 2022-07-19 15:19:52, Actualizado: 2023-09-24 19:34:38
Diseño de una estrategia de cobertura al contado de criptomonedas (2)
En el artículo anterior, implementamos una estrategia de cobertura simple juntos, y luego aprenderemos cómo actualizar esta estrategia. Los cambios de estrategia no son grandes, pero los detalles de los cambios necesitan atención.
La necesidad de actualizar esta estrategia
- Cambiar el modo de apalancamiento del objeto de intercambio spot Este cambio solo está relacionado con el bot real. Algunos intercambios al contado tienen interfaces de apalancamiento al contado, que también están encapsuladas en FMZ. Para los objetos de intercambio que han sido empaquetados directamente en FMZ y admiten apalancamiento al contado, el modo se puede cambiar directamente.
- Añadir la pantalla del gráfico de diferencias
Añadir la exhibición del gráfico de dispersión, porque es sólo dibujar la línea de dispersión de
A exchange -> B exchange,B exchange -> A exchange, y dibujar la línea horizontal que desencadena la propagación.line drawing class libraryEn el caso de las empresas de la industria de la información, la ventaja es que es fácil de usar, aquí también aprendemos a utilizar eltemplate class libraryfunción de la FMZ. - Función de cobertura unilateral Este cambio puede ser bastante significativo, ya que es difícil revertir completamente la diferencia de precio entre los dos intercambios durante transacciones de cobertura específicas. La mayoría de las veces el precio en un intercambio es consistentemente más alto que el precio en otro intercambio. En este momento, si nuestros activos han sido completamente cubiertos (es decir, las monedas están todas en intercambios con precios bajos, y el dinero está en intercambios con precios altos). La cobertura está estancada, y ya no es posible confiar en la fluctuación del spread para obtener ganancias. En este momento, necesitamos hacer la estrategia para que puedas perder un poco de dinero para cubrir las monedas de nuevo (deja que las monedas existan en el intercambio con un precio alto nuevamente), y cuando la diferencia de precio se vuelva a aumentar, podemos continuar a cubrir y obtener ganancias.
- Modificar de forma interactiva parámetros tales como líneas de cobertura de diferencias Añadir una función interactiva a la estrategia para modificar la línea de disparo de la propagación en tiempo real.
- Organizar la información de la barra de estado y mostrarla en formato de tabla Organice los datos que deben mostrarse para que sean fáciles de ver.
A continuación, implementemos estos diseños uno por uno.
Cambiar el modo de apalancamiento del objeto de intercambio spot
Tome Binance spot real bot como ejemplo, cambiar al modo apalancado spot, utilizar el códigoexchanges[i].IO, introduzca el parámetrotrade_normalpara cambiar a la posición de apalancamiento por posición, y entradatrade_super_marginPara cambiar a apalancamiento de posición completa, backtesting no es compatible.
Añadir a la fase de preparación al comienzo de lamainFunción:
// Switch leverage mode
for (var i = 0 ; i < exchanges.length ; i++) { // Traverse and detect all added exchange objects
if (exchanges[i].GetName() == "Binance" && marginType != 0) { //If the exchange object represented by the current i-index is Binance spot, and the parameter marginType of the strategy interface is not the option of "common currency", execute the switch operation
if (marginType == 1) {
Log(exchanges[i].GetName(), "Set to leveraged position-by-position")
exchanges[i].IO("trade_normal")
} else if (marginType == 2) {
Log(exchanges[i].GetName(), "Set to leveraged full position")
exchanges[i].IO("trade_super_margin")
}
}
}
La estrategia aquí solo agrega el código para cambiar el modo de apalancamiento de moneda a moneda de Binance spot, por lo que la configuración del interruptor en los parámetros de la estrategia solo es válida para Binance spot.
Se ha añadido la visualización del gráfico de diferencias
Es muy fácil de usar la plantilla de dibujo ya envuelto.Line Drawing LibrarySe puede obtener buscando directamente en el cuadrado de estrategia de la plataforma FMZ.
O haga clic en el enlace directamente:https://www.fmz.com/strategy/27293para saltar a la página de copia de esta plantilla.
Haga clic en el botón para copiar esta biblioteca de clases de plantilla en su propia biblioteca de estrategias.
Luego puede comprobar la biblioteca de clases de plantilla a utilizar en la columna de plantilla en la página de edición de estrategia. Guarde la estrategia después de comprobarla, y la estrategia se referirá a esta plantilla. Esta es solo una breve descripción del uso de la biblioteca de clases de plantilla. Esta estrategia ya ha hecho referencia a esta plantilla, por lo que no es necesario repetir la operación. Cuando copia esta estrategia en el cuadrado de estrategia, puede ver queLine Drawing Libraryse ha hecho referencia en la barra de plantillas de la página de edición de estrategias.
Aprenderemos sobre todo cómo utilizar las funciones de laLine Drawing Librarypara dibujar un gráfico.
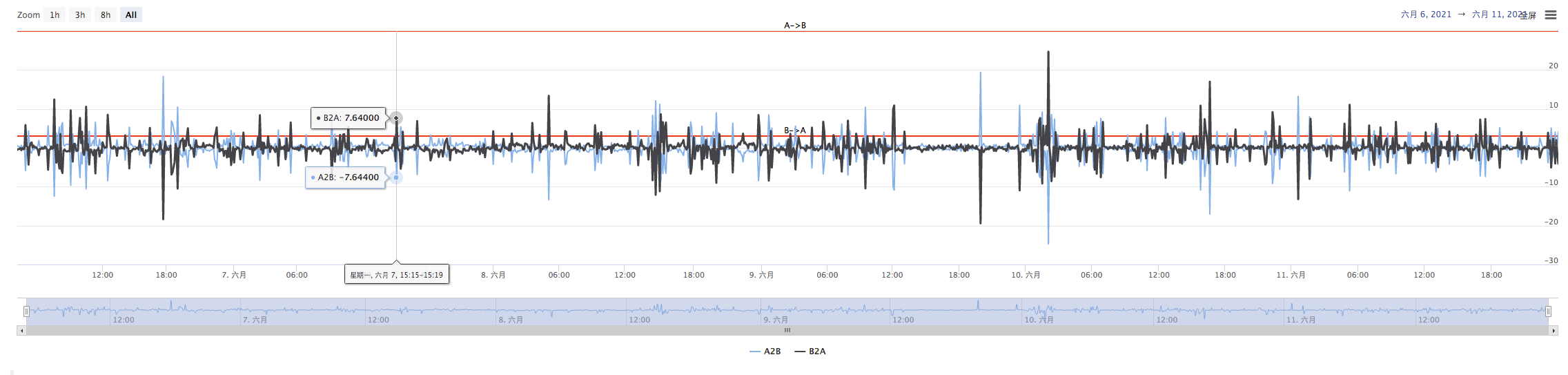
Planeamos dibujar la propagación deA->B, la propagación deB->A, y la línea de disparo de la propagación. necesitamos dibujar dos curvas (actual A a B, B a A propagación), dos líneas horizontales (línea de disparo de la propagación), como se muestra en la figura anterior.
Porque queremos diseñar cobertura unilateral, las líneas de disparo deA->ByB->ANo podemos usar el diseño del artículo anterior.
En el artículo anterior:
var targetDiffPrice = hedgeDiffPrice
if (diffAsPercentage) {
targetDiffPrice = (depthA.Bids[0].Price + depthB.Asks[0].Price + depthB.Bids[0].Price + depthA.Asks[0].Price) / 4 * hedgeDiffPercentage
}
Sólo hay un disparador de propagacióntargetDiffPrice¿ Qué pasa?
Así que aquí tenemos que transformar el código, transformar los parámetros primero.
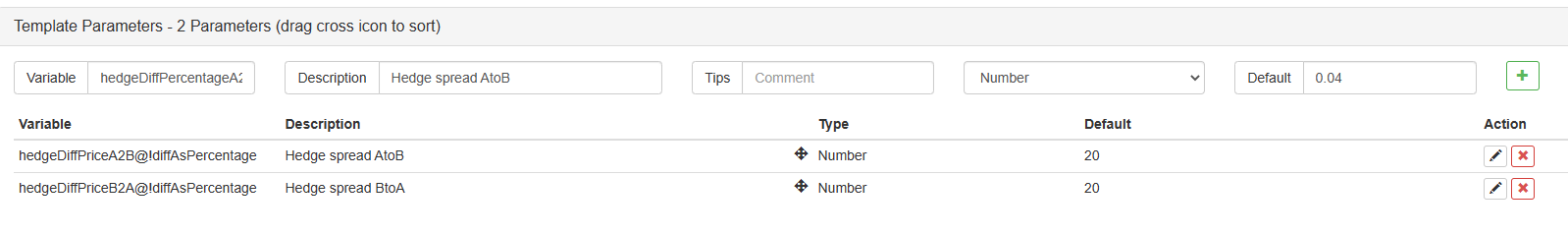
Luego modifica el código:
var targetDiffPriceA2B = hedgeDiffPriceA2B
var targetDiffPriceB2A = hedgeDiffPriceB2A
if (diffAsPercentage) {
targetDiffPriceA2B = (depthA.Bids[0].Price + depthB.Asks[0].Price + depthB.Bids[0].Price + depthA.Asks[0].Price) / 4 * hedgeDiffPercentageA2B
targetDiffPriceB2A = (depthA.Bids[0].Price + depthB.Asks[0].Price + depthB.Bids[0].Price + depthA.Asks[0].Price) / 4 * hedgeDiffPercentageB2A
}
De esta manera, la diferencia línea de disparo ha cambiado de la anteriortargetDiffPriceA las dos.targetDiffPriceA2B, targetDiffPriceB2A¿ Qué pasa?
El siguiente paso es dibujar estos datos en el gráfico utilizando la función de línea de dibujo de la biblioteca de dibujo de líneas.
// drawing
$.PlotHLine(targetDiffPriceA2B, "A->B") // The first parameter of this function is the value of the horizontal line in the Y-axis direction, and the second parameter is the display text
$.PlotHLine(targetDiffPriceB2A, "B->A")
Cuando la estrategia se está ejecutando, hay un gráfico como este.
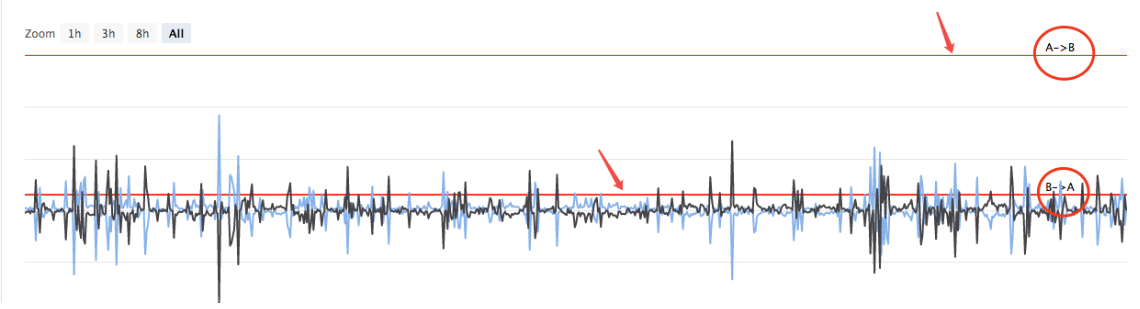
A continuación, dibuja la curva de dispersión en tiempo real, para evitar sobre dibujar la línea.
if (ts - lastKeepBalanceTS > keepBalanceCyc * 1000) {
nowAccs = _C(updateAccs, exchanges)
var isBalance = keepBalance(initAccs, nowAccs, [depthA, depthB])
cancelAll()
if (isBalance) {
lastKeepBalanceTS = ts
if (isTrade) {
var nowBalance = _.reduce(nowAccs, function(sumBalance, acc) {return sumBalance + acc.Balance}, 0)
var initBalance = _.reduce(initAccs, function(sumBalance, acc) {return sumBalance + acc.Balance}, 0)
LogProfit(nowBalance - initBalance, nowBalance, initBalance, nowAccs)
isTrade = false
}
}
$.PlotLine("A2B", depthA.Bids[0].Price - depthB.Asks[0].Price) // Draw real-time spread curves
$.PlotLine("B2A", depthB.Bids[0].Price - depthA.Asks[0].Price) // The first parameter is the name of the curve, and the second parameter is the value of the curve at the current moment, that is, the value in the Y-axis direction at the current moment
}
De esta manera, el código de dibujo es de solo 4 líneas, lo que permite que la estrategia tenga un gráfico mostrado en tiempo de ejecución.
Función de cobertura unilateral
Como se ha mencionado anteriormente, la línea de activación del diferencial se ha modificado en dos, controlando la línea de activación de cobertura deA->ByB->ADe esta manera, no se puede utilizar el algoritmo del precio de la orden anterior, y en su lugar se utiliza el método de adición del precio de entrada al precio de mercado.
if (depthA.Bids[0].Price - depthB.Asks[0].Price > targetDiffPriceA2B && Math.min(depthA.Bids[0].Amount, depthB.Asks[0].Amount) >= minHedgeAmount) { // A -> B market conditions are met
var priceSell = depthA.Bids[0].Price - slidePrice
var priceBuy = depthB.Asks[0].Price + slidePrice
var amount = Math.min(depthA.Bids[0].Amount, depthB.Asks[0].Amount)
if (nowAccs[0].Stocks > minHedgeAmount && nowAccs[1].Balance * 0.8 / priceSell > minHedgeAmount) {
amount = Math.min(amount, nowAccs[0].Stocks, nowAccs[1].Balance * 0.8 / priceSell, maxHedgeAmount)
Log("trigger A->B:", depthA.Bids[0].Price - depthB.Asks[0].Price, priceBuy, priceSell, amount, nowAccs[1].Balance * 0.8 / priceSell, nowAccs[0].Stocks) // Tips
hedge(exB, exA, priceBuy, priceSell, amount)
cancelAll()
lastKeepBalanceTS = 0
isTrade = true
}
} else if (depthB.Bids[0].Price - depthA.Asks[0].Price > targetDiffPriceB2A && Math.min(depthB.Bids[0].Amount, depthA.Asks[0].Amount) >= minHedgeAmount) { // B -> A market conditions are met
var priceBuy = depthA.Asks[0].Price + slidePrice
var priceSell = depthB.Bids[0].Price - slidePrice
var amount = Math.min(depthB.Bids[0].Amount, depthA.Asks[0].Amount)
if (nowAccs[1].Stocks > minHedgeAmount && nowAccs[0].Balance * 0.8 / priceBuy > minHedgeAmount) {
amount = Math.min(amount, nowAccs[1].Stocks, nowAccs[0].Balance * 0.8 / priceBuy, maxHedgeAmount)
Log("trigger B->A:", depthB.Bids[0].Price - depthA.Asks[0].Price, priceBuy, priceSell, amount, nowAccs[0].Balance * 0.8 / priceBuy, nowAccs[1].Stocks) //Tips
hedge(exA, exB, priceBuy, priceSell, amount)
cancelAll()
lastKeepBalanceTS = 0
isTrade = true
}
}
Dado que los precios de compra y venta se separan en dos datos, la función de coberturahedgeTambién debe modificarse.
function hedge(buyEx, sellEx, priceBuy, priceSell, amount) {
var buyRoutine = buyEx.Go("Buy", priceBuy, amount)
var sellRoutine = sellEx.Go("Sell", priceSell, amount)
Sleep(500)
buyRoutine.wait()
sellRoutine.wait()
}
También hay algunos ajustes menores basados en estos cambios, que no se repetirán aquí.
Modificar de forma interactiva parámetros tales como líneas de cobertura de diferencias
Añadir interacción a la estrategia, para que la estrategia pueda modificar la línea de disparo de propagación en tiempo real. El diseño de la estrategia de interacción también es muy simple. Primero, añadir controles de interacción a la estrategia en la página de edición de la estrategia.

Añadido dos controles, uno llamado A2B y otro llamado B2A. Después de introducir un valor en el cuadro de entrada de control, haga clic en el botón a la derecha del cuadro de entrada. Una instrucción se enviará a la estrategia inmediatamente, por ejemplo: introducir el valor123En el cuadro de entrada, haga clic enA2Bbotón, y una instrucción será enviada a la estrategia inmediatamente.
A2B:123
Diseñar código de detección y procesamiento interactivo en el código de estrategia.
// interact
var cmd = GetCommand() // Every time the loop is executed here, it checks whether there is an interactive command, and returns to an empty string if not.
if (cmd) { // An interactive command was detected, such as A2B:123
Log("command received:", cmd)
var arr = cmd.split(":") // Split out the interactive control name and the value in the input box, arr[0] is A2B, arr[1] is 123
if (arr[0] == "A2B") { // Determine whether the triggered interactive control is A2B
Log("Modify the parameters of A2B, ", diffAsPercentage ? "The parameter is the difference percentage" : "The parameter is the difference:", arr[1])
if (diffAsPercentage) {
hedgeDiffPercentageB2A = parseFloat(arr[1]) // Modify the trigger spread line
} else {
hedgeDiffPriceA2B = parseFloat(arr[1]) // Modify the trigger spread line
}
} else if (arr[0] == "B2A") { // Triggered control detected is B2A
Log("Modify the parameters of B2A, ", diffAsPercentage ? "The parameter is the difference percentage" : "The parameter is the difference:", arr[1])
if (diffAsPercentage) {
hedgeDiffPercentageA2B = parseFloat(arr[1])
} else {
hedgeDiffPriceB2A = parseFloat(arr[1])
}
}
}
Organizar la información de la barra de estado y mostrarla en formato de tabla
Haga que la muestra de datos de la barra de estado sea más organizada y fácil de observar.
var tbl = {
"type" : "table",
"title" : "data",
"cols" : ["exchange", "coin", "freeze coin", "denominated currency", "freeze denominated currency", "trigger spread", "current spread"],
"rows" : [],
}
tbl.rows.push(["A:" + exA.GetName(), nowAccs[0].Stocks, nowAccs[0].FrozenStocks, nowAccs[0].Balance, nowAccs[0].FrozenBalance, "A->B:" + targetDiffPriceA2B, "A->B:" + (depthA.Bids[0].Price - depthB.Asks[0].Price)])
tbl.rows.push(["B:" + exB.GetName(), nowAccs[1].Stocks, nowAccs[1].FrozenStocks, nowAccs[1].Balance, nowAccs[1].FrozenBalance, "B->A:" + targetDiffPriceB2A, "B->A:" + (depthB.Bids[0].Price - depthA.Asks[0].Price)])
LogStatus(_D(), "\n", "`" + JSON.stringify(tbl) + "`")

Pruebas de retroceso
El backtesting es sólo una estrategia de prueba, una función de detección preliminar, y muchos errores pueden ser probados en la etapa de backtesting en realidad.
Código fuente de la estrategia:https://www.fmz.com/strategy/302834
- Práctica cuantitativa de los intercambios DEX (2) -- Guía de usuario de hiperlíquidos
- Prácticas de cuantificación en el mercado DEX ((2) -- Guía de uso de Hyperliquid
- Práctica cuantitativa de los intercambios DEX (1) -- Guía de usuario de dYdX v4
- Introducción al arbitraje de lead-lag en criptomonedas (3)
- Prácticas de cuantificación de las bolsas DEX ((1) -- dYdX v4 Guía de uso
- Introducción al conjunto de Lead-Lag en las monedas digitales (3)
- Introducción al arbitraje de lead-lag en criptomonedas (2)
- Introducción al conjunto de Lead-Lag en las monedas digitales (2)
- Discusión sobre la recepción de señales externas de la plataforma FMZ: una solución completa para recibir señales con servicio HTTP incorporado en la estrategia
- Exploración de la recepción de señales externas de la plataforma FMZ: estrategias para una solución completa de recepción de señales de servicios HTTP integrados
- Introducción al arbitraje de lead-lag en criptomonedas (1)
- Comercio cuantitativo de criptomonedas para principiantes - acercándote a la criptomoneda cuantitativa (8)
- Comercio cuantitativo de criptomonedas para principiantes - acercándote a la criptomoneda cuantitativa (7)
- Comercio cuantitativo de criptomonedas para principiantes - acercándote a la criptomoneda cuantitativa (6)
- Visión general y arquitectura de la interfaz principal de la plataforma de negociación cuántica FMZ
- Diseño de estrategia de Martingale para futuros de criptomonedas
- Comercio cuantitativo de criptomonedas para principiantes - acercándote a la criptomoneda cuantitativa (5)
- Comercio cuantitativo de criptomonedas para principiantes - acercándote a la criptomoneda cuantitativa (4)
- Comercio cuantitativo de criptomonedas para principiantes - acercándote a la criptomoneda cuantitativa (3)
- Comercio cuantitativo de criptomonedas para principiantes: acercándote a la criptomoneda cuantitativa (2)
- Comercio cuantitativo de criptomonedas para principiantes - acercándote a la criptomoneda cuantitativa (1)
- Ejemplo de contrato de acceso al protocolo general en FMZ
- Estrategia de arbitraje de diferencias al contado de múltiples bolsas Compartición lógica
- Módulo de visualización para construir estrategias comerciales - en profundidad
- Utilice la función KLineChart para hacer más fácil el diseño del dibujo de estrategias
- Usar la función KlineChart para hacer más sencillo el diseño de gráficos de estrategias
- Múltiples bolsas comparten estrategias lógicas para los precios de los tipos de cambio
- La estrategia de backtesting de JavaScript está depurada en DevTools del navegador Chrome
- Descarga de la política de JavaScript en el navegador Chrome con DevTools
- Los módulos de visualización construyen estrategias de transacción -- en profundidad.
- Una estrategia de equilibrio sostenible para el mercado bajista