Estrategia del indicador de momentum RSI basada en interpolación polinómica
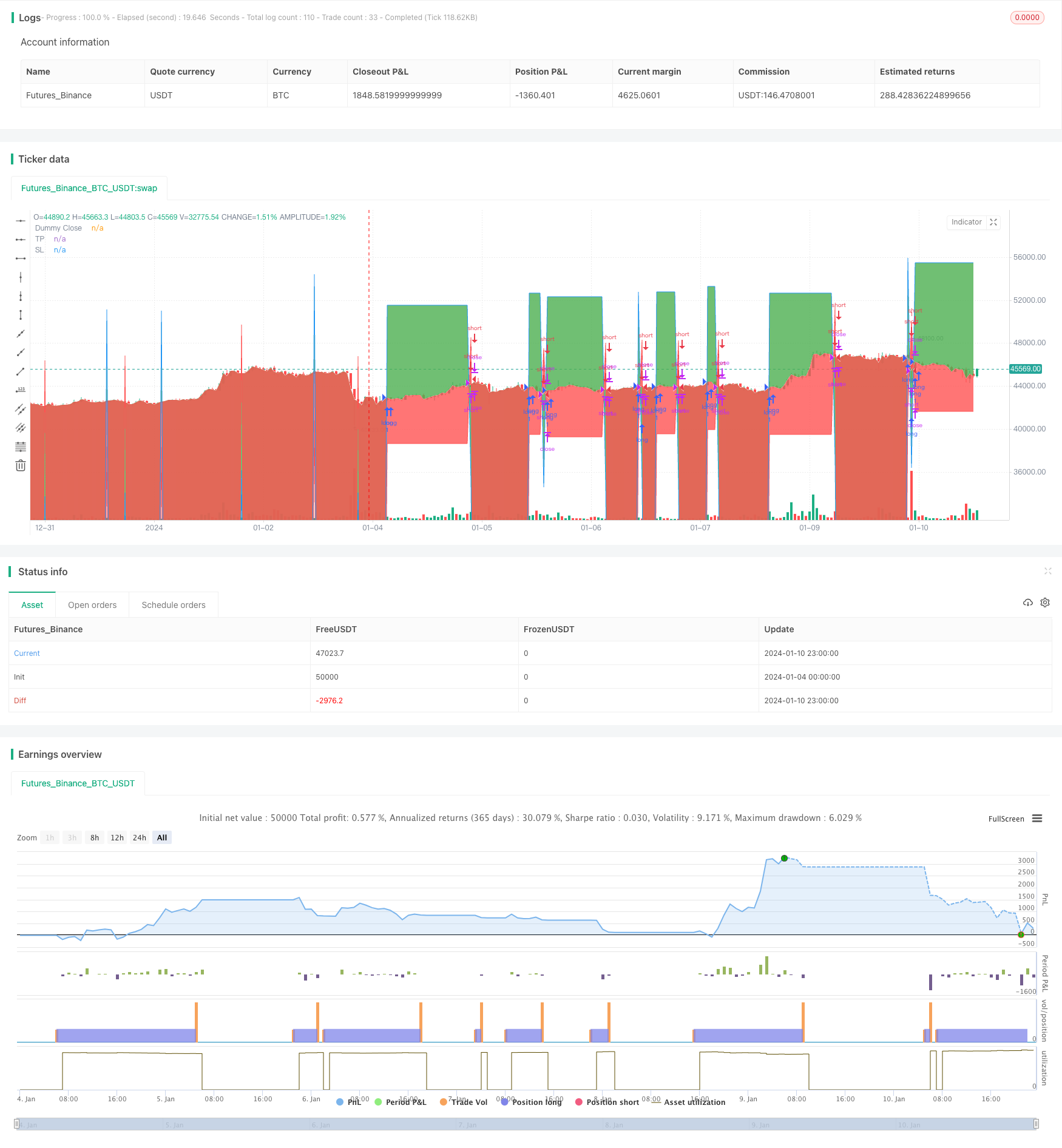
Descripción general
La estrategia utiliza el indicador de movimiento del RSI Delta-RSI basado en el intervalo de polinomios para generar señales de negociación. El Delta-RSI se suaviza el RSI mediante el método de regresión de polinomios locales, obteniendo la derivada de tiempo de un grado del RSI, que se usa como indicador de movimiento. La estrategia agrega un filtro basado en ATR, la transacción y el RSI, que puede filtrar una parte de las señales de falsedad.
El principio
El indicador central de la estrategia es el Delta-RSI, cuyos pasos de cálculo son los siguientes:
- Introducir una secuencia de tiempo RSI con una longitud de rsi_l
- En una ventana deslizante de longitud de ventana, el método de inserción múltiple se ajusta al RSI
- Calcula el derivado de unidad de la curva de ajuste en el punto actual, el Delta-RSI
- El delta-RSI sube 0 para comprar y baja 0 para vender
- También se puede combinar la línea de señal Delta-RSI para generar señales de negociación
Las estrategias para filtrar las señales a través de filtros de ATR, volumen de transacción y RSI:
- Filtro ATR: el ATR del ciclo N actual es mayor que el ATR del ciclo M, lo que indica un aumento en la fluctuación
- Filtro de transacciones: el volumen de transacciones actual es más de N veces el volumen de transacciones promedio de casi M ciclos
- Filtrador RSI: RSI por encima de la brecha 1 y por debajo de la brecha 2, filtrando las zonas de sobrecompra y sobreventa
Las ventajas
La estrategia tiene las siguientes ventajas:
- El indicador Delta-RSI es más sensible y puede capturar un cambio de tendencia temprano
- Se añade un filtro que elimina la mayoría de las señales falsas y mejora la calidad de la señal.
- Valores de inserción y parámetros de filtración multipolares que se pueden personalizar para adaptarse a diferentes entornos de mercado
- Se puede hacer más tiempo libre por separado para satisfacer diferentes preferencias
- Se puede configurar un stop loss para controlar las pérdidas y ganancias
El riesgo
La estrategia también tiene los siguientes riesgos:
- La configuración incorrecta de los parámetros puede hacer que el exceso de suavización o exceso de filtro
- Riesgo de pérdida de una posición superior o de una posición baja
- La configuración de stop loss demasiado amplia puede ampliar las pérdidas individuales
Estos riesgos pueden ser controlados y reducidos mediante la optimización de los parámetros, la adaptación de las condiciones de filtración y la configuración de un stop loss más estricto.
Dirección de optimización
La estrategia puede ser optimizada aún más:
- Optimización de los parámetros del modelo Delta-RSI para mejorar la adecuación
- Aumentar las filtraciones adaptativas basadas en el aprendizaje automático
- Ajuste de parámetros según las diferentes variedades
- Métodos como el aumento de la cartera de modelos para mejorar la estabilidad
Resumir
La estrategia aprovecha las características de alta sensibilidad del indicador Delta-RSI, junto con un mecanismo de filtración riguroso, para mejorar la calidad de la estrategia, a la vez que se controla el riesgo. A través de la optimización continua de los parámetros y modelos, se espera que la estrategia amplíe aún más la rentabilidad positiva, una estrategia de comercio cuantitativa eficaz.
/*backtest
start: 2024-01-04 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-11 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
// This source code is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License 2.0 at https://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/
// © tbiktag
//
// Delta-RSI Oscillator Strategy With Filters
//
// This is a version of the Delta-RSI Oscillator Strategy compatible with
// the Strategy Tester.
//
// This version also allows filtering the trade signals generated by Delts-RSI
// by means of volatility (defined by ATR), relative volume and RSI(14).
//
// Delta-RSI (© tbiktag) is a smoothed time derivative of the RSI designed
// as a momentum indicator. For the original publication, see link below:
// https://www.tradingview.com/script/OXQVFTQD-Delta-RSI-Oscillator/
//
// D-RSI model parameters:
// RSI Length: The timeframe of the RSI that serves as an input to D-RSI.
// Frame Length: The length of the lookback frame used for local regression.
// Polynomial Order: The order of the local polynomial function used to interpolate
// the RSI.
// Trade signals are generated based on three optional conditions:
// - Zero-crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses zero from negative to positive
// values (bearish otherwise)
// - Signal Line Crossing: bullish when D-RSI crosses from below to above the signal
// line (bearish otherwise)
// - Direction Change: bullish when D-RSI was negative and starts ascending
// (bearish otherwise)
//
//@version=4
strategy(title="Delta-RSI Strategy with Filters", shorttitle = "D-RSI with filters", overlay = true)
// ---Subroutines---
matrix_get(_A,_i,_j,_nrows) =>
// Get the value of the element of an implied 2d matrix
//input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _i :: integer: row number
// _j :: integer: column number
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in the implied 2d matrix
array.get(_A,_i+_nrows*_j)
matrix_set(_A,_value,_i,_j,_nrows) =>
// Set a value to the element of an implied 2d matrix
//input:
// _A :: array, changed on output: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _value :: float: the new value to be set
// _i :: integer: row number
// _j :: integer: column number
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in the implied 2d matrix
array.set(_A,_i+_nrows*_j,_value)
transpose(_A,_nrows,_ncolumns) =>
// Transpose an implied 2d matrix
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumns :: integer: number of columns in _A
// output:
// _AT :: array: pseudo 2d matrix with implied dimensions: _ncolums x _nrows
var _AT = array.new_float(_nrows*_ncolumns,0)
for i = 0 to _nrows-1
for j = 0 to _ncolumns-1
matrix_set(_AT, matrix_get(_A,i,j,_nrows),j,i,_ncolumns)
_AT
multiply(_A,_B,_nrowsA,_ncolumnsA,_ncolumnsB) =>
// Calculate scalar product of two matrices
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix
// _B :: array: pseudo 2d matrix
// _nrowsA :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumnsA :: integer: number of columns in _A
// _ncolumnsB :: integer: number of columns in _B
// output:
// _C:: array: pseudo 2d matrix with implied dimensions _nrowsA x _ncolumnsB
var _C = array.new_float(_nrowsA*_ncolumnsB,0)
int _nrowsB = _ncolumnsA
float elementC= 0.0
for i = 0 to _nrowsA-1
for j = 0 to _ncolumnsB-1
elementC := 0
for k = 0 to _ncolumnsA-1
elementC := elementC + matrix_get(_A,i,k,_nrowsA)*matrix_get(_B,k,j,_nrowsB)
matrix_set(_C,elementC,i,j,_nrowsA)
_C
vnorm(_X,_n) =>
//Square norm of vector _X with size _n
float _norm = 0.0
for i = 0 to _n-1
_norm := _norm + pow(array.get(_X,i),2)
sqrt(_norm)
qr_diag(_A,_nrows,_ncolumns) =>
//QR Decomposition with Modified Gram-Schmidt Algorithm (Column-Oriented)
// input:
// _A :: array: pseudo 2d matrix _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(n-1)]]
// _nrows :: integer: number of rows in _A
// _ncolumns :: integer: number of columns in _A
// output:
// _Q: unitary matrix, implied dimenstions _nrows x _ncolumns
// _R: upper triangular matrix, implied dimansions _ncolumns x _ncolumns
var _Q = array.new_float(_nrows*_ncolumns,0)
var _R = array.new_float(_ncolumns*_ncolumns,0)
var _a = array.new_float(_nrows,0)
var _q = array.new_float(_nrows,0)
float _r = 0.0
float _aux = 0.0
//get first column of _A and its norm:
for i = 0 to _nrows-1
array.set(_a,i,matrix_get(_A,i,0,_nrows))
_r := vnorm(_a,_nrows)
//assign first diagonal element of R and first column of Q
matrix_set(_R,_r,0,0,_ncolumns)
for i = 0 to _nrows-1
matrix_set(_Q,array.get(_a,i)/_r,i,0,_nrows)
if _ncolumns != 1
//repeat for the rest of the columns
for k = 1 to _ncolumns-1
for i = 0 to _nrows-1
array.set(_a,i,matrix_get(_A,i,k,_nrows))
for j = 0 to k-1
//get R_jk as scalar product of Q_j column and A_k column:
_r := 0
for i = 0 to _nrows-1
_r := _r + matrix_get(_Q,i,j,_nrows)*array.get(_a,i)
matrix_set(_R,_r,j,k,_ncolumns)
//update vector _a
for i = 0 to _nrows-1
_aux := array.get(_a,i) - _r*matrix_get(_Q,i,j,_nrows)
array.set(_a,i,_aux)
//get diagonal R_kk and Q_k column
_r := vnorm(_a,_nrows)
matrix_set(_R,_r,k,k,_ncolumns)
for i = 0 to _nrows-1
matrix_set(_Q,array.get(_a,i)/_r,i,k,_nrows)
[_Q,_R]
pinv(_A,_nrows,_ncolumns) =>
//Pseudoinverse of matrix _A calculated using QR decomposition
// Input:
// _A:: array: implied as a (_nrows x _ncolumns) matrix
//. _A = [[column_0],[column_1],...,[column_(_ncolumns-1)]]
// Output:
// _Ainv:: array implied as a (_ncolumns x _nrows) matrix
// _A = [[row_0],[row_1],...,[row_(_nrows-1)]]
// ----
// First find the QR factorization of A: A = QR,
// where R is upper triangular matrix.
// Then _Ainv = R^-1*Q^T.
// ----
[_Q,_R] = qr_diag(_A,_nrows,_ncolumns)
_QT = transpose(_Q,_nrows,_ncolumns)
// Calculate Rinv:
var _Rinv = array.new_float(_ncolumns*_ncolumns,0)
float _r = 0.0
matrix_set(_Rinv,1/matrix_get(_R,0,0,_ncolumns),0,0,_ncolumns)
if _ncolumns != 1
for j = 1 to _ncolumns-1
for i = 0 to j-1
_r := 0.0
for k = i to j-1
_r := _r + matrix_get(_Rinv,i,k,_ncolumns)*matrix_get(_R,k,j,_ncolumns)
matrix_set(_Rinv,_r,i,j,_ncolumns)
for k = 0 to j-1
matrix_set(_Rinv,-matrix_get(_Rinv,k,j,_ncolumns)/matrix_get(_R,j,j,_ncolumns),k,j,_ncolumns)
matrix_set(_Rinv,1/matrix_get(_R,j,j,_ncolumns),j,j,_ncolumns)
//
_Ainv = multiply(_Rinv,_QT,_ncolumns,_ncolumns,_nrows)
_Ainv
norm_rmse(_x, _xhat) =>
// Root Mean Square Error normalized to the sample mean
// _x. :: array float, original data
// _xhat :: array float, model estimate
// output
// _nrmse:: float
float _nrmse = 0.0
if array.size(_x) != array.size(_xhat)
_nrmse := na
else
int _N = array.size(_x)
float _mse = 0.0
for i = 0 to _N-1
_mse := _mse + pow(array.get(_x,i) - array.get(_xhat,i),2)/_N
_xmean = array.sum(_x)/_N
_nrmse := sqrt(_mse) /_xmean
_nrmse
diff(_src,_window,_degree) =>
// Polynomial differentiator
// input:
// _src:: input series
// _window:: integer: wigth of the moving lookback window
// _degree:: integer: degree of fitting polynomial
// output:
// _diff :: series: time derivative
// _nrmse:: float: normalized root mean square error
//
// Vandermonde matrix with implied dimensions (window x degree+1)
// Linear form: J = [ [z]^0, [z]^1, ... [z]^degree],
// with z = [ (1-window)/2 to (window-1)/2 ]
var _J = array.new_float(_window*(_degree+1),0)
for i = 0 to _window-1
for j = 0 to _degree
matrix_set(_J,pow(i,j),i,j,_window)
// Vector of raw datapoints:
var _Y_raw = array.new_float(_window,na)
for j = 0 to _window-1
array.set(_Y_raw,j,_src[_window-1-j])
// Calculate polynomial coefficients which minimize the loss function
_C = pinv(_J,_window,_degree+1)
_a_coef = multiply(_C,_Y_raw,_degree+1,_window,1)
// For first derivative, approximate the last point (i.e. z=window-1) by
float _diff = 0.0
for i = 1 to _degree
_diff := _diff + i*array.get(_a_coef,i)*pow(_window-1,i-1)
// Calculates data estimate (needed for rmse)
_Y_hat = multiply(_J,_a_coef,_window,_degree+1,1)
float _nrmse = norm_rmse(_Y_raw,_Y_hat)
[_diff,_nrmse]
/// --- main ---
degree = input(title="Polynomial Order", group = "Model Parameters:",
inline = "linepar1", type = input.integer, defval=3, minval = 1)
rsi_l = input(title = "RSI Length", group = "Model Parameters:",
inline = "linepar1", type = input.integer, defval = 21, minval = 1,
tooltip="The period length of RSI that is used as input.")
window = input(title="Length ( > Order)", group = "Model Parameters:",
inline = "linepar2", type = input.integer, defval=50, minval = 2)
signalLength = input(title="Signal Length", group = "Model Parameters:",
inline = "linepar2", type=input.integer, defval=9,
tooltip="The signal line is a EMA of the D-RSI time series.")
islong = input(title = "Long", group = "Allowed Entries:",
inline = "lineent",type = input.bool, defval = true)
isshort = input(title = "Short", group = "Allowed Entries:",
inline = "lineent", type = input.bool, defval= true)
buycond = input(title="Buy", group = "Entry and Exit Conditions:",
inline = "linecond",type = input.string, defval="Signal Line Crossing",
options=["Zero-Crossing", "Signal Line Crossing","Direction Change"])
sellcond = input(title="Sell", group = "Entry and Exit Conditions:",
inline = "linecond",type = input.string, defval="Signal Line Crossing",
options=["Zero-Crossing", "Signal Line Crossing","Direction Change"])
endcond = input(title="Exit", group = "Entry and Exit Conditions:",
inline = "linecond",type = input.string, defval="Signal Line Crossing",
options=["Zero-Crossing", "Signal Line Crossing","Direction Change"])
filterlong =input(title = "Long Entries", inline = 'linefilt', group = 'Apply Filters to',
type = input.bool, defval = true)
filtershort =input(title = "Short Enties", inline = 'linefilt', group = 'Apply Filters to',
type = input.bool, defval = true)
filterend =input(title = "Exits", inline = 'linefilt', group = 'Apply Filters to',
type = input.bool, defval = true)
usevol =input(title = "", inline = 'linefiltvol', group = 'Relative Volume Filter:',
type = input.bool, defval = false)
rvol = input(title = "Volume >", inline = 'linefiltvol', group = 'Relative Volume Filter:',
type = input.integer, defval = 1)
len_vol = input(title = "Avg. Volume Over Period", inline = 'linefiltvol', group = 'Relative Volume Filter:',
type = input.integer, defval = 30, minval = 1,
tooltip="The current volume must be greater than N times the M-period average volume.")
useatr =input(title = "", inline = 'linefiltatr', group = 'Volatility Filter:',
type = input.bool, defval = false)
len_atr1 = input(title = "ATR", inline = 'linefiltatr', group = 'Volatility Filter:',
type = input.integer, defval = 5, minval = 1)
len_atr2 = input(title = "> ATR", inline = 'linefiltatr', group = 'Volatility Filter:',
type = input.integer, defval = 30, minval = 1,
tooltip="The N-period ATR must be greater than the M-period ATR.")
usersi =input(title = "", inline = 'linersi', group = 'Overbought/Oversold Filter:',
type = input.bool, defval = false)
rsitrhs1 = input(title = "", inline = 'linersi', group = 'Overbought/Oversold Filter:',
type = input.integer, defval = 0, minval=0, maxval=100)
rsitrhs2 = input(title = "< RSI (14) >", inline = 'linersi', group = 'Overbought/Oversold Filter:',
type = input.integer, defval = 100, minval=0, maxval=100,
tooltip="RSI(14) must be in the range between N and M.")
issl = input(title = "SL", inline = 'linesl1', group = 'Stop Loss / Take Profit:',
type = input.bool, defval = false)
slpercent = input(title = ", %", inline = 'linesl1', group = 'Stop Loss / Take Profit:',
type = input.float, defval = 10, minval=0.0)
istrailing = input(title = "Trailing", inline = 'linesl1', group = 'Stop Loss / Take Profit:',
type = input.bool, defval = false)
istp = input(title = "TP", inline = 'linetp1', group = 'Stop Loss / Take Profit:',
type = input.bool, defval = false)
tppercent = input(title = ", %", inline = 'linetp1', group = 'Stop Loss / Take Profit:',
type = input.float, defval = 20)
fixedstart =input(title="", group = "Fixed Backtest Period Start/End Dates:",
inline = "linebac1", type = input.bool, defval = true)
backtest_start=input(title = "", type = input.time, inline = "linebac1",
group = "Fixed Backtest Period Start/End Dates:",
defval = timestamp("01 Jan 2017 13:30 +0000"),
tooltip="If deactivated, backtest staring from the first available price bar.")
fixedend = input(title="", group = "Fixed Backtest Period Start/End Dates:",
inline = "linebac2", type = input.bool, defval = false)
backtest_end =input(title = "", type = input.time, inline = "linebac2",
group = "Fixed Backtest Period Start/End Dates:",
defval = timestamp("30 Dec 2080 23:30 +0000"),
tooltip="If deactivated, backtesting ends at the last available price bar.")
if window < degree
window := degree+1
src = rsi(close,rsi_l)
[drsi,nrmse] = diff(src,window,degree)
signalline = ema(drsi, signalLength)
// Conditions for D-RSI
dirchangeup = (drsi>drsi[1]) and (drsi[1]<drsi[2]) and drsi[1]<0.0
dirchangedw = (drsi<drsi[1]) and (drsi[1]>drsi[2]) and drsi[1]>0.0
crossup = crossover(drsi,0.0)
crossdw = crossunder(drsi,0.0)
crosssignalup = crossover(drsi,signalline)
crosssignaldw = crossunder(drsi,signalline)
// D-RSI signals
drsilong = (buycond=="Direction Change"?dirchangeup:(buycond=="Zero-Crossing"?crossup:crosssignalup))
drsishort= (sellcond=="Direction Change"?dirchangedw:(sellcond=="Zero-Crossing"?crossdw:crosssignaldw))
drisendlong = (endcond=="Direction Change"?dirchangedw:(endcond=="Zero-Crossing"?crossdw:crosssignaldw))
drisendshort= (endcond=="Direction Change"?dirchangeup:(endcond=="Zero-Crossing"?crossup:crosssignalup))
// Filters
rsifilter = usersi?(rsi(close,14) > rsitrhs1 and rsi(close,14) < rsitrhs2):true
volatilityfilter = useatr?(atr(len_atr1) > atr(len_atr2)):true
volumefilter = usevol?(volume > rvol*sma(volume,len_vol)):true
totalfilter = volatilityfilter and volumefilter and rsifilter
//Filtered signals
golong = drsilong and islong and (filterlong?totalfilter:true)
goshort = drsishort and isshort and (filtershort?totalfilter:true)
endlong = drisendlong and (filterend?totalfilter:true)
endshort = drisendlong and (filterend?totalfilter:true)
// Backtest period
//backtest_start = timestamp(syminfo.timezone, startYear, startMonth, startDate, 0, 0)
//backtest_end = timestamp(syminfo.timezone, endYear, endMonth, endDate, 0, 0)
isinrange = true
// Entry price / Take profit / Stop Loss
startprice = valuewhen(condition=golong or goshort, source=close, occurrence=0)
pm = golong?1:goshort?-1:1/sign(strategy.position_size)
takeprofit = startprice*(1+pm*tppercent*0.01)
// fixed stop loss
stoploss = startprice * (1-pm*slpercent*0.01)
// trailing stop loss
if istrailing and strategy.position_size>0
stoploss := max(close*(1 - slpercent*0.01),stoploss[1])
else if istrailing and strategy.position_size<0
stoploss := min(close*(1 + slpercent*0.01),stoploss[1])
tpline = plot(takeprofit,color=color.blue,transp=100, title="TP")
slline = plot(stoploss, color=color.red, transp=100, title="SL")
p1 = plot(close,transp=100,color=color.white, title="Dummy Close")
fill(p1, tpline, color=color.green, transp=istp?70:100, title="TP")
fill(p1, slline, color=color.red, transp=issl?70:100, title="SL")
// Backtest: Basic Entry and Exit Conditions
if golong and isinrange and islong
strategy.entry("long", true )
alert("D-RSI Long " + syminfo.tickerid, alert.freq_once_per_bar_close)
if goshort and isinrange and isshort
strategy.entry("short", false)
alert("D-RSI Short " + syminfo.tickerid, alert.freq_once_per_bar_close)
if endlong
strategy.close("long", alert_message="Close Long")
alert("D-RSI Exit Long " + syminfo.tickerid, alert.freq_once_per_bar_close)
if endshort
strategy.close("short", alert_message="Close Short")
alert("D-RSI Exit Short " + syminfo.tickerid, alert.freq_once_per_bar_close)
// Exit via SL or TP
strategy.exit(id="sl/tp long", from_entry="long", stop=issl?stoploss:na,
limit=istp?takeprofit:na, alert_message="Close Long")
strategy.exit(id="sl/tp short",from_entry="short",stop=issl?stoploss:na,
limit=istp?takeprofit:na, alert_message="Stop Loss Short")
// Close if outside the range
if (not isinrange)
strategy.close_all()