Estrategia típica de seguimiento de tendencias
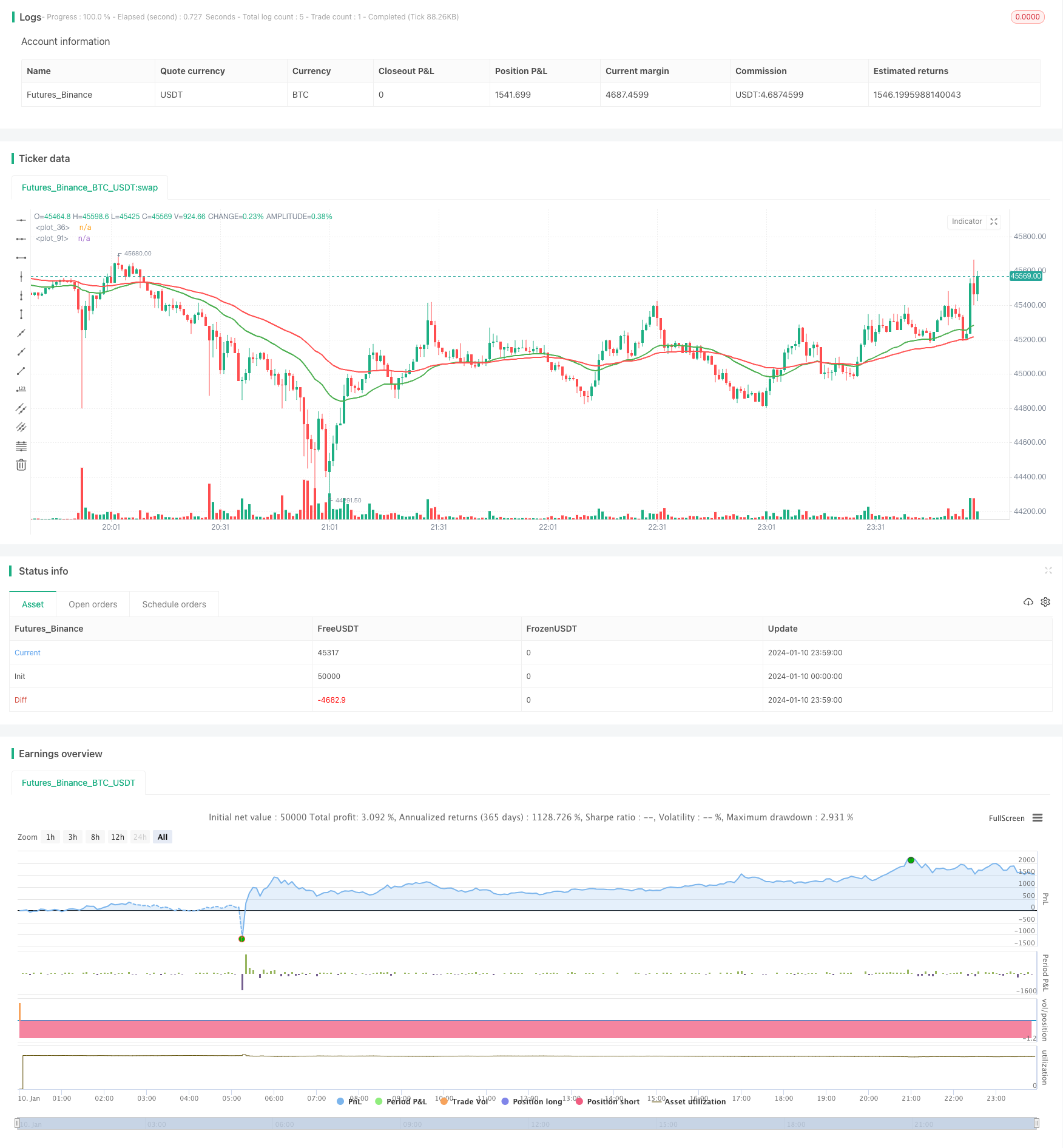
Descripción general
La estrategia de cruce de dos medias es una estrategia típica de seguimiento de tendencias. Utiliza las medias de EMA de dos períodos diferentes, haciendo más cuando las medias de corto período atraviesan las medias de largo período, y haciendo hueco cuando las medias de corto período atraviesan las medias de largo período, para capturar el punto de inflexión de la tendencia de los precios.
Principio de estrategia
El indicador central de la estrategia son las dos medias EMA, de 30 y 60 periodos respectivamente. En el código se calculan las dos medias EMA a través de funciones personalizadas:
emaLen1 = emaFuncOne(close, lenMA1)
emaLen2 = emaFuncTwo(close, lenMA2)
La señal de negociación de la estrategia proviene de la intersección de dos líneas medias EMA:
currentState = if emaLen2 > emaLen1
0
else
1
previousState = if emaLastLen2 > emaLastLen1
0
else
1
convergence = if currentState != previousState
1
else
0
Cuando un EMA a corto plazo se cruza con un EMA a largo plazo, el estado actual no es el mismo que el estado anterior. Cuando el EMA corto atraviesa el EMA largo, el estado actual no es igual al estado anterior, y se produce una señal de cruce.
Análisis de las ventajas
La estrategia tiene las siguientes ventajas:
- La estrategia es sencilla, intuitiva, fácil de entender y de implementar
- Utiliza las propiedades suaves de la línea media de la EMA para filtrar el ruido del mercado
- El seguimiento automático de las tendencias no es fácil de perder.
Análisis de riesgos
La estrategia también tiene sus riesgos:
- Las señales de cruce de línea recta pueden retrasarse y no capturar el giro a tiempo.
- Las señales falsas pueden aparecer varias veces durante una conmoción.
- La configuración incorrecta de los parámetros puede resultar demasiado sensible o demasiado retrasado
Se puede optimizar ajustando el ciclo EMA o añadiendo condiciones de filtración.
Dirección de optimización
La estrategia puede ser optimizada en los siguientes aspectos:
- Prueba de combinaciones de EMA de diferentes longitudes
- Las condiciones de aumento de volumen o fluctuación filtran las falsas señales
- Combinado con otros indicadores que confirman tendencias, como el MACD
- Optimización de la gestión de fondos y establecimiento de paradas de pérdidas
Resumir
La estrategia de cruce de dos líneas uniformes es una estrategia de seguimiento de tendencias sencilla y práctica en general. Es directa, fácil de implementar y puede seguir la tendencia automáticamente. Pero también existe el riesgo de algunas señales atrasadas y falsas.
/*backtest
start: 2024-01-10 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-11 00:00:00
period: 1m
basePeriod: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=2
strategy("ParkerMAStrat", overlay=true)
lenMA1=input(title="Length 1", defval=30)
lenMA2=input(title="Length 2", defval=60)
x = 0
checkLines(current, last) =>
if current > last
x = 1
else
x = 0
x
//plot ema based on len1
emaFuncOne(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[1])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
emaLen1 = emaFuncOne(close, lenMA1)
plot(emaLen1, color=green, transp=0, linewidth=2)
// now we plot the _10_period_ema
//plot ema based on len2
emaFuncTwo(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[1])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
//plot ema based on len2
emaFuncOneLast(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[0])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
//plot ema based on len2
emaFuncTwoLast(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[0])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
emaLastLen1 = emaFuncOneLast(close, lenMA1)
emaLastLen2 = emaFuncTwoLast(close, lenMA2)
emaLen2 = emaFuncTwo(close, lenMA2)
plot(emaLen2, color=red, transp=30, linewidth=2)
// now we plot the _10_period_ema
//now we compare the two and when green crosses red we buy/sell (line1 vs line2)
previousState = if emaLastLen2 > emaLastLen1
0
else
1
currentState = if emaLen2 > emaLen1
0
else
1
convergence = if currentState != previousState
1
else
0
lineCheck = if convergence == 1
checkLines(currentState, previousState)
if lineCheck == 1
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
else
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)