Stratégie de trading de régression à moyenne mobile bidirectionnelle
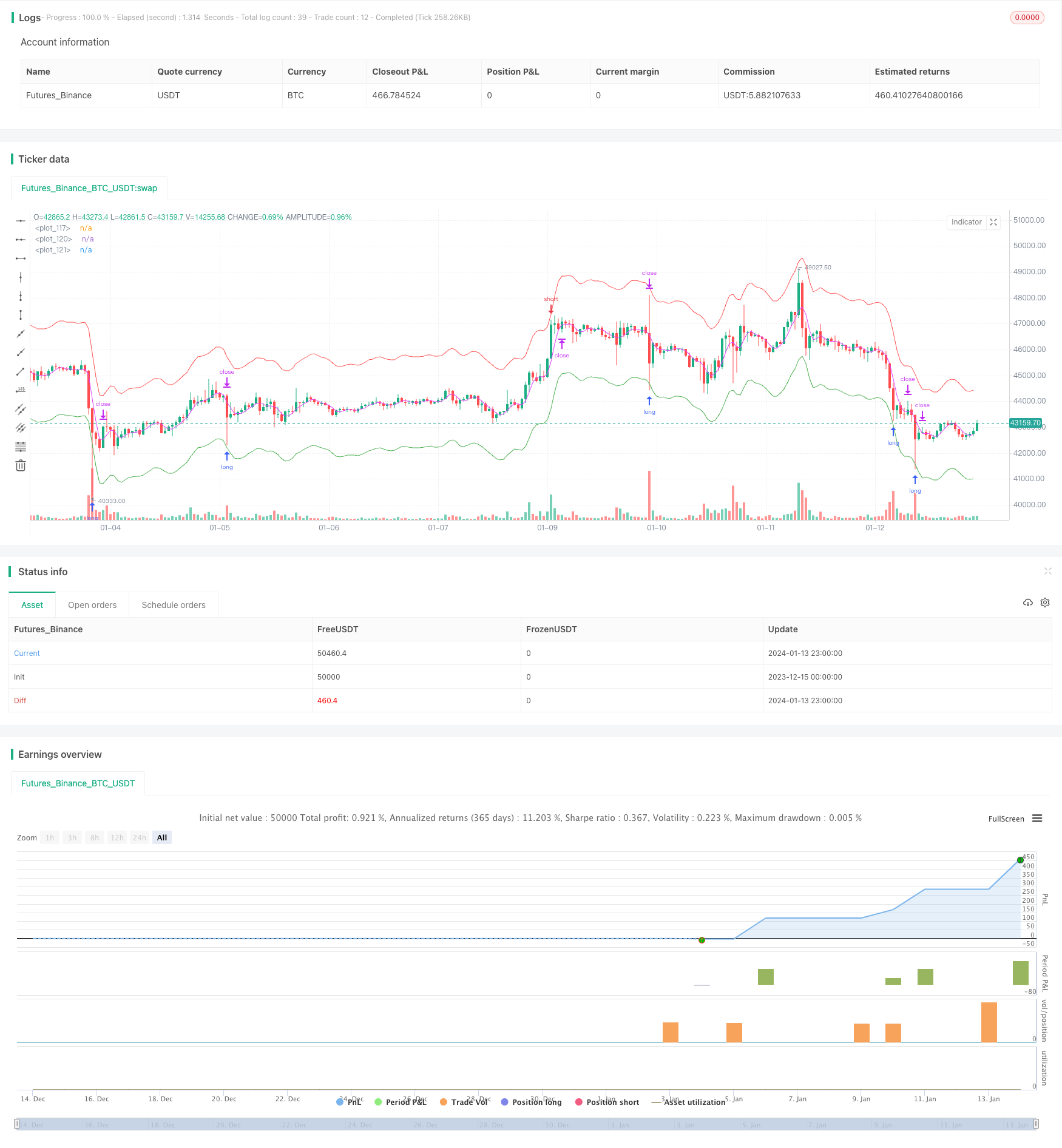
Aperçu
La stratégie de négociation bidirectionnelle de réversion de la moyenne mobile est une stratégie de négociation quantitative construite en utilisant le principe de la réversion de la moyenne des prix. La stratégie permet de saisir les occasions de réversion des prix en définissant plusieurs groupes de moyennes mobiles.
Principe de stratégie
La stratégie est basée sur la théorie de la régression moyenne des prix. Elle considère que les prix tournent toujours autour d’une fluctuation de la valeur moyenne et sont plus susceptibles de revenir à la valeur moyenne lorsque les prix s’écartent fortement de la valeur moyenne. Plus précisément, la stratégie met en place simultanément trois ensembles de courbes moyennes: la courbe moyenne d’ouverture, la courbe moyenne de clôture et la courbe moyenne de limite.
D’un point de vue logique du code, la moyenne de l’ouverture de position est divisée en une ligne longue et une ligne courte, composées respectivement d’une ligne longue et d’une ligne courte. Le degré d’écart entre elles et le prix détermine la taille de la position. De plus, la moyenne de l’aplatissement est une moyenne distincte qui est utilisée pour déterminer le moment de l’aplatissement.
Analyse des avantages
Les principaux avantages de la stratégie de régression à deux voies sont:
- Capture d’une inversion de prix, adaptée à la tendance de rattrapage
- Contrôle des risques par des pertes limites
- Une combinaison de paramètres personnalisable et adaptative
- Facile à comprendre et à optimiser
Cette stratégie s’applique à des variétés à faible volatilité et à des variétés à faible gamme de fluctuations de prix, en particulier celles qui entrent dans la phase de reprise. Elle permet de saisir efficacement les occasions de revers temporaire des prix. De plus, ses mesures de contrôle des risques sont relativement parfaites et permettent de contrôler les pertes dans une certaine mesure, même si les prix ne reviennent pas.
Analyse des risques
La stratégie de régression bilatérale est également risquée:
- Le risque de chute de la poursuite. Lorsque le prix est sur une vague de forte tendance, la stratégie peut potentiellement ouvrir des positions successives qui finissent par éclater.
- Le risque de fluctuation des prix est trop élevé. Si les fluctuations des prix sont trop importantes, les positions risquent d’atteindre le seuil de perte et d’être forcées à la liquidation.
- Le paramétrage de la stratégie a un impact important sur sa rentabilité, et un paramétrage inapproprié peut réduire considérablement la probabilité d’obtenir un profit.
Les risques mentionnés ci-dessus peuvent être optimisés dans les domaines suivants:
- Les restrictions sur l’ouverture de magasins sont renforcées pour éviter des ouvertures trop fréquentes.
- Réduire la taille de la position de manière appropriée afin de prévenir le risque de rupture
- Optimisation des paramètres tels que la périodicité de la ligne moyenne et les paramètres de la ligne de plafonnement
Direction d’optimisation
Cette stratégie a également beaucoup de marge d’optimisation, principalement sous les angles suivants:
- Augmentation de la logique des conditions d’ouverture pour éviter une reprise de la tendance
- Ajout d’une logique de baisse de position pour prévenir les risques de fortes fluctuations de prix
- Essayez différents types d’indicateurs de moyenne pour trouver une meilleure combinaison de paramètres
- Optimiser automatiquement les paramètres à l’aide de l’apprentissage automatique
- Augmentation des stratégies de stop-loss automatiques pour une meilleure maîtrise des risques
Résumer
La stratégie de trading de régression de la courbe des deux sens est rentable en saisissant les opportunités de reprise après que le prix s’est écarté de la courbe des deux sens. Elle maîtrise efficacement les risques et permet d’obtenir de meilleurs rendements grâce à l’optimisation des paramètres. Bien que la stratégie présente également des risques, elle peut être contrôlée en améliorant la logique d’ouverture des positions, en réduisant la taille des positions, etc.
/*backtest
start: 2023-12-15 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-14 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy(title = "hamster-bot MRS 2", overlay = true, default_qty_type = strategy.percent_of_equity, initial_capital = 100, default_qty_value = 30, pyramiding = 1, commission_value = 0.1, backtest_fill_limits_assumption = 1)
info_options = "Options"
on_close = input(false, title = "Entry on close", inline=info_options, group=info_options)
OFFS = input.int(0, minval = 0, maxval = 1, title = "| Offset View", inline=info_options, group=info_options)
trade_offset = input.int(0, minval = 0, maxval = 1, title = "Trade", inline=info_options, group=info_options)
use_kalman_filter = input.bool(false, title="Use Kalman filter", group=info_options)
//MA Opening
info_opening = "MA Opening Long"
maopeningtyp_l = input.string("SMA", title="Type", options=["SMA", "EMA", "TEMA", "DEMA", "ZLEMA", "WMA", "Hma", "Thma", "Ehma", "H", "L", "DMA"], title = "", inline=info_opening, group=info_opening)
maopeningsrc_l = input.source(ohlc4, title = "", inline=info_opening, group=info_opening)
maopeninglen_l = input.int(3, minval = 1, title = "", inline=info_opening, group=info_opening)
long1on = input(true, title = "", inline = "long1")
long1shift = input.float(0.96, step = 0.005, title = "Long", inline = "long1")
long1lot = input.int(10, minval = 0, maxval = 10000, step = 10, title = "Lot 1", inline = "long1")
info_opening_s = "MA Opening Short"
maopeningtyp_s = input.string("SMA", title="Type", options=["SMA", "EMA", "TEMA", "DEMA", "ZLEMA", "WMA", "Hma", "Thma", "Ehma", "H", "L", "DMA"], title = "", inline=info_opening_s, group=info_opening_s)
maopeningsrc_s = input.source(ohlc4, title = "", inline=info_opening_s, group=info_opening_s)
maopeninglen_s = input.int(3, minval = 1, title = "", inline=info_opening_s, group=info_opening_s)
short1on = input(true, title = "", inline = "short1")
short1shift = input.float(1.04, step = 0.005, title = "short", inline = "short1")
short1lot = input.int(10, minval = 0, maxval = 10000, step = 10, title = "Lot 1", inline = "short1")
//MA Closing
info_closing = "MA Closing"
maclosingtyp = input.string("SMA", title="Type", options=["SMA", "EMA", "TEMA", "DEMA", "ZLEMA", "WMA", "Hma", "Thma", "Ehma", "H", "L", "DMA"], title = "", inline=info_closing, group=info_closing)
maclosingsrc = input.source(ohlc4, title = "", inline=info_closing, group=info_closing)
maclosinglen = input.int(3, minval = 1, maxval = 200, title = "", inline=info_closing, group=info_closing)
maclosingmul = input.float(1, step = 0.005, title = "mul", inline=info_closing, group=info_closing)
startTime = input(timestamp("01 Jan 2010 00:00 +0000"), "Start date", inline = "period")
finalTime = input(timestamp("31 Dec 2030 23:59 +0000"), "Final date", inline = "period")
HMA(_src, _length) => ta.wma(2 * ta.wma(_src, _length / 2) - ta.wma(_src, _length), math.round(math.sqrt(_length)))
EHMA(_src, _length) => ta.ema(2 * ta.ema(_src, _length / 2) - ta.ema(_src, _length), math.round(math.sqrt(_length)))
THMA(_src, _length) => ta.wma(ta.wma(_src,_length / 3) * 3 - ta.wma(_src, _length / 2) - ta.wma(_src, _length), _length)
tema(sec, length)=>
tema1= ta.ema(sec, length)
tema2= ta.ema(tema1, length)
tema3= ta.ema(tema2, length)
tema_r = 3*tema1-3*tema2+tema3
donchian(len) => math.avg(ta.lowest(len), ta.highest(len))
ATR_func(_src, _len)=>
atrLow = low - ta.atr(_len)
trailAtrLow = atrLow
trailAtrLow := na(trailAtrLow[1]) ? trailAtrLow : atrLow >= trailAtrLow[1] ? atrLow : trailAtrLow[1]
supportHit = _src <= trailAtrLow
trailAtrLow := supportHit ? atrLow : trailAtrLow
trailAtrLow
f_dema(src, len)=>
EMA1 = ta.ema(src, len)
EMA2 = ta.ema(EMA1, len)
DEMA = (2*EMA1)-EMA2
f_zlema(src, period) =>
lag = math.round((period - 1) / 2)
ema_data = src + (src - src[lag])
zl= ta.ema(ema_data, period)
f_kalman_filter(src) =>
float value1= na
float value2 = na
value1 := 0.2 * (src - src[1]) + 0.8 * nz(value1[1])
value2 := 0.1 * (ta.tr) + 0.8 * nz(value2[1])
lambda = math.abs(value1 / value2)
alpha = (-math.pow(lambda, 2) + math.sqrt(math.pow(lambda, 4) + 16 * math.pow(lambda, 2)))/8
value3 = float(na)
value3 := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(value3[1])
//SWITCH
ma_func(modeSwitch, src, len, use_k_f=true) =>
modeSwitch == "SMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ta.sma(src, len)) : ta.sma(src, len) :
modeSwitch == "RMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ta.rma(src, len)) : ta.rma(src, len) :
modeSwitch == "EMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ta.ema(src, len)) : ta.ema(src, len) :
modeSwitch == "TEMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(tema(src, len)) : tema(src, len):
modeSwitch == "DEMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(f_dema(src, len)) : f_dema(src, len):
modeSwitch == "ZLEMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(f_zlema(src, len)) : f_zlema(src, len):
modeSwitch == "WMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ta.wma(src, len)) : ta.wma(src, len):
modeSwitch == "VWMA" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ta.vwma(src, len)) : ta.vwma(src, len):
modeSwitch == "Hma" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(HMA(src, len)) : HMA(src, len):
modeSwitch == "Ehma" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(EHMA(src, len)) : EHMA(src, len):
modeSwitch == "Thma" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(THMA(src, len/2)) : THMA(src, len/2):
modeSwitch == "ATR" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ATR_func(src, len)): ATR_func(src, len) :
modeSwitch == "L" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ta.lowest(len)): ta.lowest(len) :
modeSwitch == "H" ? use_kalman_filter and use_k_f ? f_kalman_filter(ta.highest(len)): ta.highest(len) :
modeSwitch == "DMA" ? donchian(len) : na
//Var
sum = 0.0
maopening_l = 0.0
maopening_s = 0.0
maclosing = 0.0
pos = strategy.position_size
p = 0.0
p := pos == 0 ? (strategy.equity / 100) / close : p[1]
truetime = true
loss = 0.0
maxloss = 0.0
equity = 0.0
//MA Opening
maopening_l := ma_func(maopeningtyp_l, maopeningsrc_l, maopeninglen_l)
maopening_s := ma_func(maopeningtyp_s, maopeningsrc_s, maopeninglen_s)
//MA Closing
maclosing := ma_func(maclosingtyp, maclosingsrc, maclosinglen) * maclosingmul
long1 = long1on == false ? 0 : long1shift == 0 ? 0 : long1lot == 0 ? 0 : maopening_l == 0 ? 0 : maopening_l * long1shift
short1 = short1on == false ? 0 : short1shift == 0 ? 0 : short1lot == 0 ? 0 : maopening_s == 0 ? 0 : maopening_s * short1shift
//Colors
long1col = long1 == 0 ? na : color.green
short1col = short1 == 0 ? na : color.red
//Lines
// plot(maopening_l, offset = OFFS, color = color.new(color.green, 50))
// plot(maopening_s, offset = OFFS, color = color.new(color.red, 50))
plot(maclosing, offset = OFFS, color = color.fuchsia)
long1line = long1 == 0 ? close : long1
short1line = short1 == 0 ? close : short1
plot(long1line, offset = OFFS, color = long1col)
plot(short1line, offset = OFFS, color = short1col)
//Lots
lotlong1 = p * long1lot
lotshort1 = p * short1lot
//Entry
if truetime
//Long
sum := 0
strategy.entry("L", strategy.long, lotlong1, limit = on_close ? na : long1, when = long1 > 0 and pos <= sum and (on_close ? close <= long1[trade_offset] : true))
sum := lotlong1
//Short
sum := 0
pos := -1 * pos
strategy.entry("S", strategy.short, lotshort1, limit = on_close ? na : short1, when = short1 > 0 and pos <= sum and (on_close ? close >= short1[trade_offset] : true))
sum := lotshort1
strategy.exit("Exit", na, limit = maclosing)
if time > finalTime
strategy.close_all()