विचलन दर BIAS व्यापार रणनीति
लेखक:अच्छाई, बनाया गयाः 2020-06-30 09:58:26, अद्यतन किया गयाः 2025-01-14 20:33:24[TOC]

सारांश
जैसा कि कहा जाता है, यह दुनिया लंबे समय तक एकजुट होने के बाद अलग हो जाएगी। लंबे समय तक विभाजित होने के बाद भी विपरीत होगा। और यह घटना वायदा बाजार में भी मौजूद है। कोई विविधता नहीं है जो केवल बढ़ती है लेकिन गिरती नहीं है। लेकिन कब बढ़ना है और कब गिरना है, यह विचलन दर पर निर्भर करता है। इस लेख में, हम एक सरल ट्रेडिंग रणनीति बनाने के लिए विचलन दर का उपयोग करेंगे।
संक्षिप्त परिचय
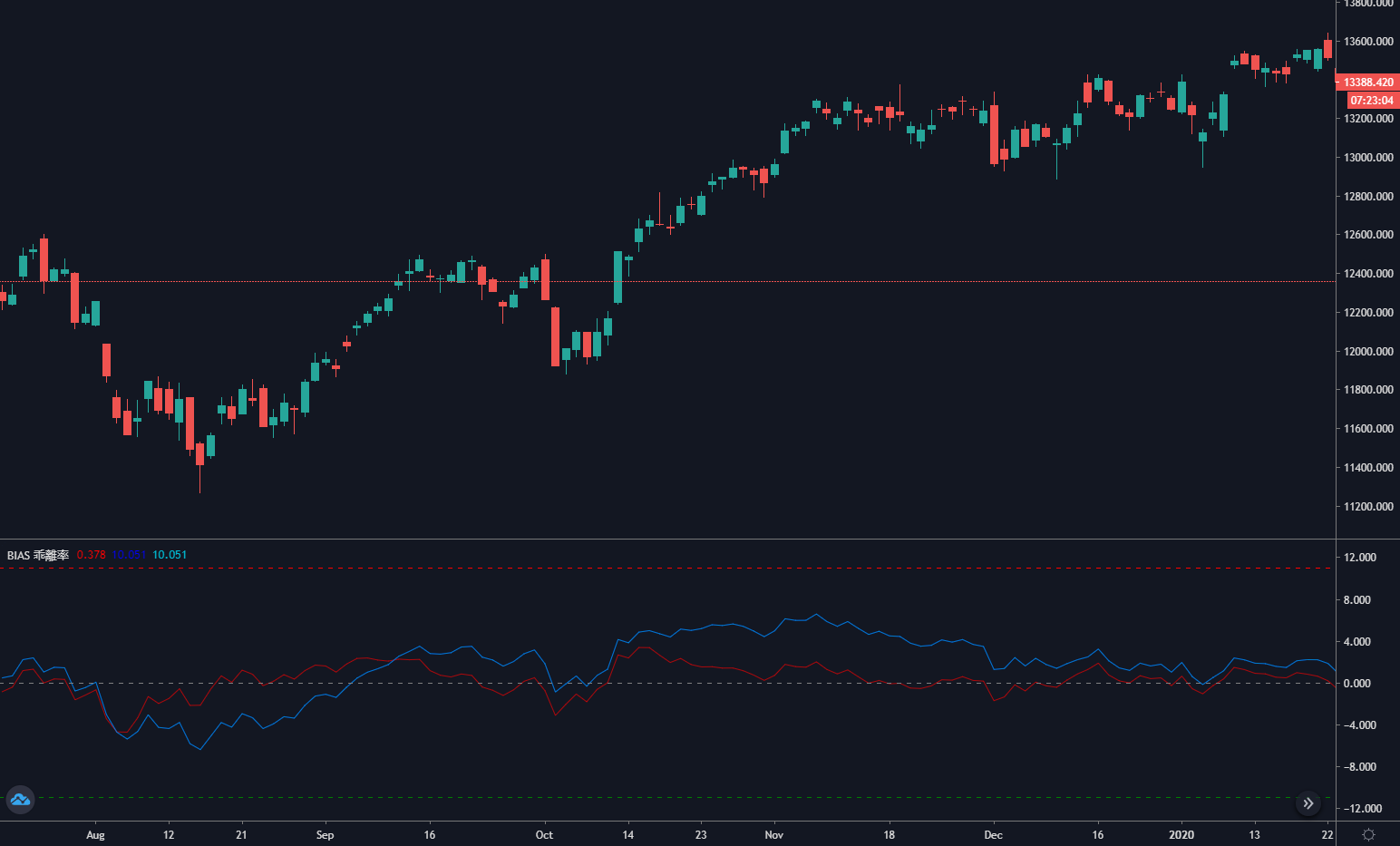
विचलन दर BIAS चलती औसत से प्राप्त एक तकनीकी संकेतक है। यह मुख्य रूप से उतार-चढ़ाव में चलती औसत से मूल्य विचलन की डिग्री को मापने के लिए प्रतिशत के रूप में है। यदि चलती औसत एक व्यापारी की औसत लागत है, तो विचलन दर व्यापारी की औसत रिटर्न दर है।
विचलन दर का सिद्धांत
विचलन दर का सैद्धांतिक आधार व्यापारी के दिल का विश्लेषण है। जब कीमत बाजार की औसत लागत से अधिक होती है, तो इसका मतलब है कि लंबी स्थिति के व्यापारियों के पास मुनाफे को नकद करने का विचार होगा, जिससे कीमत गिर जाएगी। जब कीमत बाजार की औसत लागत से कम होती है, तो इसका मतलब है कि शॉर्ट-सेलर्स लाभदायक होते हैं, और लाभ को नकद करने का विचार कीमत में वृद्धि का कारण बनेगा।
जब कीमत चलती औसत से ऊपर की ओर विचलित होती है, तो विचलन दर बहुत बड़ी होती है, और भविष्य में कीमत गिरने की उच्च संभावना होती है।
जब कीमत चलती औसत से नीचे की ओर विचलित होती है, तो विचलन दर बहुत छोटी होती है, और भविष्य में कीमत बढ़ने की उच्च संभावना होती है।
हालांकि चलती औसत की गणना कीमत से की जाती है, बाहरी रूप के संदर्भ में, कीमत निश्चित रूप से चलती औसत के करीब चलेगी, या कीमत हमेशा चलती औसत के आसपास उतार-चढ़ाव करेगी। यदि कीमत चलती औसत से बहुत दूर हट जाती है, चाहे कीमत चलती औसत से ऊपर या नीचे हो, तो यह अंततः चलती औसत की ओर झुक सकती है, और विचलन दर वह प्रतिशत मूल्य है जो कीमत चलती औसत से विचलित होती है।
विचलन दर की गणना के लिए सूत्र
विचलन दर = [(दिन का समापन मूल्य - N दिन का औसत मूल्य) / N दिन का औसत मूल्य] * 100%
उनमें से, N चलती औसत पैरामीटर है, क्योंकि N की अवधि अलग है, विचलन दर का गणना परिणाम भी अलग है। आम तौर पर, N के मान हैंः 6, 12, 24, 36, आदि। वास्तविक उपयोग में, इसे विभिन्न किस्मों के अनुसार गतिशील रूप से समायोजित भी किया जा सकता है। हालांकि, मापदंडों का चयन बहुत महत्वपूर्ण है। यदि पैरामीटर बहुत छोटा है, तो विचलन दर बहुत संवेदनशील होगी, यदि पैरामीटर बहुत बड़ा है, तो विचलन दर बहुत धीमी होगी। विचलन दर के गणना परिणाम सकारात्मक और नकारात्मक हैं। सकारात्मक विचलन दर जितनी बड़ी होगी, बुल्स का लाभ उतना ही बड़ा होगा और मूल्य सुधार की संभावना उतनी ही अधिक होगी। जितनी बड़ी होगी, लघु विचलन दर उतनी ही अधिक होगी, नकारात्मक लाभ की दर उतनी ही अधिक होगी और रिबाउंड की संभावना उतनी ही अधिक होगी।
रणनीतिक तर्क
चूंकि विचलन दर चलती औसत का एक और रूप है, इसलिए हम डबल चलती औसत रणनीति के आधार पर एक डबल विचलन दर रणनीति को भी अनुकूलित कर सकते हैं। अल्पकालिक विचलन दर और दीर्घकालिक विचलन दर के बीच स्थित संबंध को देखते हुए, वर्तमान बाजार की स्थिति का न्याय किया जाता है। यदि दीर्घकालिक विचलन दर अल्पकालिक विचलन दर से अधिक है, तो यह वास्तव में दीर्घकालिक चलती औसत के पार अल्पकालिक चलती औसत का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है, और इसके विपरीत।
- लंबी स्थिति खोलनाः यदि कोई वर्तमान होल्डिंग स्थिति नहीं है और दीर्घकालिक विचलन दर अल्पकालिक विचलन दर से अधिक है
- शॉर्ट पोजीशन खोलनाः यदि कोई वर्तमान होल्डिंग पोजीशन नहीं है और दीर्घकालिक विचलन दर अल्पकालिक विचलन दर से कम है
- लंबी स्थिति का समापनः यदि एक लंबी स्थिति है, और दीर्घकालिक विचलन दर अल्पकालिक विचलन दर से कम है
- शॉर्ट पोजीशन बंद करनाः यदि एक होल्डिंग शॉर्ट पोजीशन है, और दीर्घकालिक विचलन दर अल्पकालिक विचलन दर से अधिक है
रणनीति लेखन
चरण 1: एक रणनीति ढांचा लिखें
# Strategy main function
def onTick():
pass
# Program entry
def main():
while True: # Enter infinite loop mode
onTick() # execution strategy main function
Sleep(1000) # sleep for 1 second
एफएमजेड प्लेटफॉर्म रोटेशन ट्रेनिंग मोड को अपनाता है।mainकार्य और एकonTickfunction को परिभाषित करने की आवश्यकता है. मुख्य कार्य रणनीति का प्रवेश कार्य है, और कार्यक्रम मुख्य कार्य से शुरू करके कोड लाइन द्वारा लाइन निष्पादित करेगा. मुख्य कार्य में, एक लिखेंwhileलूप और बार-बार निष्पादितonTickरणनीति का सारा कोर कोडonTick function.
चरण 2: आभासी पदों को परिभाषित करें
mp = 0
आभासी पदों का लाभ यह है कि यह लिखना सरल है, और पुनरावर्ती संचालन तेज़ है। यह आम तौर पर बैकटेस्ट वातावरण में उपयोग किया जाता है। यह माना जाता है कि प्रत्येक आदेश पूरी तरह से भरा हुआ है, लेकिन वास्तविक स्थिति आमतौर पर वास्तविक व्यापार में उपयोग की जाती है। चूंकि आभासी स्थिति खोलने और बंद होने के बाद राज्य को रिकॉर्ड करना है, इसलिए इसे वैश्विक चर के रूप में परिभाषित करने की आवश्यकता है।
चरण 3: K लाइन प्राप्त करें
exchange.SetContractType('rb000') # Subscribe to futures varieties
bars_arr = exchange.GetRecords() # Get K-line array
if len(bars_arr) <long + 1: # If the number of K lines is too small
return
FMZ फ़ंक्शन का प्रयोग करनाSetContractType, आप GetRecordsचूंकि यह विचलन दर की गणना करने के लिए एक निश्चित अवधि लेता है, कार्यक्रम त्रुटियों से बचने के लिए, यदि पर्याप्त K लाइनें नहीं हैं, उपयोगifफ़िल्टर करने के लिए कथन।
चरण 4: विचलन दर की गणना करें
close = bars_arr[-2]['Close'] # Get the closing price of the previous K line
ma1 = TA.MA(bars_arr, short)[-2] # Calculate the short-term moving average value of the previous K line
bias1 = (close-ma1) / ma1 * 100 # Calculate the short-term deviation rate value
ma2 = TA.MA(bars_arr, long)[-2] # Calculate the long-term average of the previous K line
bias2 = (close-ma2) / ma2 * 100 # Calculate the long-term deviation rate value
विचलन दर की गणना के लिए सूत्र के अनुसार, हम पहले समापन मूल्य प्राप्त करते हैं। इस रणनीति में, हम पिछले के-लाइन समापन मूल्य का उपयोग करते हैं, जिसका अर्थ है कि वर्तमान के-लाइन संकेत स्थापित किया गया है और अगली के-लाइन ऑर्डर देने के लिए है। फिर एफएमजेड अंतर्निहित का उपयोग करेंtalibचलती औसत की गणना करने के लिए पुस्तकालय. उदाहरण के लिए चलती औसत हैःTA.MAइस फलन को 2 पैरामीटर प्राप्त होते हैं, अर्थात्: K रेखा सरणी और चलती औसत अवधि।
चरण 5: ऑर्डर देना
global mp # global variables
current_price = bars_arr[-1]['Close'] # latest price
if mp> 0: # If you are holding long positions
if bias2 <= bias1: # If the long-term deviation rate is less than or equal to the short-term deviation rate
exchange.SetDirection("closebuy") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Sell(current_price-1, 1) # Closing long positions
mp = 0 # reset virtual holding positions
if mp <0: # If you are holding short positions
if bias2 >= bias1: # If the long-term deviation rate is greater than or equal to the short-term deviation rate
exchange.SetDirection("closesell") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Buy(current_price + 1, 1) # closing short positions
mp = 0 # reset virtual holding positions
if mp == 0: # If there is no holding position
if bias2> bias1: # Long-term deviation rate is greater than short-term deviation rate
exchange.SetDirection("buy") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Buy(current_price + 1, 1) # open long positions
mp = 1 # reset virtual holding position
if bias2 <bias1: # The long-term deviation rate is less than the short-term deviation rate
exchange.SetDirection("sell") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Sell(current_price-1, 1) # open short positions
mp = -1 # reset virtual holding position
पूर्ण रणनीति
# Backtest configuration
'''backtest
start: 2018-01-01 00:00:00
end: 2020-01-01 00:00:00
period: 1h
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_CTP","currency":"FUTURES"}]
'''
# External parameters
short = 10
long = 50
# Global variables
mp = 0
# Strategy main function
def onTick():
# retrieve data
exchange.SetContractType('rb000') # Subscribe to futures varieties
bars_arr = exchange.GetRecords() # Get K-line array
if len(bars_arr) <long + 1: # If the number of K lines is too small
return
# Calculate BIAS
close = bars_arr[-2]['Close'] # Get the closing price of the previous K line
ma1 = TA.MA(bars_arr, short)[-2] # Calculate the short-term moving average of the previous K line
bias1 = (close-ma1) / ma1 * 100 # Calculate the short-term deviation rate value
ma2 = TA.MA(bars_arr, long)[-2] # Calculate the long-term average of the previous K line
bias2 = (close-ma2) / ma2 * 100 # Calculate the long-term deviation rate value
# Placing Orders
global mp # global variables
current_price = bars_arr[-1]['Close'] # latest price
if mp> 0: # If you are holding long positions
if bias2 <= bias1: # If the long-term deviation rate is less than or equal to the short-term deviation rate
exchange.SetDirection("closebuy") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Sell(current_price-1, 1) # closing long positions
mp = 0 # reset virtual holding position
if mp <0: # If you are holding short positions
if bias2 >= bias1: # If the long-term deviation rate is greater than or equal to the short-term deviation rate
exchange.SetDirection("closesell") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Buy(current_price + 1, 1) # closing short positions
mp = 0 # reset virtual holding position
if mp == 0: # If there is no holding position
if bias2> bias1: # Long-term deviation rate is greater than short-term deviation rate
exchange.SetDirection("buy") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Buy(current_price + 1, 1) # opening long positions
mp = 1 # reset virtual holding position
if bias2 <bias1: # The long-term deviation rate is less than the short-term deviation rate
exchange.SetDirection("sell") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Sell(current_price-1, 1) # open short positions
mp = -1 # reset virtual holding position
# Program entry function
def main():
while True: # loop
onTick() # execution strategy main function
Sleep(1000) # sleep for 1 second
पूरी रणनीति एफएमजेड की वेबसाइट पर प्रकाशित की गई हैःhttps://www.fmz.com/strategy/215129
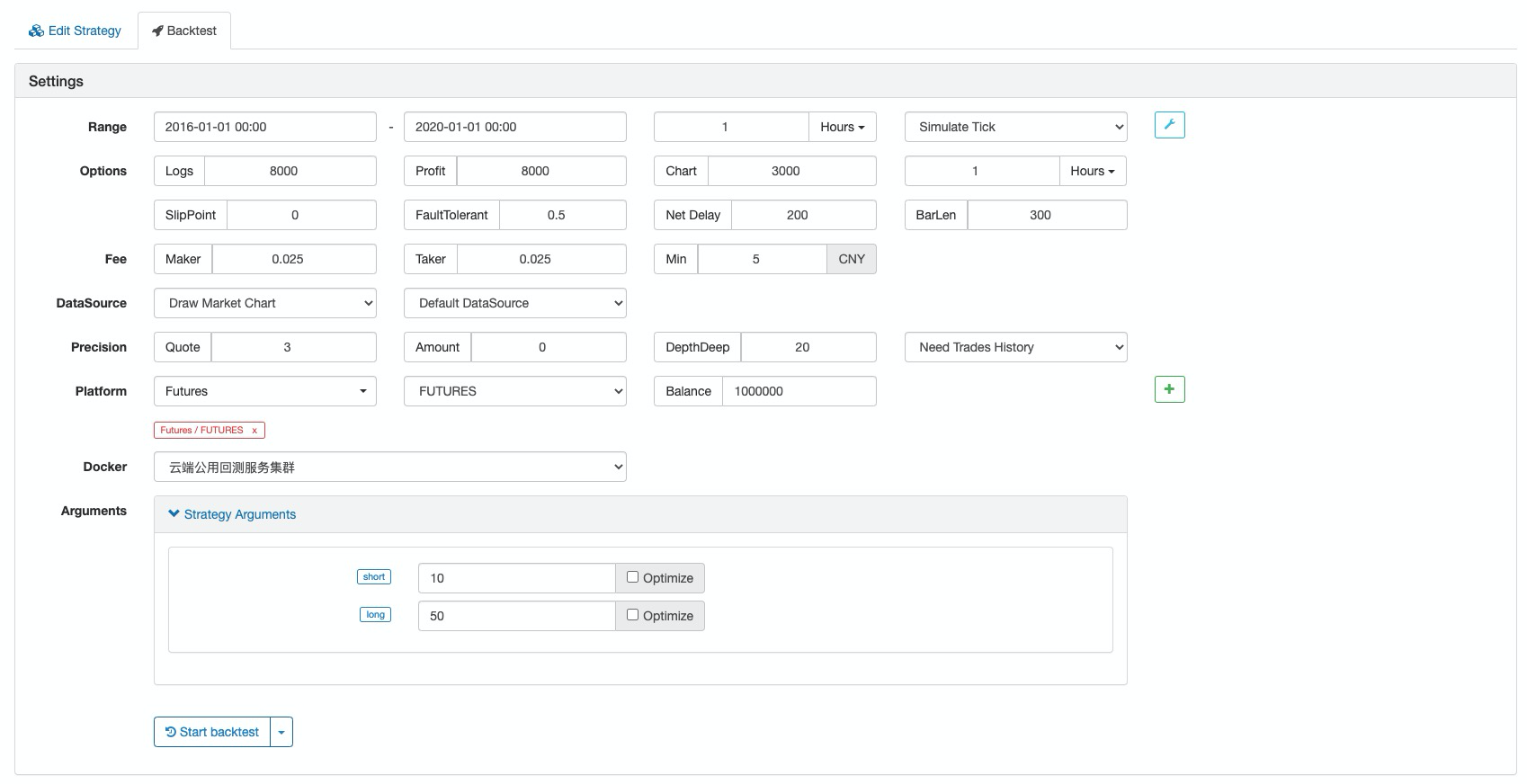
रणनीति बैकटेस्ट
बैकटेस्ट कॉन्फ़िगरेशन
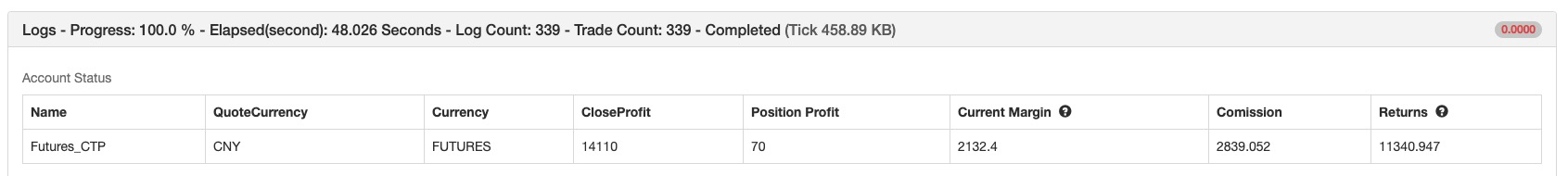
प्रदर्शन रिपोर्ट
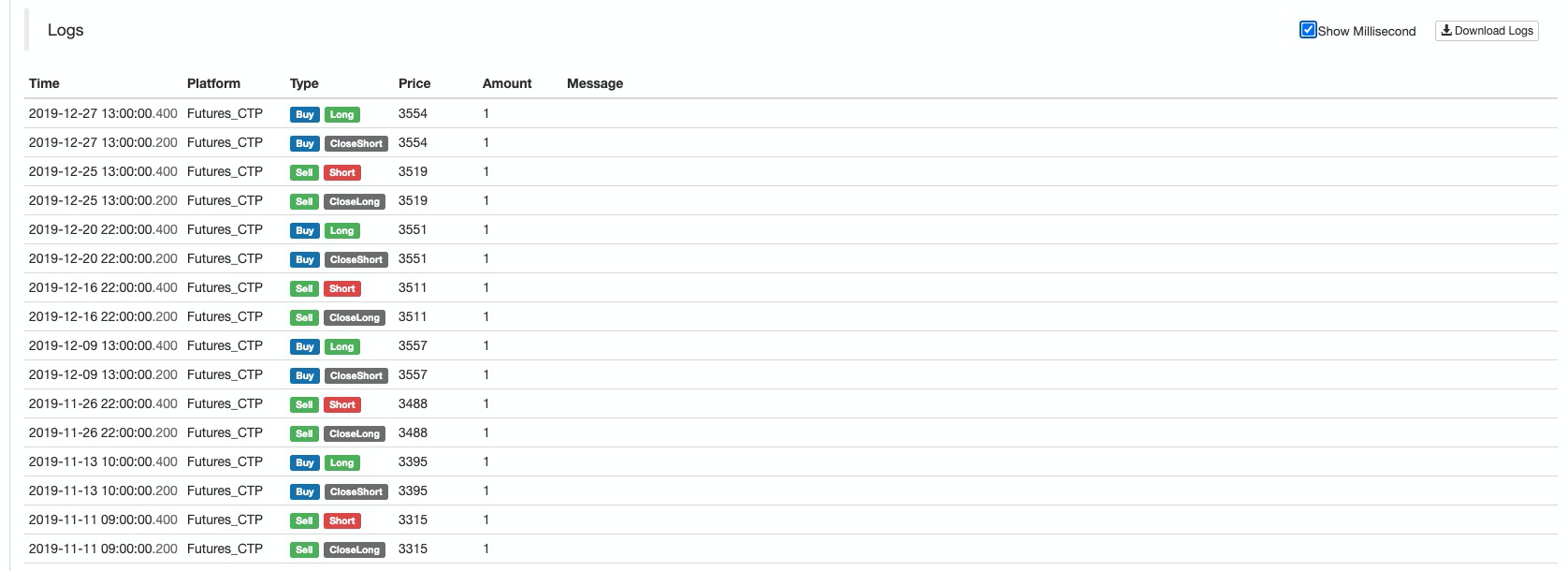
निधि वक्र
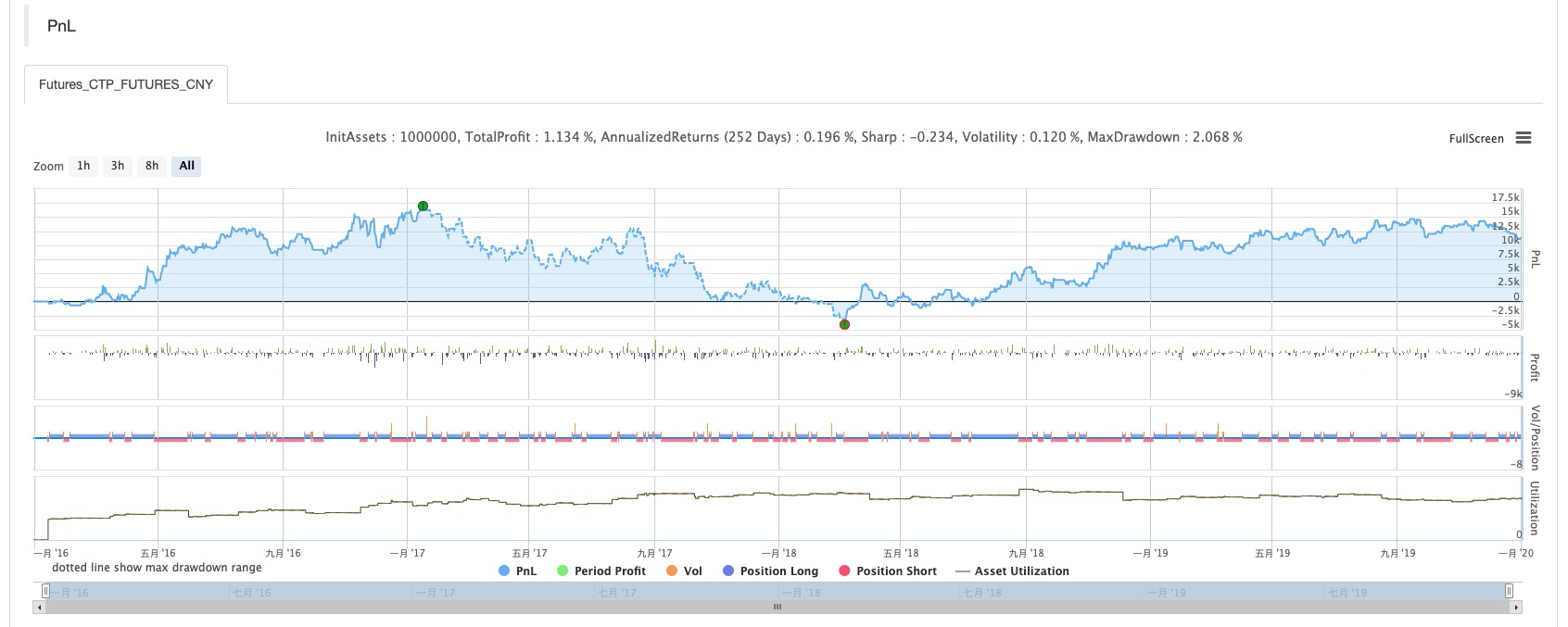
सारांश
विचलन दर एक सरल और प्रभावी ट्रेडिंग उपकरण है जो व्यापारियों के लिए एक प्रभावी संदर्भ प्रदान कर सकता है। वास्तविक उपयोग में, इसे वास्तव में अपने मूल्य को प्रतिबिंबित करने के लिए एमएसीडी और बोलिंगर बैंड संकेतकों के साथ लचीले ढंग से लागू किया जा सकता है।
- डीईएक्स एक्सचेंजों का मात्रात्मक अभ्यास (2) -- हाइपरलिक्विड यूजर गाइड
- DEX एक्सचेंज क्वांटिफाइंग प्रैक्टिस ((2) -- हाइपरलिक्विड उपयोग गाइड
- डीईएक्स एक्सचेंजों का मात्रात्मक अभ्यास (1) -- dYdX v4 उपयोगकर्ता गाइड
- क्रिप्टोकरेंसी में लीड-लैग आर्बिट्रेज का परिचय (3)
- DEX एक्सचेंज क्वांटिफाइड प्रैक्टिस ((1)-- dYdX v4 उपयोग गाइड
- डिजिटल मुद्रा में लीड-लैग सूट का परिचय (3)
- क्रिप्टोकरेंसी में लीड-लैग आर्बिट्रेज का परिचय (2)
- डिजिटल मुद्राओं में लीड-लैग सूट का परिचय (2)
- एफएमजेड प्लेटफॉर्म के बाहरी सिग्नल रिसेप्शन पर चर्चाः रणनीति में अंतर्निहित एचटीपी सेवा के साथ सिग्नल प्राप्त करने के लिए एक पूर्ण समाधान
- एफएमजेड प्लेटफॉर्म के लिए बाहरी सिग्नल प्राप्त करने का अन्वेषणः रणनीति अंतर्निहित एचटीटीपी सेवा के लिए सिग्नल प्राप्त करने के लिए पूर्ण समाधान
- क्रिप्टोकरेंसी में लीड-लैग आर्बिट्रेज का परिचय (1)
- जावास्क्रिप्ट रणनीति डिजाइन में संख्यात्मक गणना सटीकता समस्या का समाधान
- एक स्थानीय फ़ाइल में पायथन रणनीति को कैप्सूल करने के लिए आप सिखाएँ
- एफएमईएक्स ट्रेडिंग से ऑर्डर वॉल्यूम का अनुकूलन होता है भाग 2
- एफएमईएक्स ट्रेडिंग ऑर्डर वॉल्यूम अनुकूलन को अनलॉक करती है
- कमोडिटी फ्यूचर्स वॉल्यूम फुटप्रिंट चार्ट का विश्लेषण और निष्पादन
- एफएमईएक्स क्रमबद्ध अनलॉक अधिकतम न्यूनतम मात्रा अनुकूलन
- चिपचिपा इंटरफेस को बुलाकर रोबोट संदेश भेजने में सक्षम
- एफएमईएक्स लेन-देन को अनलॉक करने के लिए सबसे कम मात्रा में अनुकूलन
- सरल अस्थिरता ईएमवी रणनीति
- हाथ से हाथ मिलाकर आप एक पायथन नीति पैकेज लागत प्रभावी रूप से फ़ाइल
- "पाइफोलियो" उपकरण का उपयोग करके बैकटेस्ट पूंजी वक्र का मूल्यांकन
- FMZ क्वांटिफाइड माइ भाषा - इंटरफ़ेस ग्राफ
- कमोडिटी फ्यूचर्स इंटरटेम्पोरल बोलिंगर हेज रणनीति का पायथन संस्करण (केवल अध्ययन उद्देश्य)
- "ट्रेडिंग व्यू" संकेतक का उपयोग करके एफएमजेड रोबोट के साथ इंटरफेस करना
- FMZ क्वांटिफाइड मय भाषा (My) - मय भाषा लेनदेन वर्ग सूची पैरामीटर
- कमोडिटी "फ्यूचर्स और स्पॉट" मध्यस्थता चार्ट FMZ मौलिक आंकड़ों के आधार पर
- प्रत्येक लेनदेन और के-लाइन बैकटेस्ट के दोषों के आधार पर उच्च आवृत्ति बैकटेस्ट प्रणाली
- कमोडिटी फ्यूचर्स की अंतराल-समय की हेजिंग रणनीति का पायथन संस्करण
- क्रिप्टोकरेंसी फ्यूचर्स ट्रेडिंग के तर्क पर कुछ विचार
- अल्फा101 व्याकरण विकास पर आधारित उन्नत विश्लेषण उपकरण