Estratégia típica de acompanhamento de tendências
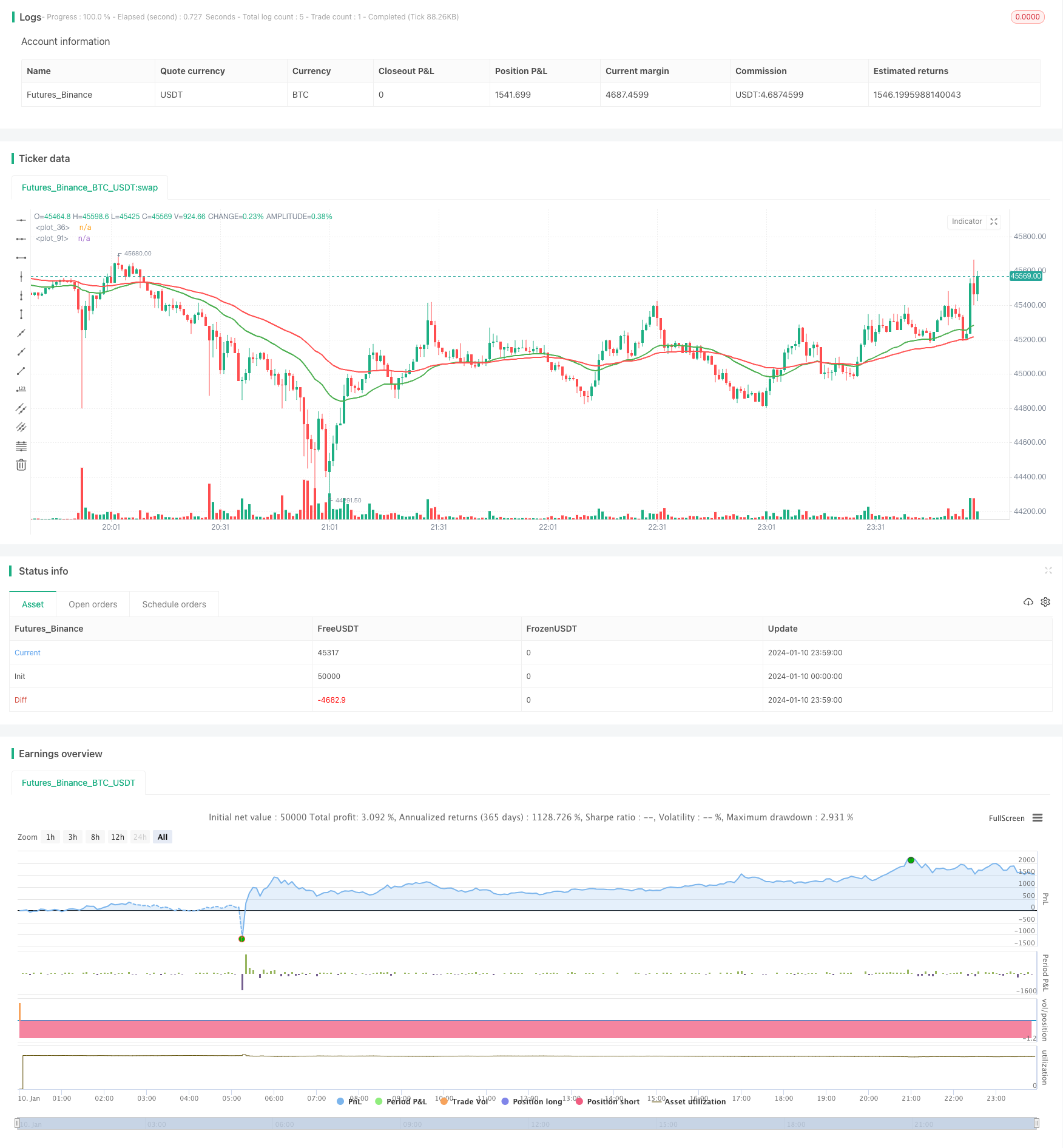
Visão geral
A estratégia de cruzamento de duas equações é uma estratégia típica de acompanhamento de tendências. Utiliza a média EMA de dois períodos diferentes, fazendo mais quando a média de curta duração atravessa a média de longa duração e fazendo menos quando a média de curta duração atravessa a média de longa duração, para capturar o ponto de viragem da tendência de preços.
Princípio da estratégia
O indicador central da estratégia são as duas linhas médias do EMA, com 30 e 60 ciclos respectivamente. O código calcula as duas linhas médias do EMA por meio de funções personalizadas:
emaLen1 = emaFuncOne(close, lenMA1)
emaLen2 = emaFuncTwo(close, lenMA2)
Os sinais de negociação da estratégia vêm da interseção de duas linhas médias EMA:
currentState = if emaLen2 > emaLen1
0
else
1
previousState = if emaLastLen2 > emaLastLen1
0
else
1
convergence = if currentState != previousState
1
else
0
Quando o EMA curto é excedido pelo EMA longo, o estado atual não é igual ao estado anterior e um sinal de cruzamento ocorre. Quando o EMA curto atravessa o EMA longo, o estado atual não é igual ao estado anterior, ocorrendo um sinal de cruzamento.
Análise de vantagens
A estratégia tem as seguintes vantagens:
- A estratégia é simples, intuitiva, fácil de entender e de implementar.
- Utilizando as propriedades suaves da EMA para filtrar o ruído do mercado
- Seguindo as tendências automaticamente, não é fácil perder a oportunidade de comprar e vender.
Análise de Riscos
A estratégia também apresenta alguns riscos:
- O sinal de cruzamento entre duas linhas equiláreas pode estar atrasado e não conseguir capturar a viragem a tempo.
- A situação de tremor pode levar a vários sinais errados.
- Parâmetros mal definidos podem resultar em excesso de sensibilidade ou excesso de lag
Pode-se otimizar ajustando o ciclo EMA ou adicionando condições de filtragem.
Direção de otimização
A estratégia pode ser melhorada em vários aspectos:
- Testar combinações de períodos EMA de diferentes comprimentos
- Filtração de falsos sinais de aumento de volume de transação ou de taxa de flutuação
- Combinação com outros indicadores de confirmação de tendências, como o MACD
- Optimizar a gestão de fundos, estabelecer um stop loss
Resumir
A estratégia de duplo equilíbrio de cruzamento é uma estratégia de acompanhamento de tendências simples e práticas em geral. É direta-forward, fácil de implementar e pode acompanhar a tendência automaticamente. Mas também existe o risco de alguns atrasos e falsos sinais.
/*backtest
start: 2024-01-10 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-11 00:00:00
period: 1m
basePeriod: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=2
strategy("ParkerMAStrat", overlay=true)
lenMA1=input(title="Length 1", defval=30)
lenMA2=input(title="Length 2", defval=60)
x = 0
checkLines(current, last) =>
if current > last
x = 1
else
x = 0
x
//plot ema based on len1
emaFuncOne(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[1])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
emaLen1 = emaFuncOne(close, lenMA1)
plot(emaLen1, color=green, transp=0, linewidth=2)
// now we plot the _10_period_ema
//plot ema based on len2
emaFuncTwo(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[1])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
//plot ema based on len2
emaFuncOneLast(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[0])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
//plot ema based on len2
emaFuncTwoLast(src, time_period) =>
alpha = 2 / (time_period + 1)
// we have defined the alpha function above
ema = 0.0
// this is the initial declaration of ema, since we dont know the first ema we will declare it to 0.0 [as a decimal]
ema := alpha * src + (1 - alpha) * nz(ema[0])
// this returns the computed ema at the current time
// notice the use of : (colon) symbol before =, it symbolises, that we are changing the value of ema,
// since the ema was previously declared to 0
// this is called mutable variale declaration in pine script
ema
// return ema from the function
emaLastLen1 = emaFuncOneLast(close, lenMA1)
emaLastLen2 = emaFuncTwoLast(close, lenMA2)
emaLen2 = emaFuncTwo(close, lenMA2)
plot(emaLen2, color=red, transp=30, linewidth=2)
// now we plot the _10_period_ema
//now we compare the two and when green crosses red we buy/sell (line1 vs line2)
previousState = if emaLastLen2 > emaLastLen1
0
else
1
currentState = if emaLen2 > emaLen1
0
else
1
convergence = if currentState != previousState
1
else
0
lineCheck = if convergence == 1
checkLines(currentState, previousState)
if lineCheck == 1
strategy.entry("Long", strategy.long)
else
strategy.entry("Short", strategy.short)