Estratégia de negociação baseada em padrões de pico a pico
Autora:ChaoZhang, Data: 2024-02-20 15:40:58Tags:
Resumo
A estratégia é chamada de
Princípio da estratégia
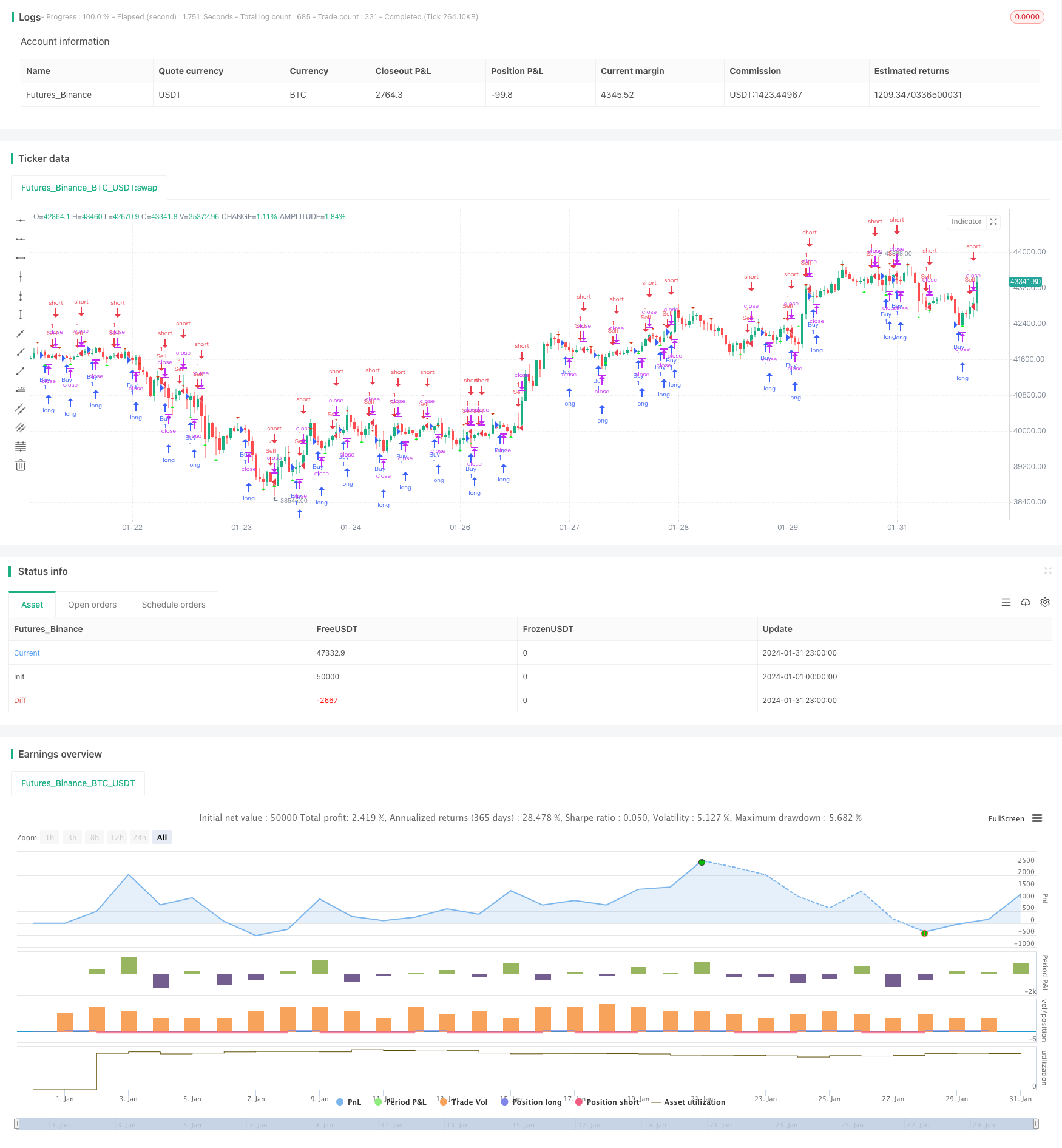
A estratégia define um pico ascendente (upFractal) e um pico descendente (downFractal) para identificar o padrão de pico a pico nos gráficos de velas.
Especificamente, a lógica de julgamento para o pico ascendente é: o máximo do candelabro atual é o mais alto dos n candelabros recentes, e o máximo dos candelabros subsequentes não excede o atual.
A lógica de julgamento para o pico em queda é: o mínimo do candelabro atual é o mais baixo dos n candelabros recentes, e o mínimo dos candelabros subsequentes não cai abaixo do atual.
Variaveis e loops booleanos são usados aqui para determinar a relação entre n candelabros anteriores e posteriores
Por conseguinte, a lógica central desta estratégia é a seguinte:
- Identificar picos em ascensão e picos em queda
- Longos nos picos em ascensão e curtos nos picos em queda
Análise das vantagens
As vantagens desta estratégia incluem:
- Padrão de pico para pico é fácil de identificar, simples de operar
- Baseado no padrão técnico, não afetado pelos fundamentos
- Possíveis saques menores
Análise de riscos
Há também alguns riscos com esta estratégia:
- Julgamento do padrão de pico para pico impreciso, pode perder o melhor momento de entrada
- Difícil definir stop loss quando o mercado se move violentamente
- Só depende de padrões, ignora outros fatores.
Contramedidas:
- Ajustar os parâmetros do padrão de pico a pico para otimizar a lógica
- Combinar com outros indicadores para determinar a posição de stop loss
- Utilização em conjunto com análises fundamentais ou outras análises
Orientações de otimização
Algumas orientações para otimizar a estratégia:
- Aumentar as opções de ajuste de parâmetros para identificar melhor os padrões de pico a pico
- Adicionar lógica de stop loss
- Considerar o volume de negociação, a volatilidade e outros indicadores
- Combinar análises de diferentes prazos
Resumo
Esta estratégia é simples de operar com possivelmente menores drawdowns com base no princípio do padrão de pico a pico. Mas ainda tem alguns riscos e precisa ser combinada com outros métodos de análise para maximizar seu desempenho.
/*backtest
start: 2024-01-01 00:00:00
end: 2024-01-31 23:59:59
period: 1h
basePeriod: 15m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=5
strategy("sanju parmar", shorttitle="sanju trading empire", overlay=true)
// Define "n" as the number of periods and keep a minimum value of 2 for error handling.
n = input.int(title="Periods", defval=2, minval=2)
// UpFractal
bool upflagDownFrontier = true
bool upflagUpFrontier0 = true
bool upflagUpFrontier1 = true
bool upflagUpFrontier2 = true
bool upflagUpFrontier3 = true
bool upflagUpFrontier4 = true
for i = 1 to n
upflagDownFrontier := upflagDownFrontier and (high[n-i] < high[n])
upflagUpFrontier0 := upflagUpFrontier0 and (high[n+i] < high[n])
upflagUpFrontier1 := upflagUpFrontier1 and (high[n+1] <= high[n] and high[n+i + 1] < high[n])
upflagUpFrontier2 := upflagUpFrontier2 and (high[n+1] <= high[n] and high[n+2] <= high[n] and high[n+i + 2] < high[n])
upflagUpFrontier3 := upflagUpFrontier3 and (high[n+1] <= high[n] and high[n+2] <= high[n] and high[n+3] <= high[n] and high[n+i + 3] < high[n])
upflagUpFrontier4 := upflagUpFrontier4 and (high[n+1] <= high[n] and high[n+2] <= high[n] and high[n+3] <= high[n] and high[n+4] <= high[n] and high[n+i + 4] < high[n])
flagUpFrontier = upflagUpFrontier0 or upflagUpFrontier1 or upflagUpFrontier2 or upflagUpFrontier3 or upflagUpFrontier4
upFractal = (upflagDownFrontier and flagUpFrontier)
// downFractal
bool downflagDownFrontier = true
bool downflagUpFrontier0 = true
bool downflagUpFrontier1 = true
bool downflagUpFrontier2 = true
bool downflagUpFrontier3 = true
bool downflagUpFrontier4 = true
for i = 1 to n
downflagDownFrontier := downflagDownFrontier and (low[n-i] > low[n])
downflagUpFrontier0 := downflagUpFrontier0 and (low[n+i] > low[n])
downflagUpFrontier1 := downflagUpFrontier1 and (low[n+1] >= low[n] and low[n+i + 1] > low[n])
downflagUpFrontier2 := downflagUpFrontier2 and (low[n+1] >= low[n] and low[n+2] >= low[n] and low[n+i + 2] > low[n])
downflagUpFrontier3 := downflagUpFrontier3 and (low[n+1] >= low[n] and low[n+2] >= low[n] and low[n+3] >= low[n] and low[n+i + 3] > low[n])
downflagUpFrontier4 := downflagUpFrontier4 and (low[n+1] >= low[n] and low[n+2] >= low[n] and low[n+3] >= low[n] and low[n+4] >= low[n] and low[n+i + 4] > low[n])
flagDownFrontier = downflagUpFrontier0 or downflagUpFrontier1 or downflagUpFrontier2 or downflagUpFrontier3 or downflagUpFrontier4
downFractal = (downflagDownFrontier and flagDownFrontier)
plotshape(downFractal, style=shape.triangleup, location=location.belowbar, offset=-n, color=#18f523, size = size.small)
plotshape(upFractal, style=shape.triangledown, location=location.abovebar, offset=-n, color=#cf3d11, size = size.small)
// Strategy Conditions
longCondition = upFractal
shortCondition = downFractal
// Strategy Entry and Exit
if (longCondition)
strategy.entry("Buy", strategy.long)
if (shortCondition)
strategy.entry("Sell", strategy.short)
- Estratégia de negociação adaptativa baseada numa plataforma de negociação quantitativa
- Estratégia de negociação quantitativa baseada na nuvem de Ichimoku e na média móvel
- Estratégia de acompanhamento da inversão da média móvel dupla
- Estratégia de inversão das bandas de Bollinger
- Ichimoku Kinko Hyo Cloud + QQE Estratégia Quantitativa
- Tudo Sobre a Estratégia de Negociação de Momentum com Stop Loss para Ouro
- Parabola Oscilador Procurando altos e baixos Estratégia
- Estratégia de ruptura das bandas de Bollinger
- Estratégia de avanço da diferença de valor justo
- Sistema de cruzamento de média móvel adaptativa com ruptura de impulso
- Estratégia de compra de EMA múltipla
- Tendência de cruzamento da OBV EMA na sequência da estratégia
- Estratégia de acompanhamento da tendência cruzada do RSI e do MA
- Estratégia de reversão do impulso com dupla confirmação
- Crossover da EMA para a Estratégia Quant Long Line
- Estratégia de acompanhamento da reversão extrema
- Estratégia de reversão da média da faixa de Bollinger com índice de intensidade intradiária
- B-Xtrender Estratégia de cruzamento de média móvel exponencial
- Estratégia de acompanhamento da tendência da média móvel
- Uma estratégia combinada de RSI com média móvel e MACD