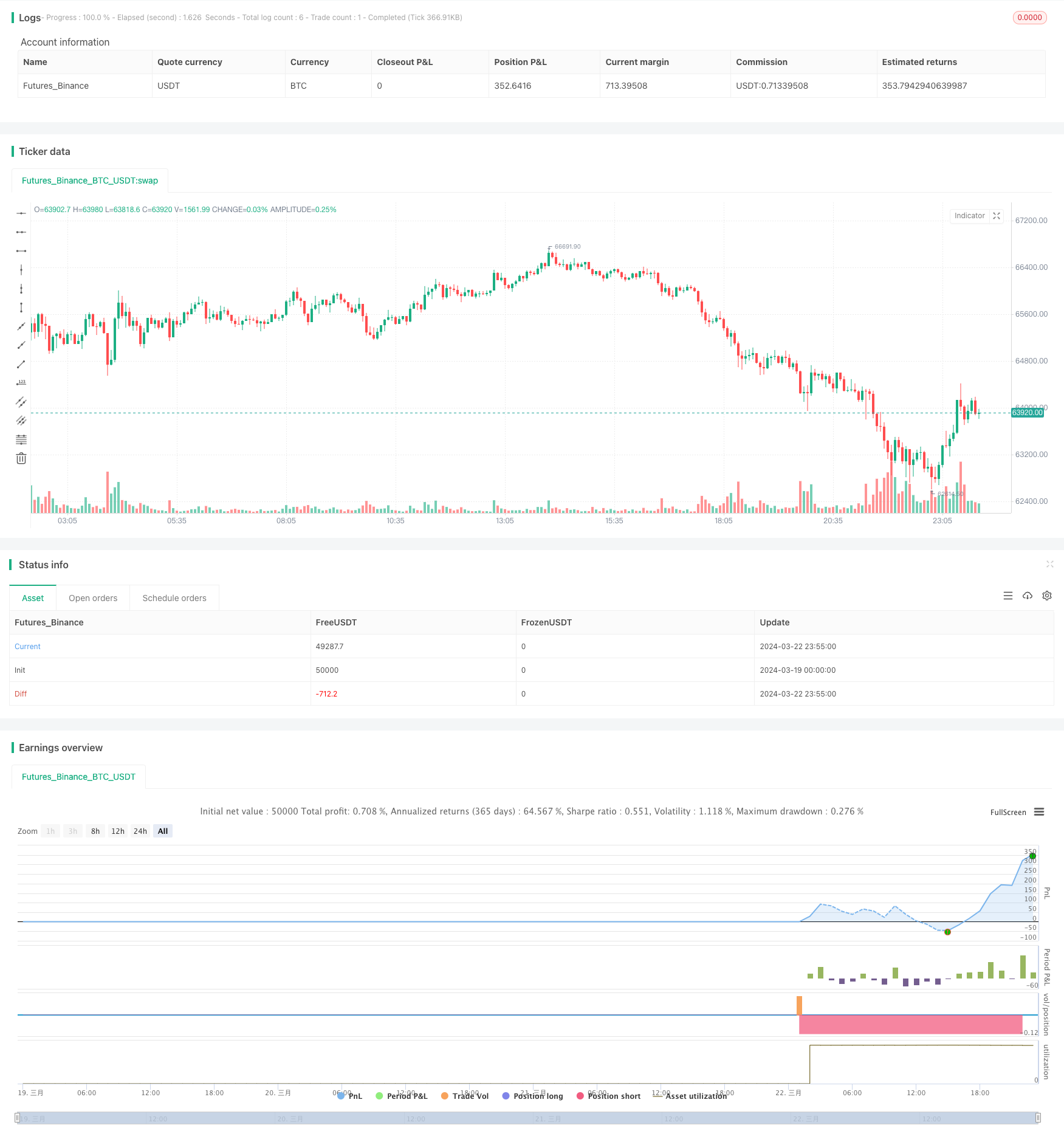
策略概述
网格交易风险对冲策略是一种基于网格交易理念,结合风险对冲思想的量化交易策略。该策略通过在预设的价格区间内布置多个买卖订单,从而在价格波动中获利。同时,该策略还引入了风险对冲机制,通过动态调整网格边界,以适应市场环境的变化,降低策略风险。
策略原理
该策略的核心原理是网格交易。首先,根据用户设置的参数,确定网格的上下边界和网格线的数量。然后,在网格线上布置买卖订单:当价格触及网格线时,如果该网格线之前没有订单,则开仓;如果之前有订单,则平仓。通过这种方式,策略可以在价格波动中不断开仓平仓,从而获利。
同时,为了降低风险,该策略还引入了动态网格边界调整机制。根据用户的选择,网格的上下边界可以通过两种方式自动调整:1)根据最近一段时间的最高价和最低价,并考虑用户设置的偏移量;2)根据移动平均线,并考虑用户设置的偏移量。通过动态调整网格边界,可以使得网格始终围绕着当前价格,从而降低价格突破网格边界带来的风险。
此外,该策略在开仓时,会将总资金等分为N份,每次开仓都使用等量的资金,这样可以降低单次交易的风险。
优势分析
适应性强:通过动态调整网格边界,策略可以适应不同的市场环境,无论是趋势还是震荡行情,都能够自动调整,从而获得较好的收益。
风险可控:策略在开仓时使用等量资金,单次交易风险较小;同时,动态网格边界调整机制,可以降低价格突破网格边界的风险。
交易频率高:由于网格通常布置较多的订单,因此交易频率较高,在波动行情中更容易获利。
参数灵活:用户可以根据自己的偏好,设置网格的数量、上下边界、动态调整的参数等,从而适应不同的交易风格。
风险分析
趋势行情中表现欠佳:如果价格持续单边上涨或下跌,突破了网格的边界,且动态调整跟不上价格变化的速度,则策略可能会面临较大的风险。
手续费:由于策略交易频率较高,因此手续费可能会对收益造成一定影响。
参数设置不当:如果参数设置不当,如网格数量过多、网格边界设置不合理等,可能会导致策略表现不佳。
解决方法:1)在趋势行情中,可以考虑增大网格边界的调整幅度,或者与趋势策略相结合;2)选择手续费较低的交易所和币种;3)在实际运行前,需要对参数进行充分的回测和优化。
优化方向
与其他策略相结合:可以考虑将网格交易策略与其他类型的策略相结合,如趋势策略、均值回归策略等,从而提高策略的适应性和稳定性。
改进动态调整机制:目前策略中的动态调整机制相对简单,可以进一步优化,如考虑更多的因素(如成交量、波动率等),采用更高级的算法(如自适应算法、机器学习算法等)。
优化资金管理:目前策略采用了等额资金管理,可以考虑引入更高级的资金管理方法,如Kelly法则、最优化方法等,以进一步提高资金利用效率和收益。
引入止盈止损:在网格交易的基础上,可以引入一些止盈止损的逻辑,如移动止盈止损、波动率止盈止损等,以进一步降低策略风险。
总结
网格交易风险对冲策略是一种自动化程度高、适应性强、风险可控的量化交易策略。通过网格交易和动态网格调整,策略可以在各种行情中获利,同时也能够控制风险。但策略在趋势行情中的表现可能欠佳,且手续费可能会对收益造成影响,因此在实际应用中还需要进一步的优化和改进。总的来说,该策略提供了一种较为成熟的量化交易思路,值得进一步研究和应用。
/*backtest
start: 2024-03-19 00:00:00
end: 2024-03-23 00:00:00
period: 5m
basePeriod: 1m
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=4
strategy("(IK) Grid Script", overlay=true, pyramiding=14, close_entries_rule="ANY", default_qty_type=strategy.cash, initial_capital=100.0, currency="USD", commission_type=strategy.commission.percent, commission_value=0.1)
i_autoBounds = input(group="Grid Bounds", title="Use Auto Bounds?", defval=true, type=input.bool) // calculate upper and lower bound of the grid automatically? This will theorhetically be less profitable, but will certainly require less attention
i_boundSrc = input(group="Grid Bounds", title="(Auto) Bound Source", defval="Hi & Low", options=["Hi & Low", "Average"]) // should bounds of the auto grid be calculated from recent High & Low, or from a Simple Moving Average
i_boundLookback = input(group="Grid Bounds", title="(Auto) Bound Lookback", defval=250, type=input.integer, maxval=500, minval=0) // when calculating auto grid bounds, how far back should we look for a High & Low, or what should the length be of our sma
i_boundDev = input(group="Grid Bounds", title="(Auto) Bound Deviation", defval=0.10, type=input.float, maxval=1, minval=-1) // if sourcing auto bounds from High & Low, this percentage will (positive) widen or (negative) narrow the bound limits. If sourcing from Average, this is the deviation (up and down) from the sma, and CANNOT be negative.
i_upperBound = input(group="Grid Bounds", title="(Manual) Upper Boundry", defval=0.285, type=input.float) // for manual grid bounds only. The upperbound price of your grid
i_lowerBound = input(group="Grid Bounds", title="(Manual) Lower Boundry", defval=0.225, type=input.float) // for manual grid bounds only. The lowerbound price of your grid.
i_gridQty = input(group="Grid Lines", title="Grid Line Quantity", defval=8, maxval=15, minval=3, type=input.integer) // how many grid lines are in your grid
f_getGridBounds(_bs, _bl, _bd, _up) =>
if _bs == "Hi & Low"
_up ? highest(close, _bl) * (1 + _bd) : lowest(close, _bl) * (1 - _bd)
else
avg = sma(close, _bl)
_up ? avg * (1 + _bd) : avg * (1 - _bd)
f_buildGrid(_lb, _gw, _gq) =>
gridArr = array.new_float(0)
for i=0 to _gq-1
array.push(gridArr, _lb+(_gw*i))
gridArr
f_getNearGridLines(_gridArr, _price) =>
arr = array.new_int(3)
for i = 0 to array.size(_gridArr)-1
if array.get(_gridArr, i) > _price
array.set(arr, 0, i == array.size(_gridArr)-1 ? i : i+1)
array.set(arr, 1, i == 0 ? i : i-1)
break
arr
var upperBound = i_autoBounds ? f_getGridBounds(i_boundSrc, i_boundLookback, i_boundDev, true) : i_upperBound // upperbound of our grid
var lowerBound = i_autoBounds ? f_getGridBounds(i_boundSrc, i_boundLookback, i_boundDev, false) : i_lowerBound // lowerbound of our grid
var gridWidth = (upperBound - lowerBound)/(i_gridQty-1) // space between lines in our grid
var gridLineArr = f_buildGrid(lowerBound, gridWidth, i_gridQty) // an array of prices that correspond to our grid lines
var orderArr = array.new_bool(i_gridQty, false) // a boolean array that indicates if there is an open order corresponding to each grid line
var closeLineArr = f_getNearGridLines(gridLineArr, close) // for plotting purposes - an array of 2 indices that correspond to grid lines near price
var nearTopGridLine = array.get(closeLineArr, 0) // for plotting purposes - the index (in our grid line array) of the closest grid line above current price
var nearBotGridLine = array.get(closeLineArr, 1) // for plotting purposes - the index (in our grid line array) of the closest grid line below current price
strategy.initial_capital = 50000
for i = 0 to (array.size(gridLineArr) - 1)
if close < array.get(gridLineArr, i) and not array.get(orderArr, i) and i < (array.size(gridLineArr) - 1)
buyId = i
array.set(orderArr, buyId, true)
strategy.entry(id=tostring(buyId), long=true, qty=(strategy.initial_capital/(i_gridQty-1))/close, comment="#"+tostring(buyId))
if close > array.get(gridLineArr, i) and i != 0
if array.get(orderArr, i-1)
sellId = i-1
array.set(orderArr, sellId, false)
strategy.close(id=tostring(sellId), comment="#"+tostring(sellId))
if i_autoBounds
upperBound := f_getGridBounds(i_boundSrc, i_boundLookback, i_boundDev, true)
lowerBound := f_getGridBounds(i_boundSrc, i_boundLookback, i_boundDev, false)
gridWidth := (upperBound - lowerBound)/(i_gridQty-1)
gridLineArr := f_buildGrid(lowerBound, gridWidth, i_gridQty)
closeLineArr := f_getNearGridLines(gridLineArr, close)
nearTopGridLine := array.get(closeLineArr, 0)
nearBotGridLine := array.get(closeLineArr, 1)