Marktnoten-Sammler erneut aktualisieren
Schriftsteller:Gutes, Erstellt: 2020-05-26 14:25:15, Aktualisiert: 2024-12-10 20:35:48
Unterstützung des CSV-Dateiimports zur Bereitstellung einer benutzerdefinierten Datenquelle
In letzter Zeit muss ein Händler seine eigene CSV-Formatdatei als Datenquelle für das FMZ-Plattform-Backtest-System verwenden. Unser Backtest-System unserer Plattform hat viele Funktionen und ist einfach und effizient zu bedienen, so dass Benutzer, solange sie über ihre eigenen Daten verfügen, ein Backtesting nach diesen Daten durchführen können, das nicht mehr auf die von unserem Plattform-Rechenzentrum unterstützten Börsen und Sorten beschränkt ist.
Designideen
Die Design-Idee ist eigentlich sehr einfach. wir müssen nur etwas ändern, basierend auf der vorherigen Markt Sammler. wir fügen einen ParameterisOnlySupportCSVDer Parameter wird von der Datenbank an den Marktverwalter übermittelt, um zu überprüfen, ob nur die CSV-Datei als Datenquelle für das Backtestsystem verwendet wird.filePathForCSVDer Markt-Sammler-Roboter wird in der Regel von einem Computer ausgestellt, der sich in einem anderen System befindet.isOnlySupportCSVParameter ist aufTrueDiese Änderung erfolgt hauptsächlich in derdo_GETFunktion derProvider class.
Was ist eine CSV-Datei?
Die CSV-Datei besteht aus einer beliebigen Anzahl von Datensätzen, die durch ein neues Zeichen getrennt werden; jeder Datensatz besteht aus Feldern, und die Trennscheine zwischen den Feldern sind andere Zeichen oder Zeichenfolgen, und die häufigsten sind Kommas oder Tabs. Im Allgemeinen haben alle Datensätze die gleiche Folge von Feldern. Sie sind normalerweise einfache Textdateien.WORDPADoderExcel- Ich will sie öffnen.
Der allgemeine Standard des CSV-Dateiformats existiert nicht, aber es gibt bestimmte Regeln, in der Regel ein Datensatz pro Zeile, und die erste Zeile ist die Kopfzeile.
Zum Beispiel wird die CSV-Datei, die wir zum Testen benutzt haben, mit diesem Notizblock geöffnet:
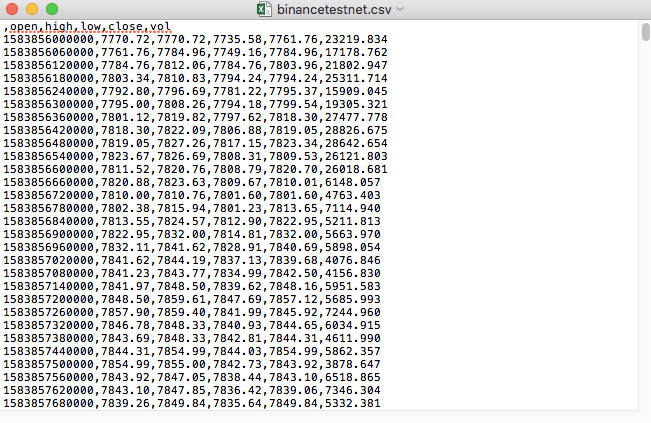
Es wurde festgestellt, dass die erste Zeile der CSV-Datei die Tabellenüberschrift ist.
,open,high,low,close,vol
Wir müssen nur diese Daten analysieren und sortieren und dann in das Format konstruieren, das von der benutzerdefinierten Datenquelle des Backtestsystems verlangt wird.
Geänderter Code
import _thread
import pymongo
import json
import math
import csv
from http.server import HTTPServer, BaseHTTPRequestHandler
from urllib.parse import parse_qs, urlparse
def url2Dict(url):
query = urlparse(url).query
params = parse_qs(query)
result = {key: params[key][0] for key in params}
return result
class Provider(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
def do_GET(self):
global isOnlySupportCSV, filePathForCSV
try:
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header("Content-type", "application/json")
self.end_headers()
dictParam = url2Dict(self.path)
Log("The custom data source service receives the request,self.path:", self.path, "query parameter:", dictParam)
# At present, the backtest system can only select the exchange name from the list. When adding a custom data source, set it to Binance, that is: Binance
exName = exchange.GetName()
# Note that period is the bottom K-line period
tabName = "%s_%s" % ("records", int(int(dictParam["period"]) / 1000))
priceRatio = math.pow(10, int(dictParam["round"]))
amountRatio = math.pow(10, int(dictParam["vround"]))
fromTS = int(dictParam["from"]) * int(1000)
toTS = int(dictParam["to"]) * int(1000)
# Request data
data = {
"schema" : ["time", "open", "high", "low", "close", "vol"],
"data" : []
}
if isOnlySupportCSV:
# Handle CSV reading, filePathForCSV path
listDataSequence = []
with open(filePathForCSV, "r") as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
# Get table header
header = next(reader)
headerIsNoneCount = 0
if len(header) != len(data["schema"]):
Log("The CSV file format is wrong, the number of columns is different, please check!", "#FF0000")
return
for ele in header:
for i in range(len(data["schema"])):
if data["schema"][i] == ele or ele == "":
if ele == "":
headerIsNoneCount += 1
if headerIsNoneCount > 1:
Log("The CSV file format is incorrect, please check!", "#FF0000")
return
listDataSequence.append(i)
break
# Read content
while True:
record = next(reader, -1)
if record == -1:
break
index = 0
arr = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
for ele in record:
arr[listDataSequence[index]] = int(ele) if listDataSequence[index] == 0 else (int(float(ele) * amountRatio) if listDataSequence[index] == 5 else int(float(ele) * priceRatio))
index += 1
data["data"].append(arr)
Log("data: ", data, "Respond to backtest system requests.")
self.wfile.write(json.dumps(data).encode())
return
# Connect to the database
Log("Connect to the database service to obtain data, the database: ", exName, "table: ", tabName)
myDBClient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017")
ex_DB = myDBClient[exName]
exRecords = ex_DB[tabName]
# Construct query conditions: greater than a certain value {'age': {'$ gt': 20}} less than a certain value {'age': {'$lt': 20}}
dbQuery = {"$and":[{'Time': {'$gt': fromTS}}, {'Time': {'$lt': toTS}}]}
Log("Query conditions: ", dbQuery, "Number of inquiries: ", exRecords.find(dbQuery).count(), "Total number of databases: ", exRecords.find().count())
for x in exRecords.find(dbQuery).sort("Time"):
# Need to process data accuracy according to request parameters round and vround
bar = [x["Time"], int(x["Open"] * priceRatio), int(x["High"] * priceRatio), int(x["Low"] * priceRatio), int(x["Close"] * priceRatio), int(x["Volume"] * amountRatio)]
data["data"].append(bar)
Log("data: ", data, "Respond to backtest system requests.")
# Write data response
self.wfile.write(json.dumps(data).encode())
except BaseException as e:
Log("Provider do_GET error, e:", e)
def createServer(host):
try:
server = HTTPServer(host, Provider)
Log("Starting server, listen at: %s:%s" % host)
server.serve_forever()
except BaseException as e:
Log("createServer error, e:", e)
raise Exception("stop")
def main():
LogReset(1)
if (isOnlySupportCSV):
try:
# _thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("localhost", 9090), )) # local test
_thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("0.0.0.0", 9090), )) # Test on VPS server
Log("Start the custom data source service thread, and the data is provided by the CSV file. ", "#FF0000")
except BaseException as e:
Log("Failed to start the custom data source service!")
Log("Error message: ", e)
raise Exception("stop")
while True:
LogStatus(_D(), "Only start the custom data source service, do not collect data!")
Sleep(2000)
exName = exchange.GetName()
period = exchange.GetPeriod()
Log("collect", exName, "Exchange K-line data,", "K line cycle:", period, "Second")
# Connect to the database service, service address mongodb: //127.0.0.1: 27017 See the settings of mongodb installed on the server
Log("Connect to the mongodb service of the hosting device, mongodb://localhost:27017")
myDBClient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017")
# Create a database
ex_DB = myDBClient[exName]
# Print the current database table
collist = ex_DB.list_collection_names()
Log("mongodb", exName, "collist:", collist)
# Check if the table is deleted
arrDropNames = json.loads(dropNames)
if isinstance(arrDropNames, list):
for i in range(len(arrDropNames)):
dropName = arrDropNames[i]
if isinstance(dropName, str):
if not dropName in collist:
continue
tab = ex_DB[dropName]
Log("dropName:", dropName, "delete:", dropName)
ret = tab.drop()
collist = ex_DB.list_collection_names()
if dropName in collist:
Log(dropName, "failed to delete")
else :
Log(dropName, "successfully deleted")
# Start a thread to provide a custom data source service
try:
# _thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("localhost", 9090), )) # local test
_thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("0.0.0.0", 9090), )) # Test on VPS server
Log("Open the custom data source service thread", "#FF0000")
except BaseException as e:
Log("Failed to start the custom data source service!")
Log("Error message:", e)
raise Exception("stop")
# Create the records table
ex_DB_Records = ex_DB["%s_%d" % ("records", period)]
Log("Start collecting", exName, "K-line data", "cycle:", period, "Open (create) the database table:", "%s_%d" % ("records", period), "#FF0000")
preBarTime = 0
index = 1
while True:
r = _C(exchange.GetRecords)
if len(r) < 2:
Sleep(1000)
continue
if preBarTime == 0:
# Write all BAR data for the first time
for i in range(len(r) - 1):
bar = r[i]
# Write root by root, you need to determine whether the data already exists in the current database table, based on timestamp detection, if there is the data, then skip, if not write
retQuery = ex_DB_Records.find({"Time": bar["Time"]})
if retQuery.count() > 0:
continue
# Write bar to the database table
ex_DB_Records.insert_one({"High": bar["High"], "Low": bar["Low"], "Open": bar["Open"], "Close": bar["Close"], "Time": bar["Time"], "Volume": bar["Volume"]})
index += 1
preBarTime = r[-1]["Time"]
elif preBarTime != r[-1]["Time"]:
bar = r[-2]
# Check before writing data, whether the data already exists, based on time stamp detection
retQuery = ex_DB_Records.find({"Time": bar["Time"]})
if retQuery.count() > 0:
continue
ex_DB_Records.insert_one({"High": bar["High"], "Low": bar["Low"], "Open": bar["Open"], "Close": bar["Close"], "Time": bar["Time"], "Volume": bar["Volume"]})
index += 1
preBarTime = r[-1]["Time"]
LogStatus(_D(), "preBarTime:", preBarTime, "_D(preBarTime):", _D(preBarTime/1000), "index:", index)
# Increase drawing display
ext.PlotRecords(r, "%s_%d" % ("records", period))
Sleep(10000)
Laufprüfung
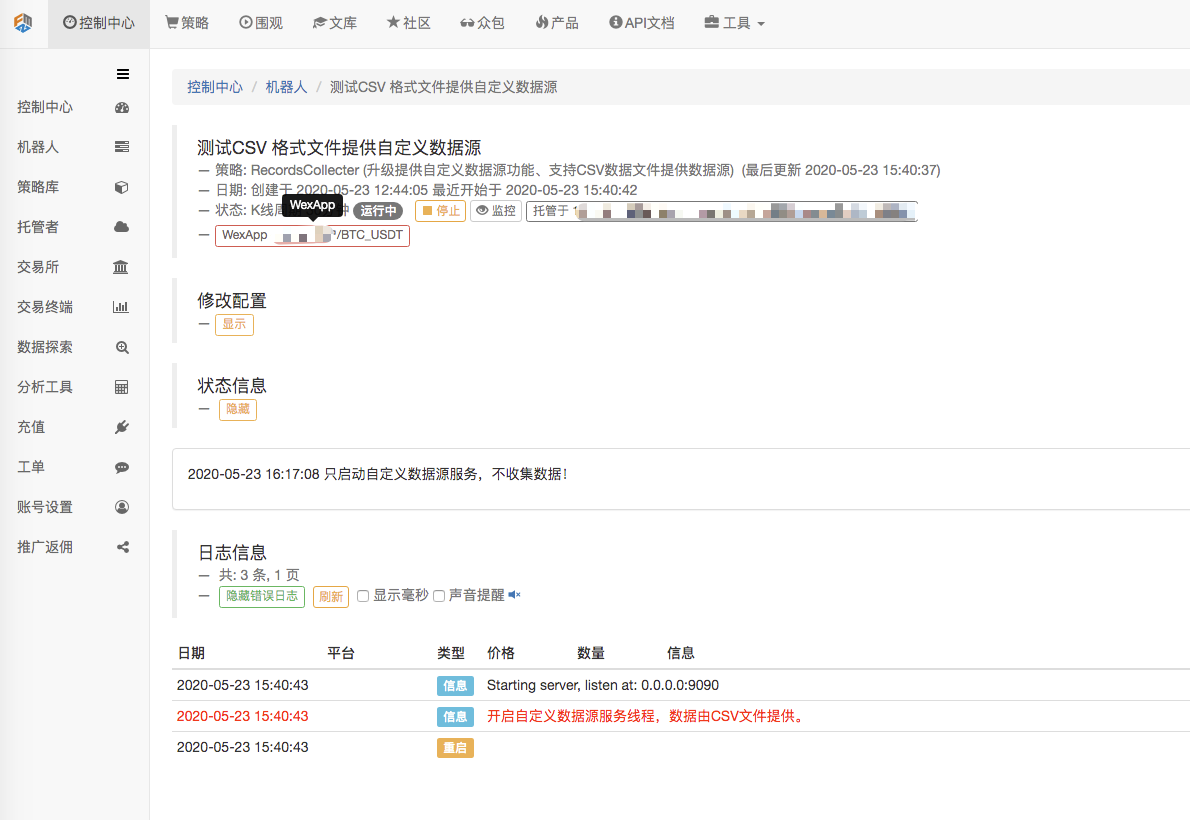
Zuerst starten wir den Marktkollektor-Roboter, fügen dem Roboter einen Austausch hinzu und lassen den Roboter laufen.
Parameterkonfiguration:
Dann erstellen wir eine Teststrategie:
function main() {
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
}
Die Strategie ist sehr einfach, nur drei Mal K-Liniendaten abrufen und drucken.
Auf der Backtest-Seite setzen Sie die Datenquelle des Backtest-Systems als benutzerdefinierte Datenquelle ein und füllen die Adresse des Servers ein, auf dem der Market Collector-Roboter ausgeführt wird. Da die Daten in unserer CSV-Datei eine 1-minütige K-Zeile sind.
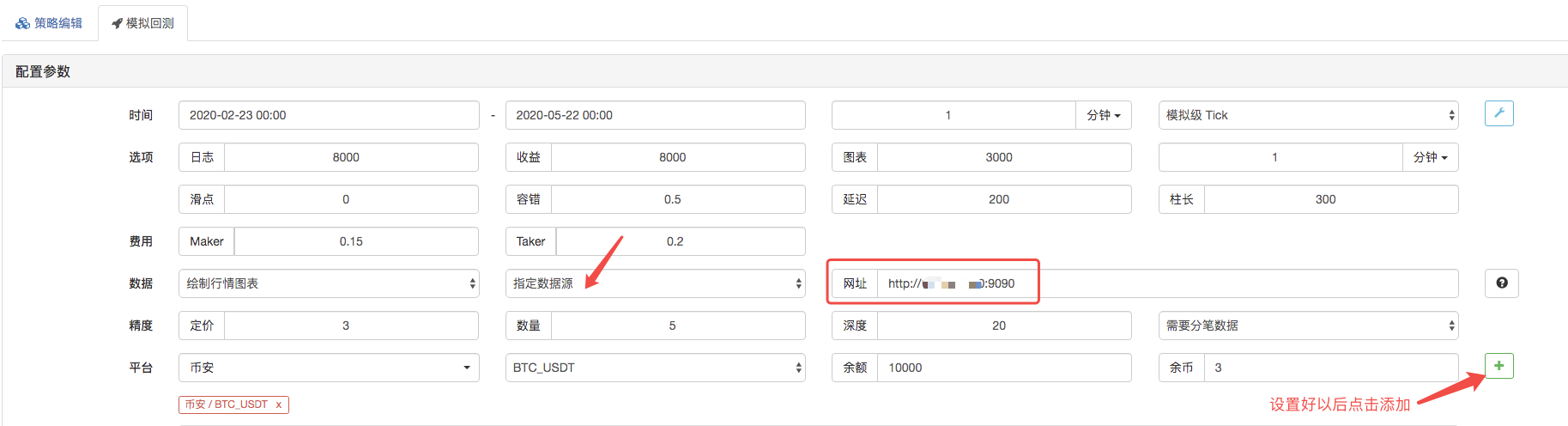
Klicken Sie, um den Backtest zu starten, und der Markt Sammlerroboter erhält die Datenanfrage:
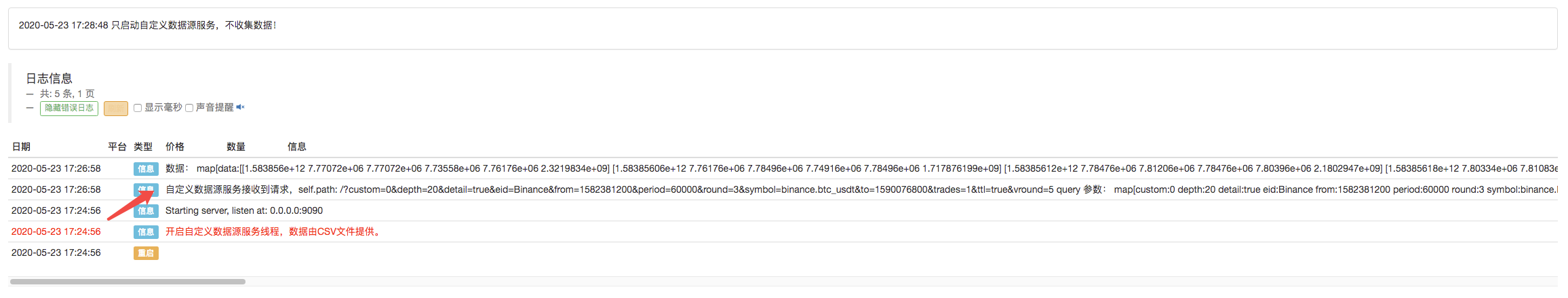
Nach Abschluss der Ausführungsstrategie des Backtestsystems wird auf der Grundlage der K-Liniendaten in der Datenquelle ein K-Liniendiagramm erstellt.
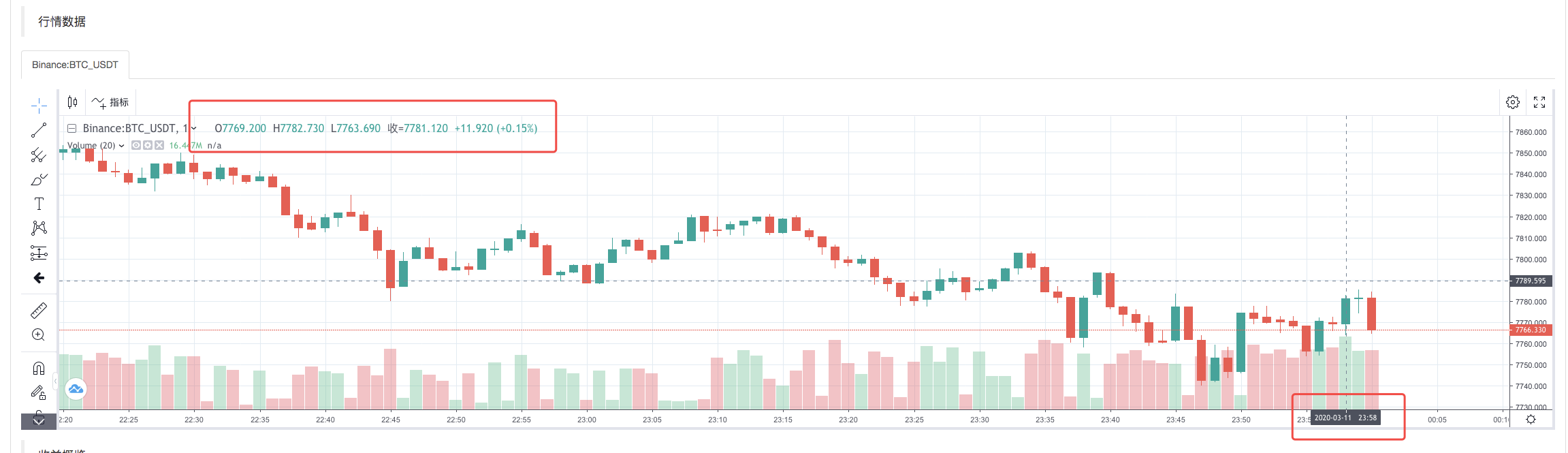
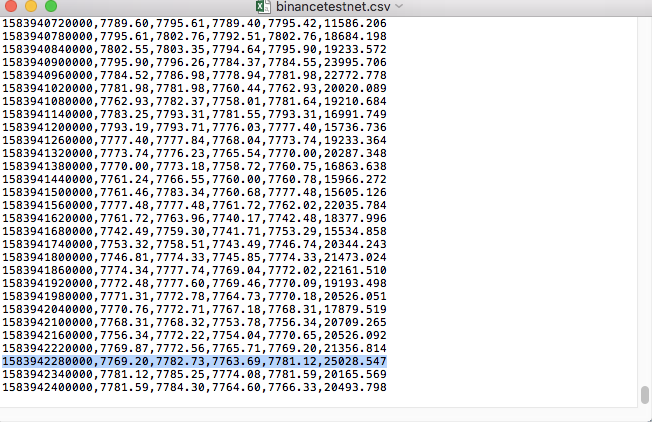
Vergleichen Sie die Daten in der Datei:

- Einführung der Lead-Lag-Suite in der Kryptowährung (3)
- Einführung in Lead-Lag-Arbitrage in Kryptowährungen (2)
- Einführung der Lead-Lag-Suite in der digitalen Währung (2)
- Diskussion über den externen Signalempfang der FMZ-Plattform: Eine Komplettlösung für den Empfang von Signalen mit integriertem Http-Service in der Strategie
- FMZ-Plattform: Erforschung von Signalempfangsstrategien für externe Netzwerke
- Einführung in Lead-Lag-Arbitrage in Kryptowährungen (1)
- Einführung der Lead-Lag-Suite in der Kryptowährung (1)
- Diskussion über den externen Signalempfang der FMZ-Plattform: Erweiterte API VS Strategie eingebauter HTTP-Service
- FMZ-Plattform-External Signal Reception: Erweiterung der API vs. Strategien für den eingebauten HTTP-Dienst
- Diskussion über die Strategie-Testmethode auf Basis eines Zufalls-Ticker-Generators
- Strategie-Testmethoden basierend auf Random-Market-Generatoren untersucht
- Einige Gedanken zur Logik des Crypto-Währungs-Futures-Handels
- Erweitertes Analyse-Tool basierend auf der Alpha101-Grammatikentwicklung
- Ich zeige Ihnen, wie Sie den Market Collector aktualisieren und die benutzerdefinierte Datenquelle testen.
- Schwachstellen von Hochfrequenz-Rückmeldungssystemen und K-Linien-Rückmeldung auf Basis von Transaktionen pro Stück
- Beschreibung des Mechanismus für die Rückprüfung der FMZ-Simulationsstufe
- Der beste Weg zum Installieren und Upgrade von FMZ Docker auf Linux VPS
- Strategie für Rohstoff-Futures
- Ein Gedanke an die Logik des digitalen Futures-Handels
- Ich zeige Ihnen, wie man einen Marktzins-Sammler implementiert.
- Strategie für Rohstofffutures mit gleitendem Durchschnitt in Python-Version
- Upgrade des Datenerfassers - Unterstützung für CSV-Dateien, um eine benutzerdefinierte Datenquelle zu erhalten
- Strategie für den Hochfrequenzhandel mit Rohstofffutures, geschrieben in C++
- Larry Connors RSI2 Mittelumkehrstrategie
- OK Handshake lehrt Sie, wie man FMZ mit der JS-Pairing-API erweitert
- Auf der Grundlage der Verwendung eines neuen relativen Stärkenindex in Intraday-Strategien
- Forschung über Binance Futures Multi-Währung Hedging Strategie Teil 4
- Larry Connors Larry Connors RSI2 Mittelwert-Rückkehr-Strategie
- Forschung über Binance Futures Multi-Währung Hedging Strategie Teil 3
- Forschung über Binance Futures Multi-Währung Hedging Strategie Teil 2
- Forschung über Binance Futures Multi-Währung Hedging Strategie Teil 1