Ausgeglichener gleitender Durchschnittswert
Schriftsteller:ChaoZhang, Datum: 2023-11-06 10:29:24Tags:
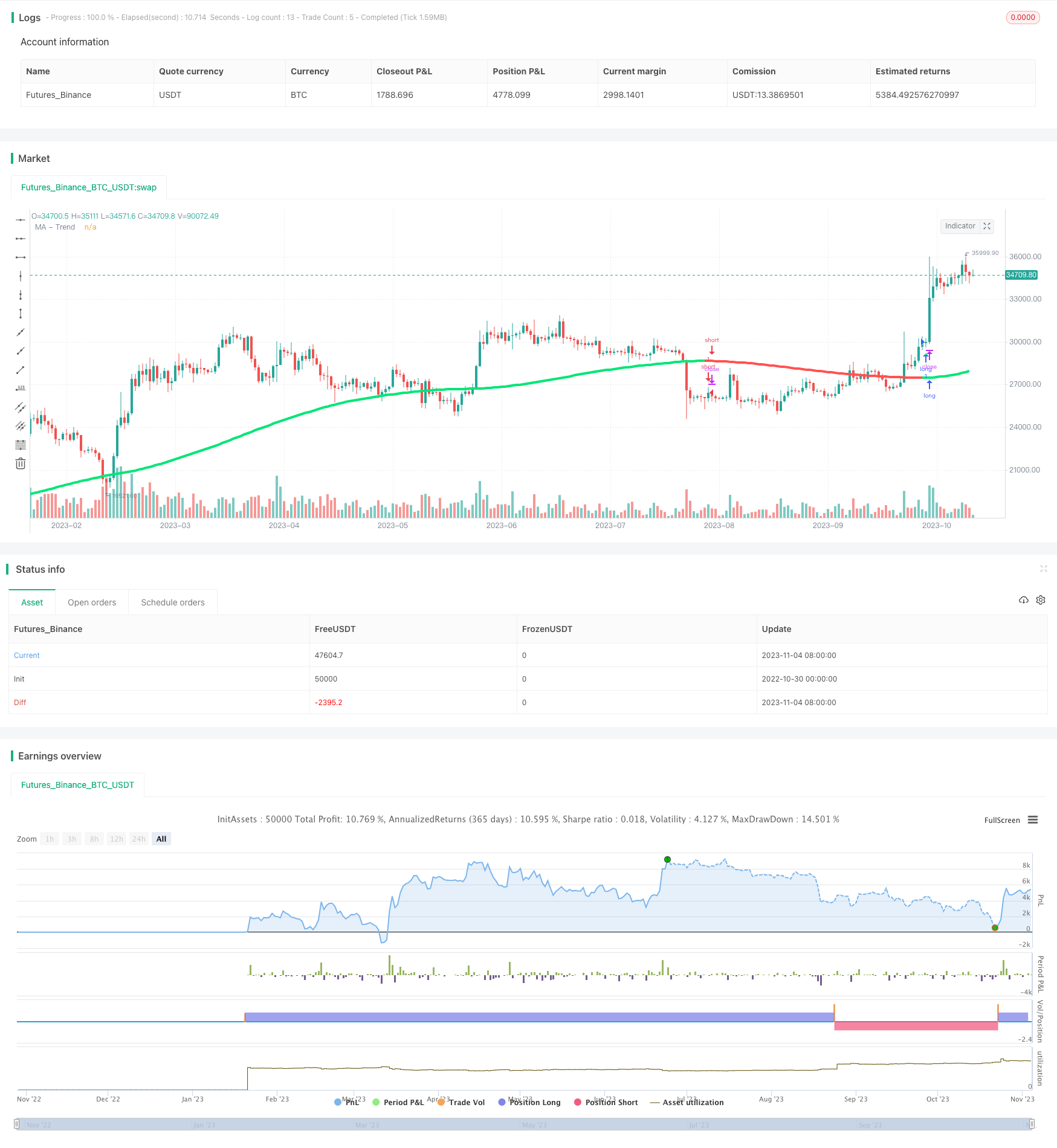
Übersicht
Diese Strategie kombiniert mehrere gleitende Durchschnitte, um eine einfache Trendfolgestrategie umzusetzen.
Strategie Logik
Die Strategie gleicht zunächst den Schlusskurs aus, mit der Option, den Schlusskurs von Heiken Ashi zu verwenden. Anschließend ruft sie die SmoothMA-Funktion auf, um mehrere glättete gleitende Durchschnitte zu überlagern. Die SmoothMA-Funktion ruft zunächst die Variantenfunktion auf, die verschiedene Arten von gleitenden Durchschnitten wie SMA, EMA, DEMA usw. generieren kann. Nachdem die Variantenfunktion den angegebenen gleitenden Durchschnitt generiert hat, ruft smoothMA mehrmals die Variante rekursiv an, um das Glättungssystem zu überlagern. Dies führt zu einem gleitenden Durchschnitt mit hoher Geschwindigkeit. Es erzeugt Kaufsignale, wenn der glättete MA nach oben geht und Verkaufssignale, wenn er nach unten geht.
Analyse der Vorteile
- Mehrere Überlagerungen gleitender Durchschnitte können Marktlärm effektiv filtern und Trends erkennen.
- Unterstützt verschiedene gleitende Durchschnittsarten wie SMA, EMA, DEMA usw., ermöglicht flexible Kombinationen.
- Heiken Ashi-Technik filtert falsche Ausbrüche aus.
- Einfach und einfach umzusetzen.
- Die angepasste MA-Länge, der Typ und die Glättungszeiten ermöglichen eine Optimierung für verschiedene Produkte.
Risikoanalyse
- Mehrfache Glättungen können zu Verzögerungen führen und frühe Trendänderungen verpassen.
- Ein einfaches MA-System kämpft um Gewinn in verschiedenen Märkten.
- Es ignoriert die Transaktionskosten, was die Rentabilität im tatsächlichen Handel beeinträchtigt.
- Keine Stop-Loss-Regelung, Risiken für größere Verluste.
Erwägen Sie, andere Indikatoren wie MACD, KDJ zu kombinieren, um die Signalgenauigkeit zu verbessern. Optimieren Sie die MA-Parameter, um die Verzögerung zu reduzieren. Verwenden Sie einen angemessenen Stop-Loss, um Einzelhandelsverluste zu kontrollieren. Steuern Sie auch die Handelsfrequenz, um die Transaktionskosten zu minimieren.
Optimierungsrichtlinien
- Versuche verschiedene MA-Länge und -Typen für die beste Kombination.
- Hinzufügen anderer technischer Indikatoren für systematischere Ein- und Ausstiegsvorschriften.
- Setzen Sie die Handelssitzung ein, um den Einfluss großer Ereignisse zu vermeiden.
- Anpassung der Parameter anhand der Produktmerkmale.
- Setzen Sie Stop-Loss und Gewinn nehmen, um Risiken zu kontrollieren.
Zusammenfassung
Die Strategie folgt den Trends über mehrere Überlagerungen von gleitenden Durchschnitten und filtert damit effektiv Marktlärm. Die Vorteile sind Einfachheit und Flexibilität.
/*backtest
start: 2022-10-30 00:00:00
end: 2023-11-05 00:00:00
period: 1d
basePeriod: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid":"Futures_Binance","currency":"BTC_USDT"}]
*/
//@version=4
// Copyright (c) 2007-present Jurik Research and Consulting. All rights reserved.
// Copyright (c) 2018-present, Alex Orekhov (everget)
// Thanks to everget for code for more advanced moving averages
// Smooth Moving Average [STRATEGY] @PuppyTherapy script may be freely distributed under the MIT license.
strategy( title="Smooth Moving Average [STRATEGY] @PuppyTherapy", overlay=true )
// ---- CONSTANTS ----
lsmaOffset = 1
almaOffset = 0.85
almaSigma = 6
phase = 2
power = 2
// ---- GLOBAL FUNCTIONS ----
kama(src, len)=>
xvnoise = abs(src - src[1])
nfastend = 0.666
nslowend = 0.0645
nsignal = abs(src - src[len])
nnoise = sum(xvnoise, len)
nefratio = iff(nnoise != 0, nsignal / nnoise, 0)
nsmooth = pow(nefratio * (nfastend - nslowend) + nslowend, 2)
nAMA = 0.0
nAMA := nz(nAMA[1]) + nsmooth * (src - nz(nAMA[1]))
t3(src, len)=>
xe1_1 = ema(src, len)
xe2_1 = ema(xe1_1, len)
xe3_1 = ema(xe2_1, len)
xe4_1 = ema(xe3_1, len)
xe5_1 = ema(xe4_1, len)
xe6_1 = ema(xe5_1, len)
b_1 = 0.7
c1_1 = -b_1*b_1*b_1
c2_1 = 3*b_1*b_1+3*b_1*b_1*b_1
c3_1 = -6*b_1*b_1-3*b_1-3*b_1*b_1*b_1
c4_1 = 1+3*b_1+b_1*b_1*b_1+3*b_1*b_1
nT3Average_1 = c1_1 * xe6_1 + c2_1 * xe5_1 + c3_1 * xe4_1 + c4_1 * xe3_1
// The general form of the weights of the (2m + 1)-term Henderson Weighted Moving Average
getWeight(m, j) =>
numerator = 315 * (pow(m + 1, 2) - pow(j, 2)) * (pow(m + 2, 2) - pow(j, 2)) * (pow(m + 3, 2) - pow(j, 2)) * (3 * pow(m + 2, 2) - 11 * pow(j, 2) - 16)
denominator = 8 * (m + 2) * (pow(m + 2, 2) - 1) * (4 * pow(m + 2, 2) - 1) * (4 * pow(m + 2, 2) - 9) * (4 * pow(m + 2, 2) - 25)
denominator != 0
? numerator / denominator
: 0
hwma(src, termsNumber) =>
sum = 0.0
weightSum = 0.0
termMult = (termsNumber - 1) / 2
for i = 0 to termsNumber - 1
weight = getWeight(termMult, i - termMult)
sum := sum + nz(src[i]) * weight
weightSum := weightSum + weight
sum / weightSum
get_jurik(length, phase, power, src)=>
phaseRatio = phase < -100 ? 0.5 : phase > 100 ? 2.5 : phase / 100 + 1.5
beta = 0.45 * (length - 1) / (0.45 * (length - 1) + 2)
alpha = pow(beta, power)
jma = 0.0
e0 = 0.0
e0 := (1 - alpha) * src + alpha * nz(e0[1])
e1 = 0.0
e1 := (src - e0) * (1 - beta) + beta * nz(e1[1])
e2 = 0.0
e2 := (e0 + phaseRatio * e1 - nz(jma[1])) * pow(1 - alpha, 2) + pow(alpha, 2) * nz(e2[1])
jma := e2 + nz(jma[1])
variant(src, type, len ) =>
v1 = sma(src, len) // Simple
v2 = ema(src, len) // Exponential
v3 = 2 * v2 - ema(v2, len) // Double Exponential
v4 = 3 * (v2 - ema(v2, len)) + ema(ema(v2, len), len) // Triple Exponential
v5 = wma(src, len) // Weighted
v6 = vwma(src, len) // Volume Weighted
v7 = na(v5[1]) ? sma(src, len) : (v5[1] * (len - 1) + src) / len // Smoothed
v8 = wma(2 * wma(src, len / 2) - wma(src, len), round(sqrt(len))) // Hull
v9 = linreg(src, len, lsmaOffset) // Least Squares
v10 = alma(src, len, almaOffset, almaSigma) // Arnaud Legoux
v11 = kama(src, len) // KAMA
ema1 = ema(src, len)
ema2 = ema(ema1, len)
v13 = t3(src, len) // T3
v14 = ema1+(ema1-ema2) // Zero Lag Exponential
v15 = hwma(src, len) // Henderson Moving average thanks to @everget
ahma = 0.0
ahma := nz(ahma[1]) + (src - (nz(ahma[1]) + nz(ahma[len])) / 2) / len //Ahrens Moving Average
v16 = ahma
v17 = get_jurik( len, phase, power, src)
type=="EMA"?v2 : type=="DEMA"?v3 : type=="TEMA"?v4 : type=="WMA"?v5 : type=="VWMA"?v6 :
type=="SMMA"?v7 : type=="Hull"?v8 : type=="LSMA"?v9 : type=="ALMA"?v10 : type=="KAMA"?v11 :
type=="T3"?v13 : type=="ZEMA"?v14 : type=="HWMA"?v15 : type=="AHMA"?v16 : type=="JURIK"?v17 : v1
smoothMA(c, maLoop, type, len) =>
ma_c = 0.0
if maLoop == 1
ma_c := variant(c, type, len)
if maLoop == 2
ma_c := variant(variant(c ,type, len),type, len)
if maLoop == 3
ma_c := variant(variant(variant(c ,type, len),type, len),type, len)
if maLoop == 4
ma_c := variant(variant(variant(variant(c ,type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len)
if maLoop == 5
ma_c := variant(variant(variant(variant(variant(c ,type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len),type, len)
ma_c
// Smoothing HA Function
smoothHA( o, h, l, c ) =>
hao = 0.0
hac = ( o + h + l + c ) / 4
hao := na(hao[1])?(o + c / 2 ):(hao[1] + hac[1])/2
hah = max(h, max(hao, hac))
hal = min(l, min(hao, hac))
[hao, hah, hal, hac]
// ---- Main Selection ----
haSmooth = input(false, title=" Use HA as source ? " )
length = input(60, title=" MA1 Length", minval=1, maxval=1000)
maLoop = input(2, title=" Nr. of MA1 Smoothings ", minval=1, maxval=5)
type = input("EMA", title="MA Type", options=["SMA", "EMA", "DEMA", "TEMA", "WMA", "VWMA", "SMMA", "Hull", "LSMA", "ALMA", "KAMA", "ZEMA", "HWMA", "AHMA", "JURIK", "T3"])
// ---- BODY SCRIPT ----
[ ha_open, ha_high, ha_low, ha_close ] = smoothHA(open, high, low, close)
_close_ma = haSmooth ? ha_close : close
_close_smoothed_ma = smoothMA( _close_ma, maLoop, type, length)
maColor = _close_smoothed_ma > _close_smoothed_ma[1] ? color.lime : color.red
plot(_close_smoothed_ma, title= "MA - Trend", color=maColor, transp=85, linewidth = 4)
long = _close_smoothed_ma > _close_smoothed_ma[1] and _close_smoothed_ma[1] < _close_smoothed_ma[2]
short = _close_smoothed_ma < _close_smoothed_ma[1] and _close_smoothed_ma[1] > _close_smoothed_ma[2]
plotshape( short , title="Short", color=color.red, transp=80, style=shape.triangledown, location=location.abovebar, size=size.small)
plotshape( long , title="Long", color=color.lime, transp=80, style=shape.triangleup, location=location.belowbar, size=size.small)
//* Backtesting Period Selector | Component *//
//* Source: https://www.tradingview.com/script/eCC1cvxQ-Backtesting-Period-Selector-Component *//
testStartYear = input(2018, "Backtest Start Year",minval=1980)
testStartMonth = input(1, "Backtest Start Month",minval=1,maxval=12)
testStartDay = input(1, "Backtest Start Day",minval=1,maxval=31)
testPeriodStart = timestamp(testStartYear,testStartMonth,testStartDay,0,0)
testStopYear = 9999 //input(9999, "Backtest Stop Year",minval=1980)
testStopMonth = 12 // input(12, "Backtest Stop Month",minval=1,maxval=12)
testStopDay = 31 //input(31, "Backtest Stop Day",minval=1,maxval=31)
testPeriodStop = timestamp(testStopYear,testStopMonth,testStopDay,0,0)
testPeriod() => time >= testPeriodStart and time <= testPeriodStop ? true : false
if testPeriod() and long
strategy.entry( "long", strategy.long )
if testPeriod() and short
strategy.entry( "short", strategy.short )
- Montag Umkehrung Intraday Trend nach Strategie
- ADX Filter Chande Kroll Stop Loss Trend nach der Strategie
- Trend-Abweichungsindex mit gleitender Durchschnittsstrategie
- Strategie für dynamische Integralindikatoren
- MACD Moving Average Crossover-Trend nach Strategie mit Trailing Stop Loss
- Zwei-Strecken-Trend-Erfassung Fusionsstrategie
- Preisdurchbruch Bollinger Band A Strategie
- RSI auf Basis der Handelsstrategie der ROC
- Die gestrige Strategie für einen hohen Ausbruch
- Trend nach der Strategie
- Handelsstrategie für den Handel mit doppelten gleitenden Durchschnitten
- Connecticut Schildkröten-System
- Trend nach der Strategie
- Strategie zur Trendsuche mit doppelten Lasern
- Trend des EMA-Oszillators nach Strategie
- Strategie für die Verlagerung von drei gleitenden Durchschnitten
- Trendverfolgungsstrategie auf Basis von Momentum-Breakout
- Strategie der zufälligen Schwingung
- Strategie für eine Super-Impulsentwicklung
- Größenblockstrategie