Cotizaciones de mercado recolector actualizar de nuevo
El autor:La bondad, Creado: 2020-05-26 14:25:15, Actualizado: 2024-12-10 20:35:48
Apoyo a la importación de archivos en formato CSV para proporcionar un origen de datos personalizado
Recientemente, un comerciante necesita usar su propio archivo de formato CSV como fuente de datos para el sistema de backtest de la plataforma FMZ. nuestro sistema de backtest de la plataforma tiene muchas funciones y es simple y eficiente de usar, por lo que mientras los usuarios tengan sus propios datos, pueden realizar backtesting de acuerdo con estos datos, que ya no se limita a los intercambios y variedades soportados por nuestro centro de datos de la plataforma.
Ideas de diseño
La idea de diseño es en realidad muy simple. Sólo tenemos que cambiar ligeramente basado en el colector del mercado anterior.isOnlySupportCSVEn el caso de los datos CSV, se utilizará un parámetro de control de los datos CSV para determinar si se utiliza el archivo CSV como fuente de datos para el sistema de backtest.filePathForCSVEl sistema de control de datos CSV se utiliza para establecer la ruta del archivo de datos CSV colocado en el servidor en el que se ejecuta el robot de recogida de mercado.isOnlySupportCSVel parámetro está establecido enTruePara decidir qué fuente de datos utilizar (recolectados por usted mismo o los datos en el archivo CSV), este cambio se produce principalmente en eldo_GETLa función de laProvider class.
¿Qué es un archivo CSV?
Los valores separados por comas, también conocidos como CSV, a veces se denominan valores separados por caracteres, porque el carácter separador tampoco puede ser una coma. Su archivo almacena los datos de la tabla (números y texto) en texto plano. El texto plano significa que el archivo es una secuencia de caracteres y no contiene datos que deban interpretarse como un número binario. El archivo CSV consiste en cualquier número de registros, separados por algún carácter de línea nueva; cada registro está compuesto por campos, y los separadores entre campos son otros caracteres o cadenas, y los más comunes son comas o pestañas.WORDPADo bienExcelpara abrir.
El estándar general del formato de archivo CSV no existe, pero hay ciertas reglas, generalmente un registro por línea, y la primera línea es el encabezado.
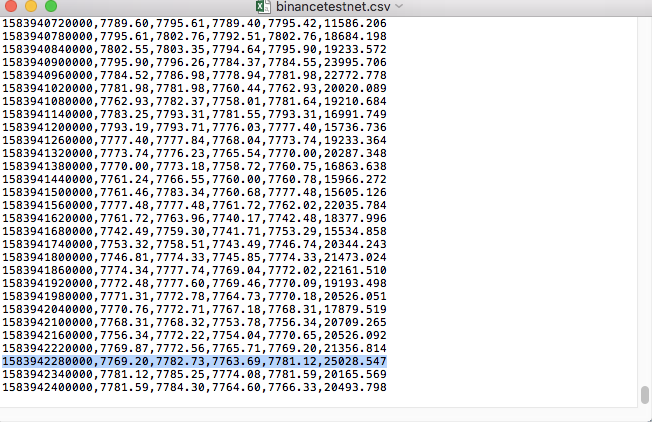
Por ejemplo, el archivo CSV que usamos para las pruebas se abre con el Bloc de notas así:
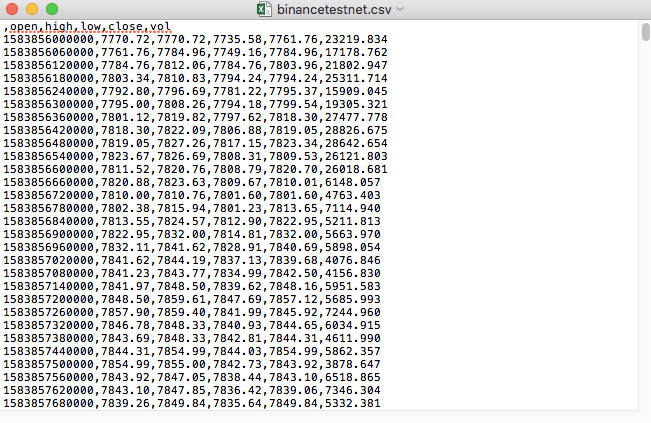
Observado que la primera línea del archivo CSV es el encabezado de la tabla.
,open,high,low,close,vol
Sólo tenemos que analizar y ordenar estos datos, y luego construir en el formato requerido por la fuente de datos personalizados del sistema de backtest.
Código modificado
import _thread
import pymongo
import json
import math
import csv
from http.server import HTTPServer, BaseHTTPRequestHandler
from urllib.parse import parse_qs, urlparse
def url2Dict(url):
query = urlparse(url).query
params = parse_qs(query)
result = {key: params[key][0] for key in params}
return result
class Provider(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
def do_GET(self):
global isOnlySupportCSV, filePathForCSV
try:
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header("Content-type", "application/json")
self.end_headers()
dictParam = url2Dict(self.path)
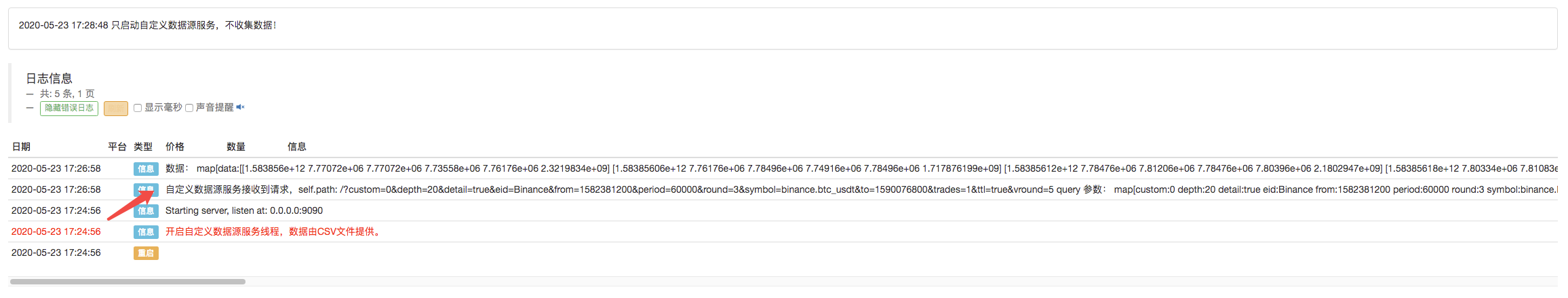
Log("The custom data source service receives the request,self.path:", self.path, "query parameter:", dictParam)
# At present, the backtest system can only select the exchange name from the list. When adding a custom data source, set it to Binance, that is: Binance
exName = exchange.GetName()
# Note that period is the bottom K-line period
tabName = "%s_%s" % ("records", int(int(dictParam["period"]) / 1000))
priceRatio = math.pow(10, int(dictParam["round"]))
amountRatio = math.pow(10, int(dictParam["vround"]))
fromTS = int(dictParam["from"]) * int(1000)
toTS = int(dictParam["to"]) * int(1000)
# Request data
data = {
"schema" : ["time", "open", "high", "low", "close", "vol"],
"data" : []
}
if isOnlySupportCSV:
# Handle CSV reading, filePathForCSV path
listDataSequence = []
with open(filePathForCSV, "r") as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
# Get table header
header = next(reader)
headerIsNoneCount = 0
if len(header) != len(data["schema"]):
Log("The CSV file format is wrong, the number of columns is different, please check!", "#FF0000")
return
for ele in header:
for i in range(len(data["schema"])):
if data["schema"][i] == ele or ele == "":
if ele == "":
headerIsNoneCount += 1
if headerIsNoneCount > 1:
Log("The CSV file format is incorrect, please check!", "#FF0000")
return
listDataSequence.append(i)
break
# Read content
while True:
record = next(reader, -1)
if record == -1:
break
index = 0
arr = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
for ele in record:
arr[listDataSequence[index]] = int(ele) if listDataSequence[index] == 0 else (int(float(ele) * amountRatio) if listDataSequence[index] == 5 else int(float(ele) * priceRatio))
index += 1
data["data"].append(arr)
Log("data: ", data, "Respond to backtest system requests.")
self.wfile.write(json.dumps(data).encode())
return
# Connect to the database
Log("Connect to the database service to obtain data, the database: ", exName, "table: ", tabName)
myDBClient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017")
ex_DB = myDBClient[exName]
exRecords = ex_DB[tabName]
# Construct query conditions: greater than a certain value {'age': {'$ gt': 20}} less than a certain value {'age': {'$lt': 20}}
dbQuery = {"$and":[{'Time': {'$gt': fromTS}}, {'Time': {'$lt': toTS}}]}
Log("Query conditions: ", dbQuery, "Number of inquiries: ", exRecords.find(dbQuery).count(), "Total number of databases: ", exRecords.find().count())
for x in exRecords.find(dbQuery).sort("Time"):
# Need to process data accuracy according to request parameters round and vround
bar = [x["Time"], int(x["Open"] * priceRatio), int(x["High"] * priceRatio), int(x["Low"] * priceRatio), int(x["Close"] * priceRatio), int(x["Volume"] * amountRatio)]
data["data"].append(bar)
Log("data: ", data, "Respond to backtest system requests.")
# Write data response
self.wfile.write(json.dumps(data).encode())
except BaseException as e:
Log("Provider do_GET error, e:", e)
def createServer(host):
try:
server = HTTPServer(host, Provider)
Log("Starting server, listen at: %s:%s" % host)
server.serve_forever()
except BaseException as e:
Log("createServer error, e:", e)
raise Exception("stop")
def main():
LogReset(1)
if (isOnlySupportCSV):
try:
# _thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("localhost", 9090), )) # local test
_thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("0.0.0.0", 9090), )) # Test on VPS server
Log("Start the custom data source service thread, and the data is provided by the CSV file. ", "#FF0000")
except BaseException as e:
Log("Failed to start the custom data source service!")
Log("Error message: ", e)
raise Exception("stop")
while True:
LogStatus(_D(), "Only start the custom data source service, do not collect data!")
Sleep(2000)
exName = exchange.GetName()
period = exchange.GetPeriod()
Log("collect", exName, "Exchange K-line data,", "K line cycle:", period, "Second")
# Connect to the database service, service address mongodb: //127.0.0.1: 27017 See the settings of mongodb installed on the server
Log("Connect to the mongodb service of the hosting device, mongodb://localhost:27017")
myDBClient = pymongo.MongoClient("mongodb://localhost:27017")
# Create a database
ex_DB = myDBClient[exName]
# Print the current database table
collist = ex_DB.list_collection_names()
Log("mongodb", exName, "collist:", collist)
# Check if the table is deleted
arrDropNames = json.loads(dropNames)
if isinstance(arrDropNames, list):
for i in range(len(arrDropNames)):
dropName = arrDropNames[i]
if isinstance(dropName, str):
if not dropName in collist:
continue
tab = ex_DB[dropName]
Log("dropName:", dropName, "delete:", dropName)
ret = tab.drop()
collist = ex_DB.list_collection_names()
if dropName in collist:
Log(dropName, "failed to delete")
else :
Log(dropName, "successfully deleted")
# Start a thread to provide a custom data source service
try:
# _thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("localhost", 9090), )) # local test
_thread.start_new_thread(createServer, (("0.0.0.0", 9090), )) # Test on VPS server
Log("Open the custom data source service thread", "#FF0000")
except BaseException as e:
Log("Failed to start the custom data source service!")
Log("Error message:", e)
raise Exception("stop")
# Create the records table
ex_DB_Records = ex_DB["%s_%d" % ("records", period)]
Log("Start collecting", exName, "K-line data", "cycle:", period, "Open (create) the database table:", "%s_%d" % ("records", period), "#FF0000")
preBarTime = 0
index = 1
while True:
r = _C(exchange.GetRecords)
if len(r) < 2:
Sleep(1000)
continue
if preBarTime == 0:
# Write all BAR data for the first time
for i in range(len(r) - 1):
bar = r[i]
# Write root by root, you need to determine whether the data already exists in the current database table, based on timestamp detection, if there is the data, then skip, if not write
retQuery = ex_DB_Records.find({"Time": bar["Time"]})
if retQuery.count() > 0:
continue
# Write bar to the database table
ex_DB_Records.insert_one({"High": bar["High"], "Low": bar["Low"], "Open": bar["Open"], "Close": bar["Close"], "Time": bar["Time"], "Volume": bar["Volume"]})
index += 1
preBarTime = r[-1]["Time"]
elif preBarTime != r[-1]["Time"]:
bar = r[-2]
# Check before writing data, whether the data already exists, based on time stamp detection
retQuery = ex_DB_Records.find({"Time": bar["Time"]})
if retQuery.count() > 0:
continue
ex_DB_Records.insert_one({"High": bar["High"], "Low": bar["Low"], "Open": bar["Open"], "Close": bar["Close"], "Time": bar["Time"], "Volume": bar["Volume"]})
index += 1
preBarTime = r[-1]["Time"]
LogStatus(_D(), "preBarTime:", preBarTime, "_D(preBarTime):", _D(preBarTime/1000), "index:", index)
# Increase drawing display
ext.PlotRecords(r, "%s_%d" % ("records", period))
Sleep(10000)
Prueba de ejecución
Primero, arrancamos el robot recolector del mercado, le añadimos un intercambio al robot y lo dejamos funcionar.
Configuración de parámetros:
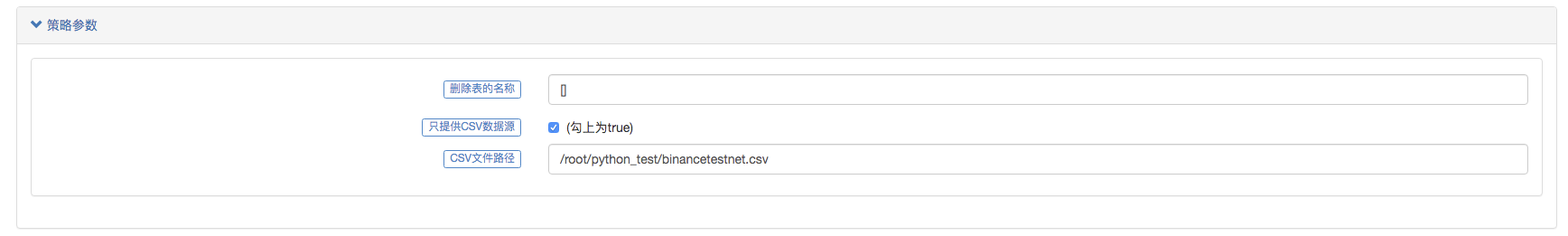
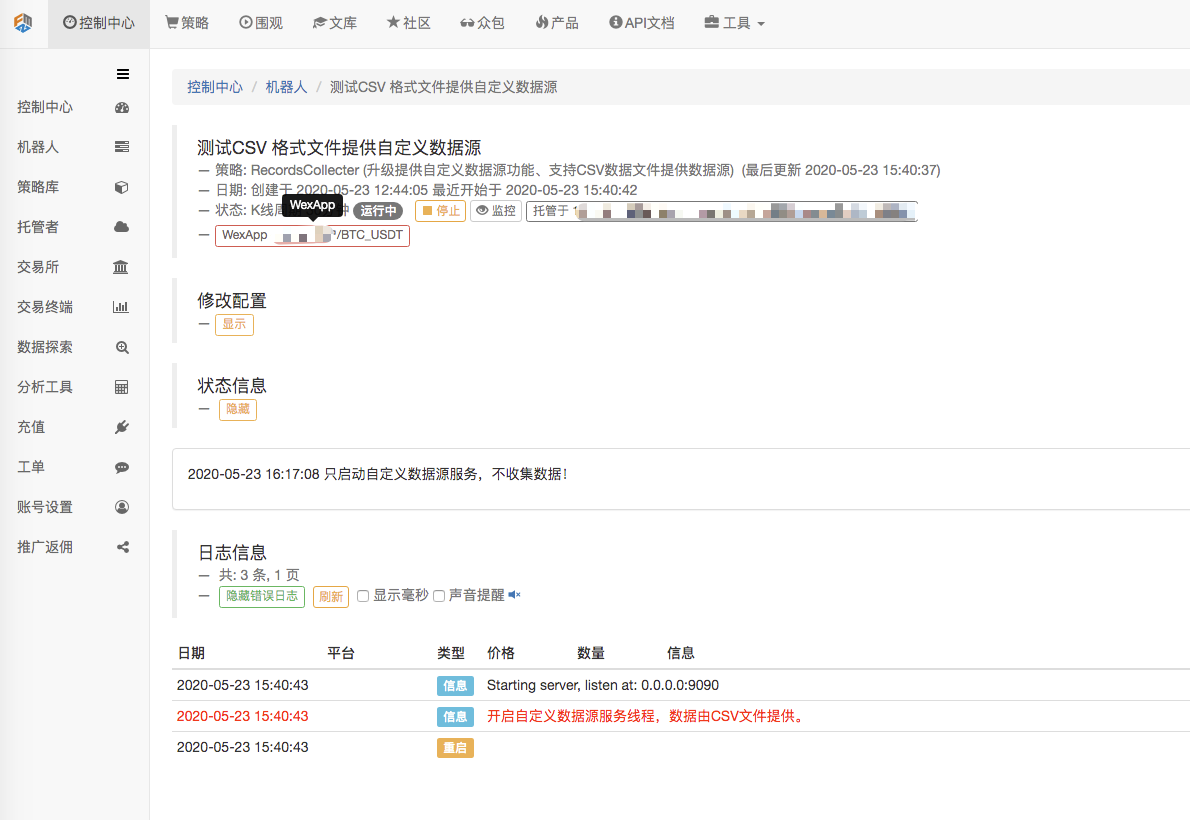
Luego creamos una estrategia de prueba:
function main() {
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
Log(exchange.GetRecords())
}
La estrategia es muy simple, sólo obtener e imprimir datos de la línea K tres veces.
En la página de backtest, configure la fuente de datos del sistema de backtest como una fuente de datos personalizada, y rellene la dirección del servidor donde se ejecuta el robot recolector de mercado.
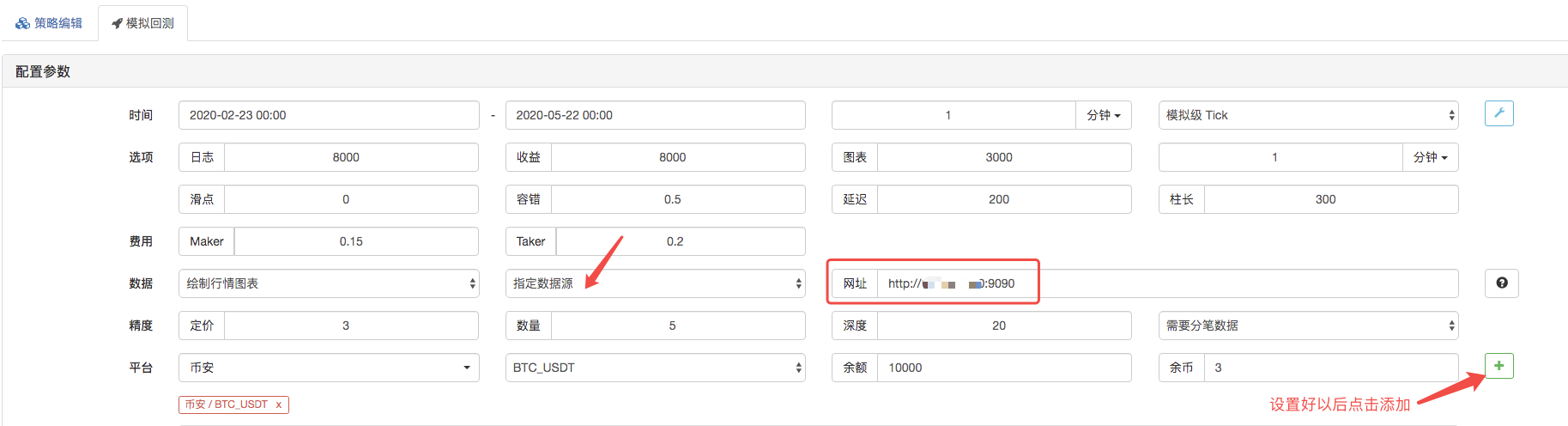
Haga clic para iniciar el backtest, y el robot recolector de mercado recibe la solicitud de datos:
Una vez completada la estrategia de ejecución del sistema de backtest, se genera un gráfico de líneas K basado en los datos de líneas K de la fuente de datos.
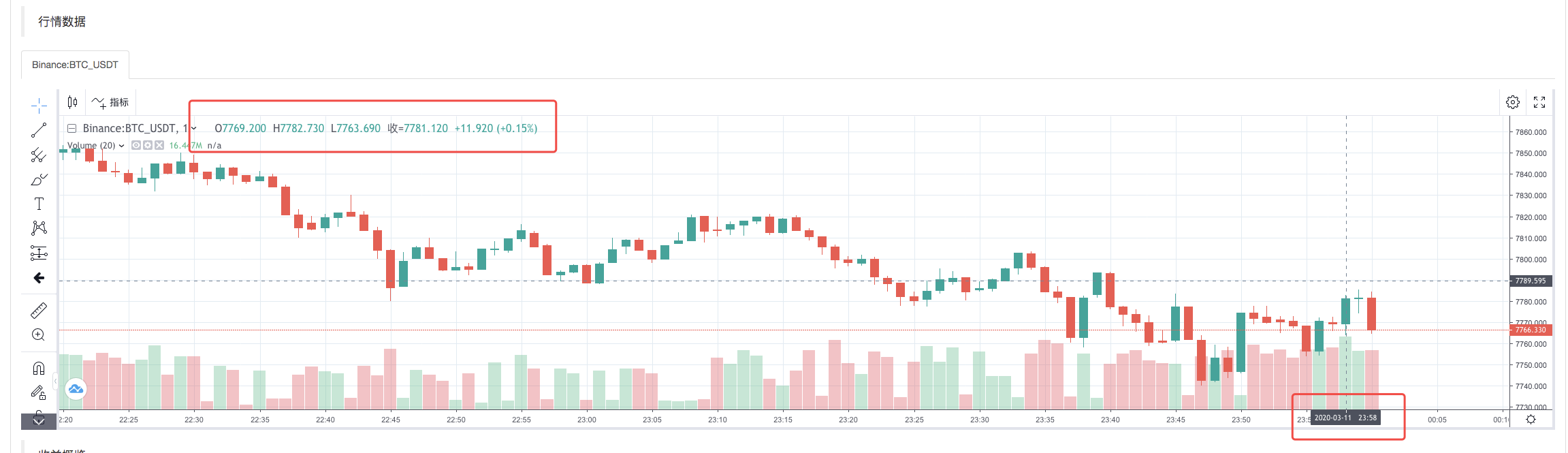
Compare los datos en el archivo:

- Introducción al conjunto de Lead-Lag en las monedas digitales (3)
- Introducción al arbitraje de lead-lag en criptomonedas (2)
- Introducción al conjunto de Lead-Lag en las monedas digitales (2)
- Discusión sobre la recepción de señales externas de la plataforma FMZ: una solución completa para recibir señales con servicio HTTP incorporado en la estrategia
- Exploración de la recepción de señales externas de la plataforma FMZ: estrategias para una solución completa de recepción de señales de servicios HTTP integrados
- Introducción al arbitraje de lead-lag en criptomonedas (1)
- Introducción al conjunto de Lead-Lag en las monedas digitales (1)
- Discusión sobre la recepción de señales externas de la plataforma FMZ: API extendida VS estrategia Servicio HTTP incorporado
- Exploración de la recepción de señales externas de la plataforma FMZ: API de expansión vs estrategia de servicio HTTP incorporado
- Discusión sobre el método de prueba de estrategias basado en el generador de tickers aleatorios
- Explorar métodos de prueba de estrategias basados en generadores de mercado aleatorios
- Algunos pensamientos sobre la lógica del comercio de futuros de criptomonedas
- Herramienta de análisis mejorada basada en el desarrollo gramatical de Alpha101
- Enseñarle a actualizar el colector de mercado backtest la fuente de datos personalizados
- Defectos de los sistemas de resonancia de alta frecuencia basados en transacciones por letra y resonancia de línea K
- Explicación del mecanismo de ensayo posterior de nivel de simulación FMZ
- La mejor manera de instalar y actualizar FMZ docker en Linux VPS
- Estrategia R-Breaker de futuros de materias primas
- Un poco de reflexión sobre la lógica del comercio de futuros de monedas digitales
- Enseñarle a implementar un coleccionista de cotizaciones de mercado
- Versión de Python Estrategia de promedio móvil de futuros de materias primas
- Actualización del recolector de transacciones - soporte para la importación de archivos en formato CSV para proporcionar fuentes de datos personalizadas
- Commodity Futures High Frequency Trading Strategy escrito por C++
- Larry Connors RSI2 estrategia de reversión media
- El hombre de Oak te enseñará cómo usar la API para la extensión de FMZ con JS.
- Basado en el uso de un nuevo índice de fortaleza relativa en las estrategias intradiarias
- Investigación sobre Binance Futures estrategia de cobertura multi-moneda Parte 4
- Larry Connors Larry Connors RSI2 estrategia de retorno de la media
- Investigación sobre la estrategia de cobertura de divisas múltiples de Binance Futures Parte 3
- Investigación sobre Binance Futures estrategia de cobertura multi-moneda Parte 2
- Investigación sobre la estrategia de cobertura de divisas de futuros de Binance Parte 1