Système de négociation de ligne de crocodile version Python
Auteur:La bonté, Créé: 2020-05-07 14:33:19, Mis à jour: 2025-01-14 20:38:03
Résumé
Les gens qui ont fait du trading financier auront probablement une expérience. Parfois, les fluctuations de prix sont régulières, mais le plus souvent, cela montre un état instable de marche aléatoire. C'est cette instabilité qui est à l'origine des risques et des opportunités du marché. L'instabilité signifie également imprévisible, donc comment rendre les rendements plus stables dans un environnement de marché imprévisible est également un problème pour chaque trader. Cet article présentera la stratégie des règles de trading du crocodile, dans l'espoir d'inspirer tout le monde.
C' est quoi une ligne de crocodile?
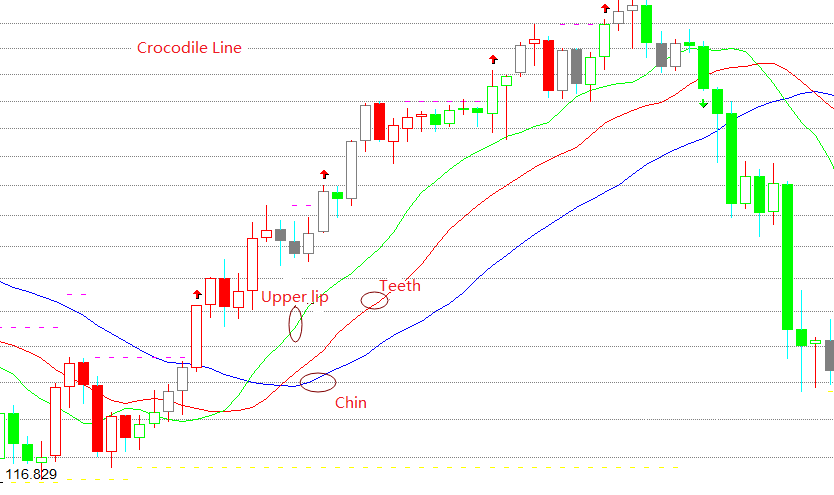
La ligne du crocodile est en fait trois moyennes mobiles spéciales, qui correspondent au menton de la ligne bleue, aux dents de la ligne rouge et à la lèvre supérieure de la ligne verte.
Principe de la ligne du crocodile
La ligne du crocodile est un ensemble de méthodes d'analyse technique résumées sur la base de la géométrie et de la dynamique non linéaire. Lorsque le menton, les dents et la lèvre supérieure du crocodile sont fermés ou enchevêtrés, cela signifie que le crocodile est endormi.
Plus le crocodile dort longtemps, plus il aura faim quand il se réveillera, donc une fois qu'il se réveillera, il ouvrira largement la bouche. Si la lèvre supérieure est au-dessus des dents et que les dents sont au-dessus du menton, cela indique que le marché est entré dans un marché haussier et que les crocodiles vont manger du bœuf. Si la lèvre supérieure est au-dessous des dents et que les dents sont au-dessous du menton, cela indique que le marché est entré dans un marché ours et que les crocodiles vont manger de la viande d'ours. Jusqu'à ce qu'il soit plein, il fermera à nouveau sa bouche (restez et faites un profit).
Formule de calcul de la ligne du crocodile
Le niveau d'humidité est calculé en fonction de la température de l'air. Les dents = REF ((SMA ((VAR1,8,1),5) Le nombre d'heures de travail est calculé en fonction de la fréquence de travail.
Composition de la stratégie du crocodile
Étape 1: Écrire un cadre stratégique
# Strategy main function
def onTick():
pass
# Program entry
def main ():
while True: # Enter infinite loop mode
onTick() # execute strategy main function
Sleep(1000) # sleep for 1 second
FMZ en utilisant le mode de sondage, l'un est la fonction onTick, et l'autre est la fonction principale, dans laquelle la fonction onTick est exécutée en boucle infinie dans la fonction principale.
Étape 2: Importer la bibliothèque Python
import talib
import numpy as np
La fonction SMA est utilisée dans notre stratégie. SMA est la moyenne arithmétique. Il y a déjà des fonctions SMA prêtes à l'emploi dans la bibliothèque talib, donc importez directement la bibliothèque talib Python et appelez-la ensuite directement. Parce que lorsque vous appelez cette fonction, vous devez passer des paramètres de format numpy, nous devons donc utiliser import pour importer ces deux bibliothèques Python au début de la stratégie.
Étape 3: Conversion des données du tableau de lignes K
# Convert the K-line array into an array of highest price, lowest price, and closing price, for conversion to numpy.array
def get_data(bars):
arr = []
for i in bars:
arr.append(i['Close'])
return arr
Ici, nous avons créé une fonction get_data, le but de cette fonction est de traiter le tableau K-line ordinaire en données de format numpy.
Étape 4: Obtenir les données de position
# Get the number of positions
def get_position ():
# Get position
position = 0 # The number of assigned positions is 0
position_arr = _C (exchange.GetPosition) # Get array of positions
if len (position_arr)> 0: # If the position array length is greater than 0
for i in position_arr:
if i ['ContractType'] == 'rb000': # If the position symbol is equal to the subscription symbol
if i ['Type']% 2 == 0: # If it is long position
position = i ['Amount'] # Assigning a positive number of positions
else:
position = -i ['Amount'] # Assigning a negative number of positions
return position
Le statut de position implique une logique de stratégie. Nos dix premières leçons ont toujours utilisé des positions virtuelles, mais dans un environnement de trading réel, il est préférable d'utiliser la fonction GetPosition pour obtenir des informations de position réelles, notamment: direction de position, profit et perte de position, nombre de positions, etc.
Étape 5: obtenir les données
exchange.SetContractType('rb000') # Subscribe the futures varieties
bars_arr = exchange.GetRecords() # Get K line array
if len(bars_arr) < 22: # If the number of K lines is less than 22
return
Avant d'acquérir des données, vous devez d'abord utiliser la fonction SetContractType pour souscrire aux variétés de contrats à terme pertinentes. FMZ prend en charge toutes les variétés de contrats à terme chinois. Après avoir souscrit au symbole des contrats à terme, vous pouvez utiliser la fonction GetRecords pour obtenir des données de ligne K, qui renvoie un tableau.
Étape 6: Calculer les données
np_arr = np.array (get_data (bars_arr)) # Convert closing price array
sma13 = talib.SMA (np_arr, 130) [-9] # chin
sma8 = talib.SMA (np_arr, 80) [-6] # teeth
sma5 = talib.SMA (np_arr, 50) [-4] # upper lip
current_price = bars_arr [-1] ['Close'] # latest price
Avant de calculer le SMA à l'aide de la bibliothèque talib, vous devez utiliser la bibliothèque numpy pour traiter le tableau K-line ordinaire en données numpy. Puis obtenir le menton, les dents et la lèvre supérieure de la ligne du crocodile séparément.
Étape 7: Faire une commande
position = get_position ()
if position == 0: # If there is no position
if current_price> sma5: # If the current price is greater than the upper lip
exchange.SetDirection ("buy") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Buy (current_price + 1, 1) # open long position order
if current_price <sma13: # If the current price is less than the chin
exchange.SetDirection ("sell") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Sell (current_price-1, 1) # open short position order
if position> 0: # If you have long positions
if current_price <sma8: # If the current price is less than teeth
exchange.SetDirection ("closebuy") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Sell (current_price-1, 1) # close long position
if position <0: # If you have short position
if current_price> sma8: # If the current price is greater than the tooth
exchange.SetDirection ("closesell") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Buy (current_price + 1, 1) # close short position
Avant de passer un ordre, vous devez obtenir la position réelle. La fonction get_position que nous avons définie précédemment renverra le nombre réel de positions. Si la position actuelle est longue, elle renverra un nombre positif. Si la position actuelle est courte, elle renverra un nombre négatif. S'il n'y a pas de position, elle renvoie 0. Enfin, les fonctions d'achat et de vente sont utilisées pour passer des ordres selon la logique de trading ci-dessus, mais avant cela, la direction et le type de trading doivent également être définis.
Stratégie complète
'' 'backtest
start: 2019-01-01 00:00:00
end: 2020-01-01 00:00:00
period: 1h
exchanges: [{"eid": "Futures_CTP", "currency": "FUTURES"}]
'' '
import talib
import numpy as np
# Convert the K-line array into an array of highest price, lowest price, and closing price, used to convert to numpy.array type data
def get_data (bars):
arr = []
for i in bars:
arr.append (i ['Close'])
return arr
# Get the number of positions
def get_position ():
# Get position
position = 0 # The number of assigned positions is 0
position_arr = _C (exchange.GetPosition) # Get array of positions
if len (position_arr)> 0: # If the position array length is greater than 0
for i in position_arr:
if i ['ContractType'] == 'rb000': # If the position symbol is equal to the subscription symbol
if i ['Type']% 2 == 0: # If it is long
position = i ['Amount'] # Assign a positive number of positions
else:
position = -i ['Amount'] # Assign a negative number of positions
return position
# Strategy main function
def onTick ():
# retrieve data
exchange.SetContractType ('rb000') # Subscribe to futures varieties
bars_arr = exchange.GetRecords () # Get K line array
if len (bars_arr) <22: # If the number of K lines is less than 22
return
# Calculation
np_arr = np.array (get_data (bars_arr)) # Convert closing price array
sma13 = talib.SMA (np_arr, 130) [-9] # chin
sma8 = talib.SMA (np_arr, 80) [-6] # teeth
sma5 = talib.SMA (np_arr, 50) [-4] # upper lip
current_price = bars_arr [-1] ['Close'] # latest price
position = get_position ()
if position == 0: # If there is no position
if current_price> sma5: # If the current price is greater than the upper lip
exchange.SetDirection ("buy") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Buy (current_price + 1, 1) # open long position order
if current_price <sma13: # If the current price is less than the chin
exchange.SetDirection ("sell") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Sell (current_price-1, 1) # open short position order
if position> 0: # If you have long positions
if current_price <sma8: # If the current price is less than teeth
exchange.SetDirection ("closebuy") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Sell (current_price-1, 1) # close long position
if position <0: # If you have short positions
if current_price> sma8: # If the current price is greater than the tooth
exchange.SetDirection ("closesell") # Set the trading direction and type
exchange.Buy (current_price + 1, 1) # close short position
# Program main function
def main ():
while True: # loop
onTick () # execution strategy main function
Sleep (1000) # sleep for 1 second
Cliquez directement sur le lien ci-dessous pour copier la stratégie complète sans configuration:https://www.fmz.com/strategy/199025
Finition
Le plus grand rôle de la règle de trading du crocodile est de nous aider à maintenir la même direction que le marché lors de la négociation, indépendamment de la façon dont le prix actuel du marché change, et de continuer à tirer profit jusqu'à ce que le marché de consolidation apparaisse.
- Pratiques quantitatives des échanges DEX (2) -- Guide de l'utilisateur des hyperliquides
- Expérience de la quantification sur les échanges DEX (2) -- Guide d'utilisation de Hyperliquid
- Pratique quantitative des échanges DEX (1) -- Guide de l'utilisateur dYdX v4
- Introduction à l'arbitrage au retard de plomb dans les crypto-monnaies (3)
- Pratiques de quantification de l'échange DEX ((1) -- dYdX v4 Guide d'utilisation
- Introduction à la suite de Lead-Lag dans les monnaies numériques (3)
- Introduction à l'arbitrage au retard de plomb dans les crypto-monnaies (2)
- Introduction à la suite de Lead-Lag dans les monnaies numériques (2)
- Discussion sur la réception de signaux externes de la plateforme FMZ: une solution complète pour la réception de signaux avec un service Http intégré dans la stratégie
- Exploration de la réception de signaux externes sur la plateforme FMZ: stratégie intégrée pour la réception de signaux sur le service HTTP
- Introduction à l'arbitrage au retard de plomb dans les crypto-monnaies (1)
- Stratégie de négociation à haute fréquence sur les contrats à terme sur matières premières écrite en C++
- Larry Connors RSI2 Stratégie d'inversion moyenne
- Les ouvriers vous apprennent à utiliser l'API de couplage JS pour étendre FMZ
- Basé sur l'utilisation d'un nouvel indice de résistance relative dans les stratégies intraday
- Recherche sur la stratégie de couverture multi-monnaie des contrats à terme de Binance Partie 4
- Larry Connors Larry Connors RSI2 stratégie de régression moyenne
- Recherche sur la stratégie de couverture multi-monnaie des contrats à terme de Binance Partie 3
- Recherche sur la stratégie de couverture multi-monnaie des contrats à terme de Binance Partie 2
- Recherche sur la stratégie de couverture multi-monnaie des contrats à terme de Binance Partie 1
- Le manuel vous apprend à mettre à niveau la fonctionnalité de récupération des sources de données personnalisées pour le collecteur de transactions
- L'API de l'extension de la plate-forme de négociation quantitative utilisée par les inventeurs pour réaliser des transactions de signaux d'alarme TradingView (recommandé)
- Version JavaScript de la stratégie SuperTrend
- SuperTrend V.1 - Système de ligne de tendance supérieure
- La stratégie de SuperTrend de la version JavaScript
- [Guerre des millénaires] Résultats de la rétrospective récente et de la revue de la ligne K à l'échelle de la minute sur les stratégies de couverture multi-monnaies monétaires et monétaires (article 4)
- La main à la main vous apprend à réaliser un collecteur de transactions
- [Guerre des millénaires] Les contrats à terme monétaires à l'inflation sur le marché des changes sur le marché des changes sur le marché des changes sur le marché des changes sur le marché des changes sur le marché des changes sur le marché des changes sur le marché des changes sur le marché des changes sur le marché des changes sur le marché des changes sur le marché des changes sur le marché des changes sur le marché des changes sur le marché des changes
- [Guerre des millénaires] Optimisation importante de la stratégie de l'optimisation de la stratégie de l'optimisation de la stratégie de l'optimisation de la stratégie de l'optimisation de la stratégie de l'optimisation de la stratégie de l'optimisation de la stratégie de l'optimisation de la stratégie de l'optimisation de la stratégie de l'optimisation de la stratégie de l'optimisation de la stratégie de l'optimisation de la stratégie de l'optimisation de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la stratégie de la
- [Guerre des millénaires] Une étude sur les stratégies de couverture multi-monnaies pour les devises et les options monétaires (article 1)
- Une pièce de monnaie de l'étudiant de premier cycle de 98 et le chemin de la quantification